2. 中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所 农业农村部海洋渔业 可持续发展重点实验室 青岛 266071;
3. 青岛海洋科学与技术试点国家实验室海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程 功能实验室 青岛 266071;
4. 广西水产科学研究院 南宁 530021
2. Key Laboratory of Sustainable Development of Marine Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Qingdao 266071;
3. Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology Qingdao, Qingdao 266071;
4. Guangxi Academy of Fishery Science, Nanning 530021
副溶血弧菌(Vibrio parahaemolyticus)是一种常见的致病菌,能引起石斑鱼(Epinephelus spp.)、九孔鲍(Haliotis diversicolor supertexta)、大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea)等诸多水产养殖对象病变(Shyne et al, 2008; Cai et al, 2010;蔡林婷等, 2013)。近期发现副溶血弧菌也是引发凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei)重要疫病—急性肝胰腺坏死病(Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease, AHPND)的主要病原之一(Soto-Rodriguez et al, 2015; Kumar et al, 2018; Zheng et al, 2018;陈蒙蒙等, 2018;贾丹等, 2018)。随着绿色健康的水产养殖理念不断深入人心,中草药在水产病害防控中的运用受到广泛关注(Pu et al, 2017)。地榆(Sanguisorba officinalis)作为常用中草药之一,富含鞣质、皂苷等生物活性物质,具有抗炎(Yang et al, 2016)、抑菌(Lee et al, 2004)等作用。本研究团队前期研究表明,地榆对急性肝胰腺坏死病致病株副溶血弧菌(VPAHPND)有明显的抑制作用,且以地榆为主要成分的复方中草药在防控由副溶血弧菌引发的AHPND时效果显著(姜燕, 2016)。利用qRT-PCR技术探究不同浓度地榆醇提物作用下VPAHPND毒力因子的表达量及功能的变化,将有助于解析地榆对VPAHPND的作用机理,对以地榆为核心药物的AHPND防控技术的建立具有重要意义。
在研究基因差异表达过程中,需要选择稳定、高效的内参基因(Reference gene)对数据进行标准化处理(Vanguilder et al, 2008),以校正qRT-PCR技术运用过程中因mRNA质量、反转效率、进样量差异等因素导致的技术误差。Radonic等(2004)认为,理想的内参基因应在各种实验条件、各种组织细胞中均能稳定表达,并对传统内参基因的适用性提出质疑,并通过实验证明了人体各组织最适内参基因并非传统意义上的18S rRNA。Zhong等(1999)研究发现,癌细胞在正常和缺氧条件下gapdh和β-actin的表达水平差异显著。这些研究表明,内参基因稳定性在不同物种、不同组织以及不同环境条件下存在差异。因此,筛选适于评价地榆对VPAHPND基因差异表达的内参基因是对地榆抑菌机理深入探究的基础。
目前,常用的副溶血弧菌内参基因主要有rec A、pvs A、pvu A、16S rRNA、gapdh和rpo S (Ma et al, 2015; Coutard et al, 2007; Li et al, 2013;李沁, 2013)。本文以上述研究为基础,利用qRT-PCR技术检测了地榆醇提物作用下VPAHPND中这6种内参基因表达的稳定性,筛选出该条件下最稳定的内参基因,为后续地榆胁迫下VPAHPND相关基因表达研究提供基础数据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料地榆购自北京同仁堂药店。VPAHPND为对虾AHPND致病菌,分离自天津患AHPND凡纳滨对虾的肝胰腺组织,保存于本实验室-80℃超低温冰箱。
1.2 地榆醇提药物配制取5 g地榆粉于烧杯中,加入70%的乙醇溶液150 ml,超声提取50 min,置于真空抽滤机中进行抽滤,将滤液置于90℃恒温水浴锅中,浓缩药液至45 ml左右,再用蒸馏水定容至50 ml,即配制成浓度为100 mg/ml的地榆醇提药液,4℃储存待用。
1.3 引物验证以金属浴加热法提取正常培养条件下VPAHPND的DNA为模板进行普通PCR扩增,6种内参基因引物信息见表 1。普通PCR程序为:95℃ 10 min; 95℃ 5 s,55℃ 34 s,72℃ 45 s,40个循环。用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检法检测条带完整性,并通过TaKaRa MiniBEST Agarose Gel DNA Extraction Kit Ver.4.0 (大连宝生物公司)对目的条带进行切胶回收,使用pMD18-T Vector Cloning Kit (大连宝生物公司)对目的基因进行克隆。将克隆好的菌液送至生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行测序,验证目的片段是否成功导入质粒。用TaKaRa MiniBEST Plasmid Purification Kit Ver.4.0(大连宝生物公司)提取克隆成功菌液的质粒,并以此标准品为模板,进行qRT-PCR分析,检测引物效率。qRT-PCR程序为:95℃ 10 min; 95℃ 5 s,55℃ 34 s,72℃ 45 s,40个循环; 熔解曲线分析使用Eppendorf的默认程序:95℃ 15 s,60℃ 15 s,95℃ 15 s。
