长链多不饱和脂肪酸(LC-PUFA)是动物维持正常生长发育和生理功能的重要营养物质,具有细胞膜磷脂组分、类花生酸前体和调节基因表达等功能(Xie et al, 2015)。根据第1个双键距离烃链尾的碳原子数目,可将LC-PUFA分为n-3和n-6系列。其中,n-3 LC-PUFA主要包括亚麻酸(ALA)、二十碳五烯酸(EPA)和二十二碳六烯酸(DHA);n-6系主要包括亚油酸(LA)和花生四烯酸(AA)(左然涛等, 2015)。鱼油中的n-3 LC-PUFA含量较高,而大部分植物油中的n-6系含量较高,n-3系含量较低甚至没有(如葵花油、花生油)(Turchini et al, 2009)。不同鱼类LC-PUFA合成能力不同,一般认为,淡水鱼和鲑鳟类具有将C18 PUFA转化为LC-PUFA的能力,而海水鱼类,除少数种类外,大多从食物中获取LC-PUFA,特别是养殖种类,故LC-PUFA被称为必需脂肪酸(EFA)(Geay et al, 2015)。
海洋鱼类资源有限,导致鱼油原料短缺且价格昂贵,严重制约水产养殖业可持续发展。植物油资源较丰富,且价格低廉,是较适宜的鱼油替代品(梅琳等, 2015)。但由于植物油中含有大量的n-6 LC-PUFA,而相对缺乏n-3 LC-PUFA,用植物油取代鱼油会导致饲料中的n-6/n-3 LC-PUFA比例发生改变(谢帝芝等, 2015)。配合饲料中利用植物油替代鱼油虽然对生长性能影响不大,但因鱼体自身的LC-PUFA合成能力较弱,会导致鱼肉品质显著下降。n-6/n-3 LC-PUFA摄入比例不均衡,会影响脂类代谢,造成某些脂类大量积累,势必增加鱼体组织中发生脂质过氧化的风险,进而会影响组织的抗氧化水平。细胞膜磷脂结构中的LC-PUFA对脂类过氧化反应十分敏感(Villasante et al, 2015),并且n-3 LC-PUFA比n-6 LC-PUFA更容易发生脂质过氧化反应(田晶晶等, 2015)。而脂类过氧化产物,如丙二醛(MDA)会损害细胞膜的结构与功能,削弱机体抗氧化与免疫功能。因此,适当的LC-PUFA配比既可节约饲料成本,又能提高饲料转化率、促进鱼类健康生长。
银鲳(Pampus argenteus)在中国各海域均有分布(刘静等, 2002),以东海北部近海(江苏吕四和浙江舟山渔场)的资源量最高,是沿海重要的经济鱼类,具有较高的养殖开发潜力(孙鹏飞等, 2015)。自21世纪初,国内陆续开展针对银鲳人工繁育及养殖技术方面的研究,尽管取得了一定科技成果(施兆鸿等, 2011; 彭士明等, 2010a),但也存在着饲料成本过高、生长速度较慢、发育不均衡等问题(彭士明等, 2010b; Peng et al, 2013),尚未实现其稳定且规模化的人工繁育及养殖推广技术。本研究通过在饲料中添加不同比例的鱼油与大豆油,分析大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼血清溶菌酶和组织抗氧化性能的影响,以期为养殖银鲳幼鱼人工配合饲料的研发、降低饲料成本、增强鱼体体质、提高存活率提供参考依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验用鱼及饲料制备实验用鱼为人工培育的银鲳幼鱼(4月龄),初始规格:体重为(17.2±6.7) g,叉长为(8.5±0.9) cm。饲养时间为2013年7–9月,整个实验期间水温为24–29℃,盐度为24–27。
分别以100%鱼油(FO)、70%鱼油和30%大豆油(FSO)、30%鱼油和70%大豆油(SFO)、100%大豆油(SO)为脂肪源配制等氮、等能、等脂的4组饲料,其饲料组成见表 1,脂肪酸组成见表 2。饲料蛋白水平约为50%,脂肪水平约为16%。所有饲料原料经过充分混合后,用绞肉机制成2 mm的颗粒,于25℃烘箱中烘干后,于–20℃冰箱中保存备用。
|
|
表 1 实验饲料的组成 Table 1 Ingredients and proximate composition of the experimental diets |
|
|
表 2 饲料脂肪酸组成(%, 占总脂肪酸比例) Table 2 Fatty acid composition of the experimental diets (% of total fatty acids) |
挑选600条体表无伤、体色正常的银鲳幼鱼,平均分配于16 m3的室内圆形水泥池中,每个饲料组设3个重复,共12个水泥池。以不添加大豆油饲料预饲1周,饲养时间为2013年8–9月,共计60 d。饲养期间,24 h不间断充气,每天饱食投喂2次(08:00和16:00),日换水量为40%。
每个水泥池取3尾鱼(样本数为9),经100 mg/L MS-222麻醉后,用1 ml无菌注射器尾静脉采血,置于无菌离心管中,4℃静止12 h,4000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液。采血后,在碎冰上解剖,取两侧肌肉、肝脏组织。用生理盐水润洗,并用滤纸片吸干水分,血清、肌肉和肝脏置于–70℃保存备用。
1.3 指标检测血清溶菌酶(LZM)活力采用比浊法。肌肉和肝脏丙二醛(MDA)含量采用硫代巴比妥酸缩合比色法。超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活力采用黄嘌呤氧化酶法,酶活单位(U/mg prot或U/ml)定义为:每毫克组织蛋白或每毫升血清在1 ml反应液中超氧自由基抑制率达50%时所对应的SOD量。过氧化氢酶(CAT)活力采用比色法,酶活单位(U/mg prot或U/ml)定义为:每毫克组织蛋白或每毫升血清每秒钟分解1 μmol量的H2O2。总抗氧化能力(T-AOC)包括酶促和非酶促体系,单位U/mg prot或U/ml表示:每分钟每毫克组织或蛋白每分钟每毫升血清使反应体系吸光度(OD)增加0.01。各项指标由南京建成生物工程研究所试剂盒检测,按说明书要求操作并计算。
