大黄鱼(Pseudosciaena crocea)为我国传统四大海产鱼之一,是海水养殖的重要经济鱼类,在中国东南沿海各省市已形成规模化的养殖产业(苏永全, 2004)。然而,大黄鱼养殖生产中的病害问题已成为制约其产业发展的主要瓶颈(刘家富, 2013)。大黄鱼病害类型较多,细菌性疾病的危害仍较严重,尤其是近年来暴发流行的大黄鱼内脏白点病,给养殖产业造成了重大的经济损失(Zhang et al, 2014)。该疾病具有流行区域广、感染性强、死亡率高、潜伏期较长和水温偏低时发生(18-22℃)等特点,病鱼体表无明显症状,解剖才可见脾、肾、肝等脏器呈现大量白色结节。引起该疾病的致病菌已被鉴定为杀香鱼假单胞菌(Pseudomonas plecoglossicida),大黄鱼是首个报道感染杀香鱼假单胞菌患病的海水鱼类(Zhang et al, 2014)。尽管已有多篇关于大黄鱼内脏白点病的研究报道(沈锦玉等, 2008; 邱杨玉等, 2012; 胡娇等, 2014),然而对于内脏白点病的病理学分析很少涉及。本研究通过对自然患病大黄鱼与正常大黄鱼的组织病理及超微病理变化进行比较研究,探讨大黄鱼内脏白点病的病理过程和发病机理,为该病的诊断和防治提供理论基础和依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验用鱼患病大黄鱼于2014年11月采自浙江省宁波市象山县大网箱养殖的大黄鱼养殖网箱,体长为15-20 cm,体重为120-180 g,选取濒死大黄鱼3尾。正常大黄鱼采自同一海区邻近网箱养殖的大黄鱼养殖网箱,经检查确认无病后作为对照使用。
1.2 实验方法 1.2.1 解剖观察常规显微镜检查大黄鱼体内外有无寄生虫。活体解剖濒死大黄鱼,观察病鱼体表与内脏组织病变情况,并与健康大黄鱼进行比较,以确定该病主要病变情况及病变部位,并以此为依据合理选择组织切片的病理材料。
1.2.2 光镜样品制备及观察用锐利刀、剪分别取患病大黄鱼和正常大黄鱼的肝脏、肾脏、脾脏、肠、心脏、肌肉6种组织。用Bouin氏液固定24 h,直接用70%乙醇洗数次,再用70%-100%乙醇逐级脱水45-60 min,然后二甲苯透明,石蜡包埋,用KD-202石蜡切片机切片,HE染色,中性树胶封片,T2-7E03680型OLYMPUS显微镜下观察并拍照保存。
1.2.3 电镜样品制备及观察分别取患病大黄鱼和正常大黄鱼的肝脏、肾脏、脾脏、肠、心脏、肌肉6种组织,切成0.5-1.0 mm3的小块,用2.5%戊二醛和1%锇酸双固定(戊二醛和锇酸均用pH值=7.4的0.2 mol/L磷酸缓冲液配制),再用4%醋酸铀染色30 min。乙醇逐级脱水后,用100 %丙酮脱水。无水丙酮与包埋剂渗透组织,震荡,包埋,环氧树脂E-pon812包埋,并置烘箱内于37 ℃、45 ℃和60 ℃逐级聚合。修块后用LKB超薄切片机制备100-120 nm切片,醋酸双氧铀-—柠檬酸铅双染法染色,在TECNAI 10型透射电镜下观察并拍照保存。
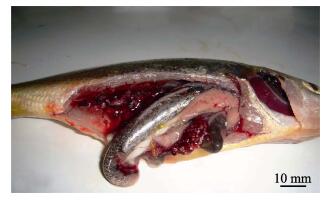
2 结果与分析 2.1 解剖观察与临床症状病鱼体表和体内器官经显微镜检查未见寄生虫。大黄鱼发病初期的主要症状是,病鱼活力下降,、游动缓慢,、食欲减退或彻底丧失,但体表无明显症状,偶见溃疡;剖检后可见内脏器官病变严重,脾脏、肾脏和肝脏均出现直径为1.0-2.0 mm的白色结节,病情严重者整个肾脏和脾脏均被白色结节包围覆盖(图 1)。
|
图 1 自然发病大黄鱼内脏白点症状 Figure 1 Symptoms of diseased wild layge yellow cyoaker infected with visceral white-spot |
与正常大黄鱼比较,患病大黄鱼的肝、脾、肾均表现出明显的组织病理变化,有典型的肉芽肿,并伴有脂肪变性、炎性细胞浸润等现象。而心脏、肠、肌肉等组织与正常大黄鱼比较后未发现明显病变,故未将图片列出。
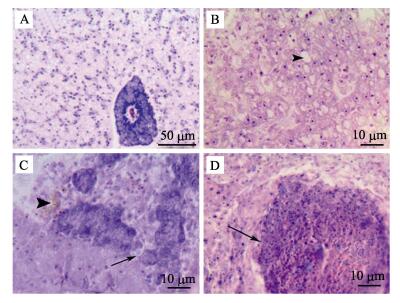
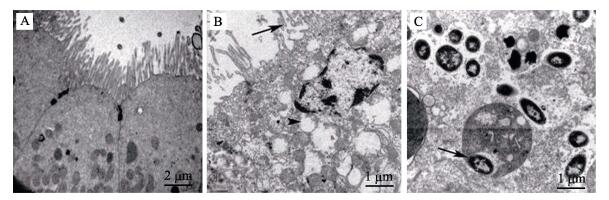