|
|
表 1 候选内参基因引物序列及其相关信息 Tab.1 Nucleotide sequences of primers of the six candidate reference genes |
利用TSB培养基(Tryptic soy broth medium)对VPAHPND进行活化和扩大培养,培养条件为28℃、190 r/min恒温振荡培养10 h (指数增长期为8~11 h),离心收集所培养的细菌并用1.5%灭菌NaCl溶液配制成1.0×104 CFU/ml的菌液。利用地榆醇提物配制浓度分别为0、0.2、0.4、0.8和1.6 mg/ml的含药TSB培养基,按照1‰的接种量向其中接种VPAHPND,随后将其置于28℃恒温振荡培养箱中190 r/min振荡培养。每个浓度梯度设置3个生物学重复。
自接种VPAHPND后开始计时,在振荡培养0、2、4、6、8、10、12、14、16、18、20和22 h时从锥形瓶中取100 μl菌悬液适当稀释,均匀涂布于固体TSB培养基上,置于28℃恒温培养箱中培养12 h后进行平板菌落计数。
用于提取RNA的样品采样时间由预实验确定。各实验组VPAHPND菌液浓度达到指数增长期所需的时间分别为9 h (0 mg/ml)、11 h (0.2 mg/ml)、14 h (0.4 mg/ml)、16 h (0.8 mg/ml)和17 h (1.6 mg/ml)。因此,分别在9、11、14、16和17 h采集相应实验组的菌液,根据菌液浓度确定各组总菌量,用于RNA提取。
1.5 RNA提取和cDNA反转录采用TaKaRa MiniBEST Universal RNA Extraction Kit (大连宝生物公司)提取各实验组细菌的总RNA。用NanoDrop 1000超微量分光光度计检测RNA浓度和纯度,用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检法检测其条带的完整性。利用PrimeScriptTM RT reagent kit with gDNA Eraser(大连宝生物公司)试剂盒进行反转录制备各实验组qRT-PCR模板。
1.6 qRT-PCR分析qRT-PCR扩增在Eppendorf实时荧光定量PCR仪(Mastercycler ep)上进行。采用TB GreenTM Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ(大连宝生物)进行荧光定量PCR扩增,qRT-PCR程序和熔解曲线分析程序同1.3。每个样品进行3个技术重复。用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测qRT-PCR产物的条带。
1.7 数据处理利用Eppendrof实时荧光定量PCR仪自带的软件程序计算各基因扩增的Ct值、熔解曲线效率(E%)及其相关系数(R2)。采用SPSS 19.0统计软件对各基因Ct值进行单因素方差(One-way ANOVE)分析。分别利用GeNorm、Norm Finder、Best Keeper、Delta CT以及Ref Finder这5种方法对6种内参基因表达稳定性进行分析。其中,Best Keeper和Delta CT直接使用Ct值进行计算; GeNorm和Norm Finder软件需要将Ct值转化为2-ΔCt后再进行下一步计算; Ref Finder结果为前4种计算方法所得名次的几何平均数; 适宜的内参基因选择数量以GeNorm软件计算的配对变异系数(Vn/Vn+1<0.15)为选择标准。
2 结果 2.1 引物验证结果菌液测序结果显示,利用pMD18-T为载体,将目的片段成功插入到感受态细胞中,并且目的片段长度与文献中相同。rec A、pvs A、pvu A、16S rRNA、gapdh和rpo S的扩增曲线均为单峰,引物效率(E%)分别为1.01、1.08、0.99、0.98、1.02和0.93;相关系数(R2)分别为0.998、0.998、0.999、0.994、0.998和0.998。这表明6个候选内参基因的引物特异性良好,可用于后续实验。
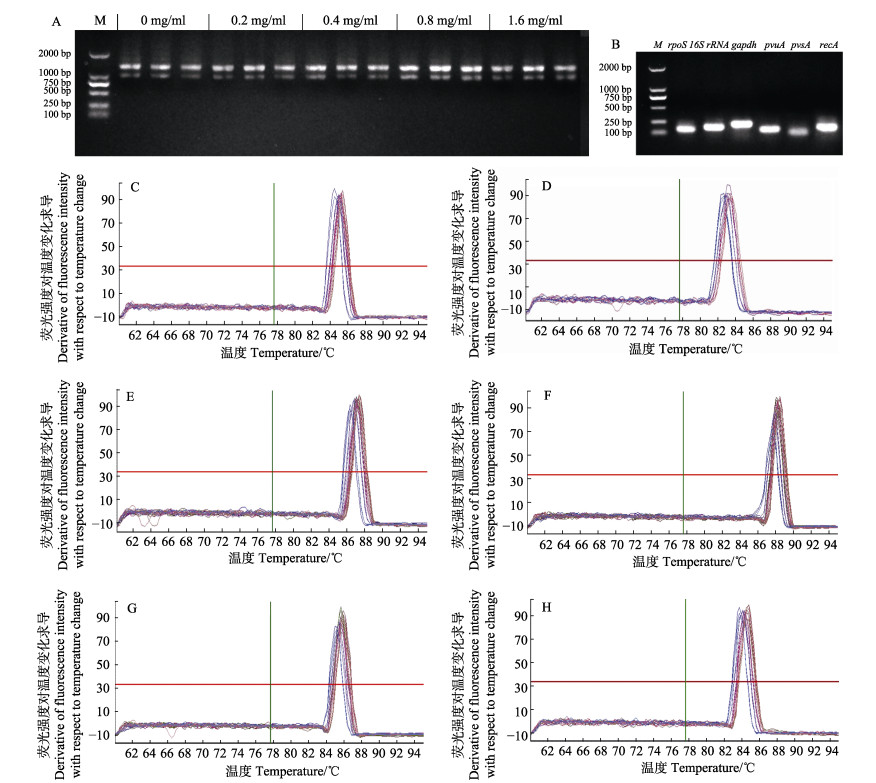
由各样品提取的RNA琼脂糖电泳结果(图 1A)可以看出,各样品条带完整,23S rRNA与16S rRNA条带亮度之比约为2:1,同时A260 nm/A230 nm > 2.0,表明所提取的RNA完整性良好。对样本qRT-PCR扩增产物的琼脂糖电泳结果显示,6个基因片段扩增产物单一,无杂带(图 1B)。各内参基因在不同浓度地榆作用下的熔解曲线均为单峰(图 1C~图 1H)。
|
图 1 各样品RNA琼脂糖电泳结果及引物扩增特异性检测结果
Fig.1 Results of RNA electrophoretogram and primers specificity detection
