禾花鱼泛指在华南地区稻田养殖的温水性鲤鱼(Cyprinus carpio),因为鱼食禾花后,鱼肉具有禾花香味而得名。稻田养殖鲤鱼这种稻鱼共生的农业生产模式在我国具有悠久的历史和文化传承,稻渔产业化水产养殖是具有稳粮、促渔、增收、提质、环境友好、发展可持续等多种生态系统功能的稻、渔结合的种养模式(马达文等, 2016; Xie et al, 2011)。稻田养鱼模式在保护环境和保证水稻增产的同时,增加了水产养殖的产量,是目前水产养殖的研究热点之一(Hu et al, 2013)。广东地区的禾花鱼养殖业已成为发展农村经济的一条重要途径,但对目前广东地区禾花鱼的形态学研究和种质调查才刚刚起步。根据广东省乳源瑶族自治县养殖户反映,当地的禾花鱼养殖品种形态变异大,品种混杂,其中的‘石鲤’体型为典型的团圆体型,而‘柴鲤’为典型的长体型。分析其原因,一方面可能是经过长期的养殖驯化过程,不同地区的鲤鱼因受到不同的自然环境的选择和人工选择,在遗传和形态上已发生了不同方向的分化(Xu et al, 2014)。另一方面,可能是因为不同鲤鱼种内(刘淑琴等, 1990)和种间(谢洪民, 1985)的杂交,导致鲤鱼养殖品种非常混杂,形态各异。
在自然界中,生物体的形态特征是生物体的遗传结构与生活环境长期相互作用的结果,是物种多样性最直观的表现形式(Endler, 1986; 顾志敏等, 2008)。而在农业生产中的生物种群会在自然环境和人工选择压力下形成明显不同于自然生态系统的种群或者类群(Hall, 2004; Clutton-Brock, 1999)。无论是在自然生态系统中,还是农业生产系统中,鱼类形态特征的变化与生理机能和生活习性的变化相比,更为具体、易于比较观察,是鱼类分类学的重要依据(曹文宣等, 1981)。鱼类形态特征中的可数可量性状不仅是鱼类分类的依据,也是鱼类人工选择育种时的基本选择指标,即优良品种选择时的重要依据(闫学春等, 2007)。所以,对鱼类形态学的研究是经济鱼类研究的基础。
以世代生活在广东地区的稻鱼养殖系统中的禾花鱼为研究对象,将传统的形态学研究方法与几何形态学研究方法相结合,分析具有代表性的稻田养殖禾花鱼的形态学特征,并与其他鲤鱼品系的形态学分析数据进行比较。同时,通过对禾花鱼线粒体COⅡ基因序列的扩增与分析,确定广东粤北地区稻田养殖禾花鱼在遗传学上的分类地位。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验鱼实验用禾花鱼取自广东省韶关乳源瑶族自治县的稻田养鱼基地,为当年的禾花鱼鱼苗,在鱼苗长至平均全长约为5 cm时放入稻田中进行养殖,养殖期为5个月,期间不投喂人工配合饲料,仅以稻田中的杂草、田螺和昆虫等天然饵料为食。
1.2 形态观察与测量从稻田里随机取67尾体重在10 g以上的禾花鱼,用麻醉剂麻醉后,快速测量体宽WB (Body width),并用相机拍照,将照片导入本研究室自主研制开发的鱼类外部形态测量软件1.0,测量每尾鱼的全长LT (Total length)、体长LS (Soma length)、体高DB(Body depth)、头长LH (Head length)、头高HH (Head height)、吻长LM (Snout length)、眼径DE (Eye diameter)、尾柄长LCP (Length of caudal peduncle)、尾柄高DCP (Depth of caudal peduncle)和尾鳍长LC (Caudal fin length)共11个生长性状。同时,取鳍条放入无水乙醇中,-20℃保存备用。
1.3 数量性状分析和统计在对上述测量的生长性状进行统计时,为消除由于鱼的体型大小不同而引起的对数据可靠性的影响,分析时用头部形态测量值除以头长,尾部形态测量值除以尾柄高,分别计算头高/头长(HH/LH)、吻长/头长(LM/LH)、眼径/头长(DE/LH)、尾柄高/尾柄长(DCP/LCP)、尾鳍长/尾柄长(LC/LCP),其他的形态测量值除以体长,如全长/体长(LT/LS)、头长/体长(LH/LS)、体高/体长(DB/LS)、体宽/体长(WB/LS)、尾柄长/体长(LCP/LS)。
采用Microsoft Excel软件分析禾花鱼的形态测量数据及其比值,然后使用SPSS 11.0对10个比值进行单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)、主成分分析和聚类判别分析(张文彤, 2002)。
1.4 禾花鱼与其他6种鲤鱼形态学比较分析按照郭梁等(2017)的方法从CNKI数据库(http://www.cnki.net)中查找鲤属(Cyprinus)鱼类的生长性状测量值,用取平均值的方法将不同文献所报道的同种鱼的相同部位形态测量数据进行合并,去掉测量部位数据少的品种,得到黄河鲤(Cyprinus carpio)、荷包红鲤(C. carpio var. wuyuannensis)、兴国红鲤(C. carpio var. Xingguonensis)、建鲤(C. carpio var. Jian)、镜鲤(C. carpio var. specularis)和瓯江彩鲤(C. carpio var. color) 6种鲤鱼的7个生长形态性状比值:全长/体长(LT/LS)、体高/体长(DB/LS)、体宽/体长(WB/LS)、尾柄高/尾柄长(DCP/LCP)、头长/体长(LH/LS)、头高/头长(HH/LH)和眼径/头长(DE/LH)(表 1)。统计分析方法参照1.3。
|
|