2.2.1 肝脏正常大黄鱼肝脏色泽一致,质地均匀,组织结构排列清晰,实质细胞为近似椭圆的多角形细胞,以中央静脉为中心向四周呈放射状排列,部分胰脏组织嵌入肝组织中,胰腺细胞间结缔组织的HE染色为紫蓝色,呈现较强的嗜碱性(图 2-A)。患有内脏白点病的大黄鱼肝脏,病变较轻者呈现明显的脂肪变性,经HE染色后可见大量的空泡(图 2-B);病变较重者,嵌入肝组织中的胰腺组织崩解,周边有铁黄素沉积(图 2-C);肝实质组织纤维化,细胞排列不规则,部分细胞淀粉样变性,细胞核固缩,细胞失去原有结构,病原菌与坏死细胞混杂在一起形成的病灶部位近似圆形,经HE染色为深红色,呈现极强的嗜酸性,此即为肉眼观察到的“白点”(图 2-D)。
|
图 2 病鱼肝脏组织病理变化 Figure 2 Pathological changes of liver tissues of diseased fishes A.:正常大黄鱼肝脏;B.:病鱼肝细胞排列疏松,空泡明显;C.:病鱼胰腺组织崩解(箭头),铁黄素沉积(三角箭头);D.:病鱼肝脏嗜酸性结节(箭头) A. : Normal liver; B. : Liver cell arranged loosely and presence of vacuole; C. : Pancreas tissues disintegration (arrowArrow), hemosiderin deposition (triangular Triangular arrow); D. : Eosinophilic nodules (arrowArrow) |
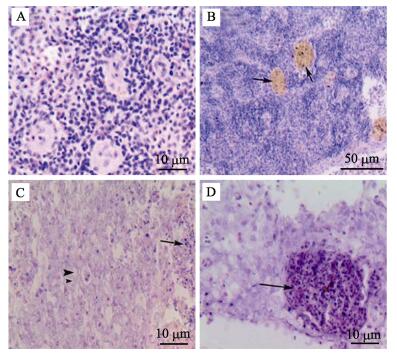
正常大黄鱼脾脏含有脾髓,由淋巴细胞、巨噬细胞和各类粒细胞等组成,和多数硬骨鱼类一样,显示有红细胞集中区域和淋巴细胞集中区域(图 3-A)。患有内脏白点病的大黄鱼脾脏坏死最为严重,组织结构变性,细胞间空隙明显变大,血铁素出现明显的沉淀,经HE染色后着色加深,呈黄色(图 3-B);脾脏实质可见大量淋巴细胞和网状细胞坏死,红髓和白髓现象消失,大量中性粒细胞浸润(图 3-C);与病变肝脏类似,病原菌与坏死细胞混杂在一起形成的病灶部位经HE染色为深红色,呈现较强的嗜酸性(图 3-D)。
|
图 3 病鱼脾脏组织病理变化 Figure 3 Pathological changes of spleen tissues of diseased fishes A.:正常大黄鱼脾脏;B.:病鱼脾脏大量血铁素沉积(箭头);C.:病鱼脾脏中性粒细胞浸润(箭头),细胞空泡化(三角箭头);D.:病鱼脾脏嗜酸性结节(箭头) A. : Normal spleen; B: Hemosiderin deposition (arrowArrow); C. : Neutrophil infiltration (arrowArrow), vacuole formation (triangular Triangular arrow); D. : Eosinophilic nodules (Arrow) |
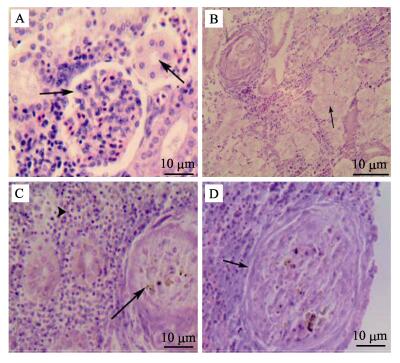
同其他硬骨鱼类一样,大黄鱼的肾脏主要由肾小球、肾小管和填充其中的肾间质组织构成。正常大黄鱼肾小球为毛细血管围成的血管球,肾小管由单层上皮细胞构成,核圆形,位于细胞中部,细胞间排列紧凑,界限清晰,肾间质组织致密,并与肾小球和肾小管紧密嵌合(图 4-A)。患有内脏白点病的大黄鱼肾脏病变严重,肾小球萎缩变形甚至开始崩解,肾小囊腔扩大,肾小管形状不规则,上皮细胞间界限模糊或间隙变大,部分肾小管管腔闭塞,有的仅有肾小管基底膜轮廓,失去原有结构(图 4-B);肾间质出现大面积组织坏死和崩解并形成结节,部分坏死组织淀粉样变性(图 4-C,图 4-D)。
|
图 4 病鱼肾脏组织病理变化 Figure 4 Pathological changes of kidney tissues of diseased fishes A.:正常大黄鱼肾脏;B.:病鱼肾小管形状不规则,管腔闭塞(箭头);C.:病鱼肾脏实质组织局部坏死形成结节(箭头),组织淀粉样变性(三角箭头);D.:病鱼肾脏病理性结节(箭头) A. : Normal kidney; B. : Renal tubular deformation and blockage in kidney (arrowArrow); C. : Regional parenchymatous tissue is putrescence (arrowArrow), amyloidosis (triangular Triangular arrow); D: Pathological nodules (arrowArrow) |
