2. 青岛海洋科学与技术国家实验室 海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程功能实验室 青岛 266071;
3. 大连海洋大学 大连 116023
2. Laboratory for Marine Fisheries and Food Production Processes, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266071;
3. Dalian Ocean University, Dalian 116023
孕酮受体膜组分1 (Progesterone receptor membrane component 1, PGRMC1)是单次跨膜蛋白,属于膜相关孕激素受体(Membrane-associated progesterone receptor, MAPR)家族。Meyer等(1996)从猪肝脏实质细胞微粒体膜中提取并纯化了与孕激素高亲和力的PGRMC1蛋白。已有研究证明,PGRMC1作为接头蛋白,与配体分子共同参与调节与它结合的蛋白之间的相互作用和跨膜转运;与孕激素结合,介导调控孕激素信号通路(Cahill, 2007; Lösel et al, 2008)。PGRMC1 mRNA表达和定位在牛(Bovine) (Dode et al, 2006)、大鼠(Rattus norvegicus) (Peluso et al, 2006)和人(Homo sapiens)的卵母细胞(Wood et al, 2007),参与调控雌性配子发育和抑制卵母细胞凋亡。PGRMC1在人和鼠等哺乳动物成熟过程中具有重要的调控作用(Peluso et al, 2008)。
膜相关孕激素受体家族基因在鱼类中的相关研究并不多,国外报道的有云纹犬牙石首鱼(Cynoscion nebulosus) (Patiño et al, 1990)、条纹狼鲈(Morone saxatilis) (King et al, 1997)、金鱼(Carassius auratus) (Tokumoto et al, 2012)、斑点叉尾
本实验室前期研究表明,PGRMC1 mRNA在半滑舌鳎性成熟期时,在与繁殖相关的脑、垂体和卵巢组织中表达丰富,说明半滑舌鳎PGRMC1参与了卵母细胞的发育、成熟过程(张金勇等, 2016)。为了进一步了解半滑舌鳎下丘脑-垂体-性腺轴(HPG轴)中PGRMC1对卵子发育成熟的作用机制,本研究采用qRT-PCR和Western blotting技术分析体外培养条件下不同卵巢发育时期和不同发育时相的卵母细胞PGRMC1的表达特征,为阐明PGRMC1参与调控半滑舌鳎卵母细胞成熟提供重要资料。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料实验用半滑舌鳎取自山东烟台海阳市黄海水产有限公司,挑取人工培育达到性成熟的3龄雌性亲鱼21尾,全长为52-59 cm,体重为1183.9-1349.2 g。实验用鱼的培育条件:在室内水泥池中(5 m×5 m×1 m)全年开放流水培育,水温为10-25℃,盐度为27-31,pH为7.8-8.4,溶解氧为5 mg/L以上,饲喂人工配合饲料。取样时,使用质量浓度为210 mg/L的MS-222将亲鱼麻醉后解剖,为了获得不同发育时相的卵母细胞,选择性腺发育至Ⅳ期和Ⅴ期的卵巢,从卵巢中分离出不同发育时相的、未受损的卵母细胞(李晓晓, 2013)1),用于体外培养,分析不同时相卵母细胞PGRMC1的表达。
1) Li XX. Study on the physiological function of membrane progestin receptor in the reproductive cycle of flatfish. Master's Thesis of Shanghai Ocean University, 2013, 1-73 [李晓晓.膜孕激素受体在鲆鲽类繁殖周期中的生理功能研究.上海海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2013, 1-73]
1.2 卵母细胞体外孵育24孔细胞培养板的每个孔放入pH=7.6的1 ml DMEM培养液(SIGMA)。剥离的卵母细胞样品用于促性腺激素(HCG)调控实验,同时设置对照组。每孔放入30个卵母细胞,HCG孵育浓度分别为0、10 IU/ml和20 IU/ml,共3个浓度组,使用振荡培养箱BSD-250(上海博迅)孵育卵母细胞,24℃培养6 h,每30 min检查孵育情况,观察卵母细胞发育进程。卵母细胞体外培养结束后,分别将实验用卵母细胞在液氮速冻并转至-80℃冰箱存放,用于mRNA和蛋白表达分析。
