2. 宁波大学 宁波 315211
2. Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211
大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea)隶属鲈形目(Perciformes)、石首鱼科(Sciaenidae)、黄鱼属(Larimichthys),自20世纪福建省科技人员率先突破大黄鱼人工繁殖和育苗技术难关,大黄鱼逐步发展成为我国海水养殖鱼类主要品种之一,养殖规模和产量迅猛发展。伴随大黄鱼养殖产量的不断提升,品质问题日渐成为制约大黄鱼产业发展的重要因素,大黄鱼的品质研究逐渐成为大黄鱼研究新的热点。学者们就大黄鱼不同群体(郑炜强等, 2014; 李明云等, 2010)、不同饵料组分(易新文等, 2013)等对其生长、品质影响进行了相关研究,但对养殖大黄鱼外在品质集中体现的形态研究较少,缺乏不同养殖模式及饵料对大黄鱼形态影响的研究。
利用聚类分析、主成分分析、判别分析等多元分析方法开展形态差异研究,已在包括鱼类(林艳红等, 2010; 邵锋等, 2008; 庆宁等, 2007; 廖锐等, 2009; 胡海彦等, 2011; 岳亮等, 2016)、贝类(钱荣华等, 2003)、甲壳类(王志铮等, 2016)等多个物种中应用,具有良好的适用性。形态作为物种的外在特征,不仅是物种鉴别的依据,同时也是生物遗传和生存环境共同作用的外在表现。在影响鱼类形态的诸多外在因素中,环境和饵料是两个重要的非遗传因子。因此,本研究通过对不同养殖模式及饲料对岱衢洋大黄鱼形态的影响进行研究,以期为仿野生大黄鱼品质养殖技术及不同饲料选择提供依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料实验选取浙江象山港湾水产苗种公司繁育的F2代岱衢洋大黄鱼,初始规格为(8.5±1.1) g。选择配合饲料和天然饵料2种养殖饲料。配合料由中国海洋大学麦康森院士团队提供,由七好生物科技有限公司制造;天然饵料为宁波地区海水鱼养殖常规青占鱼(Pneumatophorus japonicus)冰鲜料。
1.2 实验方法将实验大黄鱼暂养驯化3 d后,进行分组。实验设置冰鲜饲料组、配合饲料组、深水网箱组3个组,每组设置3个平行网箱。其中,冰鲜饲料组设置在象山西护港大黄鱼养殖区,投喂普通冰鲜饲料,养殖网箱规格为5 m×5 m×3.5 m;配合饲料组设置于冰鲜饲料组同一渔排,投喂配合饲料,养殖网箱规格同为5 m×5 m×3.5 m;深水网箱组设置在象山港白石山海区,投喂普通冰鲜饲料,养殖网箱为直径12 m的深水网箱。3个组均采用相同养殖管理操作,饲料日投喂量以鱼群摄食情况做适当调整,并做好日常投喂管理记录,至翌年12月养殖大黄鱼达22月龄商品规格,测定各组大黄鱼形态。
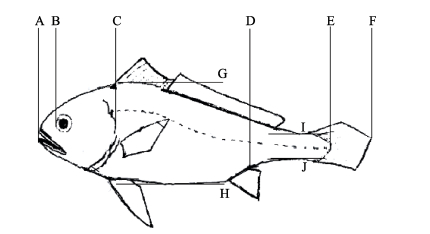
1.3 形态测定方法形态测量选择大黄鱼传统形态学可量性状,包括:体重、体长、全长、头长、吻长、体高、尾柄长、尾柄高、体厚作为常规形态参数,测定标准参照(GB/T18654.3-2008)性状测定部分(图 1),并测定大黄鱼形态框架,测量位点见图 2。每组随机取30尾鱼进行测量。使用电子天平测量体重,精确到0.1 g;使用普通直尺测量体长及全长,精确到0.1 cm;用游标卡尺测量其他数据,精确到0.01 mm。
|
图 1 大黄鱼常规形态测量 Figure 1 Morphological characters of L. crocea AF:全长 Total length; AE:体长 Body length; AC:头长 Head length; AB:吻长 Snout length; DE:尾柄长 Caudal peduncle length; IJ:尾柄高 Caudal peduncle width; GH:体高 Body height |

|