透射电镜观察结果显示,病鱼的肝、脾、肾等内脏组织出现了明显的病理变化,脾脏和肾脏中均有大量细菌积聚,细胞结构破坏严重。心、肠、肌肉等组织与正常鱼相比没有发现明显病理变化,故未将图片列出。
2.3.1 肝脏正常大黄鱼肝细胞呈多边形,边界清晰。细胞质内有丰富的细胞器,线粒体呈圆形或椭圆形,嵴褶皱清晰,富含粗面内质网,绕细胞核环形排列(图 5-A)。患病大黄鱼肝细胞结构混乱,细胞间界限模糊,脂滴大量积聚(图 5-B);细胞核异常,核仁消失,异染色质积聚成块或边集,线粒体肿胀甚至破裂,嵴断裂,基质稀释,电子密度降低(图 5-C);病原菌侵入细胞间,破坏组织结构(图 5-D)。
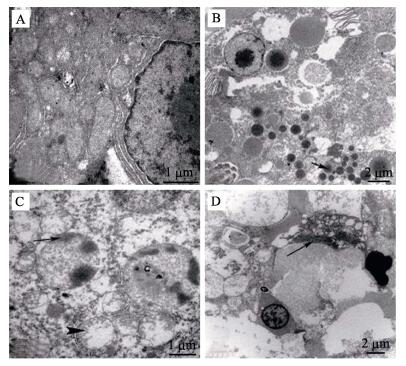
|
图 5 病鱼肝脏超微病理变化 Figure 5 Ultrasturctural changes of liver tissues of diseased fishes A:正常大黄鱼肝细胞;B:病鱼肝脏大量脂肪滴积聚(箭头);C:病鱼细胞核染色质边集(箭头),线粒体空泡,嵴断裂(三角箭头);D:病原菌侵入细胞间,破坏组织结构(箭头) A: Normal liver cell; B: Generous oil drop accumulation; C: Chromatin margination (Arrow), mitochondrial vacuoles and cristae loss (friangular arrow); D: Pathogenic invasion in cells and damage of cellular structure (Arrow) |
正常大黄鱼脾脏组织是由红细胞、淋巴细胞和巨噬细胞等多种细胞组成,细胞排列紧密,界限清晰,富含线粒体等细胞器(图 6-A)。患病大黄鱼脾脏有大量短杆状细菌积聚,与坏死细胞形成结节(图 6-B),细胞结构遭到严重破坏;细胞间有大量不同切面的细菌菌体,菌体的细胞壁电子密度较高(图 6-C)。

|
图 6 病鱼脾脏超微病理变化 Figure 6 Ultrasturctural changes of spleen tissues of diseased fishes A.:正常大黄鱼脾脏多种细胞;B.:病鱼脾脏中大量病原菌积聚,破坏细胞结构;C.:病原菌纵切面(箭头) A. : Normal spleen cells; B. : Accumulated bacteria in spleen and damage of cellular structure; C.: Longitudinal section of bacteria (arrowArrow) |
正常大黄鱼肾脏近曲小管管壁由单层上皮细胞构成,游离端具刷状缘,细胞排列紧凑,界限清晰,细胞核圆形,靠近基底部,细胞质含有大量细胞器(图 7-A)。患病大黄鱼肾小管上皮细胞线粒体肿胀,空泡变性,嵴断裂,刷状缘排列稀疏,并且发生断裂,细胞核染色质不均匀,异染色质边集,核膜边界不清晰(图 7-B);细胞间有大小不一的短杆状细菌积聚,细胞内有大小不一的空泡,细菌侵入细胞内,破坏细胞结构(图 7-C)。
|
图 7 病鱼肾脏超微病理变化 Figure 7 Ultrasturctural changes of kidney tissues of diseased fishes A.:正常大黄鱼肾脏;B.:病鱼刷状缘断裂(箭头),线粒体空泡变性,嵴断裂(三角箭头);C.:细菌侵入细胞,核膜破裂 A. : Normal kidney; B. : Brush border are fractured (arrowArrow), mitochondrial vacuoles and cristae loss (Arrow); C. : Pathogenic invasion in cells and disruption of nuclear membrane (arrowArrow) |
