2. 青岛海洋科学与技术国家实验室 海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程功能实验室 青岛 266071;
3. 上海海洋大学水产与生命学院 上海 201306
2. Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266071 ;
3. College of Fisheries and Life Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306
半滑舌鳎(Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther)是我国北方常见的大型底栖鱼类,主要分布于我国的渤海、黄海海域,其活动范围小、营养等级低、生长快,鱼肉营养丰富、口感细腻,具有较高的经济价值,已成为我国沿海地区海水养殖鱼类的优良品种之一。随着半滑舌鳎人工繁殖技术取得成功,养殖规模不断扩大,并逐步开始了集约化养殖(姜言伟等,1993)。但是,由于养殖密度过大、养殖环境恶化和病原传播等原因,各种疾病也不断增多。其中,大部分疾病为细菌性疾病,病毒性疾病报道较少(Tang et al,2008; 张晓君等,2009; Zhang et al,2011; 陈政强等,2012)。
2012年和2013年,山东某育苗场的半滑舌鳎鱼苗先后发生大规模死亡,患病半滑舌鳎鱼苗呈现身体畸形弯曲、狂游或螺旋型游动等临床症状,但体表及内脏无出血、溃烂等现象,疑为感染了鱼类神经坏死病毒。已有的研究表明,鱼类神经坏死病毒可以分为4种基因型,即:黄带拟鲹神经坏死病毒(Striped jack nervous necrosis virus,SJNNV)、红鳍东方鲀神经坏死病毒(Tiger puffer nervous necrosis virus,TPNNV)、赤点石斑鱼神经坏死病毒(Red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus,RGNNV)和条斑星鲽神经坏死病毒(Barfin flounder nervous necrosis virus,BFNNV)(Nishizawa et al,1997)。据报道,鱼类神经坏死病毒可以感染10目33科50余种鱼类(Munday et al,2002; Sano et al,2011),对海水养殖鱼类尤其是鱼类育苗造成了极大的威胁。然而,未见半滑舌鳎感染鱼类神经坏死病毒的报道。
本研究运用组织病理学和分子生物学方法,对上述患病鱼苗进行病原分析,首次证实半滑舌鳎是鱼类神经坏死病毒的天然宿主,该发现在半滑舌鳎疾病防治和鱼类神经坏死病毒的流行机制研究方面都具有重要的意义。
1 材料与方法 1.1 样品采集与处理2012年和2013年,山东某育苗场培育的半滑舌鳎鱼苗出现大规模死亡,本研究对发病情况调查,记录病鱼的临床特征,采集具有典型临床症状的15-20日龄半滑舌鳎鱼苗。一部分鱼苗用RNAlater(Qiagen,北京)保存,用于RNA提取和病毒检测。一部分鱼苗用Davidson's AFA固定液固定,用于组织病理研究。
1.2 组织病理切片对Davidson's AFA固定液固定的病鱼,剪取鱼苗头部组织,进行石蜡组织切片和苏木精-伊红染色,封片后用光学显微镜(Nikon E800,日本)观察病理变化。
