2. 青岛海洋科学与技术国家实验室海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程功能实验室 青岛 266071;
3. 农业部海洋渔业可持续发展重点实验室 中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所 青岛 266071
2. Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266071;
3. Key Laboratory of Sustainable Development of Marine Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture, Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Qingdao 266071
三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)是一种重要的海洋经济动物,在中国、朝鲜、日本等海域均有分布,在我国黄渤海及东海分布尤为广泛(薛俊增等, 1997)。由于养殖规模的不断扩大、水体环境污染加重、累代养殖造成的种质退化,三疣梭子蟹的病害也日趋严重,给养殖业带来了巨大的经济损失(高保全等, 2015)。研究表明,对虾白斑综合征病毒(WSSV)和副溶血弧菌(Vibrio parahemolyticus)均会造成三疣梭子蟹组织病变乃至死亡(王忠发等, 2008; 阎斌伦等, 2010)。此外,盐度作为一种重要的水体环境因子,也对三疣梭子蟹的免疫功能产生较大影响。三疣梭子蟹等甲壳动物在水体盐度发生急剧变化时,可能会产生应激反应和生理代谢紊乱,导致其免疫力下降,从而促使病害暴发并造成大量死亡(王林等, 2016; 付萍等, 2016)。然而,三疣梭子蟹等无脊椎动物没有类似于哺乳动物的B淋巴细胞和T淋巴细胞,因此,其不具有获得性免疫系统(Uematsus et al, 2008),但可以依赖独特的先天性免疫系统通过免疫信号通路级联反应清除入侵机体的病原微生物。
三疣梭子蟹等甲壳动物的先天免疫是由Toll样受体(Toll-like receptors, TLRs)等模式识别受体(Pathogen recognize receptors, PRRs)所介导(Carty et al, 2010),通过识别保守的病原相关分子模式(Pathogen associated molecular patterns, PAMPs),启动先天性免疫应答(Aderem et al, 2000)。Toll受体蛋白于1980年首次在果蝇(Drosophila)中发现,参与果蝇背腹侧轴形成,缺失Toll受体蛋白会引起果蝇成体不对称(Nusslein-Volhard et al, 1980)。Hoffmann等(1996)发现并证实Toll受体蛋白在先天免疫中起到了重要作用。各物种的Toll样受体都具有多名成员,目前,已在果蝇中发现了9种类型的Toll受体蛋白,而在哺乳动物中也有13种Toll样受体被陆续发现(Iwasaki et al, 2004; Bilak et al, 2003)。
目前,TLRs家族基因在哺乳动物和果蝇中已有较为深入的研究,但在甲壳动物中,TLRs家族基因的研究还处于起步阶段。Yang等(2007)在凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei)中发现了一个Toll样受体,命名为LvToll,这是在甲壳动物中发现的首个TLRs家族基因。目前,在三疣梭子蟹中仅发现了3种Toll样受体(Zhou et al, 2015)。
为进一步完善TLRs基因家族在三疣梭子蟹先天免疫中发挥的功能,本研究利用RACE技术克隆了一个新的三疣梭子蟹TLRs家族基因,命名为PtToll4,并对其序列进行分析,阐明了其系统进化关系。利用实时荧光定量PCR检测了经副溶血弧菌和WSSV感染后,PtToll4基因在血细胞中的表达变化。此外,初步探究了低盐胁迫对PtToll4基因表达量的影响。旨在为进一步研究PtToll4基因在三疣梭子蟹先天免疫中发挥的功能提供理论支持。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验动物本实验所用三疣梭子蟹取自中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所实验基地山东省昌邑市海丰水产养殖有限责任公司,体重为(35±5) g,置于整理箱(560 mm×360 mm×280 mm)中暂养7 d,暂养期间保持水温为(20±2)℃,盐度为31,pH=8.2。期间持续充氧,定时换水清污,换水量为原水量的1/3,定时投喂饵料并对暂养个体进行筛选,保留活力形态均较好的个体。
1.2 实验方法 1.2.1 RNA的提取及RACE第一链合成用TRIzol法分别提取三疣梭子蟹各组织总RNA,利用核酸定量仪(Thermo, NanoDrop 2000)与琼脂糖凝胶电泳等方法,检测所提总RNA的质量和完整性。按照SMARTTM RACE Amplification Kit(Clontech)说明书,取等量所取各组织总RNA混匀,用来合成3'和5'RACE第一链,用于后续实验。