目前,国内外对鱼类细菌性白点病的研究比较广泛,但大多研究着重于病原学方面,有关病理学的报道较少。能引起鱼类内脏白色结节病的病原菌较多,有杀鱼巴斯德氏菌(Pateurella piscicida) (Toranzo et al, 1991; Zorrilla et al, 1999)、鰤鱼诺卡氏菌(Nocardia seriolae)(王国良等, 2006)、美人鱼发光杆菌(Photobacterium damselae)(张晓君等, 2009)、舒伯特气单胞菌(Aeromonas schubertii)(刘春等, 2012)等。由杀香鱼假单胞菌引起大黄鱼内脏白点病的组织病理特征是肝、脾、肾等器官为主要病变组织,肝细胞坏死,胰腺组织崩解,空泡化严重;肾小球萎缩,肾小管管腔变窄或闭塞,炎性细胞浸润;脾脏铁黄素大量沉积,组织间空隙变大,细胞排列紊乱。邱杨玉等(2012)对患有内脏白点病大黄鱼的组织病理观察结果与本研究结果相似,但未能开展超微病理研究。本研究在超微病理观察中发现,肝细胞核内异染色质边集,线粒体肿胀,嵴断裂,空泡化严重;肾脏内病原菌侵入细胞,细胞膜破裂,细胞结构崩解;脾脏内细胞间有大量细菌聚集成团。病原菌呈短杆状,横切面为椭圆形,与王国良等(2006)报道的大黄鱼结节病病原菌结构不同。反映了杀香鱼假单胞菌感染大黄鱼能引起组织和细胞结构的明显病变,尤其对脾脏和肾脏组织的损伤严重。各病变组织均出现细胞纤维化并包围细菌及坏死组织,形成肉眼可见的“白点”。HE染色呈强嗜酸性,与苏友禄等(2012)报道的美人鱼发光杆菌感染卵形鲳鲹(Trachinotus ovatus)的结果相似,但Chiro等(2009)观察到人工感染的黄尾鰤内脏结节经HE染色为嗜碱性。可见,鱼类细菌性白点病虽症状相似,但不同鱼类感染不同病原菌后其组织病理变化有差异。
3.2 发病机理分析马向东等(1999)研究表明,pH、渗透压、温度、环境及其他营养成分等环境因素都会影响病原菌毒力作用的发挥,水温是一个重要的影响因子。余为一等(1999)研究发现,温度是假单胞菌引起中华绒螯蟹(Eriocheir sinensis)发病和死亡的启动因子。杀香鱼假单胞菌感染大黄鱼发病的特点是水温在20℃左右,这可能与水温较低时杀香鱼假单胞菌胞外毒力因子开始分泌或表达量增加相关联,从而促进对宿主的感染和病理的发展(袁雪梅等, 2015)。已有研究表明,温度是在环境中能被细菌感知的一个重要的环境因子,其变化是很多致病菌毒力基因表达的一个信号(Shapiro et al, 2012)。研究表明,大黄鱼网箱养殖处于较高密度,且网箱之间、鱼排之间排列紧密,水体交换差,环境污染加重,鱼类常处于应激状态。因此,当水体温度适宜时,杀香鱼假单胞菌乘虚侵入大黄鱼体内,通过血液循环进入脾脏、肾脏和肝脏等主要靶器官,本研究中,组织细胞的病理变化特征显示了病原菌的入侵和危害。病原菌胞外毒力因子致使组织病变,造成鱼体生理代谢紊乱,免疫力和抵抗力下降,为病原菌的进一步入侵创造了有利条件,鱼体终因无法维持正常的生命活动而导致死亡。
| Chrio N, Seiko I, Kenji K, et al. Repeatable immersion infection with Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida reproducing clinical signs and moderate mortality. Fisheries Sciences, 2009, 75(3): 707-714 DOI:10.1007/s12562-009-0099-8 | |
| Hu J, Zhang F, Xu XJ, et al. Isolation, identification and virulence of the pathogen of white-spots disease in internal organs of Pseudosciaena crocea.. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2014, 45(2): 409-417 DOI:10.11693/hyhz20140300078 [胡娇, 张飞, 徐晓津, 等. 大黄鱼(Pseudosciaena crocea)内脏白点病病原分离鉴定及致病性研究. 海洋与湖沼, 2014, 45(2): 409-417] | |
| Liu C, Li KB, Wang Q, et al. Isolation, identification and characterization of Aeromonas schubertii from hybrid snakehead (Channa maculata♀×C. argus♂). Journal Of of Fisheries Of of China, 2012, 36(7): 1119-1125 [刘春, 李凯彬, 王庆, 等. 杂交鳢(斑鳢♀×乌鳢♂)内脏类结节病病原菌的分离、鉴定与特性分析. 水产学报, 2012, 36(7): 1119-1125] | |