1.4 数据处理数据以平均值±标准差(Mean±SD)表示,采用SPSS 19.0软件对银鲳幼鱼各项指标数据进行统计与分析,运用单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA),先进行方差齐性检验,不满足方差齐性时,对数据进行自然对数或平方根转换,采用Duncan’s进行多重比较,P < 0.05为显著性差异。用Excel 2007绘制图表。
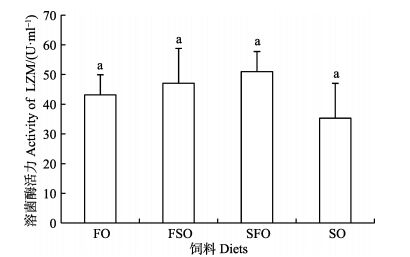
2 结果与分析 2.1 银鲳幼鱼血清LZM活力饲料中,大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼血清LZM活力影响见图 1。由图 1可知,SFO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 3.02%) LZM活力最高[(50.98±6.79) U/ml],SO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 2.22%)最低[(35.29±11.77) U/ml],但各组间差异不显著(P > 0.05)。
|
图 1 饲料中大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼血清溶菌酶活力的影响 Figure 1 The effects of dietary substitution of fish oil by soybean oil on LZM activity in serum of juvenile P. argenteus 不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05),下同 Different letters indicated significant difference (P < 0.05), the same as below |
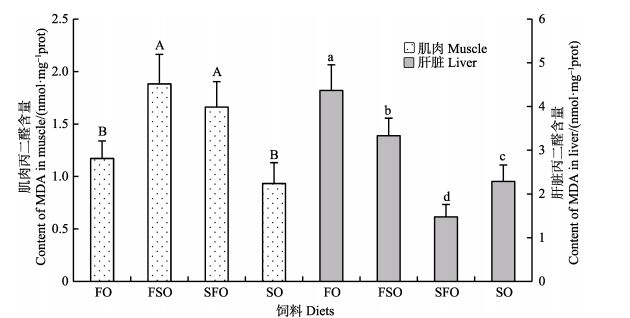
如图 2所示,银鲳幼鱼肌肉和肝脏MDA含量随饲料大豆油替代鱼油水平呈现不同变化趋势。肌肉MDA含量最高的是FSO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 4.01%),为(1.88± 0.28) nmol/mg prot,含量最低的是SO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 2.22%),为(0.93±0.20) nmol/mg prot,FSO和SFO组显著高于FO和SO组(P < 0.05)。肝脏MDA含量最高的是FO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 5.18%),为(4.37±0.59) nmol/mg prot,含量最低的是SFO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 3.02%),为(1.48± 0.28) nmol/mg prot,各组间均存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。
|
图 2 饲料中大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼肌肉和肝脏丙二醛含量的影响 Figure 2 The effects of dietary substitution of fish oil by soybean oil on MDA content in muscle and liver of juvenile P. argenteus |
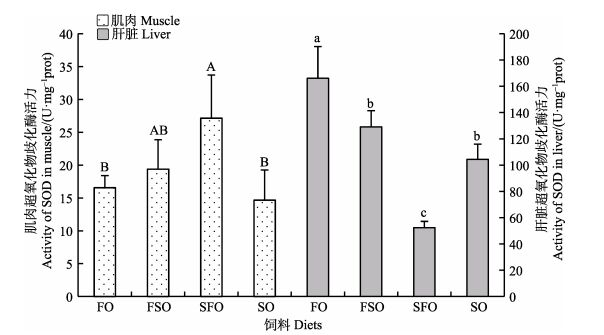
饲料大豆油替代鱼油水平对银鲳幼鱼血清、肌肉和肝脏SOD活力的影响见图 3、图 4。从图 3可以看出,血清SOD活力最高的是SFO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 3.02%),为(50.32±6.15) U/ml,活力最低的是SO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 2.22%),为(29.81±6.60) U/ml (P < 0.05)。从图 4可以看出,SFO组肌肉SOD活力最高,为(27.14± 6.57) U/mg prot,活力最低的为SO组,为(14.67± 4.59) U/mg prot,SFO组显著高于FO和SO组(P < 0.05)。肝脏SOD活力最高的是FO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 5.18%),为(166.06±24.21) U/mg prot,活力最低的是SFO组,为(52.40±4.82) U/mg prot,FO组显著高于其他3组,SFO组显著低于其他3组(P < 0.05)。

|