1.2.2 PtToll4基因cDNA序列全长的克隆根据本实验室三疣梭子蟹转录组库中所得到的PtToll4基因EST序列,利用Primer Premier 5.0软件分别设计3'和5'末端特异性引物(表 1),由擎科梓熙生物技术有限公司合成。参照SMART RACE说明书,利用Advantange 2 PCR Kit(Clontech)使UPM与相应的特异性引物分别结合,进行PtToll4基因cDNA 3'和5'末端扩增。PCR程序:94℃ 30 s,60℃ 30 s,72℃ 90 s,30个循环。扩增产物使用NucleoSpin Gel and PCR Clean-Up试剂盒(TaKaRa)切胶回收得到目的片段。将目的片段和pMD19-T进行载体连接,16℃反应3 h,将连接产物转入到大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞中,37℃平板培养12 h。挑取阳性菌落在LB液体培养基(含AMP)中培养5 h,随后进行菌液PCR检测,由擎科梓熙生物技术有限公司完成测序。
|
|
表 1 PtToll4克隆和mRNA表达分析所用引物序列 Table 1 Primers used for PtToll4 cloning and mRNA expression analysis |
利用Contig Express Project软件去除载体序列,并保留目的片段,将所得到的目的片段序列与PtToll4基因EST序列进行比对,通过拼接得到PtToll4基因cDNA序列全长。将得到的PtToll4基因的cDNA序列利用BLAST (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)进行同源性比对。利用EditSeq和Gene Tool预测开放阅读框(ORF)并翻译得到其氨基酸序列。氨基酸序列分子量及等电点使用在线ExPASy进行预测,利用SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de)进行蛋白质功能结构域预测与分析。利用DNAMAN将PtToll4氨基酸序列和其他物种相应氨基酸序列进行多重序列比对,使用MEGA 5.0软件构建Neighbor-Joining系统进化树,对PtToll4基因的亲缘关系分析。
1.2.4 病原感染实验将实验所用三疣梭子蟹暂养7 d后分为2个实验组和1个对照组,即副溶血弧菌感染组、WSSV感染组、PBS对照组,每组80只。通过预实验,三疣梭子蟹注射感染副溶血弧菌和WSSV后,72 h三疣梭子蟹的半致死浓度分别为2.6×107 CFU/ml、3.2×107拷贝/ml,分别以此浓度进行感染实验。将3组三疣梭子蟹分别注射100 μl副溶血弧菌、WSSV和PBS,实验期间的饲养与管理与暂养期保持一致。分别于0、3、6、12、24、48和72 h进行取样,每个时间点各取3只三疣梭子蟹,取其血淋巴,4000 r/min离心15 min,弃血清,保留血细胞并立即加入300 ml TRIzol,置于液氮中保存。
1.2.5 低盐胁迫实验选取暂养后的三疣梭子蟹120只,均分为2组,即盐度胁迫组和正常对照组。通过预实验,得到三疣梭子蟹低盐胁迫72 h半致死盐度为11,以此盐度进行低盐胁迫实验。实验水体由自然海水和自来水调配所得并充分曝气,正常对照组所用实验水体为正常海水(盐度为31)。实验期间的饲养与管理与暂养期保持一致。分别于0、3、6、12、24、48和72 h取样,每个时间点各取3只,取其血淋巴,4000 r/min离心15 min,弃血清,保留血细胞并立即加入300 ml TRIzol,置于液氮中保存,以便用于后续实验。
1.2.6 PtToll4基因的定量表达分析将经过暂养的正常状态下的三疣梭子蟹的血细胞、肝胰腺、鳃、肌肉、心脏、眼柄、表皮、胃和肠等组织以及不同实验组所取组织分别提取RNA,用核酸定量仪和琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测RNA的质量和完整性,确保RNA质量与完整性均好,随后用PrimeScript RT reagent kit进行反转录合成cDNA,具体方法按照说明书进行。
根据本实验中已经得到的PtToll4基因的开放阅读框cDNA序列,设计合成一对正反向特异荧光定量引物,并且以内参基因β-actin作为对照(β-actin-F和β-actin-R;PtToll4-F和PtToll4-R)(表 1)。参照SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM Ⅱ说明书,利用Applied Biosystems 7500 Real Time PCR仪分析所提三疣梭子蟹各组织中PtToll4基因的相对表达量。反应体系10 μl:5 μl SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM Ⅱ,0.4 μl 10 μmol/L的正反向引物,0.2 μl ROX Reference Dye Ⅱ,1.0 μl cDNA,3.0 μl灭菌双蒸水。反应程序:95℃ 30 s;95℃ 5 s,60℃ 34 s,40个循环;95℃ 15 s,60℃ 1 min,95℃ 15 s。各样本均设3个重复,实验结果采用相对标准曲线法2–ΔΔCt(Livak et al, 2001)进行相对定量计算,并利用SPSS 19.0软件对结果进行单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA),并对其显著性进行检验。
2 结果 2.1 PtToll4基因cDNA的克隆及其序列分析将提取得到的三疣梭子蟹各组织总RNA用核酸定量仪和琼脂糖凝胶电泳对其质量和完整性进行检测,结果显示,其OD260 nm/OD280 nm均在1.9~2.0之间,28S、18S和5S rRNA条带清晰,表明所提总RNA质量较好,可用于合成RACE模板。利用合成的cDNA第一链作为模板,进行5'和3'末端RACE扩增。PCR产物经公司测序后与已知的EST序列分析比较测序结果,拼接得到PtToll4基因cDNA全长序列。利用EditSeq软件以及BLAST对序列分析,发现已知序列包含完整的开放阅读框(ORF),表明所得到的基因序列完整可靠。PtToll4基因cDNA序列(GenBank登录号:KY432366)全长4276个核苷酸,包含2685 bp的开放阅读框(ORF)、339 bp的5'端非编码区(UTR)和1252 bp的3'端非编码区(UTR),3'末端具有由28个腺嘌呤核苷酸组成的poly(A)尾(图 1)。