图 2 大黄鱼框架 Figure 2 The scheme of L. crocea 1:下颌骨末端;2:吻前沿;3:腹鳍基起点;4:背鳍基起点;5:臀鳍基起点;6:背鳍鳍棘基部末端;7:臀鳍基末端;8:背鳍基末端;9:尾鳍基腹部起点;10:尾鳍基背部起点 1: Mandible end; 2: Snout frontier; 3: Pelvic fin starting point; 4: Dorsal fin starting point; 5: Anal fin starting point; 6: Dorsal fin spines ending point; 7: Anal fin ending point; 8: Dorsal fin ending point; 9: Caudal fin ventral starting point; 10: Caudal fin back starting point |
利用SPSS 23.0对测量数据进行分析,采用聚类分析、主成分分析、判别分析对大黄鱼形态差异进行分析。由于大黄鱼个体之间存在大小差异,将各鱼所有形态测量数据除以其体长后进行统计分析。判别准确率的计算公式为:
判别准确率P1=判别正确的尾数/实际尾数
判别准确率P2=判别正确的尾数/判别尾数
综合判别率=
式中,Ai为第i个判别准确的尾数,Bi为第i个群体的实际尾数,K为群体数。
2 结果 2.1 养殖生长情况测量结果显示,配合饲料组平均体重为(406.7± 65.5) g,平均体长为(28.6±1.2) cm。冰鲜饲料组平均体重为(435.8± 82.6) g,平均体长为(28.4±1.8) cm。深水网箱组的平均体重为(428.6±97.9) g,平均体长为(27.9±1.9) cm。各组生长经方差分析,无显著差异(P > 0.05)。
2.2 外形参数方差分析通过对测量数据进行方差分析,结果显示,不同的养殖环境及饲料条件下,岱衢洋大黄鱼在体高、尾柄长、尾柄高、体厚上存在极显著差异,而形态框架参数D4–6、D5–6、D7–8存在显著差异,在D3–4、D3–6上存在极显著差异(表 1)。各组间差异主要集中于躯干部及尾部。
|
|
表 1 大黄鱼形态参数方差分析 Table 1 ANOVA of morphological traits of L. crocea |
从表 2可以看出,通过Duncan检验,在体高性状上3组间均存在显著差异,深水网箱组体高最大、冰鲜饲料组次之、配合饲料组最小。在尾长性状上,深水网箱组尾柄最长,且与其他2组存在显著差异。在尾柄高性状上,冰鲜饲料组尾柄最高,与其他2组存在显著差异。在体厚性状上,配合饲料组最小,与其他2组存在显著差异。在D3–4、D3–6、D4–6表征躯干部前端参数上,配合饲料组与其他2组存在显著差异;而表征躯干末端及尾部形态的D7–8参数,深水网箱组与其他2组存在显著差异。
|
|
表 2 岱衢洋大黄鱼形态多重比较 Table 2 Duncan's multiple range test of morphological traits of L. crocea |
利用3组大黄鱼形态参数平均值,以最近邻元素法进行聚类分析。结果显示,深水网箱组与配合饲料组首先聚为一类,而与冰鲜饲料组相距较远(图 3),深水网箱组与配合饲料组形态更为接近。

|
图 3 不同组大黄鱼形态聚类分析 Figure 3 The cluster analysis of L. crocea in different groups |
通过对不同饵料组成和养殖环境数据进行主成分分析(表 3),获取前3个主成分,各主成分贡献率分别为51.022%、9.440%、8.419%,累积贡献率为68.882%,其中,主成分1为大黄鱼体型差异的主要来源。成分矩阵得分表明,主成分1主要表征躯干部位框架形态差异;主成分2表征尾部形态变异;主成分3表征体高与体厚形态差异。
|
|
表 3 主成分分析因子成分矩阵及主成分对变异的贡献率 Table 3 The component matrix and the contribution of principal components to the total variance in PCA analysis |
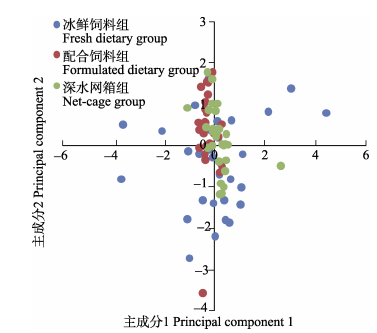
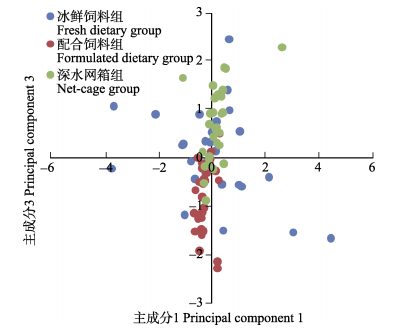
对各组主成分1与主成分2、主成分1与主成分3绘制散点图(图 4、图 5)。结果显示,不同饲料与不同养殖条件下,养殖大黄鱼体型呈现不同的分布趋势。其中,配合饲料组与深水网箱组在主成分1、主成分2上较为集中,但在主成分3上存在分离,表明二者在体高与体厚上存在较大差异,这与方差分析结果吻合。而冰鲜饲料组则在3个主成分上均呈现一定的离散性,表明小网箱冰鲜饲料养殖大黄鱼个体间形态差异较大。