1.3 RNA的提取取RNAlater保存的病鱼头部组织约30 mg,采用GB核酸释放试剂盒(诺晶生物公司,上海),参照说明书步骤提取组织总RNA。
1.4 RT-PCR检测根据GenBank中已经公布的鱼类神经坏死病毒的基因序列,选取保守区设计RT-PCR引物,F1:CTG GTC GGC TGA TAC TCCT,R1:CAA CGC CAT CTG TGA ACG,目标扩增片段大小为399 bp。
以1.3中提取的组织总RNA为模板,采用TransScript First-Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix(TransGen,北京)进行反转录,合成cDNA模板。20 μl反转录体系:0.1 μg/μl随机引物1 μl、反转录酶1 μl、2 × TS反转录缓冲液10 μl、组织总RNA 3 μl、DEPC水5 μl。反转录程序:25℃ 10 min,42℃ 30 min,85℃ 5 min。
取上述合成的cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增。25 μl PCR反应体系: 10 μmol/L F1和R1引物各0.5 μl、2 × GB-Direct PCR Mix 12.5 μl、cDNA模板2 μl、DEPC水9.5 μl。PCR反应程序:94℃ 5 min;然后94℃ 30 s;58℃ 30 s; 72℃ 1 min,35个循环;最后72℃ 5 min。取扩增产物进行1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,观察结果并拍照。
1.5 序列比对与相似性分析PCR产物由生工生物工程(上海)有限公司进行双向测序,拼接后的序列输入计算机,用BioEdit软件和BLAST软件进行序列相似性分析。
2 结果 2.1 发病情况和临床特征调查发现,半滑舌鳎鱼苗发病时的养殖水温一般在22-24℃,养殖水体盐度为30,pH为7-8。1-12日龄以及30日龄以上的鱼苗发病较轻。13-30日龄的鱼苗发病严重,死亡率高达90%-100%。50日龄以上的鱼苗不发病。患病鱼苗呈现上下翻游、螺旋性游动或全身大幅度波浪状浮动等症状。鱼体无力,随着水流漂动,部分鱼苗有短暂的狂游现象。患病严重的鱼苗脊柱出现弯曲畸形,但病鱼体表无出血、溃烂等现象(图 1)。
|
图 1 水中患病的半滑舌鳎鱼苗 Figure 1 The diseased fry of half-smooth tongue sole C. semilaevis in water |
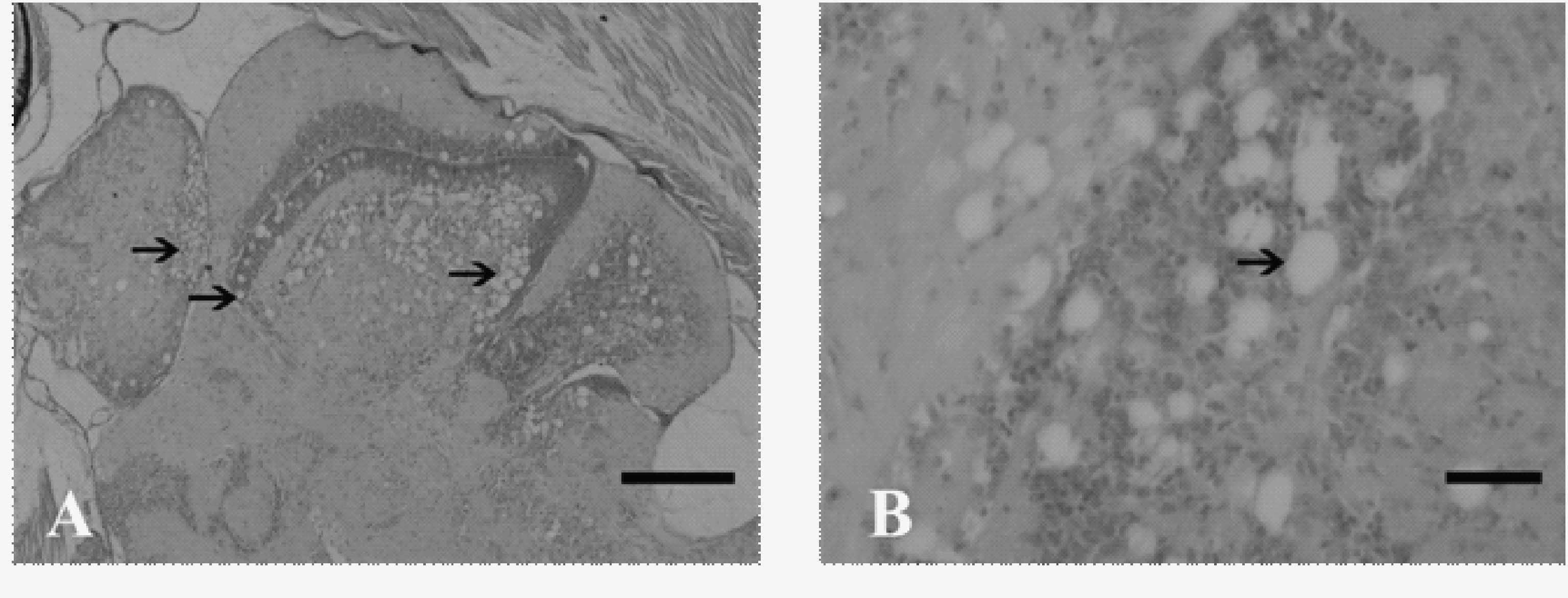
对采集的患病半滑舌鳎鱼苗进行组织病理学观察,可以看到典型的病毒性神经坏死病理特征,即病鱼的脑和视网膜组织大量空泡化。在患病半滑舌鳎鱼苗的头部组织切片中,最明显的空泡化病变主要出现在视网膜的视细胞层、双极细胞层以及节细胞层,中枢神经组织的空泡化病变主要出现在脑灰质部位,并且在空泡周围有大量的嗜碱性的病毒包涵体(图 2)。
|
图 2 患病半滑舌鳎的组织病理变化 Figure 2 The histopathological characteristics of diseased half-smooth tongue sole A. 脑组织空泡化(标尺,100 µm); B. 视网膜组织空泡化(标尺,20 µm) A. vacuolation of brain(Scale bar = 100 µm); B. vacuolation of retina(Scale bar = 20 µm) |