A: 5个处理组样品中总RNA琼脂糖凝胶电泳图; B: 6个内参基因qRT-PCR扩增产物琼脂糖凝胶电泳图; C~H分别为rec A、pvs A、pvu A、16S rRNA、gapdh和rpoS的熔解曲线 A: Total RNA electrophoretogram of five experimental groups; B: Specificity of six candidate reference genes for qRT-PCR amplification; C~H: Melting curves of rec A, pvs A, pvu A, 16S rRNA, gapdh, and rpoS |
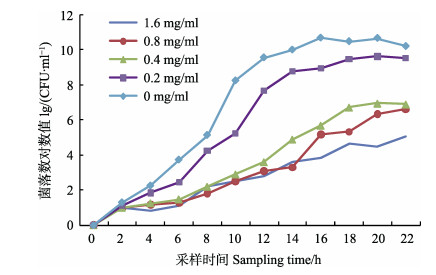
不同浓度地榆醇提物作用下VPAHPND生长曲线见图 2。不同浓度地榆醇提物能改变VPAHPND到达平台期的时间及平台期高度,且地榆浓度越高对VPAHPND的抑制效果越明显。0、0.2和0.4 mg/ml组达到平台期的时间分别为12、14和18 h; 而0.8 mg/ml和1.6 mg/ml组在培养22 h内未出现明显的平台期。
|
图 2 不同浓度地榆醇提物对VPAHPND的生长曲线 Fig.2 Growth curve of VPAHPND under stress of alcohol extracts of Sanguisorba officinalic at different concentrations |
VPAHPND中6个候选内参基因Ct值如图 3所示,其Ct值范围分别为17.55~23.68 (rce A)、17.55~25.63 (pvs A)、17.30~24.06 (pvu A)、13.28~16.80 (gapdh)、4.31~5.15 (16S rRNA)、16.87~19.41 (rpo S)。在所检测的6个基因中,内参基因表达变化差异最小的为16S rRNA (CV=3.88),说明在地榆对16S rRNA的表达影响较小。表达变化差异最显著的是pvs A (CV=12.53),说明地榆对pvs A表达影响最大。

|
图 3 6个内参基因在各处理组中Ct值 Fig.3 Ct values of six reference genes in different groups 柱形图上方字母不同表示差异显著(P < 0.05) Different letters on the column indicate significant difference (P < 0.05) |
利用5种方法对6个基因稳定性评价的结果见表 2。由GeNorm软件给出的内参基因稳定性顺序由大到小为rpo S = 16S rRNA > gapdh > rec A > pvu A > pvs A,其中,最稳定的内参基因为16S rRNA和rpo S,其稳定指数均为0.852。由Norm Finder软件计算出的内参基因稳定性顺序由大到小为gapdh > rpo S > pvu A > 16S rRNA > rec A > pvs A,最为稳定的内参基因为gapdh,稳定指数为0.584。Best Keeper分析后推荐最稳定的内参基因为16S rRNA,其标准偏差为0.13,这6个候选内参基因稳定性顺序由大到小为16S rRNA > rpo S > gapdh > rec A > pvu A > pvs A。Delta CT法计算得出6个内参基因稳定性顺序由大到小为gapdh > rpo S > pvu A > 16S rRNA > rec A > pvs A。其中,最为稳定的内参基因为gapdh,其平均标准偏差的值为1.570。Ref Finder根据上述4个软件的结果分析后得出的综合排名为rpo S > gapdh > 16S rRNA > pvu A > pvs A > rec A。
|
|
表 2 不同浓度地榆醇提物作用下副溶血弧菌中6个内参基因稳定性评价 Tab.2 Stability evaluation of six reference genes of Vibrio parahaemolyticus under different concentrations of Sanguisorba officinalis L. alcoholic extracts |
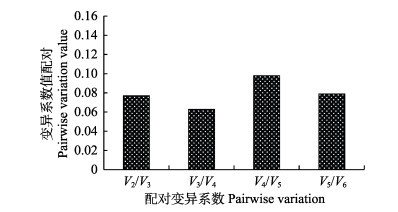
根据Vandesompele等(2002)提出的方法进行数据处理,按照rpo S、gapdh、16S rRNA、pvu A、pvs A、rec A的顺序,计算配对变异系数(Vn/Vn+1),当Vn/Vn+1 < 0.15时,表明最适内参基因个数为n,且无需继续引入其他内参基因。本实验中,V2/V3=0.077 (图 4),表明选用2个内参基因已能满足该条件下实验数据的标准化处理,结合候选内参基因的稳定性排序结果,最终得出这2个内参基因为rpo S和gapdh。
|
图 4 最适内参基因数量的确定 Fig.4 Determination of the optimal number of reference genes for normalization 配对变异系数(Vn/Vn+1)是由标准化因子NFn与NFn+1计算所得,用于确定精确标准化处理数据时所需的最适内参基因数量 Pairwise variation (Vn/Vn+1) analysis is based on the normalization factors NFn and NFn+1 to determine the number of control genes required for accurate normalization |
