2. 青岛海洋科学与技术国家实验室 海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程功能实验室 青岛 266071;
3. 上海海洋大学水产与生命学院 上海 201306
2. Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266071;
3. College of Fisheries and Life Science, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306
几丁质酶在甲壳动物的蜕皮过程中发挥着重要的生理作用,将旧的外骨骼消化成可溶性物质,被甲壳动物部分重新吸收后,再用于新的外骨骼的合成 (Huang et al, 2010)。几丁质是甲壳动物外壳的主要成分,其合成和降解在该类动物蜕皮生长过程中起着非常重要的作用。按照几丁质酶的氨基酸序列,几丁质酶可分成6类 (陈少波等, 2004),Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ型和N-乙酰葡萄糖胺酶。糖基化水解酶第19族包括Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅳ型,主要存在于植物中。第18族包括Ⅲ型和Ⅴ型,在节肢动物和昆虫中广泛存在,节肢动物门下的甲壳动物三疣梭子蟹 (Portunus trituberculatus) 的几丁质酶属于几丁质酶第18族Ⅲ型,第20族则包括N-乙酰葡萄糖胺酶 (Techkarnjanaruk et al, 1999)。三疣梭子蟹主要摄取含几丁质外壳的动物,只有几丁质酶才有助于消化几丁质。甲壳动物几丁质酶的活力与蜕皮存在密切的关系,与蜕皮激素含量亦有一定相关性 (吕黎等, 2011),因此,自身的几丁质分解是受调控的,只有在相应的蜕皮周期才会被消化分解。Watanabe等 (1998)分离出了日本囊对虾 (Penaeus japonicus) 的几丁质酶Pjchi-3,发现在其肝胰腺中高表达,与日本囊对虾对几丁质类食物的消化相关。斑节对虾 (Penaeus mondon) PmChi3也主要在肝胰腺中表达,可能在几丁质类食物的消化中发挥作用 (Proespraiwong et al, 2010)。中国明对虾 (Fenneropenaeus chinensis) Fcchi-3 (Zhang et al, 2010) 和凡纳滨对虾 (Litopenaeus vannamei) LvCHT3 (Qian et al, 2010) 也是肝胰腺特异性基因,与消化相关。
本实验室对三疣梭子蟹主要组织进行了高通量转录组测序,从中筛选获得PtCht3基因的部分序列,采用RACE技术,克隆得到该基因的全长cDNA序列,并对其在不同蜕皮周期和低盐胁迫后的三疣梭子蟹组织中的表达特征进行初步研究,以期为三疣梭子蟹PtCht3的生物学功能和渗透压调节机理的研究提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料实验材料为来自山东潍坊昌邑海丰公司养殖的健康状态良好的三疣梭子蟹1200只,体重为4.67–6.89 g。蟹池20 m3,每池养殖200只三疣梭子蟹,共6池,暂养3 d。自然海水养殖 (盐度为33),水温控制在24–26℃左右,pH=8.7,保持供氧充足,每天更换1/3的水量,暂养期间,每天18:00定时投喂蓝蛤 (Potamocorbula),投喂量为总体重的5%–8%。
1.2 实验方法 1.2.1 总RNA的提取及cDNA第一链的合成参照王渝 (2014)1),Trizol法提取所取组织的总RNA,其质量及完整性用核酸定量仪 (Biodropsis, BO-1000) 与1.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测;各取相同质量的肝胰腺和第6对鳃的总RNA混匀,按照SMARTTMRACE Amplification Kit说明书合成3' RACE和5' RACE的cDNA。
1) Wang Y. Expression analysis of salinity-related genes and development of SNP in Portunus trituberculatus. Master's Thesis of Shanghai Ocean University, 2014, 11–12 [王渝.三疣梭子蟹盐度相关基因克隆、表达分析及盐度关联SNP的开发.上海海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2014, 11–12]
1.2.2 全长cDNA的克隆及测序利用软件Primer Premier 5.0引物设计软件,依据三疣梭子蟹反转录数据库中几丁质酶基因3的已知表达序列标签 (EST),进行3'和5' RACE特异性引物的设计。用Advantage 2 PCR Kit扩增3'和5'末端。分别用特异性引物PtCht3F和PtCht3R与通用引物UPM扩增3'和5'末端 (表 1),方法参照王渝 (2014)1)。
|
|
表 1 三疣梭子蟹PtCht3克隆所用引物序列 Table 1 Sequences of primers used in the cloning of P. trituberculatus PtCht3 |