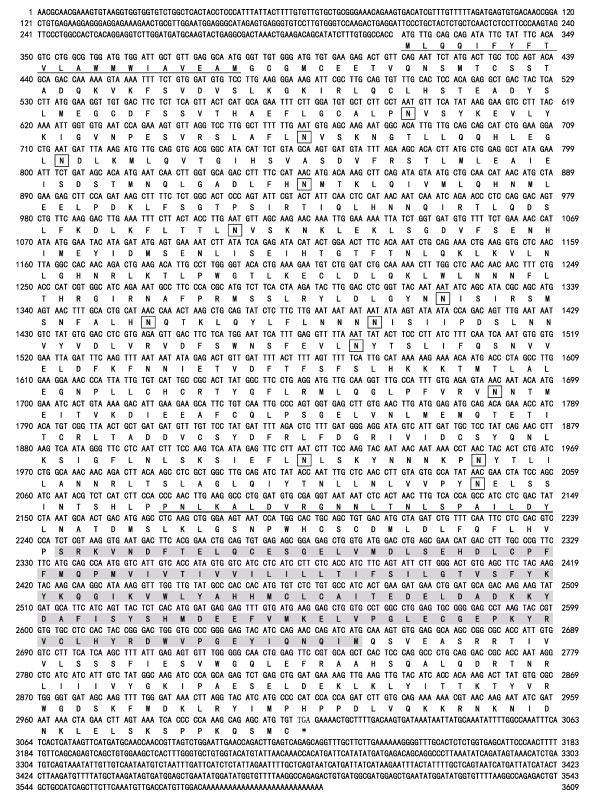
|
图 1 PtToll4基因序列全长及编码的氨基酸序列 Figure 1 PtToll4 nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acids sequence 单下划线和双下划线分别代表信号肽和跨膜区;方框表示潜在的糖基化位点;阴影部分代表TIR结构域;起始密码子(ATG)、终止密码子(TAG)用黑体表示 The single and double underlined letters represent the signal peptide and the TM region, respectively. The potential N-linked glycosylation sites are boxed. The TIR domain is shaded, the letters of the start codon (ATG) and the stop codon (TGA) are bolded |
使用EditSeq软件以及ExPASy预测得到PtToll4基因cDNA序列开放阅读框(ORF)的长度为2685 bp,编码一个由895个氨基酸组成的分子量为102.5 kDa、理论等电点为6.03的蛋白。利用SMART和Interpro-Scan对PtToll4基因编码的氨基酸序列进行在线蛋白质功能结构域分析,结果表明,PtToll4推导的氨基酸序列主要包括一个由21个氨基酸组成的信号肽(Signal peptide)、8个LRR或LRR-TYP结构域、2个LRRCT结构域(C-端LRR)、1个跨膜结构域(TM)以及1个TIR结构域组成(图 2)。
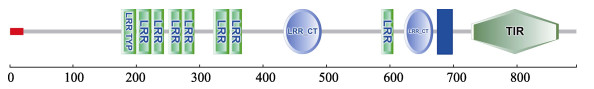
|
图 2 利用SMART在线软件预测的PtToll4的蛋白结构 Figure 2 The predicted domain architecture of PtToll4 by SMART 信号肽用红色框表示,跨膜区用深蓝色框表示,其他的结构域,包括LRR结构域和TIR结构域则分别用相应的框架加上符号表示(图中所用颜色和符号均参考网络版显示格式) Signal peptides are shown in red, TM domains in dark blue. Other domains, including LRR domains and TIR domains, are labeled accordingly (For the interpretation of the color and symbols in this figure refer to the web version of the article) |
通过BLAST同源性比对分析发现,PtToll4氨基酸序列与中华绒螯蟹(Eriocheir sinensis) EsToll2、中国明对虾(Fenneropenaeus chinensis)FcToll、斑节对虾(Penaeus monodon) PmToll、日本囊对虾(Marsupenaeus japonicus)MjToll2、凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei) LvToll、克氏原螯虾(Procambarus clarkii)PcToll2等具有较高的同源性,同源性为41%~61%,其中,与中华绒螯蟹EsToll2同源性最高,为61%(图 3)。
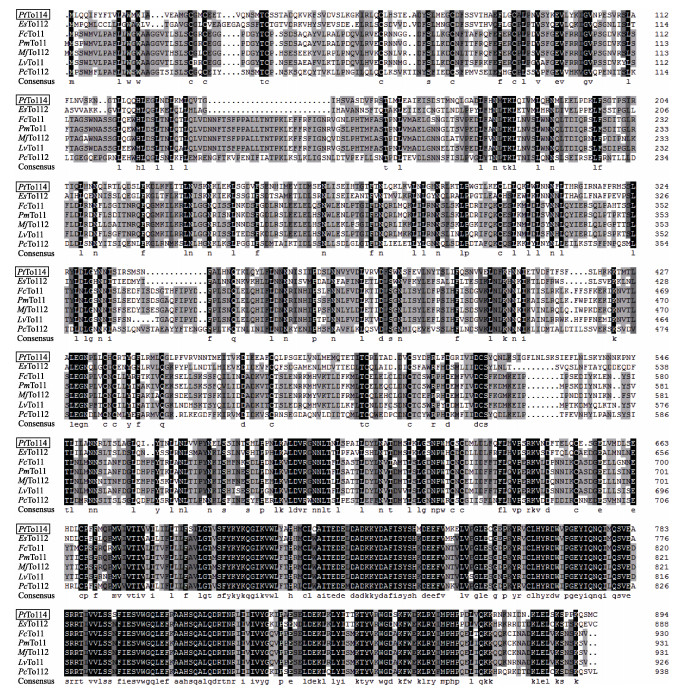
|
图 3 PtToll4基因编码的氨基酸序列与其他无脊椎动物Tolls氨基酸序列比对 Figure 3 Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of PtToll4 with other invertebrate Tolls 各物种GenBank登录号:三疣梭子蟹Toll4(KY432366)、中华绒螯蟹Toll2(AGT21374.1)、中国明对虾Toll (ACC68670.1)、斑节对虾Toll(ABO38434.1)、日本囊对虾Toll2(BAG68890.1)、凡纳滨对虾Toll(ABK58729.1)、克氏原螯虾Toll2(AOP12928.1) GenBank accession number of different species: PtToll4, P. trituberculatus Toll4 (KY432366); EsToll2, E. sinensis Toll2 (AGT21374.1); FcToll, F. chinensis Toll (ACC68670.1); PmToll, P. monodon Toll (ABO38434.1); MjToll2, M. japonicas Toll2 (BAG68890.1); LvToll, L. vannamei Toll (ABK58729.1); PcToll2 P. clarkia Toll2 (AOP12928.1) |
利用MEGA 5.0软件对PtToll4基因进行系统进化分析,结果显示,PtToll4首先与亲缘关系最近的中华绒螯蟹EsToll2聚为一支,其次与中国明对虾FcToll、凡纳滨对虾LvToll、拟穴青蟹(Scylla paramamosain)SpToll等亲缘关系较近的甲壳动物聚为一支,然后与果蝇(Drosophila melanogaster) DmToll等无脊椎动物聚为一支(图 4)。