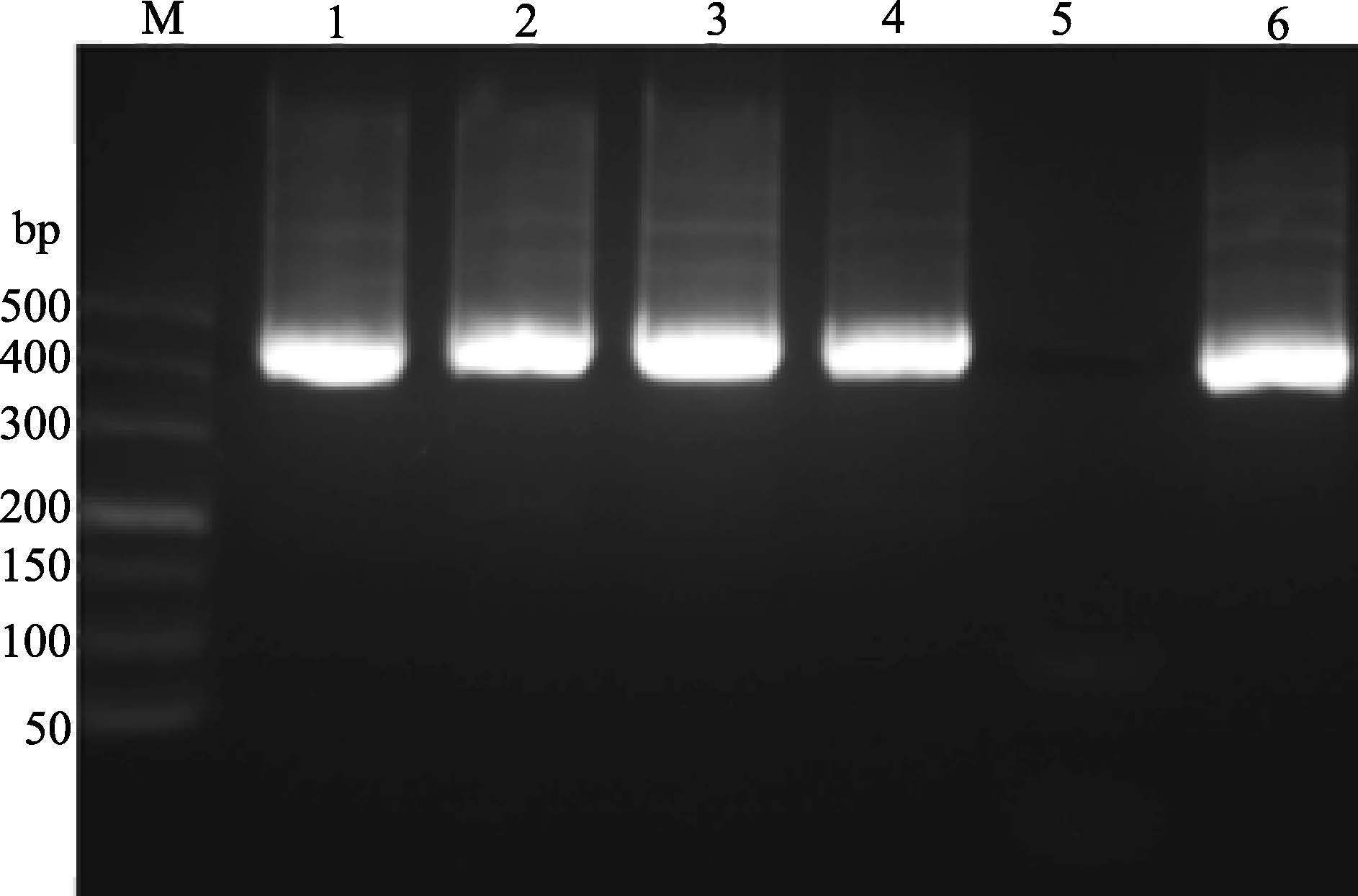
采用RT-PCR方法对于采集的半滑舌鳎鱼苗进行鱼类神经坏死病毒的检测。电泳结果显示,采集到的4批样品,病毒检测结果均为强阳性(图 3)。
|
图 3 半滑舌鳎样品的RT-PCR检测结果 Figure 3 The RT-PCR results of diseased half-smooth tongue sole M:DL 500TM DNA Marker;1-4:病鱼样品;5:阴性对照;6:阳性对照 M: DL 500TM DNA Marker; 1-4: diseased fish; 5: Negative control; 6: Positive control |
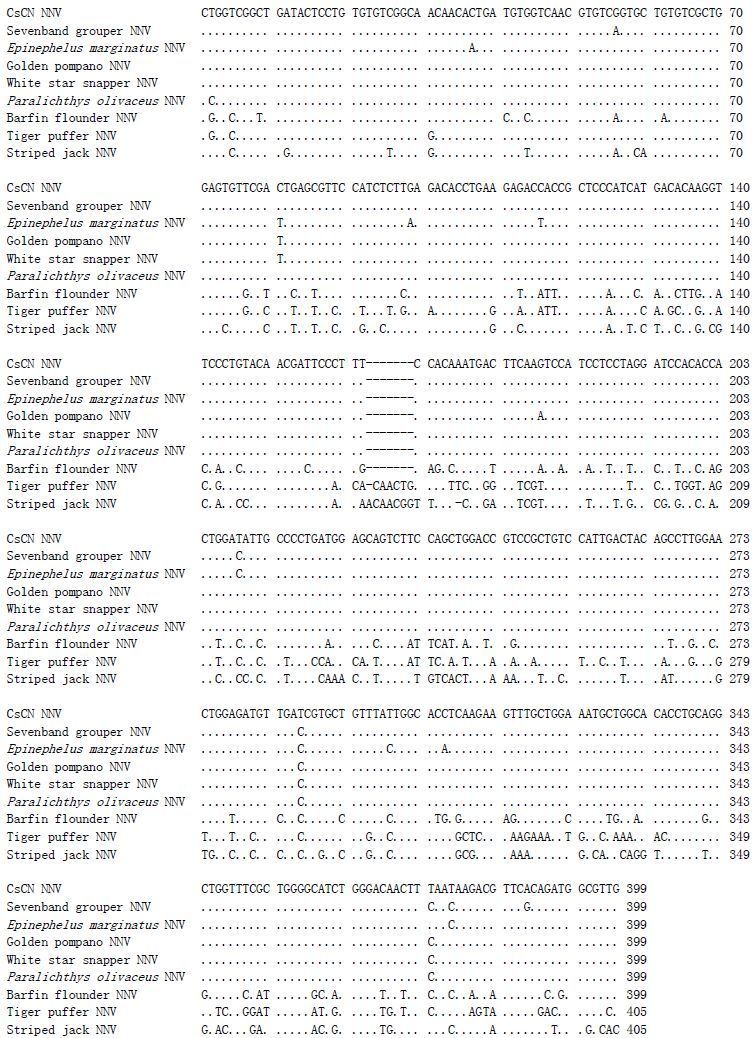
对上述RT-PCR产物测序并进行BLAST比对,结果显示,感染半滑舌鳎的神经坏死病毒(CsCN NNV)与RGNNV基因型的代表种--七带石斑鱼神经坏死病毒(Seven-band grouper nervous necrosis virus)(GenBank检索号:AY324870.1) 的序列相似性为98%,与感染白星笛鲷(Lutjanus stellatus)、东大西洋石斑鱼(Epinephelus marginatus)、牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)和布氏鲳鲹(Trachinotus blochii)的几种鱼类神经坏死病毒的序列相似性均在98%以上。另一方面,CsCN NNV与分别隶属于SJNNV、TPNNV、BFNNV基因型的黄带拟鲹(Pseudocaranx dentex)神经坏死病毒、红鳍东方鲀(Takifugu rubripes)神经坏死病毒和条斑星鲽(Verasper moseri)神经坏死病毒的序列相似性仅在71%-78%之间(图 4)。测定的半滑舌鳎的神经坏死病毒基因序列已经提交到GenBank,检索号KJ541748.2。
|
图 4 CsCN NNV与8株鱼类神经坏死病毒基因序列的比较 Figure 4 Comparison of the amplicon nucleotide sequence among nine strains of nervous necrosis viruses CsCN NNV:半滑舌鳎神经坏死病毒(KJ541748.2) ;Sevenband grouper NNV:七带石斑鱼神经坏死病毒(AY324870.1) ;Epinephelus marginatus NNV:东大西洋石斑鱼神经坏死病毒(KF748942.1) ;Golden pompano NNV:布氏鲳鲹神经坏死病毒(GQ904199.1) ;White star snapper NNV:白星笛鲷神经坏死病毒(AY835642.1) ;Paralichthys olivaceus NNV:牙鲆神经坏死病毒(KF841612.1) ;Barfin flounder NNV:条斑星鲽神经坏死病毒(EU236147.1) ;Tiger puffer