参照王渝 (2014)1),用Vector NTI 11.0软件去除所测序列中的冗余序列,并拼接;用软件DNAStar的EditSeq预测开放阅读框,翻译氨基酸;对PtCht3基因核苷酸序列和推导的氨基酸序列进行同源性比对;蛋白质理化性质预测、蛋白质跨膜区分析及蛋白质功能结构域分析参照徐文斐等 (2014);与其他物种几丁质酶3的序列进行多序列比对,然后以邻接法进行系统进化树的构建,具体方法参照段亚飞等 (2013)。
1.2.4 三疣梭子蟹蜕皮周期实验选取处在蜕皮间期、前期、后期的三疣梭子蟹各3只。参照沈洁等 (2011),各取三疣梭子蟹的第1对鳃、肌肉、肝胰腺、第6对鳃、肠、胃、心脏、表皮、眼柄、血细胞,于液氮中冻存,待提取RNA。
1.2.5 盐度胁迫实验随机挑取暂养3 d的三疣梭子蟹600只,实验设置2个盐度组,分别为低盐组 (盐度为11) 和正常组 (自然海水,盐度为33),每组设3个平行,每个平行100只,于3 m3蟹池中进行实验。低盐组盐度配制方法:参照隋延鸣等 (2012)向自然海水中注入淡水,混匀,使其盐度降至11,利用YSI盐度仪校准盐度。实验分2组,每组3个平行,分别于胁迫0、3、6、12、24、48和72 h时间点取3只三疣梭子蟹的鳃和肝胰腺,于液氮中冷冻,3只蟹子组织样品混合研磨,用于后续RNA的提取。
1.2.6 几丁质酶基因PtCht3 mRNA的Real-time PCR定量检测对照组和实验组三疣梭子蟹所取组织的总RNA提取和cDNA的反转录合成分别利用Trizol试剂和PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit完成。
根据拼接获得的PtCht3 cDNA序列全长和已知的三疣梭子蟹管家基因β-actin,分别设计1对正反特异引物 (β-actin-F和β-actin-R、PtCht3qF和PtCht3qR) (表 2),对三疣梭子蟹肝胰腺和鳃中各个基因在不同时间点盐度胁迫的相对表达量进行检测。利用Real-time PCR对各个组织中和胁迫进程中PtCht3基因的表达情况进行统计分析。PtCht3基因的相对表达量用2–ΔΔCt方法计算,使用SPSS 19.0软件进行单因素方差分析 (One-way ANOVA),P < 0.05表示差异显著。
|
|
表 2 三疣梭子蟹PtCht3 mRNA相对表达分析所用引物序列 Table 2 Sequences of primers used in the analysis of relative mRNA expression of P. trituberculatus PtCht3 |
利用核酸定量仪对所取各个组织提取获得的总RNA进行检测,其OD260 nm/OD280 nm比值均在1.8–2.0之间;1.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测呈现3条清晰的条带,分别是28S、18S和5S rRNA。检测结果显示,所提取的总RNA纯度较高且完整性较好。
2.2 几丁质酶基因PtCht3的cDNA全长克隆取三疣梭子蟹眼柄、第6对鳃和肝胰腺的总RNA的混合物作为模板,分别反转录为3′和5′ RACE的第一链cDNA。分别用特异引物PtCht3F和PtCht3R与通用引物UPM配对,进行3′和5′ RACE的扩增,得到大小分别为457 bp和567 bp的cDNA片段。与已知表达序列标签拼接,获得三疣梭子蟹几丁质酶3基因的cDNA序列全长,将其命名为PtCht3。GenBank登录号为KM100754。PtCht3的cDNA序列全长为1409 bp,包括开放阅读框 (ORF)1185 bp,3′非编码区 (3′-UTR)199 bp,5′端非编码区 (5′-UTR) 25 bp。3'端具有多聚腺苷酸Poly A尾和加尾信号AATAAA (图 1)。

|
图 1 三疣梭子蟹PtCht3核苷酸序列及其推导的氨基酸序列 Figure 1 Nucleotide sequence and the deduced amino acid sequence encoded by P. trituberculatus PtCht3 起始密码子 (ATG)、加尾信号 (AATAAA) 和终止密码子 (TGA) 用细线方框标出;粗线方框内为几丁质酶第18家族保守基序;信号肽以细下划线标出 The letters in the box indicated the start codon (ATG), the polyadenylation signal sequence (AATAAA), and the stop codon (TGA). The conserved motifs of the catalytic domain of the 18th chitinase family were framed in black boxes. The signal peptide was underlined with a thin line |
根据PtCht3基因序列推导出的氨基酸序列进行分析可知,它编码含有394个氨基酸的蛋白质,分子量为43.67 kDa,理论等电点pI为4.80。氨基酸组成分析结果显示,PtCht3蛋白含有碱性氨基酸残基27个 (Arg和Lys),酸性氨基酸残基51个 (Asp和Glu),疏水性氨基酸残基144个 (Ala、Ile、Leu、Phe、Trp和Val),极性氨基酸98个 (Ser、Cys、Asn、Gln、Tyr和Thr),PtCht3蛋白亲水性总平均数为-0.097,属于稳定蛋白。结构域分析结果显示,其N端1–20氨基酸处存在信号肽,PtCht3序列存在1个几丁质酶第18家族活性位点138FDGLDLAWT146。在22–368氨基酸处存在几丁质酶第18家族催化结构域,含4个保守基序。