地榆入药历史悠久,但相关的研究多集中于人医,在水产养殖中的研究与运用较少。姜燕(2016)研究发现,地榆对副溶血弧菌有较好的抑制效果,发现地榆与诃子、乌梅、黄连联用能显著提高对虾免疫力和抗病力。Lee等(2004)研究发现,地榆对表皮葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus epidermidis)、金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)和大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)均有显著的抑菌效果,地榆对这3种细菌抑制效果与浓度呈正相关。本研究结果与Lee等(2004)的实验结果一致,地榆的使用延缓了VPAHPND到达平台期的时间及平台期高度,并且浓度越高,作用效果越明显。研究结果证明了地榆对VPAHPND的抑制效果,为后续以地榆为核心药物的AHPND防控技术的建立提供了数据支持。
3.2 内参基因稳定性评价的意义qRT-PCR技术广泛应用于哺乳动物(Cepollaro et al, 2018)、植物(Chen et al, 2015)、细菌(Delorenzo, 2018)等各类生物体内基因表达变化的研究。在基因相对表达量分析时,需要将初始样品量、酶效率、转录活性差异等变量因素进行标准化处理,以降低这些变量对实验结果造成的误差。数据标准化处理时,常使用内参基因法。理想的内参基因被定义为在各种组织样品和实验条件下均能稳定表达的基因(Zhang et al, 2005)。为了保证实验结果的可信度,需要在实验前对筛选的内参基因进行验证。Gomes等(2018)根据实验得出,肺炎克雷伯菌(Klebsiella pneumoniae)中最为合适的内参基因组合为rec A、rho、pro C和rpo D,并通过分析肺炎克雷伯菌细胞内铁调节基因在铁富余和亏欠两种条件下的相对表达量,验证了其所筛选的内参基因的正确性。Wang等(2018)在小鼠(Mus musculus)急性酒精性肝损伤模型中,利用内质网应激相关基因的相对表达量差异验证了Hprt1作为该模型下的内参基因的可靠性。Lin等(2018)利用mleR1和mleP1基因验证了SO2胁迫下植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum)内最稳定的内参基因组合为rpo B、rpo C、rec A和ldh这一结果的正确性。随着对实验精度要求的提高,筛选合适的内参基因,并进行准确性验证将会成为实验步骤中必不可少的一部分。
研究表明,不同物种、不同组织、不同发育阶段以及不同环境条件均会影响内参基因的表达。在真核生物基因检测中,常使用β-actin、gapdh、18S rRNA、28S rRNA等作为内参基因(Suzuki et al, 2000;薛蓓等, 2017),但也有学者发现,β-actin (Selvey et al, 2001)和gapdh (Deindl et al, 2002)并不是最稳定的内参基因。Radonic等(2004)研究证明,人体各组织最适内参基因也不是传统意义上的18S rRNA,而是RPⅡ。在原核生物内参基因筛选中,内参基因的稳定性也随着环境的变化而变化。如Yang等(2018)发现劳尔氏菌(Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum)在生物(生长阶段)和非生物(温度、羟基香豆素、营养) 4种胁迫处理下,7个内参基因所表现出的稳定性差异显著,在不同的生长阶段中,gyr A和ser C是最稳定的内参基因,而在温度胁迫下,ser C、gyr A和fts Z最为稳定; 在羟基香豆素胁迫下,gyr A、fts Z和16S rRNA最为稳定; 而在营养胁迫下,ser C和16S rRNA最稳定。因此,在特定的研究背景下,需对生物的内参基因进行重新评判,以增加基因检测的稳定性和可靠性。目前,常用于副溶血弧菌基因检测的内参基因有rec A、pvs A、pvu A、16S rRNA、gapdh、rpo S (Ma et al, 2015; Coutard et al, 2007; Li et al, 2013;李沁, 2013)。Ma等(2015)将5株不同来源的副溶血弧菌培养于4种温度下,筛选出不同温度下副溶血弧菌最适内参基因为rec A。李沁(2013)以5株携带不同毒力基因的副溶血弧菌为研究对象,选取海水、过滤海水以及凡纳滨对虾作为培养介质,筛选出最适内参基因为pvs A和pvu A。结果表明,rpo S是不稳定的内参基因。但本研究结果显示,rpo S为最稳定的内参基因,这与他们的研究结果不同。Hengge-Aronis(2002)研究表明,低温与高温能分别影响Rop S蛋白的翻译与水解过程,因此,温度的变化会显著影响Rop S的调控机制,造成其不稳定表达。李沁(2013)选取的副溶血弧菌样品来源差异显著,本身并不具备相同生理条件,因而rpo S表达不够稳定。中草药中所蕴含的活性成分多为不具药理作用活性物质前体,且不同种类的中草药之间差异很大,其药效发挥的机制十分复杂(吴秋云等, 2018),对细菌的作用机理不能简单地等同于环境因子胁迫,因而rpo S表达稳定性出现了不同的结果。
本研究结果可用于地榆醇提物对VPAHPND相关基因表达量变化的探究,为以地榆为核心药物防控AHPND技术的开发做铺垫。这个现象进一步说明内参基因使用前确实需要针对实验条件进行稳定性筛选和验证,才能保证后期研究结果的可靠性。