表 1 6种鲤鱼的7个形态性状比值平均值 Tab.1 The mean values of seven morphological characteristics from six common carp populations |
根据鲤的线粒体上的细胞色素氧化酶亚基Ⅱ (Cytochrome oxidase subunit Ⅱ, COⅡ)基因序列(序列号: JN105352.1)设计引物,引物序列为:COⅡ F:5' -TAATGGCACACCCAACGCAAC-3',COⅡ R:5'-AGCTTCCTAGCGAGGCGTCTT-3',由金唯智生物科技公司合成(苏州)。禾花鱼鳍条基因组DNA的提取采用天根生化科技(北京)有限公司的“血液/细胞/组织基因组DNA提取试剂盒”,具体方法参考试剂盒说明书。用0.8%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA的完整性和纯度,-20℃保存备用。PCR扩增禾花鱼COⅡ基因,PCR产物在ABI 3500全自动测序仪上进行测序,测序结果用ClustalW软件进行比较分析。统计38尾禾花鱼COⅡ基因序列,将数目最多的TA基因型COⅡ基因序列与鲤科(Cyprinidae)鲤属鲤种的5个群体(建鲤COⅡ基因序列未见报道),如黄河鲤(KU050703.1)、兴国红鲤(KU146530.1)、镜鲤(KU146531.1)、荷包红鲤(KF856964.1)和瓯江彩鲤(KP993136.1)及鲤科鲤属的三角鲤(Cyprinus multitaeniata) (KU373073.1)和鲤科Danio属的斑马鱼(Danio rerio) (KM244705.1) COⅡ基因序列进行比对,再用Mega 7.0软件,采用最大似然法构建进化树,并用Bootstrap法进行检验,参数设置为999次。
2 结果与分析 2.1 稻田养殖禾花鱼的形态观察与数据测量目前,广东地区典型的稻田养殖禾花鱼体型从长而侧扁到团而体厚的均可见。鱼体颜色各异,有些个体鱼体背部为青灰色,有些个体鱼通体为金红色,有些个体鱼体背部为浅灰色,鳍为浅灰色略带红色或鳍为黄色桔黄至浅黄色。随机取67尾禾花鱼进行测量,体重范围为10~44 g,变化范围较大。计算其测量数据的平均值及方差(表 2)。
|
|
表 2 禾花鱼的形态测量平均值及其标准差 Tab.2 The mean value and standard deviation of the morphological traits of rice flower carp |
根据67尾禾花鱼的头高/头长(HH/LH)、吻长/头长(LM/LH)、眼径/头长(DE/LH)、尾柄高/尾柄长(DCP/LCP)、尾鳍长/尾柄长(LC/LCP)、全长/体长(LT/LS)、头长/体长(LH/LS)、体高/体长(DB/LS)、体宽/体长(WB/LS)和尾柄长/体长(LCP/LS)10个形态学比例指标,用SPSS 11.0软件进行聚类分析表明,67尾鲤鱼可以分为体型偏向修长型和偏向团圆型两大类。
2.3 稻田养殖禾花鱼形态的主成分分析对同一稻田养殖环境的67尾禾花鱼的10个形态学比例指标进行主成分分析,得到3个主成分,累积贡献率为73.5%,基本可以反映综合指标所概括的信息,每个比例性状在各主成分的载荷量见表 3。第1主成分中起最主要作用的是尾柄高/尾柄长和尾鳍长/尾柄长,可以解释为鱼体的尾部特征;第2主成分中起主要作用的是头高/头长、吻长/头长和眼径/头长,可以解释为鱼体的头部特征;第3主成分中起主要作用的是头高/头长和体高/体长,也可以解释为鱼体的总体特征。
|
|
表 3 禾花鱼10个形态特征变量的主成分载荷 Tab.3 Loading of principal components (PC) for 10 morphometric characteristics of rice flower carp |
将上述聚类分析得到的体型偏向修长型和偏向团圆型2组鱼每个个体的主成分值绘制散点图(图 2),在第1主成分上,2组体型不同的禾花鱼区分明显,在尾柄高/尾柄长、尾鳍长/尾柄长和体高/体长这3个比值中,偏长体型组鱼的平均值分别为0.78、1.57和0.37,偏团圆体型组鱼的平均值为1.07、2.08和0.44,均呈极显著差异(P < 0.01);在第2主成分上,2组体型不同的禾花鱼部分重合,区分不明显,在头高/头长、吻长/头长和眼径/头长3个比值中,偏长体型组鱼的平均值分别为0.85、0.27和0.25,偏团圆体型组鱼的平均值为0.86、0.31和0.23,除吻长/头长值有显著差异(P < 0.05)外,头高/头长和和眼径/头长值无显著差异(P > 0.05);在第3主成分上,2组体型不同的禾花鱼完全重合,头高/头长在2组禾花鱼中无显著差异。
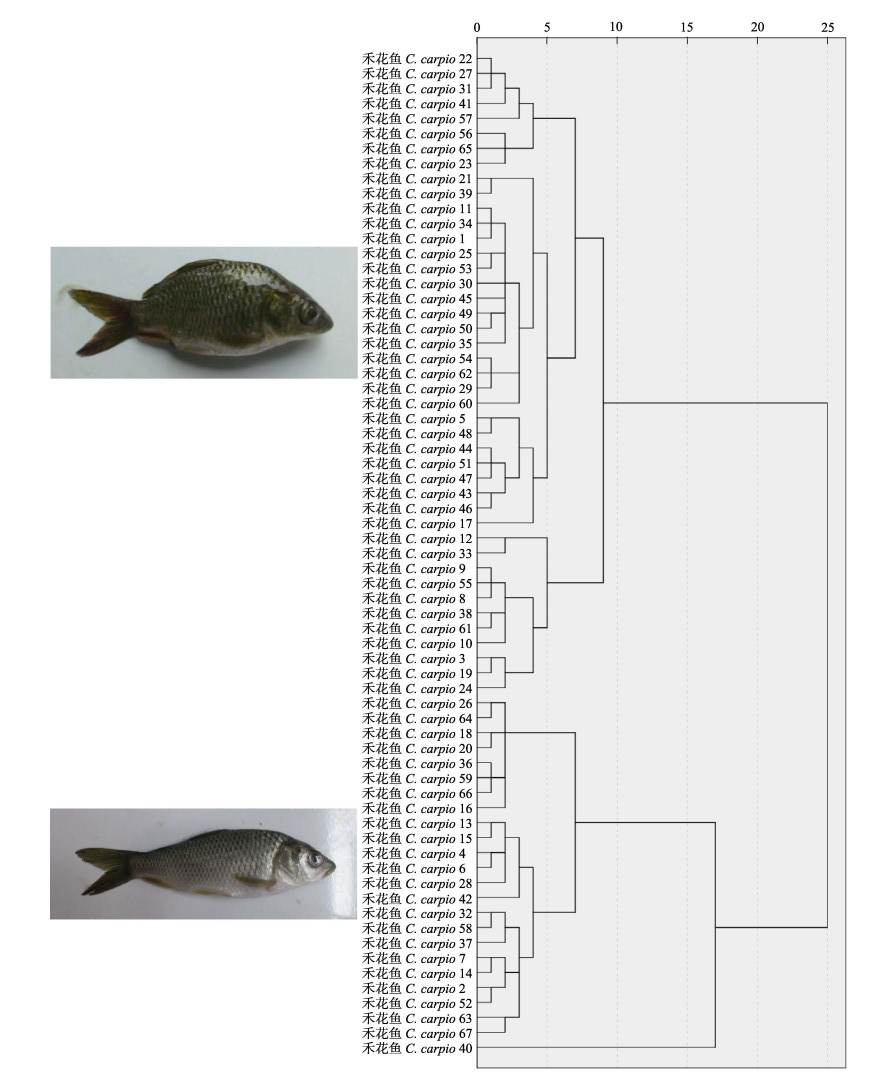
|
图 1 同一禾花鱼群体内不同个体的形态聚类关系 Fig.1 Cluster analysis of the common carp individuals cultured in paddy field according to morphological characteristics |
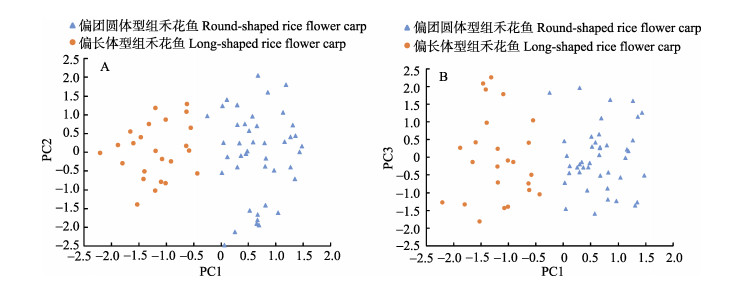
|
图 2 禾花鱼依据形态特征数据分组后的主成分分析散点图 Fig.2 Scatter diagram for the principal component analysis of the rice flower carps grouped according to morphological characteristics |