2.4 几丁质酶基因PtCht3的同源性分析BLAST同源性分析三疣梭子蟹PtCht3序列,显示PtCht3基因与日本仿长额虾 (Pandalopsis japonica) Cht3的同源性最高,为54%。与其他物种如中华绒螯蟹 (Eriocheir sinensis)、锯缘青蟹 (Scylla serrata)、日本沼虾 (Macrobrachium nipponense)、中国明对虾和日本囊对虾的同源性分别为53%、52%、51%、50%和49%。与日本仿长额虾、中华绒螯蟹和锯缘青蟹等动物的Cht3氨基酸序列比对得知,几丁质酶第18家族催化结构域的保守基序Motif Ⅰ、Motif Ⅱ、Motif Ⅲ和Motif Ⅳ在以上几个物种中都存在 (图 2)。

|
图 2 三疣梭子蟹PtCht3氨基酸序列的多序列比对 Figure 2 The multiple alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences encoded by P. trituberculatus PtCht3 and other speciesx 几丁质酶第18家族保守基序以方框表示 The conserved motifs of the 18th chitinase family were framed in black boxes |
利用软件MEGA 5.0进行系统进化 (NJ法) 分析显示,几丁质酶第18家族Ⅲ型主要聚为2大类群:甲壳类和昆虫类,三疣梭子蟹PtCht3聚类顺序依次为与中华绒螯蟹、锯缘青蟹、日本仿长额虾、日本囊对虾、日本沼虾、斑节对虾、凡纳滨对虾和中国明对虾等 (图 3)。
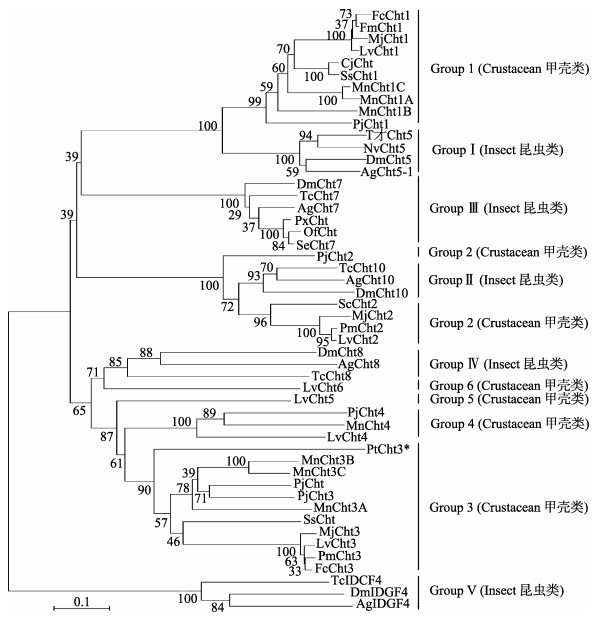
|
图 3 三疣梭子蟹几丁质酶蛋白PtCht3的系统进化树 Figure 3 The phylogenetic analysis of chitinase PtCht3 of P. trituberculatus *:三疣梭子蟹几丁质酶蛋白PtCht3;各物种几丁质酶蛋白Cht GenBank登录号:日本沼虾Cht1A (KF466274.1)、Cht1B (KF466275.1)、Cht1C (AHL24866.1)、Cht3A (KF466276.1)、Cht3B (KF466277.1)、Cht3C (KF466278.1)、Cht4 (KF466279.1);中国明对虾Cht1 (ABB85237.1)、Cht3 (DQ000159.1);斑节对虾Cht1 (AAD40313.1)、Cht2 (ADG22164.1)、Cht3 (ADG22163.1);锯缘青蟹Cht (ABY85409.1)、Cht1 (ACG60512.1)、Cht2 (ACZ53950.1);日本蟳Cht (AFF59213.1)、Cht1 (BAA12287)、Cht2(BAA14014)、Cht3 (BAA22854);凡纳滨对虾Cht1 (EU883591.1)、Cht2 (EU861222.1)、Cht3 (AAN74647.1)、Cht4 (FJ888480.1)、Cht5 (FJ888481.1)、Cht6 (GQ916594.1);日本仿长额虾Cht (AFC60660.1)、Cht1 (JF694836.1)、Cht2 (JN982965.1)、Cht3 (JF694838.1)、Cht4 (JF694837.1);黑腹果蝇Cht5 (NP_650314.1)、Cht7 (NP_647768.2)、Cht8 (NP_611542.1)、Cht10 (EAA46011.1);赤拟谷盗Cht5 (NP_001034524.1)、Cht7 (NP_001036035.1);赤拟谷盗Cht8 (NP_001036067.1)、Cht10 (NP_001038091.1);冈比亚按蚊Cht5-1 (HQ456129)、Cht7 (XP_308858.4)、Cht8 (XP_316448.2)、Cht10 (XP_317398.3);丽蝇蛹集金小蜂Cht5(NP_001155084.1);亚洲玉米螟Cht (AGX32025.1);小菜蛾Cht (AFI55112.1);甜菜夜蛾Cht7 (AFM38213.1) *: PtCht3 from Portunus trituberculatus. GenBank Accession Number of Cht: Macrobrachium nipponense Cht1A (KF466274.1), Cht1B (KF466275.1), Cht1C (AHL24866.1), Cht3A (KF466276.1), Cht3B (KF466277.1), Cht3C (KF466278.1), and Cht4 (KF466279.1); Fenneropenaeus chinensis Cht1 (ABB85237.1), and Cht3 (DQ000159.1); Penaeus monodon Cht1 (AAD40313.1), Cht2 (ADG22164.1), and Cht3 (ADG22163.1); Scylla serrata Cht (ABY85409.1), Cht1 (ACG60512.1), and Cht2 (ACZ53950.1); Charybdis japonica Cht (AFF59213.1), Cht1 (BAA12287), Cht2(BAA14014), and Cht3 (BAA22854); Litopenaeus vannamei Cht1 (EU883591.1), Cht2 (EU861222.1), Cht3 (AAN74647.1), Cht4 (FJ888480.1), Cht5 (FJ888481.1), and Cht6 (GQ916594.1); Pandalopsis japonica Cht (AFC60660.1), Cht1 (JF694836.1), Cht2 (JN982965.1), Cht3 (JF694838.1), and Cht4 (JF694837.1); Drosophila melanogaster Cht5 (NP_650314.1), Cht7 (NP_647768.2), Cht8 (NP_611542.1), and Cht10 (EAA46011.1); Tribolium castaneum Cht5 (NP_001034524.1), Cht7 (NP_001036035.1), Cht8 (NP_001036067.1), and Cht10 (NP_001038091.1); Anopheles gambia str. Cht5-1 (HQ456129), Cht7 (XP_308858.4), Cht8 (XP_316448.2), and Cht10 (XP_317398.3); Nasonia vitripennis Cht5 (NP_001155084.1); Ostrinia furnacalis Cht (AGX32025.1); Plutella xylostella Cht (AFI55112.1); Spodoptera exigua Cht7 (AFM38213.1) |
实时荧光定量PCR分析可知,PtCht3在表皮、胃、第6对鳃、肠血细胞、心脏、第1对鳃、肌肉、眼柄和肝胰腺中均有表达。PtCht3在肝胰腺表达量最高,与其他组织相比,差异显著 (P < 0.05),其次是胃,在其他组织中的表达量均很低 (图 4)。
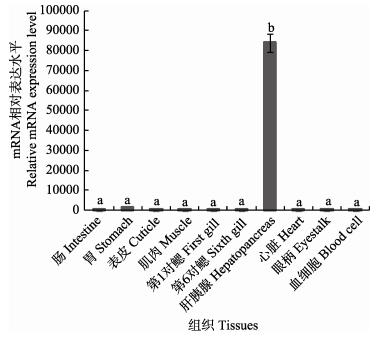
|
图 4 三疣梭子蟹PtCht3在不同组织中的表达分布 Figure 4 The distribution and relative expression of P. trituberculatus PtCht3 in different tissues 不同组织表达量均以与血细胞相比较的倍数表示,不同英文字母表示差异显著 (P < 0.05) Different letters indicated significant differences (P < 0.05) between different tissues in P. trituberculatus expression compared with blood cell |
PtCht3在蜕皮周期实验肝胰腺中的表达情况见图 5。后期经间期至前期,肝胰腺中PtCht3的相对表达量一直呈上升趋势,后期至间期出现显著性上调 (P < 0.05),间期至前期亦是明显上调表达,表达量在前期达到相对最大值。
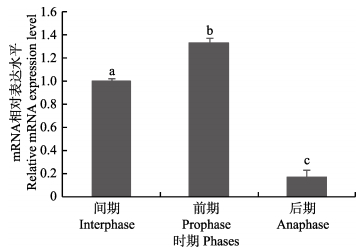
|
图 5 三疣梭子蟹蜕皮周期中PtCht3在肝胰腺中的表达 Figure 5 The relative expression of P. trituberculatus PtCht3 in hepatopancreas during molting 肝胰腺各蜕皮时期表达量均以与肝胰腺间期相比较的倍数表示,不同英文字母表示差异显著 (P < 0.05) Different letters indicated significant differences (P < 0.05) between different molting phases in P. trituberculatus expression compared with interpahse in hepatopancreas |
低盐胁迫下,三疣梭子蟹PtCht3在第6对鳃中的相对表达情况见图 6。与对照组相比,胁迫组PtCht3的表达量于3、12、48 h出现轻微下调,于48 h达到最小值,在24、72 h出现显著性上调 (P < 0.05),72 h达到最大值,为对照组的4.97倍,整体呈现上调表达趋势。
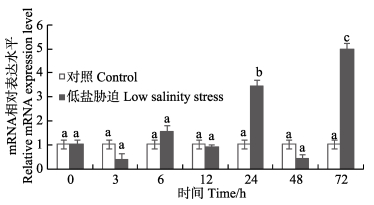
|
图 6 低盐胁迫下三疣梭子蟹PtCht3在第6对鳃中的表达 Figure 6 The relative expression of P. trituberculatus PtCht3 in the sixth gill in response to the low salinity stress 低盐胁迫下各个时间点表达量均以与各时间点对照相比较的倍数表示,不同英文字母表示差异显著 (P < 0.05) Different letters indicated significant differences (P < 0.05) between different points of time in P. trituberculatus expression compared with the control group under low salinity stress |
三疣梭子蟹PtCht3在低盐胁迫下肝胰腺中的相对表达情况见图 7。与对照组相比,胁迫组PtCht3基因的相对表达量于3 h轻微下调,3–6 h时间段内出现显著性上调 (P < 0.05);于12 h显著下调后,表达量迅速回升,24 h上调极显著 (P < 0.01),达到最大值,相对表达量为对照组的4.32倍,整体呈现波动式表达趋势。
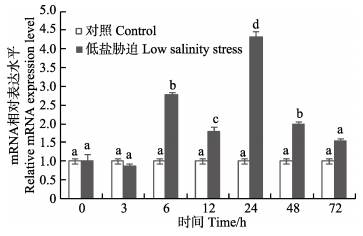
|