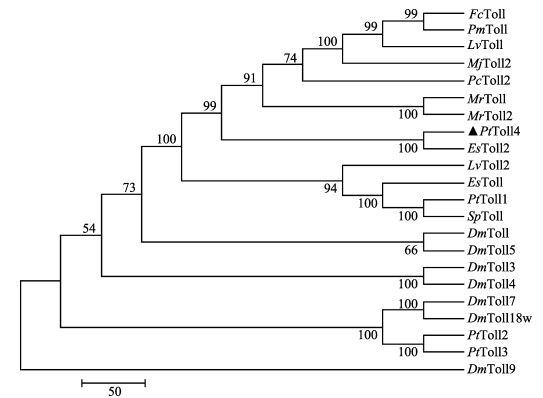
|
图 4 基于Toll4氨基酸序列构建的NJ进化树 Figure 4 NJ tree based on Toll4 amino acids 各物种基因GenBank登录号:三疣梭子蟹Toll4 (KY432366)、中华绒螯蟹Toll (AGK90305.1)、中华绒螯蟹Toll2 (AGT21374.1)、中国明对虾Toll (ACC68670.1)、斑节对虾Toll (ABO38434.1)、日本囊对虾Toll2 (BAG68890.1)、凡纳滨对虾Toll (ABK58729.1)、凡纳滨对虾Toll2 (AEK86516.1)、克氏原螯虾Toll2 (AOP12928.1)、罗氏沼虾Toll (AEI25533.1)、罗氏沼虾Toll2 (AHL39101.1)、拟穴青蟹Toll (AEX20238.1)、三疣梭子蟹Toll1 (AIZ66853.1)、三疣梭子蟹Toll2 (AKV62616.1)、三疣梭子蟹Toll3 (AKV62617.1)、果蝇Toll (AAQ64936.1)、果蝇Toll18w (AAF57509.1)、果蝇Toll3 (AAF86229.1)、果蝇Toll4 (AAF52747.3)、果蝇Toll5 (AAF86227.1)、果蝇Toll7 (AAF86225.1)、果蝇Toll9 (AAF51581.1) GenBank accession number of different species: PtToll4, P. trituberculatus Toll4 (KY432366); EsToll2, E. sinensis Toll (AGK90305.1); EsToll2, E. sinensis Toll2 (AGT21374.1); FcToll, F. chinensis (ACC68670.1); PmToll, P. monodon (ABO38434.1); MjToll2, M. japonicas (BAG68890.1); LvToll, L. vannamei (ABK58729.1); LvToll2, L. vannamei (ABK58729.1); PcToll2, P. clarkia (AOP12928.1); MrToll, M. rosenbergii Toll (AEI25533.1); MrToll2, M. rosenbergii Toll2 (AHL39101.1); SpToll S. paramamosain (AEX20238.1); PtToll1, P. trituberculatus Toll1(AIZ66853.1); PtToll2, P. trituberculatus Toll2(AKV62616.1); PtToll3, P. trituberculatus Toll3(AKV62617.1); DmToll, D. melanogaster Toll (AAQ64936.1); DmToll18, D. melanogaster Toll18 (AAF57509.1); DmToll3, D. melanogaster Toll (AAF86229.1); DmToll4, D. melanogaster Toll4 (AAF52747.3); DmToll5, D. melanogaster Toll5 (AAF86227.1); DmToll7, D. melanogaster Toll7 (AAF86225.1); DmToll9, D. melanogaster Toll9 (AAF51581.1) |
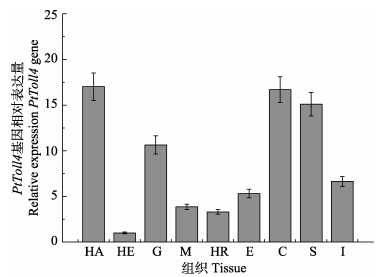
对PtToll4基因在不同组织的表达差异情况进行分析,结果显示,PtToll4基因在各组织中均有一定表达,在血细胞中的表达量最高,在表皮和胃中也有较高表达量,而在肝胰腺中的表达量最低(图 5)。
|
图 5 三疣梭子蟹PtToll4基因在不同组织中的表达分布 Figure 5 The expression of PtToll4 in different tissues of P. trituberculatus HA:血细胞; HE:肝胰腺; G:鳃; M:肌肉; HR:心脏; E:眼柄; C:表皮; S:胃; I:肠 HA: Haemocytes; HE: Hepatopancreas; G: Gill; M: Muscle; HR: Heart; E: Eyestalk; C: Cuticle; S: Stomach; I: Intestines |
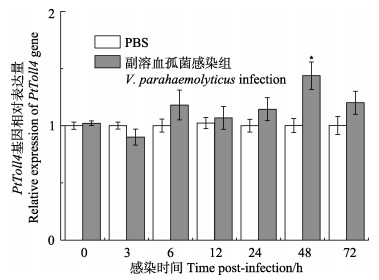
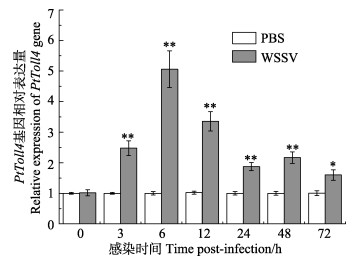
利用实时荧光定量PCR分别分析副溶血弧菌和WSSV感染后0 h、3 h、6 h、12 h、24 h、48 h和72 h三疣梭子蟹血细胞中PtToll4基因mRNA表达量的变化,经分析发现:与PBS对照组相比,经副溶血弧菌感染后,PtToll4基因在血细胞中仅在48 h出现显著上调(P<0.05),为对照组的1.41倍,在其他时间点无显著变化(图 6)。然而,经WSSV感染后,PtToll4基因在血细胞中均出现了显著上调(P<0.05)并且在6 h达到了表达量的峰值,为对照组的5.03倍(P<0.01)。经WSSV感染后,三疣梭子蟹血细胞中的PtToll4基因被诱导表达更为显著(图 7)。
|