用可以查询到的6种鲤鱼的7个生长性状比值,与偏长体型和偏团圆体型2组禾花鱼各自相对应的生长性状比值的平均值进行主成分分析,结果见表 4。得到2个主成分,其累积贡献率为82.7%,主成分分析结果基本可反映综合指标所隐含的信息,第1主成分中起主要作用的是体高/体长和尾柄高/尾柄长,以及头长/体长、体宽/体长和全长/体长,可解释为鱼体的总体体型特征;第2主成分中起主要作用的是头高/头长,可解释为鱼体的头部特征。
|
|
表 4 2种体型禾花鱼与其他6种鲤鱼7个形态特征变量的主成分载荷 Tab.4 Loading of principal components (PC) for 7 morphometric characteristics of rice flower carp and other six common carp populations |
从依据第1主成分和第2主成分绘制的散点图(图 3)可以看出,无论是长体型禾花鱼还是团圆体型禾花鱼的主成分值均介于兴国红鲤和荷包红鲤之间,且在第1主成分上,长体型禾花鱼与兴国红鲤、镜鲤和建鲤聚在一起,而与和瓯江彩鲤和荷包红鲤聚在一起的团圆体型禾花鱼区分开;在第2主成分上,长体型禾花鱼与团圆体型禾花鱼聚在一起,再与荷包红鲤、兴国红鲤、建鲤和黄河鲤聚在一起,而与镜鲤和欧江彩鲤区分开。

|
图 3 2种体型禾花鱼与其他6种鲤鱼7个生长性状比值的第1主成分、第2主成分散点图 Fig.3 Scatter plot of PC1 versus PC2 extracted from 7 morphometric characteristics of rice flower carp with two shapes and another six common carp populations |
将2.1中聚类分析得到的偏长体型组鱼和偏团圆体型组鱼生长性状比值的平均值与6种其他鲤鱼的生长性状比值进行聚类分析,结果表明,偏长体型禾花鱼与兴国红鲤聚合在一起,再与镜鲤聚合在一起,再与黄河鲤、建鲤聚为一支,荷包红鲤与瓯江彩鲤聚为另一支,偏团圆体型的禾花鱼介于两支之间(图 4)。
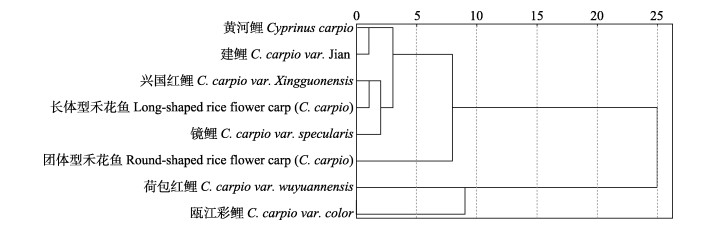
|
图 4 2种体型的禾花鱼与其他6种鲤鱼的形态学聚类分析 Fig.4 Dendrogram of rice flower carps with two shapes and another six common carp populations by cluster analysis |
对测序得到的38尾禾花鱼的COⅡ基因(606 bp,图 5)进行比较,结果表明,仅有2个多态位点,一个位于+31,为颠换位点A-T(4:34),另一个位于+597,为转换位点A-G(28:10),共4种基因型(AA:AG:TG:TA=3:1:9:25),其中,TA基因型个体数目最多,占总数的65.8%,而多态位点数仅占序列长度的0.33%。经分析,这4种基因型与体型特征之间没有对应关系,不能区分长体型禾花鱼和团圆体型禾花鱼。

|
图 5 禾花鱼的COⅡ基因部分序列 Fig.5 The partial sequence of COⅡ gene from rice flower carp 加粗字表示多态位点 Bold shows the polymorphic sites |
用TA基因型禾花鱼COⅡ部分基因序列与7种已知的鲤科鱼类COⅡ基因序列进行比对,结果表明,禾花鱼与鲤科鲤属的5种鱼COⅡ基因同源性均在99%以上,与斑马鱼COⅡ基因的同源性仅为79%。从构建的进化树可以看出(图 6),禾花鱼与荷包红鲤的COⅡ基因同源性最高,其次为兴国红鲤,而斑马鱼COⅡ基因是聚类分析的外群,可以确定禾花鱼为鲤属鲤种的一个群体。

|
图 6 禾花鱼和7种鲤科鱼的COⅡ基因进化树分析 Fig.6 Phylogenetic tree of COⅡ genes from rice flower carp and seven carp populations within Cyprinidae |
广东粤北地区养殖户反映目前禾花鱼养殖品种形态变异大,其中,团圆体型的“石鲤”在稻田养殖过程中不易逃走,而且肉厚、骨软、成活率高,而长体型的“柴鲤”易逃走,且肉少、骨硬、成活率低。为了进一步对该禾花鱼养殖品种进行选育,本研究用形态学统计聚类分析的描述方法,将禾花鱼依据形态分为体型偏团圆型和偏修长型两大类,并揭示了两类禾花鱼的形态差异主要表现在尾柄高/尾柄长、尾鳍长/尾柄长和体高/体长这3个比例性状上。而这3个比例性状,特别是“体高/体长和尾柄高/尾柄长”,是鲤鱼选育的重要考量指标,如对荷元鲤的选育研究表明,荷元鲤的体长/体高为2.35~2.55之间,可获得单位体长的最好增重效果(Ma et al, 1981; 张建森, 1985)。对广东地区传统稻田养殖禾花鱼生长形态学的统计、描述和分类,可为禾花鱼的下一步选育工作奠定形态学研究基础。