图 7 低盐胁迫下三疣梭子蟹PtCht3在肝胰腺中的表达 Figure 7 The relative expression of P. trituberculatus PtCht3 in hepatopancreas in response to the low salinity stress 低盐胁迫下不同时间点的相对表达量均以与各时间点对照相比较的倍数表示,不同英文字母表示差异显著 (P < 0.05) Different letters indicated significant differences (P < 0.05) between different time points in P. trituberculatus expression compared with the control group under low salinity stress |
本研究成功克隆三疣梭子蟹几丁质酶基因PtCht3 cDNA序列,全长为1409 bp,编码394个氨基酸,分子量为43.67 kDa,理论等电点pI为4.80,其N端1–20氨基酸处存在信号肽,存在1个几丁质酶第18家族活性位点138FDGLDLAWT146,并存在几丁质酶第18家族催化结构域,含4个保守基序Motif Ⅰ、Motif Ⅱ、Motif Ⅲ和Motif Ⅳ。该基因与日本仿长额虾Cht3的同源性最高,为54%。根据cDNA序列推导出氨基酸序列分析发现,几丁质酶PtCht3具备典型的几丁质酶基因第18家族的序列特征,包括glyco-18催化结构域、活性位点 (FDGLDLAWT) (Boot et al, 2001)。PtCht3催化结构域具有几丁质酶第18家族的保守基序,分别为MotifⅠ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ(Bleau et al, 1999)。几丁质酶第18家族催化结构域的保守基序MotifⅠ、MotifⅡ、MotifⅢ和MotifⅣ在日本仿长额虾、中华绒螯蟹和锯缘青蟹等动物的Cht3氨基酸序列中都存在。进化树分析显示,几丁质酶第18家族Ⅲ型主要聚为2大类群:甲壳类和昆虫类,三疣梭子蟹PtCht3能够很好地与甲壳类几丁质酶Group 3的其他成员聚为一类,聚类顺序依次为中华绒螯蟹、锯缘青蟹、日本仿长额虾、日本囊对虾、日本沼虾、斑节对虾、凡纳滨对虾和中国明对虾等。这些高度保守的结构域和活性位点及进化分析表明,三疣梭子蟹几丁质酶PtCht3确实是几丁质酶第18家族甲壳类几丁质酶Group 3的一员,具有几丁质酶第18家族的一些功能,如几丁质类食物的消化,参与蜕皮过程 (Coulson, 1994)。
甲壳动物几丁质酶基因家族的不同成员在其蜕皮过程中发挥的作用也可能会不同 (Broadway et al, 1995)。中国明对虾几丁质酶基因FcCht1和FcCht3在中国明对虾蜕皮的不同阶段中呈现一定的波动变化 (Priya et al, 2009)。Zhang等 (2014)研究发现,日本沼虾几丁质酶基因MnCht1A、MnCht1B和MnCht3B在蜕皮周期中发挥关键作用,MnCht4在蜕皮过程中只起辅助作用。Zou (2009)研究发现,中国明对虾的几丁质酶基因FcChi3在其整个蜕皮周期中都有表达,并伴随着一定的波动性,在蜕皮前期表达量较高。
本研究组织表达分析显示,PtCht3在各个组织中均有表达,在肝胰腺中表达量最高,具有较强的组织特异性,差异显著 (P < 0.05),说明其主要功能很可能与三疣梭子蟹对几丁质类食物的消化相关。在肝胰腺中,PtCht3在蜕皮后期表达量较低,在间期表达量出现显著性提高,到蜕皮前期表达量达到最大。在整个蜕皮周期中,PtCht3表达量整体呈上升趋势,表明PtCht3 mRNA的表达可能受到三疣梭子蟹蜕皮激素的调控,进而辅助蜕皮作用的顺利进行。以上研究表明,PtCht3在肝胰腺中的高表达量,肝胰腺PtCht3在不同蜕皮阶段的表达量的显著变化,进一步说明PtCht3可能与几丁质的消化相关,作为几丁质类食物的消化酶基因,参与了三疣梭子蟹的消化进程。与本研究结果相似的是,日本对虾 (Penaeus japonicus) PjChi-1和PjChi-2 (Watanabe et al, 1996、1997)、斑节对虾PmCht1 (Tan et al, 2000) 和PmCht2 (Enmin, 2009)、中国明对虾 (Priya et al, 2009) FcCht1和FcCht3、日本沼虾 (Zhang et al, 2014) MnCht1A、MnCht1B和MnCht3B等几丁质酶基因在不同蜕皮阶段的表达量也表现出一定的波动变化,与血淋巴中的蜕皮激素含量存在一定的相关性 (吕黎等, 2011)。几丁质酶亦存在于日本对虾肝胰腺中,涉及到日本对虾几丁质酶类食物的消化 (Watanabe et al, 1996、1998)。斑节对虾PmChi1 (Siok et al, 2000) 与日本对虾PjChi-1 (Watanabe et al, 1996) 高度同源,亦是在肝胰腺中具有组织特异性,被认为主要与几丁质类食物的降解有关。