图 3 饲料中大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼血清SOD活力的影响 Figure 3 The effects of dietary substitution of fish oil by soybean oil on SOD activity in serum of juvenile P. argenteus |
|
图 4 饲料中大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼肌肉和肝脏SOD活力的影响 Figure 4 The effects of dietary substitution of fish oil by soybean oil on SOD activity in muscle and liver of juvenile P. argenteus |
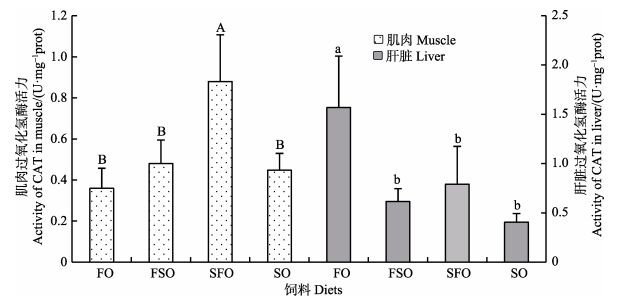
饲料大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼血清、肌肉和肝脏CAT活力的影响见图 5、图 6。从图 5可以看出,血清CAT活力最高的是SFO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 3.02%),为(1.79±0.25) U/ml,最低的是FSO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 4.01%),为(1.28±0.09) U/ml,SFO组显著高于其他组(P < 0.05)。从图 6可以看出,肌肉CAT活力最高的是SFO组,为(0.88±0.23) U/mg prot,最低的是FO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 5.18%),为(0.36±0.10) U/mg prot,SFO组CAT活力显著高于其他组(P < 0.05)。肝脏CAT活力最高的是FO组,为(1.57±0.52) U/mg prot,最低的是SO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 2.22%),为(0.41±0.09) U/mg prot,FO组CAT活力显著高于其他组(P < 0.05)。

|
图 5 饲料中大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼血清CAT活力的影响 Figure 5 The effects of dietary substitution of fish oil by soybean oil on CAT activity in serum of juvenile P. argenteus |
|
图 6 饲料中大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼肌肉和肝脏CAT活力的影响 Figure 6 The effects of dietary substitution of fish oil by soybean oil on CAT activity in muscle and liver of juvenile P. argenteus |
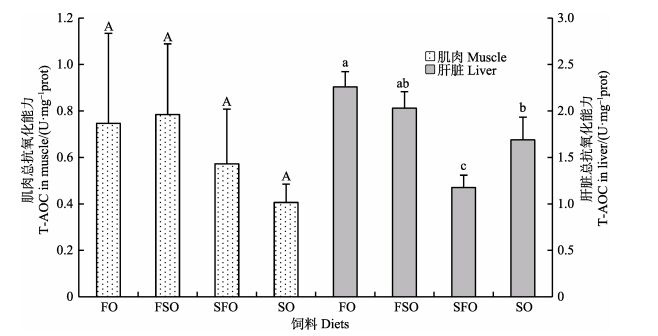
饲料大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼血清、肌肉和肝脏T-AOC影响情况见图 7、图 8。从图 7可以看出,血清T-AOC最高的是SO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 2.22%):(11.22±5.97) U/ml,最低的是FO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 5.18%),为(3.37±1.17) U/ml,SO组显著高于FO组(P < 0.05)。从图 8可以看出,肌肉T-AOC最高的是FSO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 4.01%),为(0.78±0.30) U/mg prot,最低的是SO组,为(0.41±0.08) U/mg prot,各组间差异不显著(P > 0.05)。肝脏T-AOC最高的是FO组,为(2.26±0.17) U/mg prot,最低的是SFO组(n-3 LC-PUFA, 3.02%),为(1.18±0.13) U/mg prot,FO组显著高于SFO和SO组,SFO则显著低于其他组(P < 0.05)。

|
图 7 饲料中大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼血清T-AOC的影响 Figure 7 The effects of dietary substitution of fish oil by soybean oil on T-AOC in serum of juvenile P. argenteus |
|
图 8 饲料中大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼肌肉和肝脏T-AOC的影响 Figure 8 The effects of dietary substitution of fish oil by soybean oil on T-AOC in muscle and liver of juvenile P. argenteus |