禾花鱼在养殖过程中没有投喂人工饵料,所以,生长较为缓慢,在形态数据测定时,其个体体重仅在10~44 g范围内,而与其相比较的其他种类的鲤鱼规格在100 g以上(郑水平等, 1998; 明俊超等, 2009),有些甚至达到2 kg(郭梁等, 2017)。有研究表明,不同生长阶段、雌雄差异、饲料和养殖环境等都会对鱼类的形态特征产生影响(王兰梅等, 2017; 岳亮等, 2016; 沈伟良等, 2017)。但从本研究对禾花鱼的形态数据聚类分析结果可以看出,兴国红鲤、荷包红鲤、镜鲤、黄河鲤和建鲤的聚合分析结果与之前的鲤鱼形态聚类结果相吻合(明俊超等, 2009; 郭梁等, 2017)。长体型禾花鱼与兴国红鲤、镜鲤、黄河鲤、建鲤聚合在一起,而荷包红鲤与瓯江彩鲤聚在一起,偏团圆体型的禾花鱼的形态性状处于长体型鲤与团圆体型鲤的中间类型。分析结果与观察得到的结果相似,说明禾花鱼1龄前已显示出初步的形态特征,与其他鲤鱼品种进行形态比较结果较为准确,可为其他规格差异较大种群形态学比较研究提供参考依据。另外,从目前的研究结果可以看出,粤北地区的偏团圆体型的禾花鱼形态与荷元鲤的形态相似,但对荷元鲤的形态学研究数据不足,限制了禾花鱼与其进行比较(Ma et al, 1981; 张建森, 1985)。此外,对另2种稻田养殖鲤鱼——“青田稻田鱼”和“从江稻田鱼”的形态学聚类分析发现,这2种田鱼在形态上已明显区别于兴国红鲤、黄河鲤和建鲤等8种鲤鱼种群(郭梁等, 2017)。而本研究中的稻田养殖禾花鱼形态学聚类分析表明,禾花鱼的形态仍具有明显的鲤鱼特征,虽然已经过多年的传统稻田养殖,但还不能从形态上将其从鲤鱼群体中区分出来。从上述比较结果还可以看出,目前,广东地区禾花鱼品种较为混杂,需要以形态学为基础,进一步建立家系进行选育。
稻田养殖鲤鱼在不同地区的品种有所不同,包括很多个地方种,如广东地区主要养殖的禾花鱼为华南鲤(Cyprinus carpio rubrofuscus),广西地区主要养殖的禾花鱼为乌鲤(Procypris merus)等。COⅡ基因作为鲤鱼品种的遗传标记已有大量的报道,包括25种鲤科鱼类(凌去非等, 2006)、中国红鲤(Cyprinus flammans)(王成辉等, 2004)、瓯江彩鲤(吕耀平等, 2009)及锦鲤(Cyprinus carpio)、瓯江彩鲤和长鳍鲤(Cyprinocirrhites polyactis)之间的亲缘关系(Wang et al, 2004)。在上述研究的基础上,本研究对禾花鱼的COⅡ基因序列进行了分析,确定了禾花鱼为鲤科、鲤属、鲤种的一个群体。在研究5种体色20尾瓯江彩鲤COⅡ基因(604 bp)中发现,多态位点百分率为1.49%,而本研究38尾禾花鱼的COⅡ基因(606 bp)多态位点仅占0.33%,远低于鲤鱼种间3.79%的水平(吕耀平等, 2009)。虽然禾花鱼体型差异较大,但根据COⅡ基因多样性的判别,远没有达到种间的水平。
本研究对粤北地区典型稻田养殖基地的禾花鱼进行了形态学分析和初步的遗传学分析,用科学的方法阐释了生产实践观察到的禾花鱼形态多样性丰富的现象,根据测量数据对2种体型的禾花鱼进行了分类,并用分子手段确定了地方养殖品种的分类地位,为禾花鱼接下来的育种工作奠定了基础。
Cao WX, Chen YY, Wu YF, et al. The origin and evolution of Schizothorax chongi and the relationship with the uplift of the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Beijing: Science Press, 1981: 118-130 [ 曹文宣, 陈宜瑜, 武云飞, 等. 裂腹鱼类的起源和演化及其与青藏高原隆起的关系. 北京: 科学出版社, 1981: 118-130]
|
Chen DY, Li D. Comparative study on genetic characters of distant hybridization crucian (Carassiu sauratus cuvieri ♀× Cyprinus carpio var. singuonensis♂) and its parents. Biotechnology, 2008, 18(3): 24-26 [ 陈道印, 李达. 远缘鲫(白鲫♀×兴国红鲤♂)与其亲本若干遗传性状比较. 生物技术, 2008, 18(3): 24-26] |
Clutton-Brock J. A natural history of domesticated mammals. 2nd Ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1999
|
Endler JA. Natural selection in the wild. Princeton. New Jersey: Princeton University Press, 1986
|
Gu ZM, Jia YY, Ye JY, et al. Studies on morphological characteristics and genetic analysis of the hybrid F1, Erythroculter ilishaeformis♂×Megalobrama amblycephala♀. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2008, 32(4): 533-544 [ 顾志敏, 贾永义, 叶金云, 等. 翘嘴红鲌(♀)×团头鲂(♂)杂种F1的形态特征及遗传分析. 水产学报, 2008, 32(4): 533-544] |
Guo L, Ren WZ, Hu LL, et al. Morphological traits of indigenous field carps maintained in traditional rice-based farming systems. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(2): 665-672 [ 郭梁, 任伟征, 胡亮亮, 等. 传统稻鱼系统中"田鲤鱼"的形态特征. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(2): 665-672] |