1.3 PGRMC1的qRT-PCR检测采用TaKaRa公司的RNAiso Plus抽提总RNA后,按照PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser反转录试剂盒(TaKaRa)合成cDNA第一链,用于基因表达分析。半滑舌鳎PGRMC1基因的实时定量引物参照SYBR Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ (TaKaRa)引物设计原则,设计引物RT-PGMRC1 F1(5′-GCTGAGTGGGAGGCTCAGTT-3′)和RT-PGMRC1 R1(5′-TGTCC-TTTGCTTCCTCATCGT-3′),以18S rRNA为内参基因,引物分别为18S F (5′-GGTCTGTGATGCCCTTAG ATGTC-3′)和18S R (5′-AGTGGGGTTCAGCGGGTT-AC-3′)。使用Mastercycler ep realplex Real-time PCR仪(Eppendorf)和SYBR Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ(TaKaRa)荧光试剂,PCR反应体系为20 μl:上下游引物各0.8 μl, cDNA模版1 μl, SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM Ⅱ 10 μl,补充ddH2O至20 μl。采用两步法,PCR程序为95℃ 30 s;95℃ 5 s,54.4℃ 20 s,40个循环。以18S作为内参基因来校正样品中RNA的量。程序运行完成后进行熔解曲线分析,检验产物的特异性。实验样品设3个平行,实验重复3次,同时设阴性对照(模板以ddH2O代替),用以确认实验结果的可靠性。
1.4 PGRMC1的Western blotting分析使用动物组织蛋白提取试剂提取已收集的卵母细胞总蛋白,取冻存在无酶EP管中的卵母细胞,加入0.5 ml动物组织细胞裂解液,使用无酶研磨棒充分匀浆,冰浴中静置30 min,于4℃、12000 r/min离心30 min,取上清液,即得到组织蛋白提取液。12% SDS-PAGE电泳检测提取蛋白的质量,并使用蛋白测定试剂盒测定组织总蛋白浓度。
将40 μg总蛋白质进行12%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳,60 V 1 h,然后90 V 1.5 h。将分子量标准和凝胶上的蛋白电转移到PVDF膜上。1×PBST洗涤PVDF膜2次(每次5 min),5%脱脂奶粉溶液室温封闭(1×PBST稀释) 1 h。洗涤,加入由免疫新西兰大白兔制备的一抗与5% BSA,室温摇床2 h,一抗稀释1:1500。二抗(联科生物公司)室温摇床2 h,稀释度为1:2000。TBST洗膜2次(每次10 min),TBS洗膜1次,5 min。经二氨基联苯胺(DAB)显色,Nikon E80i显微镜拍照,蛋白灰度分析。
1.5 数据统计分析利用2-△△Ct方法(Livak et al, 2001)处理PGRMC1基因的相对表达量数据。基因和蛋白表达数据使用SPSS 17.0软件进行单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA),Tukeyxs HSD检验和Duncanxs多重比较分析。相对表达量数据均以平均数±标准误(Mean±SE)表示,P < 0.05表示差异显著,AIC.AlphaView成像分析系统(Cell Biosciences Inc)分析蛋白灰度,并制成柱状图。
2 结果 2.1 卵子形成过程中PGRMC1的时序表达采用qRT-PCR方法检测了半滑舌鳎不同发育期的卵巢中不同发育时相卵母细胞的PGRMC1 mRNA的相对表达量(图 1)。结果显示,在性腺发育为Ⅳ期和Ⅴ期的卵巢中,不同发育时相卵母细胞的PGRMC1 mRNA的相对表达量随着卵母细胞的发育逐渐增高,以Ⅴ时相卵母细胞时达到峰值,Ⅵ时相时又降为较低水平(P < 0.05)。同时,比较Ⅳ期和Ⅴ期卵巢中的Ⅴ时相卵母细胞的PGRMC1 mRNA表达量可看出,以进入成熟期的Ⅴ期卵巢中的Ⅴ时相卵母细胞的PGRMC1 mRNA表达量最高(P < 0.05),表明此时的卵母细胞进入成熟期,此阶段PGRMC1基因的生理学作用效果最明显,预示PGRMC1基因在卵母细胞成熟过程中起着重要的调控作用。
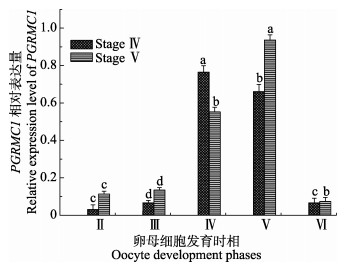
|
图 1 半滑舌鳎卵巢Ⅳ和Ⅴ期中卵母细胞不同时相PGRMC1 mRNA的表达水平 Figure 1 The relative expression levels of PGRMC1 mRNA at different oocyte phases in different development stages of C. semilaevis 不同字母间差异显著(P < 0.05),下同 Different letters represent significant difference (P < 0.05), the same as below |
使用HCG孵育半滑舌鳎Ⅴ期卵巢中不同时相的卵母细胞6 h后,采用qRT-PCR方法检测其PGRMC1基因的表达变化。由图 2得知,10 IU/ml和20 IU/ml剂量的HCG对半滑舌鳎卵母细胞中PGRMC1基因表达都有一定的促进作用,均高于对照组;不同发育时相卵母细胞的PGRMC1 mRNA的相对表达量随着卵母细胞的发育逐渐增高,第Ⅴ时相卵母细胞时达到峰值,第Ⅵ时相时又降为较低水平(P < 0.05);特别是对即将进入成熟阶段卵母细胞中PGRMC1基因的表达量提升明显(P < 0.05),表明HCG通过PGRMC1提升了卵母细胞的减数分裂成熟能力。研究结果预示,PGRMC1和卵母细胞成熟存在密切关系。此外,20 IU/ml剂量的HCG对PGRMC1基因表达的调控作用比剂量为10 IU/ml HCG作用更明显,表明PGRMC1基因表达对HCG调控作用存在剂量依存关系。