养殖鱼类饲料中的脂肪成分会反映在鱼肉脂肪组成上。近年来,鱼油资源短缺使相对低廉的植物油部分替代了饲料中的鱼油成分(Pike, 2015)。但由于大多数植物油中缺乏n-3 LC-PUFA,对一些养殖鱼类健康和鱼肉品质造成了负面影响(Zuo et al, 2015)。本研究利用大豆油和鱼油不同配比作为饲料脂肪源,通过分析血清溶菌酶、肝脏和肌肉中抗氧化指标的变化,阐述大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳机体产生的影响。
3.1 饲料大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼血清溶菌酶的影响LZM是重要的非特异性免疫因子,主要来源于巨噬细胞,对外源物有破坏作用,可以反应鱼类机体对寄生虫、细菌以及病毒的抵抗能力(Reyes-Becerril et al, 2014; 吕云云等, 2015)。适当的饲料营养配比能提高LZM水平,增强免疫能力。梁萌青等(2005)发现,鳀鱼(Engraulis japonicus)油作为脂肪源时,维生素E的添加能显著提高大菱鲆(Scophthalmus maximus)血清溶菌酶活性,而大豆油则没出现这个现象,提高n-3 LC-PUFA含量对脂溶性维生素吸收利用有促进作用。杨鸢劼等(2008)发现,在黄鳝(Monopterus albus)饲料中添加不同比例PUFA,血清溶菌酶含量有不同程度的提高。
本研究中,SFO组的银鲳幼鱼血清LZM水平最高,而SO组最低,FSO和SFO组相对较高,但各组差异并不显著。全鱼油组LZM水平不高,可能是由于过量的n-3 LC-PUFA降低了鱼类免疫器官表面病原识别受体及其接头蛋白的表达所致(Zuo et al, 2012)。而豆油部分替代鱼油,对银鲳幼鱼免疫能力略有促进作用,完全使用豆油则会对免疫能力产生负面影响。另外,过量的n-3 LC-PUFA易发生过氧化反应,超氧阴离子会攻击免疫细胞膜,从而降低免疫性能(Gill et al, 2010)。说明,饲料维持一定的n-3与n-6配比,对增强银鲳免疫性能有促进作用。
3.2 饲料大豆油替代鱼油对银鲳幼鱼抗氧化相关指标的影响生物体组织中,脂类营养特别是PUFA的大量聚集必然会在一定程度上引发脂质过氧化的发生。PUFA等脂类与氧化自由基反应时,会引发脂质过氧化,经分子内的环化、裂解等步骤作用,最终降解产生MDA,MDA和体内脂质、蛋白质、核酸等大分子进行交错连结反应,使鱼体清除自由基的能力降低,进而对机体造成伤害(王奇等, 2010)。MDA含量既可判定机体脂质过氧化程度,也可间接反映自由基产生侵害的程度、生物活性及其抗氧化能力的强弱(Viarengo et al, 1995)。
Mozanzadeh等(2015)研究发现,升高n-3 LC-PUFA水平会使矛鲷(Sparidentex hasta)肝脏和血清中MDA含量和CAT活力增加。本研究中,FSO和SFO组的银鲳肌肉MDA含量显著高于FO和SO组,肝脏MDA含量则是FO和FSO组显著较高。说明,较高的饲料n-3 LC-PUFA含量会使银鲳不同组织的MDA含量上升。
FO组肌肉MDA的含量较低,且肌肉MDA与SOD、CAT变化情况类似,推测其原因与FO组肝脏SOD、CAT和T-AOC较高,导致转运出的MDA量较少有关。另外,肝脏是鱼类脂类吸收、代谢的主要器官,营养不良会导致肝脏脂类代谢紊乱,影响肝脏对脂类的吸收和转运(Mozanzadeh et al, 2015)。Moldal等(2014)发现,植物油替代鱼油会对大西洋鲑(Salmo salar)的肠道产生不良影响,使肠壁变薄,粘膜褶皱变少,同样会影响脂肪酸的吸收。而饲料脂肪酸被吸收后,通过一些组织、器官的转运与代谢后,其脂肪酸组成对鱼类肝脏的影响比对肌肉的影响更显著(Peng et al, 2014)。
鱼类抗氧化防御系统分为酶促与非酶促两大部分,其中,SOD和CAT是2个重要的抗氧化酶,它们能有效清除体内的超氧阴离子自由基(O2−)、游离氧(O)、羟自由基(−OH)和H2O2等活性氧物质(鲁双庆等, 2002; Kanak et al, 2014)。Luo等(2012)研究发现,适宜的饲料LC-PUFA含量可有效提高矛尾复鰕虎鱼(Synechogobius hasta)的SOD和CAT活力,但过高含量也会在一定程度上抑制CAT活力。Zuo等(2015)发现,适宜的PUFA n-3/n-6值(0.5) 也可以提高大黄鱼(Pseudosciaena crocea)肝脏的SOD和CAT活力,若该比值高于0.5,则酶活力反而有所下降。
本研究中,银鲳血清和肌肉SOD和CAT活力最高的组均为SFO组,而SO组活力较低。相对地,肝脏SOD和CAT活力均是FO组最高(P < 0.05)。说明,饲料中n-3/n-6值过高会代谢更多(如MDA等)副产物,需要肝脏提高抗氧功能予以消除,同时,消耗更多能量与营养储备,而n-3/n-6值偏低又会抑制抗氧化酶活力。因此,饲料中适当的鱼油添加量可以保持适宜的n-3和n-6配比,有助于银鲳幼鱼的健康养殖。
T-AOC表示各种抗氧化大分子、抗氧化小分子和酶促体系的抗氧化能力总和,T-AOC变化可以反映机体内自由基的代谢情况,对判断机体的健康状况及抗氧化防御能力具有重要意义(Martinez-lvarez et al, 2005)。Villasante等(2015)利用饲料增加虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss)肌肉和肝脏n-3 LC-PUFA含量,可以使血清T-AOC增强。适宜的饲料n-3 LC-PUFA含量可显著提高褐菖鲉(Sebastiscus marmoratus)机体的抗氧化能力(岳彦峰等, 2013)。本研究银鲳幼鱼肌肉和肝脏T-AOC均是FO和FSO组较高,说明,较高的饲料n-3 LC-PUFA含量可增强抗氧化能力,而血清T-AOC在SO组较高,可能与体内MDA含量较低,非酶体系抗氧化能力消耗较小有关。