Hall SJG. Livestock Biodiversity: Genetic resources for the farming of the future. Oxford: Blackwell, 2004
|
Hu LL, Ren WZ, Tang JJ, et al. The productivity traditional rice-fish co-culture can be increased without increasing nitrogen loss to the environment. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2013, 177: 28–34 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167880913001849
|
Li CT, Ge YL, Hu XS, et al. Germplasm analysis of scattered mirror carp found in areas of Heilongjiang Province and Changjiang River Basin. Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 2016, 29(1): 24-28 [ 李池陶, 葛彦龙, 胡雪松, 等. 黑龙江和长江散鳞镜鲤群体的种质差异分析. 水产学杂志, 2016, 29(1): 24-28 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-3832.2016.01.005] |
Li CT, Zhang YY, Jia ZY, et al. Comparative studies on measurable characters and the number of scales in Songpu mirror carp and German mirror carp selection strain F4. Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 2009, 22(2): 53-55 [ 李池陶, 张玉勇, 贾智英, 等. 松浦镜鲤与德国镜鲤选育系(F4)的可量性状、鳞片数比较. 水产学杂志, 2009, 22(2): 53-55 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-3832.2009.02.012] |
Lin MX, Wang J, Wang J, et al. Applicability of molecular population genetics methods in analyzing common carp morphological data. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2015, 39(6): 769-778 [ 林明雪, 王剑, 王军, 等. 分子群体遗传学方法处理鲤形态学数据的适用性. 水产学报, 2015, 39(6): 769-778] |
Ling QF, Li SF. Mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase unit Ⅱ gene variability and phylogenetic relationships among 25 species of Cyprinidae. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2006, 30(6): 747-752 [ 凌去非, 李思发. 鲤科25种鱼类线粒体COⅡ基因序列差异及其系统进化关系. 水产学报, 2006, 30(6): 747-752] |
Liu MH, Shen JB, Wang Q, et al. Genetic and economic characters of Songpu mirror carp [(Scattered carp×Germany carp)F1]. Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 1993, 6(1): 19-25 [ 刘明华, 沈俊宝, 王强, 等. 松浦镜鲤[(散鳞镜鲤×德国镜鲤)F1]主要经济性状及遗传特性. 水产学杂志, 1993, 6(1): 19-25] |
Liu SQ, Wen XR, Xia DM. The test reports of tri-hybrids of [(Cyprinus carpio mirror carp♀×Cyprinus carpio wuyuanensis ♂) ♀×Cyprinus carpio Germany mirror carp ♂]. Fisheries Science, 1990(4): 6-12 [ 刘淑琴, 闻秀荣, 夏大明. 三杂交鲤[(镜鲤♀×荷包红鲤♂)♀×德国镜鲤♂]试验报告. 水产科学, 1990(4): 6-12] |