图 6 副溶血弧菌感染后三疣梭子蟹血细胞中PtToll4基因的表达 Figure 6 The expression of PtToll4 in P. trituberculatus hemocytes after V. parahaemolyticus infection *代表P<0.05,**代表P<0.01;下同 * at P < 0.05, and ** at P < 0.01; the same applies below |
|
图 7 WSSV感染后三疣梭子蟹血细胞中PtToll4基因的表达 Figure 7 The expression of PtToll4 in P. trituberculatus hemocytes after WSSV infection |
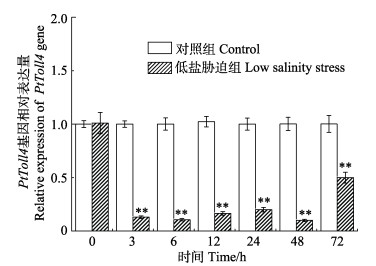
经盐度为11的水体环境对三疣梭子蟹进行低盐胁迫后,对三疣梭子蟹血细胞中PtToll4基因表达情况进行分析表明,与正常对照组相比,在0~72 h均出现了显著下调(P<0.01),其中,在48 h下调达到最低值,为正常对照组的0.1倍,在72 h表达量有所回升,为正常对照组的0.5倍(P<0.01) (图 8)。
|
图 8 低盐胁迫后三疣梭子蟹PtToll4基因在血细胞中的表达 Figure 8 The expression of PtToll4 in P. trituberculatus hemocytes under low salinity stress |
三疣梭子蟹等无脊椎动物由于不具有获得性免疫,因此,先天免疫是其抵抗外界病原入侵的重要防御机制(Liu et al, 2014)。先天免疫主要是由胚系基因所编码的模式识别受体所介导,Toll样受体便是一种重要的模式识别受体(Carty et al, 2010)。本研究通过RACE技术获得PtToll4基因cDNA序列全长(GenBank登录号:KY432366)。通过与其他无脊椎动物进行同源性比对发现,PtToll4的蛋白序列与中华绒螯蟹EsToll2的蛋白序列相似度最高,为61% (Yu et al, 2013),与其他甲壳类动物如克氏原螯虾PcToll2、罗氏沼虾(Macrobrachium rosenbergii)MrToll、斑节对虾PmToll也具有较高的同源性(Lan et al, 2016; Srisuk et al, 2014; Assavalapsakul et al, 2012)。
根据SMART预测得到的结构域可知,PtToll4具有TLRs家族的典型特征,归属I型跨膜蛋白,胞内有保守的TIR结构域,胞外含有多个亮氨酸重复(LRRs)。TIR结构域是一种进化十分保守的蛋白互作结构域,对于诱导Toll信号通路下游信号级联反应具有重要作用。TLRs家族基因胞外区的进化速度比胞内区要快,正是基于胞外结构的多样性,使得TLRs家族基因具有特异性识别病原相关分子模式的功能(Johnson et al, 2003; Ng et al, 2011)。比如在哺乳动物中,TLR1、TLR2和TLR6能够直接与脂肽结合Schneider et al, 2011),TLR2能够直接识别脂蛋白和肽聚糖(Takeuchi et al, 1999),TLR5可直接识别细菌鞭毛(Ramos et al, 2004),TLR9可直接与未甲基化的细菌CpG DNA结合(Hemmi et al, 2000)。PtToll4的LRR结构域含有8个LRR基序以及2个LRRCT帽子结构,这种结构有利于包埋暴露的疏水性氨基酸残基,从而使胞外结构更为稳定(Gay et al, 2006; Bell et al, 2005),在分子互作中具有重要作用(Leulier et al, 2008)。此外,PtToll4的胞外区有13个潜在的糖基化位点,这些位点在TLRs家族基因识别、结合病原相关分子模式中也起着重要作用(Zhang et al, 2011)。
组织表达分布结果显示,PtToll4基因在三疣梭子蟹各组织中均有不同程度的表达,其中,在血细胞中的表达量最高,而血细胞在甲壳动物的免疫系统中具有重要作用(姚翠鸾等, 2006)。在本研究中,选取了副溶血弧菌和WSSV两种病原对三疣梭子蟹分别进行感染,在感染的过程中发现,伴随着感染时间的延长,三疣梭子蟹出现了行动迟缓、不进食等现象。定量结果表明,经副溶血弧菌感染后,PtToll4基因在血细胞中表达上调并不显著,而经WSSV感染后,PtToll4在血细胞中被显著诱导表达,其中,在6 h的表达量最高,约为对照组的5倍。而Arts等(2007)发现,经WSSV感染后,斑节对虾PmToll基因在组织中的表达量并无变化,这也说明TLRs家族不同成员可能具有受体识别特异性。由此,推断PtToll4基因作为模式识别受体可能参与了WSSV的特异识别。
已有研究表明,盐度的变化可以影响甲壳动物的免疫能力,如郑萍萍等(2010)发现,盐度的变化会造成三疣梭子蟹中免疫因子的活性发生变化;Joseph等(2007)发现,低盐胁迫会使斑节对虾更容易被WSSV感染。为了探究低盐环境对PtToll4基因表达的影响,本研究选择盐度为11的水体环境对三疣梭子蟹进行低盐胁迫。定量结果显示,整个低盐胁迫的过程中,PtToll4在血细胞中的表达量均为显著下降(P < 0.01),但在72 h出现了较为明显的回升,但仍显著低于对照组。在低盐状态下,推测三疣梭子蟹TLRs等免疫相关基因的表达可能也会受到抑制,从而影响识别外来病原的能力,使得自身免疫能力下降,导致死亡率增加。
综上所述,可以确定PtToll4基因是三疣梭子蟹TLRs基因家族中的一位新成员。PtToll4在三疣梭子蟹的各个组织中均能被检测到且在血细胞中的表达量最高。通过不同病原刺激后发现,PtToll4可被WSSV显著诱导表达,从而在宿主抵抗WSSV入侵感染的过程中发挥一定的功能。此外,低盐胁迫状态下,PtToll4基因的表达受到了显著抑制,可能间接影响了三疣梭子蟹的机体免疫能力,这或许是低盐环境导致三疣梭子蟹等甲壳动物死亡率升高的一个重要因素。PtToll4基因在抵御不同病原入侵时出现的表达量的差异还需要进一步的研究,这些结果为进一步探究三疣梭子蟹TLRs家族基因对其先天免疫的影响提供了数据支持。