NNV:红鳍东方鲀神经坏死病毒(EU236149.1) ;Striped jack NNV:黄带拟鲹神经坏死病毒(AB056572.1) CsCN NNV: Cynoglossus semilaevis NNV(KJ541748.2) ; Sevenband grouper NNV: AY324870.1; Epinephelus marginatus NNV: KF748942.1; Golden pompano NNV: GQ904199.1; White star snapper NNV: AY835642.1; Paralichthys olivaceus NNV: KF841612.1; Barfin flounder NNV: EU236147.1; Tiger puffer NNV: EU236149.1; Striped jack NNV: AB056572.1 |
半滑舌鳎为我国新兴的海水养殖鱼类品种,由于其较高的经济效益,使得半滑舌鳎的养殖规模日益扩大。育苗场多为工厂化育苗模式,集约化程度高,养殖密度大,在管理不善、隔离不严时,暴发性流行病容易发生,造成鱼苗的大规模死亡。通过对发病鱼苗的临床症状、组织病理观察及病原的RT-PCR检测,可以初步确定该养殖场2012年和2013年半滑舌鳎鱼苗的大规模死亡是由鱼类神经坏死病毒的感染引起的。
调查发现,13-30日龄的患病半滑舌鳎鱼苗死亡率极高。据报道,13-35日龄的半滑舌鳎鱼苗正处于变态期,此阶段鱼苗的中枢神经系统开始迅速发育,神经细胞大量增加,同时鱼苗的视网膜结构和视觉特性发生明显改变,以适应底栖生活(Ma et al,2006、2007; 卢艳艳等,2011)。如果鱼苗此时感染了鱼类神经坏死病毒,病毒容易随着神经细胞的生长而大量复制,引起鱼苗脑部及视网膜的病变和空泡化,最终造成鱼苗的大量死亡(Tanaka et al,2004; Manin et al,2011)。
本研究通过RT-PCR技术和序列测定,得到了感染半滑舌鳎的神经坏死病毒CsCN NNV的部分基因序列。序列的比对与分析结果显示,该病毒与分离自七带石斑鱼、东大西洋石斑鱼等鱼体中的5株鱼类神经坏死病毒(全部为RGNNV基因型)的相似性超过98%,而与其他3种基因型的鱼类神经坏死病毒的相似性仅为71%-78%,因此,感染半滑舌鳎的神经坏死病毒CsCN NNV应属于RGNNV基因型(Nishizawa et al,1997; Toffolo et al,2007)。考虑到该育苗场同时进行多种石斑鱼鱼苗的繁育,且曾发生过病毒性神经坏死病,推测感染半滑舌鳎鱼苗的神经坏死病毒很可能来源于同场的其他石斑鱼鱼苗,随着育苗器具及人员的流动而水平传播。由于半滑舌鳎也是鱼类神经坏死病毒的敏感宿主,且鱼苗对病毒的抵抗力弱,因而出现了大规模死亡。这种在同一育苗场中养殖多种鱼苗,造成鱼类神经坏死病毒交叉感染的现象也发生在石斑鱼和尖吻鲈(Lates calcarifer)之间(Hick et al,2011; Manin et al,2011)。因此,在育苗过程中必须严格进行器具消毒,并加强隔离措施,从而阻断鱼类神经坏死病毒的水平传播途径。
鱼类神经坏死病毒宿主广泛,包括50余种海淡水鱼类(Munday et al,2002; Sano et al,2011),但半滑舌鳎并不在其中。本研究首次证实半滑舌鳎是鱼类神经坏死病毒的天然敏感宿主,这一发现在半滑舌鳎疾病防治和鱼类神经坏死病毒的流行机制研究方面都具有重要的意义。