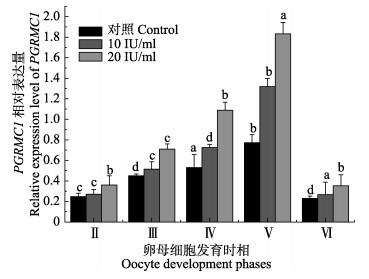
|
图 2 半滑舌鳎不同发育时相卵母细胞在不同浓度HCG调控下PGRMC1 mRNA的表达水平 Figure 2 Effects of HCG at different concentrations on PGRMC1 mRNA expression in different oocyte phases of C. semilaevis |
采用Western blotting方法检测了半滑舌鳎PGRMC1蛋白的表达情况(图 3),结果显示,检测到清晰蛋白条带,分子量大约为21 kDa,与预测的蛋白分子量20.64 kDa相当(图 3-A)(张金勇等, 2017, 待发表)。终浓度为10 IU/ml和20 IU/ml HCG处理组对各时相卵母细胞PGRMC1蛋白表达的促进作用明显,均高于对照组;不同发育时相卵母细胞的PGRMC1蛋白表达量随卵母细胞发育逐渐增高,第Ⅴ时相卵母细胞时达到峰值,第Ⅵ时相时又降为较低水平(P < 0.05),且PGRMC1蛋白表达与HCG调控作用存在剂量依存关系。结果显示,HCG在调控卵母细胞成熟过程中,PGRMC1蛋白表达规律与PGRMC1基因的表达规律相似。
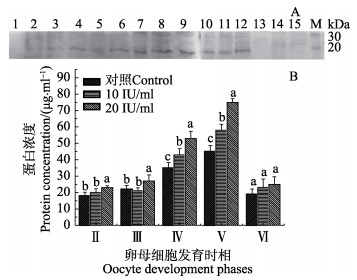
|
图 3 不同浓度HCG对半滑舌鳎不同时期卵母细胞PGRMC1蛋白表达量的影响 Figure 3 Effects of HCG at different concentrations on PGRMC1 protein expression in different oocyte phases of C. semilaevis A: PGRMC1蛋白表达量电泳; B: PGRMC1蛋白表达量化丰度A图中的1、2、3,4、5、6,7、8、9,10、11、12和13、14、15各条带组分别对应B图中Ⅱ时相、Ⅲ时相、Ⅳ时相、Ⅴ时相、Ⅵ时相的卵母细胞;M为蛋白分子量标准 A: Electrophoregram of PGRMC1 protein expression; B: Quantitative abundance of PGRMC1 protein expression Digit 1, 2, and 3; 4, 5, and 6; 7, 8, and 9; 10, 11, and 12; 13, 14, and 15 in figure A corresponded to Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ, Ⅵ groups in figure B, respectively; M: Protein molecular weight marker |
膜孕激素受体家族包括孕激素膜受体(mPRs)和孕酮受体膜组分(PGRMCs)两类受体,其中,膜孕激素受体有3个亚型,即mPRα、mPRβ和mPRγ;孕酮受体膜组分有2种亚型,即PGRMC1和PGRMC2。本实验室前期研究已克隆得到半滑舌鳎PGRMC1基因全长序列,分析了PGRMC1 mRNA在性成熟雌性半滑舌鳎卵巢不同发育时期的表达特征,发现在卵巢中PGRMC1 mRNA表达水平随卵巢发育逐步上升,Ⅴ期时达到最高值(P < 0.05) (张金勇等, 2016)。Preechaphol等(2010)报道,眼柄摘除的斑节对虾(Penaeus monodon)的不同发育阶段的卵巢中PGRMC1 mRNA的表达均高于对照组,说明PGRMC1参与斑节对虾的卵母细胞发育成熟的调控。尽管半滑舌鳎和斑节对虾处于不同进化地位,但半滑舌鳎和斑节对虾PGRMC1 mRNA在卵巢组织表达规律和生理作用上表现出相似性,这表明适当形式的孕激素有可能通过PGRMC1诱发卵母细胞发育和成熟。本研究中,半滑舌鳎卵巢发育至Ⅳ期时,PGRMC1 mRNA在第Ⅳ时相的卵母细胞中表达量最高;在卵巢发育至Ⅴ期时,PGRMC1 mRNA表达的最高值出现在第Ⅴ时相的卵母细胞中。由此看来,PGRMC1对半滑舌鳎卵母细胞发育、成熟起重要的调控作用,卵母细胞的最终成熟以及排卵等过程的完成可能需要大量PGMRC1的参与。
鱼类卵母细胞成熟是一个由多因子调控的复杂生理过程,卵母细胞减数分裂起始于胚胎期,最后发育成为可受精的卵细胞(邓晓惠, 2004)。采用HCG分别孵育金鱼和大西洋绒须石首鱼(Micropogonias undulatus)的卵母细胞,mPRα蛋白水平升高;上调的卵母细胞mPRα蛋白水平与卵母细胞成熟相关(Zhu et al, 2003; Tokumoto et al, 2006)。PGRMC1和mPRα同为膜孕激素受体家族成员,它们在不同鱼类类似的表达模式预示着在卵巢发育成熟过程中很可能都具有重要的生理功能。本研究通过不同浓度HCG处理半滑舌鳎卵巢成熟期的不同时相的卵母细胞,发现半滑舌鳎卵母细胞PGRMC1蛋白和mRNA对HCG的调控正向应答;PGRMC1蛋白和mRNA表达量的提高,可能增强了半滑舌鳎卵母细胞对孕激素的应答能力,提高了卵母细胞减数分裂成熟能力。柳学周等(2015、2014)发现,雌性半滑舌鳎血清中促黄体激素(LH)和孕激素的浓度在卵巢成熟过程中逐渐升高,并在Ⅴ期卵巢达到最高值;这两种激素变化规律与当前研究中PGRMC1蛋白和mRNA在卵母细胞表达变化趋势相吻合,表明半滑舌鳎脑垂体分泌的LH作用于HPG轴,促使卵巢分泌孕激素,PGRMC1介导孕激素诱导卵母细胞成熟。半滑舌鳎为卵巢发育非同步、分批产卵的鲆鲽类,本研究中PGRMC1蛋白和mRNA在不同时相卵母细胞中均检测到表达,这也说明PGRMC1可以介导孕激素维持卵母细胞发育和抗凋亡,这与人类PGRMC1具有抑制卵巢早衰的生理功能相一致(Mansouri et al, 2008)。