盐度改变会启动甲壳动物的渗透压调节,盐度的适度降低会导致其蜕皮周期缩短,从而使蜕皮率增高,进而促进其生长发育 (Mu et al, 2005; Bray et al, 1994; 王冲等, 2010),而鳃是三疣梭子蟹进行呼吸和调节渗透压的主要作用器官 (韩晓琳等, 2014)。本实验室Lv等 (2013)开展了三疣梭子蟹转录组的研究,结果发现,在低盐和高盐胁迫下,三疣梭子蟹鳃中几丁质酶家族基因的表达量有显著差异。张凤等 (2015)研究发现,低盐胁迫下,三疣梭子蟹几丁质酶PtCht在第6对鳃中的表达量出现了显著变化,这些结果均暗示第6对鳃可能参与三疣梭子蟹渗透压调节进程。低盐胁迫下,PtCht3基因的表达在第6对鳃中总体呈上升的趋势,在3、12、48 h出现轻微的波动下调,在肝胰腺中总体呈先上调后下调,12 h出现轻微波动的表达规律。综合分析第6对鳃和肝胰腺PtCht3基因表达情况,PtCht3对低盐胁迫的应答快且敏感,这表明了盐度影响了PtCht3的表达,不管是第6对鳃还是肝胰腺,可能参与了三疣梭子蟹抵抗低盐胁迫的渗透压调节进程。低盐胁迫下,PtCht3在第6对鳃和肝胰腺中呈现出不同的表达趋势,这可能表明PtCht3可能参与多种生理功能,如渗透调节、内环境稳定、消化和发育,并且在盐度变化时其表达可能会受到影响。
组织表达分布、蜕皮周期以及低盐胁迫实验表明,PtCht3是一个很重要的几丁质酶,既与几丁质类食物的消化相关,又参与了三疣梭子蟹渗透压调节进程,其详细的作用机制尚需进一步探索。
| Bleau G, Massicotte F, Merlen Y, et al. Mammalian chitinase-like proteins. EXS, 1999, 87: 211-221 | |
| Boot RG, Blommaart EF, Swart E, et al. Identification of a novel acidic mammalian chitinase distinct from chitotriosidase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(9): 6770-6778 DOI:10.1074/jbc.M009886200 | |
| Bray WA, Lawrence AL, Leung-Trujillo JR. The effect of salinity on growth and survival of Litopenaeus vannamei with observations on the interaction of IHHN virus and salinity. Aquaculture, 1994, 122(2-3): 133-146 DOI:10.1016/0044-8486(94)90505-3 | |
| Broadway RM, Williams DL, Kain WC, et al. Partial characterization of chitinolytic enzymes from Streptomyces albidoflavus. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 1995, 20(5): 271-276 DOI:10.1111/j.1472-765X.1995.tb00444.x | |
| Chen SB, Wu GF. Recent progress on chitinase. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2004, 20(3): 258-262 [陈少波, 吴根福. 几丁质酶研究进展. 科技通报, 2004, 20(3): 258-262] | |
| Coulson AF. A proposed structure for 'family 18' chitinase: A possible function for narhonin. FEBS Letters, 1994, 354(1): 41-44 DOI:10.1016/0014-5793(94)01084-6 | |
| Duan YF, Liu P, Li JT, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of cathepsin L cDNA of Exopalaemon carinicauda. Zoological Research, 2013, 34(1): 39-46 [段亚飞, 刘萍, 李吉涛, 等. 脊尾白虾组织蛋白酶L基因的克隆及其表达分析. 动物学研究, 2013, 34(1): 39-46] | |
| Han XL, Gao BQ, Wang HF, et al. Effects of low salinity stress on microstructure of gill and hepatopancreas and family survival rate of Portunus trituberculatus. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2014, 35(1): 104-110 DOI:10.11758/yykxjz.20140115 [韩晓琳, 高保全, 王好锋, 等. 低盐胁迫对三疣梭子蟹鳃和肝胰腺显微结构及家系存活的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2014, 35(1): 104-110] | |
| Huang QS, Yan JH, Tang JY, et al. Cloning and tissue expressions of seven chitinase family genes in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2010, 29(1): 75-81 | |