| 马爱军, 王新安, 庄志猛, 等. 半滑舌鳎仔、稚鱼视网膜结构与视觉特性. 动物学报 , 2007, 2 (53) : 354-363 | |
| 卢艳艳, 张雅芝, 常建波, 等. 半滑舌鳎的育苗效果及生物学特征的观察. 集美大学学报(自然科学版) , 2011, 16 (1) : 7-13 | |
| 张晓君, 秦国民, 阎斌伦, 等. 半滑舌鳎病原鳗利斯顿氏菌表型及分子特征研究. 海洋学报 , 2009, 31 (5) : 112-122 | |
| 陈政强, 姚志贤, 林茂, 等. 半滑舌鳎皮肤溃疡病病原研究. 水产学报 , 2012, 36 (5) : 764-771 | |
| 姜言伟, 万瑞景, 陈瑞胜, 等. 渤海半滑舌鳎人工育苗工艺技术的研究. 海洋水产研究 , 1993 (14) : 25-33 | |
| Hick P, Schipp G, Bosmans J, et al. Recurrent outbreaks of viral nervous necrosis in intensively cultured barramundi (Lates calcarifer) due to horizontal transmission of betanodavirus and recommendations for disease control. Aquaculture , 2011, 319 (1-2) : 41-52 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.06.036 | |
| Ma AJ, Liu XZ, Xu YJ, et al. Feeding rhythm and growth of the tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther, during its early life stages. Aquac Res , 2006, 37 (6) : 586-593 DOI:10.1111/are.2006.37.issue-6 | |
| Manin BO, Ransangan J. Experimental evidence of horizontal transmission of Betanodavirus in hatchery-produced Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer and brown-marbled grouper, Epinephelus fuscoguttatus fingerling. Aquaculture , 2011, 321 (1-2) : 157-165 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.08.021 | |
| Munday BL, Kwang J, Moody N. Betanodavirus infections of teleost fish: a review. J Fish Dis, , 2002, 25 : 127-142 DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2761.2002.00350.x | |