Liu XM, Shi Y. Effects of morphological traits on body weight of F1 generation of common carp in the Yellow River. Fisheries Science & Technology Information, 2015, 42(6): 324-327 [ 刘晓敏, 石英. 黄河鲤F1代形态性状对体质量的影响. 水产科技情报, 2015, 42(6): 324-327] |
Liu Y, Chen SQ, Wang YX, et al. The study on the hybrids of Cyprinus carpio wuyuanensis♂×Xiangjiang wild carp♀ and the application of F1 hybrids in production. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 1979, 2(2): 1-14 [ 刘筠, 陈淑群, 王义铣, 等. 荷包红鲤♂×湘江野鲤杂交一代的研究及其在生产上的应用. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 1979, 2(2): 1-14] |
Liu ZG, Cai WQ, Wang CH. The preliminary study on the morphological characteristics and growth of Cyprinus carpio var. color Japanese Koi and their reciprocal hybrids of F1 generation. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2003, 12(4): 289-292 [ 刘志国, 蔡完其, 王成辉. 瓯江彩鲤与日本锦鲤及其正反杂交F1形态特征和生长初步研究. 上海水产大学学报, 2003, 12(4): 289-292] |
Lü X. The study on the morphological characteristics and main traits of Cyprinus carpio wuyuanensis (♂), mirror carp(♀) and their F1 hybrids. Fisheries Science, 1983, 2(3): 1-5 [ 吕迅. 荷包红鲤(♂)、镜鲤(♀)及其杂种一代的形态特点和主要性状分析. 水产科学, 1983, 2(3): 1-5] |
Lü YP, Hu ZH, Xiao JZ, et al. Intraspecific DNA sequence polymorphism and genetic markers in the mitochondrial COⅡ gene from five color patterns of Oujiang color carp. Journal of Zhejiang University (Sciences Edition), 2009, 36(3): 323-327 [ 吕耀平, 胡则辉, 肖建中, 等. 5种体色瓯江彩鲤线粒体COⅡ基因的序列差异和遗传标记研究. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 2009, 36(3): 323-327 DOI:10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2009.03.018] |
Lü YP, Lin ZH, Lei YZ. Sexual dimorphism in morphological traits and female individual fecundity of Oujiang color common carp, Cyprinus carpio var. color. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2008, 27(2): 284-288 [ 吕耀平, 林植华, 雷焕宗, 等. 瓯江彩鲤形态特征的两性异形和雌性个体生育力. 华中农业大学学报, 2008, 27(2): 284-288 DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-2421.2008.02.025] |
Ma DW, Qian J, Liu JS, et al. Development strategy for integrated rice field aquaculture. Engineering Sciences, 2016(3): 96-100 [ 马达文, 钱静, 刘家寿, 等. 稻渔综合种养及其发展建议. 中国工程科学, 2016(3): 96-100 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2016.03.017] |
Ma ZB, Zhang XZ, Qiu QR, et al. The analysis of the economical characteristics of a hybrid from two ecological types of carps. Journal of Fisheries of China, 1981, 5(3): 187-198 [ 马仲波, 张兴忠, 仇潜如, 等. 元江鲤与荷包红鲤的生态类型及其杂交后代(荷元鲤)经济性状的分析. 水产学报, 1981, 5(3): 187-198] |