|
图 4 不同组大黄鱼形态主成分1与主成分2分析 Figure 4 The morphology analysis of principal component 1 and principal component 2 of L. crocea in different groups |
|
图 5 不同组大黄鱼形态主成分1与主成分3分析 Figure 5 The morphology analysis of principal component 1 and principal component 3 of L. crocea in different groups |
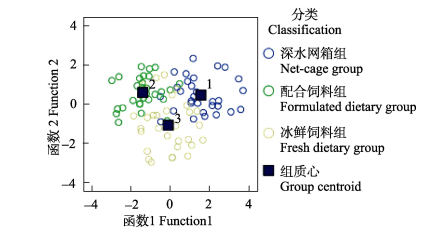
将各组大黄鱼群体性状指标进行判别分析,采用逐步判别法对27个形态参数进行判别分析,筛选得到7个对判别贡献较大的参数,分别建立3个群体的判别函数并作图(图 6),表明函数能较好区分3个群体。
|
图 6 不同组大黄鱼判别分析 Figure 6 The discriminant analysis of L. crocea in different groups |
深水网箱大黄鱼:
Y1=–694.836+1732.071X1+168.065X2+891.577X3–568.378X4+930.396X5+13.138X6–1542.221X7
配合饲料大黄鱼:
Y2=–649.384+1659.057X1+162.308X2+1129.876X3–683.916X4+858.222X5–48.065X6–1422.479X7
冰鲜饲料大黄鱼:
Y3=–636.438+1670.692X1+156.880X2+953.536X3–567.274X4+748.050X5+92.607X6–1397.701X7
式中,X1是体高体长比、X2是尾长尾高比、X3是D2–4、X4是D3–6、X5是D5–6、X6是D6–7、X7是D8–10。将大黄鱼测量值代入各判别函数计算Y值,最大Y值类别即为个体判别类别。
将本次所有测定个体相关形态参数代入进行预测分类。判别准确率P1为66.7%–93.3%,P2为79.4%–86.9%,综合判别率为62.5%。经交互验证后结果无显著差异(P > 0.05),说明上述判别公式可靠且稳定。
3 讨论形态作为鱼类的一个重要性状,在分类学上具有重要意义,通过形态差异分析能实现近缘物种或不同种群的区分。在大黄鱼研究中,已开展基于形态差异多元分析统计方法研究不同家系、不同养殖群体(张雅芝等, 2005)、不同生长阶段(刘贤德等, 2010)、不同性别(谌微等, 2014)的大黄鱼形态差异,并构建相应判别函数模型,实现对不同群体的区别。
在影响鱼类外部形态的众多非遗传影响因子中,水环境是极其重要的外部因素,对鱼类形态有着强烈的影响,因地理隔离形成的不同水环境条件是形成不同地理种群的重要因素之一。费骥慧等(2012)对不同高原湖泊中外来物种麦穗鱼(Pseudorasbora parva)的体型差异进行了研究,结果显示,相同来源的麦穗鱼会在相对隔离的环境中彼此形成种内形态差异。Haas等(2010)和Langerhans等(2003)的研究表明,水生动物外部形态的变化影响其游泳能力,且这种形态变异还受到环境因子的影响。李秀明等(2013)在对中华倒刺鲃(Spinibarbus sinensis)游泳能力的研究中发现,高游速组的体高及体高体长比显著大于低游速组,这与本研究中深水网箱组体高体长比最大的结果相一致。同时,鱼类外部形态的改变对抵抗水流的游泳能力存在显著影响。Li等(2009)对转GH基因鲤鱼(Cyprinus carpio)与非转基因鲤鱼游泳能力比较证明,尾长、尾高、尾柄基部长度等性状改变是导致游泳能力出现差异的主要原因。本研究中与游泳能力相关的尾部形态特征,如尾长、尾高、尾柄基部长度(D7–8)等也出现显著差异。由于深水网箱养殖模式与普通网箱养殖模式不仅在养殖空间、水深等方面存在差异,在流速上也存在较大差异。而本研究中,大黄鱼多个差异的形态参数与已报道研究中鱼类游泳能力相关的形态部位类同,但这些差异是否是个体对流速变化作出适应仍需进一步研究。