本研究中,FO、FSO、SFO和SO组银鲳的终末体重分别为(37.84±3.82) g、(39.95±4.01) g、(34.64± 3.75) g和(26.63±2.97) g,其他生长和营养数据另文发表。结合本研究中的LZM和抗氧化指标,发现,FSO和SFO组银鲳幼鱼机体状况较好,尤其是SFO组LZM水平较高,肌肉和肝脏MDA含量不高,各项抗氧化能力指标也较强,品质较好。考虑到鱼粉中含有一定量鱼油,因此,鱼油添加量多于SFO组(30%)少于FSO组(70%)效果可能较好。本研究表明,用大豆油替代鱼油,使饲料n-3 LC-PUFA含量占总脂肪酸的18%–24%,且n-3与n-6比例相对均衡(n3/n6值为1–2) 时,有利于银鲳的健康生长。
| Geay F, Wenon D, Mellery J, et al. Dietary linseed oil reduces growth while differentially impacting LC-PUFA synthesis and accretion into tissues in Eurasian Perch (Perca fluviatilis). Lipids, 2015, 50(12): 1219-1232 DOI:10.1007/s11745-015-4079-8 | |
| Gill R, Tsung A, Billiar T. Linking oxidative stress to inflammation: Toll-like receptors. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2010, 48(9): 1121-1132 DOI:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.01.006 | |
| Kanak EG, Dogan Z, Eroglu A, et al. Effects of fish size on the response of antioxidant systems of Oreochromis niloticus following metal exposures. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 40(4): 1083-1091 | |
| Liang MQ, Chang Q, Wang YG, et al. Influences of vitamin E and lipid sources on non-specific immunity of turbot (Scophthamus maximus Linnaeus). Marine Fisheries Research, 2005, 26(5): 15-21[梁萌青, 常青, 王印庚, 等. 维生素E及脂肪源对大菱鲆非特异性免疫的影响. 海洋水产研究, 2005, 26(5): 15-21] | |
| Liu J, Li CS, Li XS. Studies on Chinese pomfret fishes of the genus Pampus (Pisces: Stromateidae). Studia Marina Sinica, 2002(40): 240-252[刘静, 李春生, 李显森. 中国鲳属鱼类的分类研究. 海洋科学集刊, 2002(40): 240-252] | |
| Lu SQ, Liu SJ, Liu HY, et al. Effects of Cu2+ on activities of protecting enzymes SOD, CAT and GSH-PX in liver tissue of Monopterus albus. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2002, 9(2): 138-141[鲁双庆, 刘少军, 刘红玉, 等. Cu2+对黄鳝肝脏保护酶SOD、CAT、GSH-PX活性的影响. 中国水产科学, 2002, 9(2): 138-141] | |
| Lü YY, Chen SQ, Yu CL, et al. The effects of the ratio of dietary protein to lipid on the growth, digestive enzyme activities and blood biochemical parameters in spotted halibut, Verasper variegates. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2015, 36(2): 118-124 DOI:10.11758/yykxjz.20150216[吕云云, 陈四清, 于朝磊, 等. 饲粮蛋白脂肪比对圆斑星鲽(Verasper variegates)生长、消化酶及血清生化指标的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2015, 36(2): 118-124] | |