| Aderem A, Ulevitch RJ. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature, 2000, 406(6797): 782-787 DOI:10.1038/35021228 | |
| Arts JA, Cornelissen FH, Cijsouw T, et al. Molecular cloning and expression of a Toll receptor in the giant tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2007, 23(3): 504-513 | |
| Assavalapsakul W, Panyim S. Molecular cloning and tissue distribution of the Toll receptor in the black tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon. Genetics & Molecular Research, 2012, 11(1): 484-493 | |
| Bell JK, Botos I, Hall PR, et al. The molecular structure of the Toll-like receptor 3 ligand-binding domain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 2005, 102(31): 181-200 | |
| Bilak H, Tauszig-Delamasure S, Imler JL. Toll and Toll-like receptors in Drosophila. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2003, 31(3): 648-651 DOI:10.1042/bst0310648 | |
| Carty M, Bowie AG. Recent insights into the role of Toll-like receptors in viral infection. Clinical & Experimental Immunology, 2010, 161(3): 397-406 | |
| Fu P, Lü JJ, Liu P, et al. Effects of different salinities on the free amino acids composition in the gill of Portunus trituberculatus. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2016, 37(5): 122-126 [付萍, 吕建建, 刘萍, 等. 盐度胁迫对三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)鳃中游离氨基酸含量的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2016, 37(5): 122-126] | |
| Gao BQ, Liu P, Li J. Analysis of the growth and breeding value of Portunus trituberculatus 'Huangxuan No.1'. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2015, 22(1): 44-50 [高保全, 刘萍, 李健. 三疣梭子蟹'黄选1号'生长和育种性能分析. 中国水产科学, 2015, 22(1): 44-50] | |
| Gay NJ, Gangloff M. Structure and function of Toll receptors and their ligands. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2006, 76(1): 141-165 | |
| Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, et al. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature, 2000, 408(6813): 740-745 DOI:10.1038/35047123 | |
| Hoffmann JA, Kafatos FC, Janeway Jr CA, Ezekowitz RAB. Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science, 1997(284): 1313-1318 | |
| Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nature Immunology, 2004, 5(10): 987-995 DOI:10.1038/ni1112 | |