饵料是鱼类生长发育的物质能量基础,其不同的营养组成会影响养殖鱼类的生长及外部形态。陈慧等(2007)、王映等(2016)对不同来源的大黄鱼形态进行比较研究表明,养殖群体的体高、体厚等躯干参数显著高于野生群体。这些显著差异是由于2个群体在饵料营养、饱食度、生存压力等方面的不同,使养殖群体的营养物质积累远多于野生群体。表征个体肥满度的体高、体厚等躯干形态参数能在一定程度上反应鱼类生长过程中物质能量的积累状况。本研究中,不同饵料养殖大黄鱼在体高、体厚、D3–4、D3–6、D5–6存在显著差异,表明投喂不同类型饵料对养殖大黄鱼体的物质积累存在影响,这与上述研究的观点一致。高有领等(2014)对投喂不同类型饵料大黄鱼营养成分测试结果显示,投喂冰鲜饲料的养殖大黄鱼在全鱼粗脂肪含量上显著高于投喂配合饲料养殖个体。由于本研究中所使用的饵料及养殖海区均与高有领等(2014)相同,因此,饲料不同的营养配比不仅影响养殖个体的营养组成,也可能因营养代谢的不同而影响养殖大黄鱼的营养物质积累,使表征个体营养状态的体高、体厚性状出现差异。
通过本研究对不同养殖环境和饵料对大黄鱼形态的影响分析表明,通过改变流速、扩大养殖空间可影响养殖大黄鱼尾部形态,使其具有更大的尾部体长占比;使用配合饲料养殖可使养殖大黄鱼体型趋于细长,更符合消费市场价值取向,但其机理及最适养殖参数仍需进一步研究确定。
| Chen H, Chen W, Lin GW, et al. The morphological characteristics and growth pattern of cage-cultured large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in Guanjing-Yang population. Marine Fisheries, 2007, 29(4): 331-336 [陈慧, 陈武, 林国文, 等. 官井洋种群网箱养殖大黄鱼的形态特征与生长式型. 海洋渔业, 2007, 29(4): 331-336] | |
| Chen W, Wang PP, Xiao SJ, et al. Analysis of morphological index system and sexual differences of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Journal of Jimei University (Natural Science), 2014, 19(6): 401-408 [谌微, 王盼盼, 肖世俊, 等. 大黄鱼形态指标体系及雌雄差异分析. 集美大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 19(6): 401-408] | |
| Fei JH, Shao XY. Studies on the growth characteristics and morphological differences of fish in plateau lakes. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(4): 789-796 DOI:10.11693/hyhz201204016016 [费骥慧, 邵晓阳. 高原湖泊鱼类生长特性与形态差异研究. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(4): 789-796] | |
| Gao YL, Jiang LL, Xu XD, et al. Effects of dietary type on nutritional components in whole fish and muscle, body color and muscle color in Dai-Ju race large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2014, 26(8): 1-9 [高有领, 江玲丽, 徐旭栋, 等. 饵料类型对岱衢族大黄鱼鱼体和肌肉营养成分、体色、肉色的影响. 动物营养学报, 2014, 26(8): 1-9] | |
| Haas TC, Blum MJ, Heins DC, et al. Morphological responses of a stream fish to water impoundment. Biology Letters, 2010, 6(6): 803-806 DOI:10.1098/rsbl.2010.0401 | |