3.3 内参基因丰度对其稳定性评价的影响基因的表达丰度(Ct值)是筛选最适内参基因时的重要选择依据,Ct值过大或过小会使qRT-PCR数据分析时很难准确地减去基线值(Vandesompele et al, 2002)。Wan等(2011)指出,适宜作为内参基因的理想Ct值范围是15~30。本研究16S rRNA使用的是Ma等(2015)设计的引物,实验中16S rRNA的Ct值范围为8.14~9.93。本研究中,16S rRNA在副溶血弧菌遭受各种浓度地榆醇提物的胁迫下,仍表现出较强的稳定性,但其在副溶血弧菌细胞内表达的Ct值在4.32~5.16之间,表达丰度过高,不适宜作为内参基因。这两项研究检测到的副溶血弧菌16S rRNA的Ct值范围存在极显著差异,可能是菌株差异或者是培养环境不同所引起的。作者所使用的副溶血弧菌(VPAHPND)为能引起凡纳滨对虾AHPND的临床分离株,与Ma等(2015)使用的菌株存在时间、地域和环境差异。Radonic等(2004)也指出,rRNA转录是通过RNA聚合酶Ⅰ进行的,不适于作为内参基因。本研究使用的其他5种候选内参基因的平均Ct值均介于内参基因的理想Ct值范围内(15 < Ct < 30),可作为候选内参基因。
3.4 最适内参基因数量分析在基因表达检测过程中,如果实验精度要求较高,可通过计算配对变异系数确定最适内参基因数量,来减小单一内参基因引起的误差。Vandesompele等(2002)提出通过配对变异系数评价最适内参基因个数的方法,即首先计算2个最稳定的内参基因在所有样品中的标准化因子(NF2),然后,逐步引入其他内参基因,计算标准化因子(NFn),直至第n+1内参的引入对NFn+1无显著影响时停止引入。接着计算配对变异系数(Vn/Vn+1),来反映新引入的内参基因对NFn+1影响。Vandesompele等(2002)建议将Vn/(n+1)=0.15作为一个参考值,当Vn/(n+1) > 0.15时,则有必要引入第n+1个基因,而Vn/(n+1) < 0.15时,则表明该实验条件下最适内参基因个数为n。本研究得出V2/V3=0.077,即选择的最适内参基因个数为2。综合以上结果,本研究仅筛选rpo S和gapdh作为该条件下最稳定的内参基因。
4 结论本研究就地榆醇提物胁迫下VPAHPND生长变化和该条件下VPAHPND中6种常见内参基因(rec A、pvs A、pvu A、gapdh、16S rRNA和rpo S)的稳定性进行评价。结果验证了地榆对VPAHPND的抑制效果,并推荐rpo S和gapdh作为该条件下内参基因,其效果会优于只使用单一的内参基因。这为以地榆为核心药物的AHPND防控技术的建立和从基因表达角度研究地榆对VPAHPND的作用机理提供了基础,同时,也为中草药药理作用的深入挖掘提供了研究思路。
Cai JP, Li J, Thompson KD, et al. Isolation and characterization of pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus from diseased post-larvae of abalone Haliotis diversicolor supertexta. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2010, 47(1): 84-86 |
Cai LT, Li SY, Ge MF, et al. Effect of three pathogenic Vibrios on the blood biochemical parameters of Pseudosciaena crocea. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2013, 34(2): 65-72 [蔡林婷, 李思源, 葛明峰, 等. 3种致病弧菌感染对大黄鱼血液生化指标的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2013, 34(2): 65-72 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2013.02.009] |
Cepollaro S, Della BE, De BD, et al. Evaluation of RNA from human trabecular bone and identification of stable reference genes. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 2018, 233(6): 4401-4407 DOI:10.1002/jcp.26319 |
Chen IH, Chou LS, Chou SJ, et al. Selection of suitable reference genes for normalization of quantitative RT-PCR in peripheral blood samples of bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(8): 15425 |
Chen MM, Dong X, Qiu L, et al. Quantitative analysis of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease causing Vibrio parahaemolyticus (VpAHPND) in infected Litopenaeus vannamei. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, 39(4): 93-100 [陈蒙蒙, 董宣, 邱亮, 等. 凡纳滨对虾感染致急性肝胰腺坏死病副溶血弧菌(VPAHPND)的定量分析. 渔业科学进展, 2018, 39(4): 93-100] |