本研究探明了卵母细胞成熟过程中PGRMC1 mRNA的时序表达特征,解析了促性腺激素调控不同发育时相卵母细胞PGRMC1蛋白和mRNA的表达规律,但关于PGRMC1参与信号传导通路以及PGRMC1真核表达产物及其促进卵母细胞成熟作用的更深入机制尚不明了,这些问题需今后更深入的探索。
| Cahill MA. Progesterone receptor membrane component 1: An integrative review. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology , 2007, 105 (1-5) : 16-36 DOI:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.02.002 | |
| Deng XH. Technology and color atlas of reproductive medical science. Jinan: Shandong Science and Technology Press, 2004 : 93 -94. [邓晓惠. 生殖医学技术及彩色图谱. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社, 2004 : 93 -94.] | |
| Dode MAN, Dufort I, Massicotte L, et al. Quantitative expression of candidate genes for developmental competence in bovine two-cell embryos. Molecular Reproduction and Development , 2006, 73 (3) : 288-297 DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1098-2795 | |
| Kazeto Y, Goto-Kazeto R, Thomas P, et al. Molecular characterization of three forms of putative membrane-bound progestin receptors and their tissue-distribution in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology , 2005, 34 (3) : 781-791 DOI:10.1677/jme.1.01721 | |
| King W 5th, Ghosh S, Thomas P, et al. A receptor for the oocyte maturation-inducing hormone 17α, 20β, 21-trihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one on ovarian membranes of striped bass. Biology of Reproduction , 1997, 56 (1) : 266-271 DOI:10.1095/biolreprod56.1.266 | |
| Liu XZ, Shi B, Li XX, et al. Molecular characterization of the novel membrane progestin receptor gene and its role during ovarian development in the half smooth tongue sole Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China , 2015, 22 (4) : 608-619 [柳学周, 史宝, 李晓晓, 等. 半滑舌鳎新型膜孕激素受体基因分子特征及其在卵巢发育过程的作用. 中国水产科学 , 2015, 22 (4) : 608-619] | |
| Liu XZ, Shi B, Wang SS, et al. Full length cDNA cloning and expression of luteinizing hormone (LH) and which serum concentration was measured in half smooth tongue sole Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther. Engineering Science , 2014, 16 (9) : 50-60 [柳学周, 史宝, 王珊珊, 等. 半滑舌鳎促黄体激素基因克隆和表达分析及其血清浓度测定. 中国工程科学 , 2014, 16 (9) : 50-60] | |
| Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods , 2001, 25 (4) : 402-408 DOI:10.1006/meth.2001.1262 | |
| Lösel RM, Besong D, Peluso JJ, et al. Progesterone receptor membrane component 1-Many tasks for a versatile protein. Steroids , 2008, 73 (9-10) : 929-934 DOI:10.1016/j.steroids.2007.12.017 | |
| Mansouri MR, Schuster J, Badhai J, et al. Alterations in the expression, structure and function of progesterone receptor membrane component-1 (PGRMC1) in premature ovarian failure. Human Molecular Genetics , 2008, 17 (23) : 3776-3783 DOI:10.1093/hmg/ddn274 | |
| Meyer C, Schmid R, Scriba PC, et al. Purification and partial sequencing of high-affinity progesterone-binding site (s) from porcine liver membranes. European Journal of Biochemistry , 1996, 239 (3) : 726-731 DOI:10.1111/ejb.1996.239.issue-3 | |
| Mourot B, Nguyen T, Fostier A, et al. Two unrelated putative membrane bound progestin receptors, progesterone membrane receptor component 1 (PGRMC1) and membrane progestin receptor (mPR) beta, are expressed in the rainbow trout oocyte and exhibit similar ovarian expression patterns. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology , 2006, 4 (1) : 1-14 DOI:10.1186/1477-7827-4-1 | |
| Patiño R, Thomas P. Characterization of membrane receptor activity for 17 alpha, 20 beta, 21-trihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one in ovaries of spotted seatrout (Cynoscion nebulosus). General and Comparative Endocrinology , 1990, 78 (2) : 204-217 DOI:10.1016/0016-6480(90)90007-9 | |
| Peluso JJ, Pappalardo A, Losel R, et al. Progesterone membrane receptor component 1 expression in the immature rat ovary and its role in mediating progesterone's antiapoptotic action. Endocrinology , 2006, 147 (6) : 3133-3140 DOI:10.1210/en.2006-0114 | |
| Peluso JJ, Romak J, Liu X. Progesterone receptor membrane component-1 (PGRMC1) is the mediator of progesterone's antiapoptotic action in spontaneously immortalized granulosa cells as revealed by PGRMC1 small interfering ribonucleic acid treatment and functional analysis of PGRMC1 mutations. Endocrinology , 2008, 149 (2) : 534-543 DOI:10.1210/en.2007-1050 | |
| Preechaphol R, Klinbunga S, Yamano K, et al. Molecular cloning and expression of progestin membrane receptor component 1(PGRMC1) of the giant tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. General and Comparative Endocrinology , 2010, 168 (3) : 440-449 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.06.002 | |