| Nishizawa T, Furuhashi M, Nagai T, et al. Genomic classification of fish nodaviruses by molecular phylogenetic analysis of the coat protein gene. Appl Environ Microbiol , 1997, 63 (4) : 1633-1636 | |
| Sano M, Nakai T, Fijan N, Viral diseases and agents of warm water fish. In: Fish Diseases and Disorders, Vol. 3: Viral, Bacterial and Fungal Infections, 2nd edition, Woo PTK & Bruno DW, eds. CABI, London, UK, 2011, 166-244 | |
| Tanaka S, Takagi M, Miyazaki T. Histopathological studies on viral nervous necrosis of seven-band grouper, Epinephelus septemfasciatus Thunberg, at the grow-out stage. J Fish Dis , 2004, 27 (7) : 385-399 DOI:10.1111/jfd.2004.27.issue-7 | |
| Tang XQ, Zhou Li, Zhan WB, et al. Isolation and charact?erization of pathogenic Listonella anguillarum of diseased half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther). J Ocean Uiver China , 2008, 7 (3) : 343-351 DOI:10.1007/s11802-008-0343-3 | |
| Toffolo V, Negrisolo E, Maltese C, et al. Phylogeny of betanodaviruses and molecular evolution of their RNA polymerase and coat proteins. Mol Phylogenet Evol , 2007, 43 (1) : 298-308 DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2006.08.003 | |
| Zhang XJ, Qin GM, Bing XW, et al. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of Photobacterium damselae, a pathogen of the cultured tongue sole Cynoglossus semilaevis in China. New Zeal J Mar Fresh , 2011, 45 (1) : 1-13 DOI:10.1080/00288330.2010.531745 |