| Hu HY, Di Y, Zhao YF, et al. Comparative study on the morphological characteristics of four species of Culter and Culterichthys in Lihu Lake. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2011, 26(4): 488-494 [胡海彦, 狄瑜, 赵永锋, 等. 蠡湖4种鲌鱼形态特征的比较研究. 云南农业大学学报, 2011, 26(4): 488-494] | |
| Langerhans RB, Layman CA, Langerhans AK, et al. Habitat-associated morphological divergence in two neotropical fish species. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 2003, 80(4): 689-698 DOI:10.1111/j.1095-8312.2003.00266.x | |
| Li D, Hu W, Wang Y, et al. Reduced swimming abilities in fast-growing transgenic common carp Cyprinus carpio associated with their morphological variations. Journal of Fish Biology, 2009, 74(1): 186-197 DOI:10.1111/jfb.2009.74.issue-1 | |
| Li MY, Hu YZ, Miao L, et al. Studies on the growth characteristics and heterosis of genealogies of Pseudosciaena crocea. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2010, 34(6): 859-864 [李明云, 胡玉珍, 苗亮, 等. 岱衢洋和官井洋大黄鱼自交与杂交子代生长性能及杂交优势分析. 水产学报, 2010, 34(6): 859-864] | |
| Li XM, Wang C, Yu LJ, et al. The effects of aerobic exercise training on the morphological characteristics of juvenile Spinibarbus sinensis. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science), 2013, 35(7): 21-26 [李秀明, 王川, 于丽娟, 等. 有氧运动训练对中华倒刺鲃幼鱼形态特征的影响. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 35(7): 21-26] | |
Liao R, Qu YJ, Gou XW, et al. Morphological variations and discrimination of four fish species Chinese bahaba Bahaba flavolabiata, large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea, Ting'wak Wak tingi and spinyhead croaker Collichthys lucidus.
Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 2009, 24(4): 305-310 [廖锐, 区又君, 勾效伟, 等. 黄唇鱼、大黄鱼、丁氏 和棘头梅童鱼的形态差异和判别分析.
大连水产学院学报, 2009, 24(4): 305-310] 和棘头梅童鱼的形态差异和判别分析.