| Liu JF. Culture and biology of large yellow croaker. Xiamen: Xiamen University Press, 2013. [刘家富. 大黄鱼养殖与生物学. 厦门: 厦门大学出版社, 2013.] | |
| Ma XD, Lu CP, Chen HQ, et al. Effect of iron on virulent factors of Aeromonas hydrophila. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 1999, 22(1): 83-86 [马向东, 陆承平, 陈怀青, 等. 铁对嗜水气单胞菌毒力因子的影响. 南京农业大学学报, 1999, 22(1): 83-86] | |
| Qiu YY, Zheng L, Mao ZJ, et al. Isolation and identification of the causative agent and histopathology observation of white-spots disease in internal organs of Larimichthys crocea. Microbiology China, 2012, 39(3): 361-370 [邱杨玉, 郑磊, 毛芝娟, 等. 大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea)内脏白点病的病原分离和组织病理学观察. 微生物学通报, 2012, 39(3): 361-370] | |
| Shapiro RS, Cowen LE. Thermal control of microbial development and virulence: Molecular mechanisms of microbial temperature sensing. mBio, 2012, 3(5): e002381357-121365 | |
| Shen JY, Yu XP, Pan XY, et al. Isolation and identification of pseudomonassis pathogen from cultured Pseudosciaena crocea. Marine Fisheries Research, 2008, 29(1): 1-6 [沈锦玉, 余旭平, 潘晓艺, 等. 网箱养殖大黄鱼假单胞菌病病原的分离与鉴定. 海洋水产研究, 2008, 29(1): 1-6] | |
| Su YL, Feng J, Guo ZX, et al. Histopathological analysis of golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus infected with Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida. Marine Sciences, 2012, 36(2): 75-81 [苏友禄, 冯娟, 郭志勋, 等. 美人鱼发光杆菌杀鱼亚种感染卵形鲳鲹的病理学观察. 海洋科学, 2012, 36(2): 75-81] | |
| Su YQ. Breeding and farming of Pseudosciaena crocea.. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2004. [苏永全. 大黄鱼养殖. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2004.] | |
| Toranzo AE, Barreiro S, Casale JF, et al. Pasteurellosis in cultured gil the ad seabream (Sparus aurata): Fifirst report in Spain. Aquaculture, 1991, 99(1-2): 1-15 DOI:10.1016/0044-8486(91)90284-E | |