Coutard F, Lozach S, Pommepuy M, et al. Real-time reverse transcription-PCR for transcriptional expression analysis of virulence and housekeeping genes in viable but nonculturable Vibrio parahaemolyticus after recovery of culturability. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 73(16): 5183-5189 DOI:10.1128/AEM.02776-06 |
Deindl E, Boengler K, Van RN, et al. Differential expression of GAPDH and β-actin in growing collateral arteries. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 2002, 236(1-2): 139-146 |
Delorenzo DM, Moon TS. Selection of stable reference genes for RT-qPCR in Rhodococcus opacus PD630. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 6019 DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-24486-w |
Gomes AEI, Stuchi LP, Siqueira NMG, et al. Selection and validation of reference genes for gene expression studies in Klebsiella pneumoniae using reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 9001 DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-27420-2 |
Hengge-Aronis R. Signal transduction and regulatory mechanisms involved in control of the σS (RpoS) subunit of RNA polymerase. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2002, 66(3): 373-395 DOI:10.1128/MMBR.66.3.373-395.2002 |
Jia D, Shi CY, Huang J, et al. Identification and pathogenicity analysis of bacterial pathogen associated with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in the Pacific shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, 39(3): 103-111 [贾丹, 史成银, 黄倢, 等. 凡纳滨对虾急性肝胰腺坏死病(AHPND)病原分离鉴定及其致病性分析. 渔业科学进展, 2018, 39(3): 103-111] |
Jiang Y. In vitro bacteriostatis Chinese herb compound selection for acute hepatopancreas necrosis syndrome in Litopenaeus vannamei. Master's Thesis of Dalian Ocean University, 2016, 1-51 [姜燕.凡纳滨对虾急性肝胰腺坏死病防治中草药的筛选.大连海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2016, 1-51]
|
Kumar V, Baruah K, Nguyen DV, et al. Phloroglucinol-mediated Hsp70 production in crustaceans: protection against Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Artemia franciscana and Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Frontiers in Immunology, 2018, 5(9): 1091 |
Lee SA, Son JH, Kwak JH, et al. Cytotoxic and antibacterial activities of Sanguisorbae officinalis L. Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry, 2004, 47(1): 141-145 |
Li Q. Different expression level of virulence genes of Vibrio parahaemolyticus under different environmental samples and establishing a quantification method of viable Vibrio parahaemolyticus from seafood. Master's Thesis of Shanghai Ocean University, 2013, 10-26 [李沁.不同环境样品中副溶血性弧菌毒力基因表达差异研究及副溶血性弧菌活菌定量方法的建立.上海海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2013, 10-26]