| Luo Z, Tan XY, Li XD, et al. Effect of dietary arachidonic acid levels on growth performance, hepatic fatty acid profile, intermediary metabolism and antioxidant responses for juvenile Synechogobius hasta. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2012, 18(3): 340-348 DOI:10.1111/anu.2012.18.issue-3 | |
| Martinez-lvarez RM, Morales AE, Sanz A. Antioxidant defenses in fish: Biotic and abiotic factors. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 2005, 15(1): 75-88 | |
| Mei L, Zhou HH, Mai KS, et al. Effects of dietary substitution of fishmeal by fermented silkworm pupae on the growth, feed intake, digestion and immunity of juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2015, 36(3): 85-92 DOI:10.11758/yykxjz.20150314[梅琳, 周慧慧, 麦康森, 等. 蛹肽蛋白替代鱼粉对大菱鲆(Scophthalmus maximus L.)幼鱼生长、饲料利用、消化代谢酶及免疫性能的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2015, 36(3): 85-92] | |
| Moldal T, Løkka G, Wiik-Nielsen J, et al. Substitution of dietary fish oil with plant oils is associated with shortened mid intestinal folds in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). BMC Veterinary Research, 2014(10): 60 | |
| Mozanzadeh MT, Marammazi JG, Yavari V, et al. Dietary n-3 LC-PUFA requirements in silvery-black porgy juveniles (Sparidentex hasta). Aquaculture, 2015, 448: 151-161 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.06.007 | |
| Peng SM, Shi ZH, Fei Y, et al. Effect of high-dose vitamin C supplementation on growth, tissue ascorbic acid concentrations and physiological response to transportation stress in juvenile silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 2013, 29(6): 1337-1341 DOI:10.1111/jai.2013.29.issue-6 | |
| Peng SM, Shi ZH, Sun P, et al. Effects of breeding density on the growth and tissues biochemical indices of juvenile silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010a, 29(7): 1371-1376[彭士明, 施兆鸿, 孙鹏, 等. 养殖密度对银鲳幼鱼生长及组织生化指标的影响. 生态学杂志, 2010a, 29(7): 1371-1376] | |
| Peng SM, Yin F, Sun P, et al. Effects of different diets on weight gain, hepatic lipase and antioxidant enzyme of juvenile silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Journal of Fisheries of China, 2010b, 34(6): 769-774[彭士明, 尹飞, 孙鹏, 等. 不同饲料对银鲳幼鱼增重率、肝脏脂酶及抗氧化酶活性的影响. 水产学报, 2010b, 34(6): 769-774] | |
| Peng SM, Yue YF, Gao QX, et al. Influence of dietary n-3 LC-PUFA on growth, nutritional composition and immune function in marine fish Sebastiscus marmoratus. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2014, 32(5): 1000-1008 DOI:10.1007/s00343-014-3312-2 | |