Ming JC, Dong ZJ, Liang ZY, et al. Analysis of morphological variation in six common carp (Cyprinus carpio) populations. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2009, 29(6): 1-6 [ 明俊超, 董在杰, 梁政远, 等. 6个不同鲤群体的形态差异分析. 广东海洋大学学报, 2009, 29(6): 1-6 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2009.06.001] |
Shen WL, Wu XF, Shentu JK, et al. The effects of different diets and culture environments on the morphological variations in the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2017, 38(6): 70-77 [ 沈伟良, 吴雄飞, 申屠基康, 等. 不同饵料及养殖环境对大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea)形态差异的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2017, 38(6): 70-77] |
Wang CH, Li SF. Genetic variability and relationships in mitochondrial DNA COⅡ gene sequence of red common carps in China. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2004, 31(11): 1226-1231 [ 王成辉, 李思发. 中国红鲤线粒体COⅡ基因的遗传变异和亲缘关系. 遗传学报, 2004, 31(11): 1226-1231] |
Wang CH, Li SF. Phylogenetic relationship of ornamental (Koi) carp, Oujiang color carp and long fin carp revealed by mitochondrial DNA COⅡ gene sequences and RAPD analysis. Aquaculture, 2004, 131: 83-91 |
Wang LM, Zhu WB, Dong ZJ, et al. Differential analysis on growth of FFRC strain common carp (Cyprinus carpio) selection families at various culture stages. South China Fisheries Science, 2017, 13(1): 43-49 [ 王兰梅, 朱文彬, 董在杰, 等. 福瑞鲤选育家系不同养殖阶段的生长差异分析. 南方水产科学, 2017, 13(1): 43-49 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2017.01.006] |
Xie HM. The value of hybrids of Carassius auratus glibelio and Cyprinus carpio in fishery. Freshwater Fisheries, 1985(6): 41-42 [ 谢洪民. 银鲫与鲤鱼杂交种的渔业价值. 淡水渔业, 1985(6): 41-42] |
Xie J, Hu LL, Tang JJ, et al. Ecological mechanisms underlying the sustainability of the agricultural heritage rice-fish co-culture system. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108: 1381-1387 DOI:10.1073/pnas.1111043108 |
Xu P, Zhang XF, Wang XM, et al. Genome sequence and genetic diversity of the common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Nature Genetics, 2014, 46: 1212-1219 DOI:10.1038/ng.3098 |
Yan XC, Liang LQ, Cao DC, et al. Comparison of the morphological characteristics between two types of backcross progenies from the common and crucian carp. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2007, 38(6): 797-800 [ 闫学春, 梁利群, 曹顶臣, 等. 鲤鲫杂交两种回交子代鱼的形态特征比较. 东北农业大学学报, 2007, 38(6): 797-800 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2007.06.019] |