| Wang GL, Yuan SP, Jin S. Preliminary study on nocardiosis in cage-reared large croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea (Richardson). Journal Of of Fisheries Of of China, 2006, 20(1): 103-107 [王国良, 袁思平, 金珊. 网箱养殖大黄鱼诺卡氏菌病的初步研究. 水产学报, 2006, 20(1): 103-107] | |
| Yu WY, Li JN, Zu GZ. A Preliminary preliminary Report report on a Pathogenic pathogenic Bacterium bacterium from Eriocheir sinensis. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 1999, 26(2): 174-177 [余为一, 李槿年, 祖国掌. 一株中华绒螯蟹病原菌的研究初报. 安徽农业大学学报, 1999, 26(2): 174-177] | |
| Yuan XM, Ge MF, An SW, et al. Response of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida to environmental factors and detection of infection in farmed Pseudosciaena crocea.. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2015, 34(4): 579549-583553 [袁雪梅, 葛明峰, 安树伟, 等. 大黄鱼致病香鱼假单胞菌对环境因子的响应及其感染检测的分析. 应用海洋学学报, 2015, 34(4): 579549-583553] | |
| Zhang JT, Zhou SM, An SW, et al. Visceral granulomas in farmed large yellow croaker, Larimichthys crocea (Richardson), caused by a bacterial pathogen, Pseudomonas plecoglossicida. Journal of Fish Diseases, 2014, 37(2): 113-121 DOI:10.1111/jfd.2014.37.issue-2 | |
| Zhang XJ, Qin GM, Chen CZ, et al. Biological characterization and phylogenetic analysis of Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae from diseased Epinephelus lanceolatus L. Progress In Fishery Sciences, 2009, 30(3): 38-43 [张晓君, 秦国民, 陈翠珍, 等. 龙胆石斑鱼源美人鱼发光杆菌的生物学特性与系统发育学分析. 渔业科学进展, 2009, 30(3): 38-43] | |
| Zorrilla I, Balebona MC, Moriigo MA, et al. Isolation and characterization of the causative agent of pasteurellosis, Photobacterium damsela sp. piscicid a from sole Solea senegalensis(Kaup). Journal of Fish Diseases, 1999, 22(3): 167-171 DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2761.1999.00157.x |