| Shi B, Li XX, Liu XZ, et al. Molecular cloning and tissue expression analysis of membrane progestin receptor alpha gene (mPRα) from half smooth tongue sole Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther. Progress in Fishery Sciences , 2013, 34 (3) : 61-67 [史宝, 李晓晓, 柳学周, 等. 半滑舌鳎膜孕激素受体基因克隆与组织表达分析. 渔业科学进展 , 2013, 34 (3) : 61-67] | |
| Shi B, Liu XZ, Xu YJ, et al. Molecular and transcriptional characterization of GTHs and mPRa during ovarian maturation in rock bream Oplegnathus fasciatus. Journal of Experimental Zoology, Part A: Ecological Genetics and Physiology , 2015, 323 (4) : 430-444 | |
| Tokumoto T. Identification of membrane progestin receptors (mPR) in goldfish oocytes as a key mediator of steroid non-genomic action. Steroids , 2012, 77 (10) : 1013-1016 DOI:10.1016/j.steroids.2012.04.006 | |
| Tokumoto M, Nagahama Y, Thomas P, et al. Cloning and identification of a membrane progestin receptor in goldfish ovaries and evidence it is an intermediary in oocyte meiotic maturation. General and Comparative Endocrinology , 2006, 145 (1) : 101-108 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.07.002 | |
| Wood JR, Dumesic DA, Abbott DH, et al. Molecular abnormalities in oocytes from women with polycystic ovary syndrome revealed by microarray analysis. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism , 2007, 92 (2) : 705-713 DOI:10.1210/jc.2006-2123 | |
| Yoshikuni M, Shibata N, Nagahama Y. Specific binding of [3H] 17α, 20β-dihydroxy-4-prognen-3-one to oocyte cortices of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry , 1993, 11 (1-6) : 15-24 DOI:10.1007/BF00004546 | |
| Zhang JY, Liu XZ, Shi B, et al. Molecular cloning, tissue and spatio-temporal expression pattern of PGRMC1 in the half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Journal of Fishery Sciences of China , 2016, 23 (5) : 1080-1090 [张金勇, 柳学周, 史宝, 等. 半滑舌鳎孕酮受体膜组分1基因的克隆及组织和时空表达规律. 中国水产科学 , 2016, 23 (5) : 1080-1090] | |
| Zhu Y, Rice CD, Pang Y, et al. Cloning, expression, and characterization of a membrane progestin receptor and evidence it is an intermediary in meiotic maturation of fish oocyte. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA , 2003, 100 (5) : 2231-2236 DOI:10.1073/pnas.0336132100 |