| Lv JJ, Liu P, Wang Y, et al. Transcriptome analysis of Portunus trituberculatus in response to salinity stress provides insights into the molecular basis of osmoregulation. PLoS One, 2013, 8(12): e82155 DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0082155 | |
| Lv L, Ning QJ. Recent progress on gene structure and functions of crustacean chitinase. Progress in Physiological Sciences, 2011, 42(6): 457-459 [吕黎, 宁黔冀. 甲壳动物几丁质酶基因结构与功能的研究进展. 生理科学进展, 2011, 42(6): 457-459] | |
| Mu YC, Wang F, Dong SL, et al. The effects of salinity fluctuation in different ranges on intermolt period and growth of juvenile Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2005, 27(2): 122-126 | |
| Priya TA, Li F, Zhang J, et al. Molecular characterization and effect of RNA interference of retinoid X receptor (RXR) on E75 and chitinase gene expression in Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2009, 153(1): 121-129 DOI:10.1016/j.cbpb.2009.02.009 | |
| Proespraiwong P, Tassanakajon A, Rimphanitchayakit V. Chitinases from the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon: Phylogenetics, expression and activities. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2010, 156(2): 86-96 DOI:10.1016/j.cbpb.2010.02.007 | |
| Qian SH, Jiang HY, Jian YT, et al. Cloning and tissue expressions of seven chitinase family genes in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2010, 29(1): 75-81 | |
| Shen J, Zhu DF, Hu ZH, et al. Molt staging in the swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2011, 35(10): 1481-1487 [沈洁, 朱冬发, 胡则辉, 等. 三疣梭子蟹蜕皮周期的分期. 水产学报, 2011, 35(10): 1481-1487] | |
| Siok HT, Bernard MD, Sigrid AL. The Penaeus monodon chitinase 1 gene is differentially expressed in the hepatopancreas during the molt cycle. Marine Biotechnology, 2000, 2(2): 126-135 | |
| Sui YM, Gao BQ, Liu P, et al. The tolerance to and optimal salinity for growth in swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus "Huangxuan No.1". Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2012, 27(5): 398-401 [隋延鸣, 高保全, 刘萍, 等. 三疣梭子蟹"黄选l号"盐度耐受性及适宜生长盐度分析. 大连海洋大学学报, 2012, 27(5): 398-401] | |
| Tan SH, Degnan BM, Lehnert SA, et al. The Penaeus monodon chitinase 1 gene is differentially expressed in the hepatopancreas during the molt cycle. Marine Biotechnology, 2000, 2: 126-135 | |
| Techkarnjanaruk S, Goodman AE. Multiple genes involved in chitin degradation from the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain S9. Microbiology, 1999, 145(4): 925-934 | |