大连水产学院学报, 2009, 24(4): 305-310]
|
|
| Lin YH, An M, Jiang HB. Study on morphological differences among three Schizothorax species. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(10): 121-126 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2010.10.038 [林艳红, 安苗, 姜海波. 3种裂腹鱼的形态差异研究. 贵州农业科学, 2010, 38(10): 121-126] | |
| Liu XD, Cai MY, Wang ZY, et al. Correlation analysis of morphometric traits and body weight of large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea at different growth stage. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(5): 159-163 DOI:10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2010.05.159 [刘贤德, 蔡明夷, 王志勇, 等. 不同生长时期大黄鱼形态性状与体重的相关性分析. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(5): 159-163] | |
| Qian RH, Li JL, Dong ZG, et al. Morphological variations analysis among populations of Hyriopsis cumingii in five large lakes of China. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2003, 34(4): 436-443 DOI:10.11693/hyhz200304011011 [钱荣华, 李家乐, 董志国, 等. 中国五大湖三角帆蚌形态差异分析. 海洋与湖沼, 2003, 34(4): 436-443] | |
| Qing N, Lv FY, Zhao J, et al. Morphological variations and geographical differentiations of Pelteobagrus intermedius in different drainage systems from the coastal area of western south China. Zoological Research, 2007, 28(2): 207-212 [庆宁, 吕凤义, 赵俊, 等. 华南沿海地区西部入海水系中间黄颡鱼的形态变异及地理分化. 动物学研究, 2007, 28(2): 207-212] | |
| Shao F, Chen XJ, Li G, et al. Morphological variations and discriminant analysis of Scomber japonicus and Scomber australasicus in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Journal of Shanghai Fisheries University, 2008, 17(2): 204-209 [邵锋, 陈新军, 李纲, 等. 东黄海鲐鱼形态差异分析. 上海水产大学学报, 2008, 17(2): 204-209] | |
| Wang Y, Ke QZ, Liu JF, et al. Comparison on morphology, scales and otolith characteristics between cultured stock and wild stock of Larimichthys crocea. Marine Fisheries, 2016, 38(2): 149-156 [王映, 柯巧珍, 刘家富, 等. 大黄鱼养殖群体和野生群体形态、鳞片及耳石特征比较. 海洋渔业, 2016, 38(2): 149-156] | |
| Wang ZZ, Zhu HJ, Ren SY, et al. Correlation between morphological traits and flow velocity of post larva marspenaeus japonicus. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2016, 47(2): 360-367 [王志铮, 朱海军, 任夙艺, 等. 日本囊对虾(Marsupenaeus japonicus)秋繁仔虾形态表型与抗流性能间的相关性. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(2): 360-367] | |
| Yi XW, Zhang WB, Mai KS, et al. Effects of dietary fish oil replaced with rapeseed oil on the growth, fatty acid composition and skin color of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Journal of Fisheries of China, 2013, 37(5): 751-760 [易新文, 张文兵, 麦康森, 等. 饲料中菜籽油替代鱼油对大黄鱼生长、肌肉脂肪酸组成和体色的影响. 水产学报, 2013, 37(5): 751-760] | |
| Yue L, Wang XA, Ma AJ, et al. Comparison of the morphological traits between male and female individuals of Takifugu rubripes. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2016, 37(1): 30-35 DOI:10.11758/yykxjz.20141215001 [岳亮, 王新安, 马爱军, 等. 红鳍东方鲀(Takifugu rubripes)雌、雄个体的形态特征比较. 渔业科学进展, 2016, 37(1): 30-35] | |
| Zhang YZ, Wang ZY, Lin LM, et al. Comparative study on differences of morphologic characters of seven different stocks of the cultured large yellow croakers (Pseudosciaena crocea) belonging to the Min-Yuedong tribe in Guanjing-yang sea area, Fujian Province. Journal of Jimei University (Natural Science), 2005, 10(3): 193-199 [张雅芝, 王志勇, 林利民, 等. 养殖条件下闽-粤东族大黄鱼不同群体形态特征的比较研究. 集美大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 10(3): 193-199] | |
| Zheng WQ, Huang WQ, Han KH, et al. Growth traits of F1 crossed between wild and selective breeding large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Fisheries Science, 2014, 33(11): 667-673 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2014.11.001 [郑炜强, 黄伟卿, 韩坤煌, 等. 大黄鱼选育群体与野生群体杂交F1生长性状研究. 水产科学, 2014, 33(11): 667-673] |