| Pike IH. Fish oil: Supply and demand as a source of long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the human diet. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 2015, 117(6): 747-750 DOI:10.1002/ejlt.201400648 | |
| Reyes-Becerril M, Asencio F, Gracia-Lopez V, et al. Single or combined effects of Lactobacillus sakei and inulin on growth, non-specific immunity and IgM expression in leopard grouper (Mycteroperca rosacea). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 40(4): 1169-1180 | |
| Shi ZH, Peng SM, Wang JG, et al. Observation of embryonic, larval and juvenile development in Pampus argenteus offspring. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2011, 18(2): 267-274[施兆鸿, 彭士明, 王建钢, 等. 人工养殖银鲳子代胚胎发育及仔稚幼鱼形态观察. 中国水产科学, 2011, 18(2): 267-274] | |
| Sun PF, Dai FQ, Chen YL, et al. Seasonal variations in structure of fishery resource in the Yangtze River estuary and its adjacent waters. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2015, 36(6): 8-16 DOI:10.11758/yykxjz.20150602[孙鹏飞, 戴芳群, 陈云龙, 等. 长江口及其邻近海域渔业资源结构的季节变化. 渔业科学进展, 2015, 36(6): 8-16] | |
| Tian JJ, Lei CX, Ji H, et al. Effects of dietary linoleic acid (18: 2n-6) and α-linolenic acid (18:3n-3) ratio on the growth performance and health status of Cyprinus Carpio Songpu mirror. Freshwater Fisheries, 2015, 45(5): 76-82[田晶晶, 雷彩霞, 吉红. 饲料亚油酸/亚麻酸比率对松浦镜鲤生长和健康状况的影响. 淡水渔业, 2015, 45(5): 76-82] | |
| Turchini GM, Torstensen BE, Wing-Keong N. Fish oil replacement in finfish nutrition. Reviews in Aquaculture, 2009(1): 10-57 | |
| Viarengo A, Canesi L, Garcia Martinez P, et al. Pro-oxidant processes and antioxidant defence systems in the tissues of the Antarctic scallop (Adamussium colbecki) compared with the Mediterranean scallop (Pecten jacobaeus). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 1995, 111(1): 119-126 DOI:10.1016/0305-0491(94)00228-M | |
| Villasante A, Patro B, Chew B, et al. Dietary intake of purple corn extract reduces fat body content and improves antioxidant capacity and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid profile in plasma of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 2015, 46(4): 381-394 DOI:10.1111/jwas.2015.46.issue-4 | |