| Wang C, Jiang LX, Wang RJ, et al. Effect of abrupt and gradual changes in salinity on development and feeding in juvenile swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus). Fisheries Science, 2010, 29(9): 510-514 [王冲, 姜令绪, 王仁杰, 等. 盐度骤变和渐变对三疣梭子蟹幼蟹发育和摄食的影响. 水产科学, 2010, 29(9): 510-514] | |
| Watanabe T, Kono M, Aida K, et al. Isolation of cDNA encoding a putative chitinase precursor in the kuruma prawn Penaeus japonicus. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 1996, 5(4): 299-303 | |
| Watanabe T, Kono M, et al. Isolation of a cDNA encoding a chitinase family protein from cuticular tissues of the Kuruma prawn Penaeus japonicus. Zoological Science, 1997, 14(1): 65-68 DOI:10.2108/zsj.14.65 | |
| Watanabe T, Kono M, Aida K, et al. 1998. Purification and molecular cloning of a chitinase expressed in the hepatopancreas of the penaeid prawn Penaeus japonicus. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta,, 1998, 1382(2): 181-185 | |
| Xu WF, Liu P, Li JT, et al. Cloning and expression of gene vasa during ovarian development cycle in Exopalaemon carinicauda. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2014, 45(3): 574-582 DOI:10.11693/hyhz20121215002 [徐文斐, 刘萍, 李吉涛, 等. 脊尾白虾 (Exopalaemon carinicauda) vasa基因cDNA克隆及其在卵巢发育中的表达分析. 海洋与湖沼, 2014, 45(3): 574-582] | |
| Zhang F, Lv JJ, Liu P, et al. Cloning and expression of chitinase under low salinity stress during molting in Portunus trituberculatus. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2015, 46(4): 948-957 [张凤, 吕建建, 刘萍, 等. 三疣梭子蟹几丁质酶基因克隆鉴定及在低盐胁迫和蜕皮周期中的表达分析. 海洋与湖沼, 2015, 46(4): 948-957] | |
| Zhang J, Sun Y, Li F, et al. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of chitinase (Fcchi-3) from Chinese shrimp, Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Molecular Biology Reports, 2010, 37(4): 1913-1921 DOI:10.1007/s11033-009-9633-0 | |
| Zhang SY, Jiang SF, Xiong YW, et al. Six chitinases from oriental river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense: cDNA characterization, classification and mRNA expression during post-embryonic development and moulting cycle. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2014, 167(1): 30-40 | |
| Zou E. Effects of hypoxia and sedimentary naphthalene on the activity of N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase in the epidermis of the brown shrimp, Penaeus aztecus. Bulletin of Environment Contamination and Toxicology, 2009, 82(5): 579-582 DOI:10.1007/s00128-008-9619-y |