| Johnson GB, Brunn GJ. Evolutionary clues to the function of the toll-like family as surveillance receptors. Trends in Immunology, 2003, 24(l): 18-24 | |
| Joseph A, Philip R. Acute salinity stress alters the haemolymph metabolic profile of Penaeus monodon and reduces immunocompetence to white spot syndrome virus infection. Aquaculture, 2007, 272(1-4): 87-97 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.08.047 | |
| Lan JF, Zhao LJ, Wei S, et al. PcToll2 positively regulates the expression of antimicrobial peptides by promoting PcATF4 translocation into the nucleus. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2016, 58: 59-66 | |
| Leulier F, Lemaitre B. Toll-like receptors: Taking an evolutionary approach. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2008, 9(3): 165-178 DOI:10.1038/nrg2303 | |
| Liu Y, Shi G, Cui Z, et al. PtSerpin from the swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus, a putative regulator of prophenoloxidase activation with antibacterial activity. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2014, 39(2): 365-371 | |
| Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408 DOI:10.1006/meth.2001.1262 | |
| Ng A, Xavier RJ. Leucine-rich repeat (LRR) proteins: Integrators of pattern recognition and signaling in immunity. Autophagy, 2011, 7(9): 1082-1084 DOI:10.4161/auto.7.9.16464 | |
| Nusslein-Volhard C, Lohs-Schardin M, Sander K, et al. A droso-ventral shift of embryonic primordial in a new maternal-effect mutant of Drosophila. Nature, 1980(283): 474-476 | |
| Ramos HC, Rumbo M, Sirard JC. Bacterial flagellins: Mediators of pathogenicity and host immune responses in mucosa. Trends in Microbiology, 2004, 12(11): 509-517 DOI:10.1016/j.tim.2004.09.002 | |
| Schneider DS, Hudson KL, Lin TY, et al. Dominant and recessive mutations define functional domains of Toll, a transmembrane protein required for dorsal-ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Genes & Development, 1991, 5(5): 797-807 | |
| Srisuk C, Longyant S, Senapin S, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a Toll receptor gene from Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2014, 36(2): 552-562 | |
| Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, et al. Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial cell wall components. Immunity, 1999, 11(4): 443-451 DOI:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80119-3 | |
| Uematsu S, Akira S. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and their ligands. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, 2008, 183(183): 1-20 | |