Yangtze River Fisheries Research Institute. Cyprinus carpio wuyuanensis♀ and Cyprinus carpio yuankiang♂ cross breeding and its application in production. Freshwater Fisheries, 1976(7): 17-19 [ 长江水产研究所. 红荷包鯉♀与元江鲤♂的杂交育种及其生产应用. 淡水渔业, 1976(7): 17-19] |
Yu CR, Li YH, Zheng GL, et al. Comparison of morphological characteristics and flesh rate of several common carp varieties and hybrids in our province. Fisheries Science, 1995, 14(4): 13-14 [ 于春然, 李越红, 郑亘林, 等. 我省几种鲤品种和杂交种形态特征和含肉率的比较. 水产科学, 1995, 14(4): 13-14] |
Yue L, Wang XA, Ma AJ, et al. Comparison of the morphological traits between male and female individuals of Takifugu rubripes. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2016, 37(1): 30-35 [ 岳亮, 王新安, 马爱军, 等. 红鳍东方鲀(Takifugu rubripes)雌、雄个体的形态特征比较. 渔业科学进展, 2016, 37(1): 30-35] |
Zhang JS. Heyuan hybrid carp (Cyprinus carpio wuyuanensis ♀×Cyprinus carpio yuankiang♂) backcross experiment and its economic profits research. Fisheries Science & Technology Information, 1985a, 12(3): 17-19 [ 张建森. 荷元鲤(荷包红鲤♀×元江鲤♂)回交试验及其经济效益的研究. 水产科技情报, 1985a, 12(3): 17-19] |
Zhang JS. The reciprocal and backcross hybrids of Cyprinus carpio wuyuanensis × Cyprinus carpio yuankiang and the economic benefit analysis of F2. Journal of Fisheries of China, 1985b, 9(4): 375-382 [ 张建森. 荷包红鲤与元江鲤正反杂交、回交及F2经济效益的研究. 水产学报, 1985b, 9(4): 375-382] |
Zhang WT. SPSS 11 statistical analysis tutorial. Beijing: Beijing Hope Electronic Press, 2002: 27-31 [ 张文彤. SPSS11统计分析教程. 北京: 北京希望电子出版社, 2002: 27-31]
|
Zheng SP, Wang Q, Wang HL, et al. Comparison of the external morphological characteristics of the hybrids and their parents of the Yellow River carp. Journal of Hydroecology, 1998(5): 22-24 [ 郑水平, 王权, 王焕来, 等. 黄河鲤杂交一代与亲本外部形态特征比较. 水利渔业, 1998(5): 22-24] |
Zheng YG, Wu WX, Lin LA, et al. Furong carp and its parents [Scattered mirror carp (♀), Xingguo red carp (♂)] morphological test report. Current Fisheries, 1981(4): 7-13 [ 郑远刚, 吴维新, 林临安, 等. 芙蓉鲤及其亲本[散鳞镜鲤(♀)、兴国红鲤(♂)]形态特征测试报告. 内陆水产, 1981(4): 7-13] |
Zhu LY, Ma YQ, Xiang SP, et al. Observation and analysis of growth dynamics in Oujiang color common carp with different pigmentation types. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2013, 22(3): 341-348 [ 朱丽艳, 马玉清, 项松平, 等. 不同体色瓯江彩鲤生长动态的观察与分析. 上海海洋大学学报, 2013, 22(3): 341-348] |