| Wang Q, Fan CP, Chen KC, et al. Effects of three typical sulfonamides on GST activity and MDA content in liver tissue of Oreochromis niloticus. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(5): 1014-1019[王奇, 范灿鹏, 陈锟慈, 等. 三种磺胺类药物对罗非鱼肝脏组织中谷胱甘肽转移酶(GST)和丙二醛(MDA)的影响. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(5): 1014-1019] | |
| Xie D, Wang S, You C, et al. Characteristics of LC-PUFA biosynthesis in marine herbivorous teleost Siganus canaliculatus under different ambient salinities. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2015, 21(5): 541-551 DOI:10.1111/anu.2015.21.issue-5 | |
| Xie DZ, Chen F, Zhang QH, et al. Advance in the regulatory mechanisms of LC-PUFA biosynthetic metabolism of teleost. Journal of Shantou University (Natural Science), 2015, 30(2): 3-19[谢帝芝, 陈芳, 张庆昊, 等. 鱼类LC-PUFA合成代谢调控机制研究进展. 汕头大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 30(2): 3-19] | |
| Yang YJ, Bing XW, Xu ZH. Effects of unsaturated fatty acids on the growth and immunity indices of Monopterus albus. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2008, 35(2): 224-228[杨鸢劼, 邴旭文, 徐增洪. 不饱和脂肪酸对黄鳝生长及免疫指标的影响. 安徽农业大学学报, 2008, 35(2): 224-228] | |
| Yue YF, Peng SM, Shi ZH, et al. Effects of dietary n-3 HUFA levels on serum biochemistry indices, main lipid metabolism enzyme activities and antioxidant ability of Sebastiscus marmoratus. Marine Fisheries, 2013, 35(4): 460-467[岳彦峰, 彭士明, 施兆鸿, 等. 饲料n-3 HUFA水平对褐菖鲉血清生化指标、主要脂代谢酶活力及抗氧化能力的影响. 海洋渔业, 2013, 35(4): 460-467] | |
| Zuo RT, Ai QH, Mai KS, et al. Effects of dietary n-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids on growth, nonspecific immunity, expression of some immune related genes and disease resistance of large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) following natural infestation of parasites (Cryptocaryon irritans). Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2012, 32(2): 249-258 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2011.11.005 | |
| Zuo RT, Mai KS, Xu W, et al. Advance of studies on the effects of fatty acids on immune responses and nutritional regulation mechanism in fish species. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2015, 39(7): 1079-1088[左然涛, 麦康森, 徐玮, 等. 脂肪酸对鱼类免疫系统的影响及调控机制研究进展. 水产学报, 2015, 39(7): 1079-1088] | |
| Zuo RT, Mai KS, Xu W, et al. Dietary ALA, but not LNA, increase growth, reduce inflammatory processes, and increase anti-oxidant capacity in the marine finfish Larimichthys crocea. Lipids, 2015, 50(2): 149-163 DOI:10.1007/s11745-014-3970-z |