| Wang L, Pan LQ. A study on penetration physiological adaptation of P. trituberculatus under low salinity. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2016(3): 106-112 [王林, 潘鲁青. 三疣梭子蟹在低盐胁迫下渗透生理适应性的研究. 海洋湖沼通报, 2016(3): 106-112] | |
| Wang ZF, Wang ZZ, Xu WJ, et al. Quantitative study of lethal effect of WSSV on Portunus trituberculatus from mix-culture ponds of prawns and crabs. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2008, 39(2): 184-189 [王忠发, 王志铮, 许文军, 等. 虾蟹混养塘中WSSV对三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)致死效应的定量研究. 海洋与湖沼, 2008, 39(2): 184-189] | |
| Xue JZ, Du NS, Lai W, et al. A review of studies on Portunus trituberculatus in China. Donghai Marine Science, 1997, 15(4): 60-65 [薛俊增, 堵南山, 赖伟, 等. 中国三疣梭子蟹Portunus trituberculatus Miers的研究. 东海海洋, 1997, 15(4): 60-65] | |
| Yan BL, Qing GM, Bao ZH, et al. Isolation and identification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus from diseased Portunus trituberculatus L. Marine Science Bulletin, 2010, 29(5): 560-566 [阎斌伦, 秦国民, 暴增海, 等. 三疣梭子蟹病原副溶血弧菌的分离与鉴定. 海洋通报, 2010, 29(5): 560-566] | |
| Yang LS, Yin ZX, Liao JX, et al. A Toll receptor in shrimp. Molecular Immunology, 2007, 44(8): 1999-2008 DOI:10.1016/j.molimm.2006.09.021 | |
| Yao CL, Wang ZY, Xiang JH. Crustacean haemocytes and their function in immune responses. Zoological Research, 2006, 27(5): 549-557 [姚翠鸾, 王志勇, 相建海. 甲壳动物血细胞及其在免疫防御中的功能. 动物学研究, 2006, 27(5): 549-557] | |
| Yu AQ, Jin XK, Guo XN, et al. Two novel Toll genes (EsToll1 and EsToll2) from Eriocheir sinensis are differentially induced by lipopolysaccharide, peptidoglycan and zymosan. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2013, 35(4): 1282-1292 | |
| Zhang L, Li L, Zhang G. A Crassostrea gigas Toll-like receptor and comparative analysis of TLR pathway in invertebrates. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2011, 30(2): 653-660 | |
| Zheng PP, Wang CL, Song WW, et al. Effect of salinity stress on serum nonspecific immune factors in swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Fisheries Science, 2010, 29(11): 634-638 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2010.11.002 [郑萍萍, 王春琳, 宋微微, 等. 盐度胁迫对三疣梭子蟹血清非特异性免疫因子的影响. 水产科学, 2010, 29(11): 634-638] | |
| Zhou SM, Yuan XM, Liu S, et al. Three novel Toll genes (PtToll1-3) identified from a marine crab, Portunus trituberculatus: Different tissue expression and response to pathogens. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 46(2): 737-744 |