|
Li Q, Peng ZY, Chen XP, et al. Selection of reference genes for virulence gene expression in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2013, 53(3): 306-312 |
Lin XZ, He ZG, Li WX, et al. Validation of reference genes for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis in Lactobacillus plantarum R23 under sulfur dioxide stress conditions. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 2018, 24(3): 390-395 DOI:10.1111/ajgw.12331 |
Ma YJ, Sun XH, Xu XY, et al. Investigation of reference genes in Vibrio parahaemolyticus for gene expression analysis using quantitative RT-PCR. PLoS One, 2015, 10(12): e0144362 DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0144362 |
Pu HY, Li XY, Du QB, et al. Research progress in the application of Chinese herbal medicines in aquaculture: A review. Engineering, 2017, 3(5): 731-737 DOI:10.1016/J.ENG.2017.03.017 |
Radonic A, Thulke S, Mackay IM, et al. Guideline to reference gene selection for quantitative real-time PCR. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2004, 313(4): 856-862 DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.177 |
Selvey S, Thompson EW, Matthaei K, et al. β-actin: An unsuitable internal control for RT-PCR. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2001, 15(5): 307-311 DOI:10.1006/mcpr.2001.0376 |
Shyne APS, Sobhana KS, George KC, et al. Phenotypic characteristics and antibiotic sensitivity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains isolated from diseased groupers (Epinephelus spp.). Journal of the Marine Biological Association of India, 2008, 50(1): 1-6 |
Soto-Rodriguez SA, Gomez-Gil B, Lozano-Olvera R, et al. Field and experimental evidence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus as the causative agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease of cultured shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in northwestern Mexico. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(5): 1689-1699 DOI:10.1128/AEM.03610-14 |
Suzuki T, Higgins PJ, Crawford DR. Control selection for RNA quantitation. Biotechniques, 2000, 29(2): 332-337 DOI:10.2144/00292rv02 |
Vandesompele J, De PK, Pattyn F, et al. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biology, 2002, 3(7): research0034 DOI:10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-reports0034 |
Vanguilder HD, Vrana KE, Freeman WM. Twenty-five years of quantitative PCR for gene expression analysis. Biotechniques, 2008, 44(5): 619-626 DOI:10.2144/000112776 |
Wan H, Yuan W, Ruan M, et al. Identification of reference genes for reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR normalization in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2011, 416(1-2): 24-30 DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.10.105 |
Wang S, Wang JQ, Lv XW. Selection of reference genes for expression analysis in mouse models of acute alcoholic liver injury. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2018, 41(6): 3527-3536 |
Wu QY, Huang L, Pi Z, et al. Research progress of antibacterial activity and mechanism of Chinese herbal medicine. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 37(1): 25-29 [吴秋云, 黄琳, 皮真, 等. 中草药抑菌作用及其机制研究进展. 中兽医医药杂志, 2018, 37(1): 25-29] |
Xue B, Zhang P, Li ZH, et al. Cloning, expression and stability analysis of the reference gene glycer-aldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in Exopalaemon carinicauda. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2017, 24(5): 1003-1012 [薛蓓, 张培, 李志辉, 等. 脊尾白虾GAPDH基因的克隆及其内参基因稳定性分析. 中国水产科学, 2017, 24(5): 1003-1012] |
Yang J, Yoo J, Cho W, et al. Ethanol extract of Sanguisorbae Radix inhibits mast cell degranulation and suppresses 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions. Mediators of Inflammation, 2016, 2947390
|
Yang L, Chen JN, Liu Y, et al. Validation of reference genes for quantitative gene expression analysis in Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum CQPS-1 under environment stress. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2018, 148: 104-109 DOI:10.1016/j.mimet.2018.04.004 |
Zhang X, Ding L, Sandford AJ. Selection of reference genes for gene expression studies in human neutrophils by real-time PCR. BMC Molecular Biology, 2005, 6(1): 4 DOI:10.1186/1471-2199-6-4 |
Zheng Z, Aweya JJ, Wang F, et al. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) related microRNAs in Litopenaeus vannamei infected with AHPND-causing strain of Vibrio parahemolyticus. BMC Genomics, 2018, 19(1): 335 DOI:10.1186/s12864-018-4728-4 |
Zhong H, Simons JW. Direct comparison of GAPDH, β-actin, cyclophilin, and 28S rRNA as internal standards for quantifying RNA levels under hypoxia. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1999, 259(3): 523-526 DOI:10.1006/bbrc.1999.0815 |



