2. 上海海洋大学水产与生命学院 上海 201306;
3. 农业农村部海洋渔业可持续发展重点实验室 青岛 266071;
4. 南京农业大学无锡渔业学院 无锡 214081
2. College of Fisheries and Life Science, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306;
3. Key Laboratory of Sustainable Development of Marine Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Qingdao 266071;
4. Wuxi Fisheries College, Nanjing Agricultural University, Wuxi 214081
蛋白激酶C(PKC)是一类与丝氨酸/苏氨酸磷酸化密切相关的蛋白家族,可以介导多种细胞功能,例如细胞的存活、增殖和分化等(Moscat et al, 2003)。目前,至少有11个PKC家族成员被发现,根据结构和激活方式分为3类:PKC(α、βⅠ、βⅡ和γ)、PKC(δ、ε、θ、μ和η)和PKC(ζ、τ和λ) (Newton, 2001; Guo et al, 2004)。
PKCα是PKC家族成员中一种典型的丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶(Nakashima, 2002)。PKCα在机体中普遍存在,可以通过多种方式被激活,并参与多种细胞功能,包括细胞增殖、分化、能动性、凋亡和炎症(Nakashima, 2002; Singh et al, 2017)。至今,已有大量关于PKCα参与免疫与炎症反应的研究报道,与免疫应答密切相关。如Alvaro等(1997)指出,抑制PKCα可以显著抑制细菌性脂多糖(LPS)诱导巨噬细胞产生细胞因子;Volkov等(2001)研究发现,PKCα参与PI3K/Akt信号通路的激活,进而调控T细胞的多种生理功能,参与产生特异性淋巴细胞效应因子(Baier et al, 2009);在转基因小鼠(Mus musculus)的表皮中过表达PKCα的研究表明,其可以显著改变12-O-十四烷酰佛波醇-13-醋酸酯(TPA)诱导的炎症反应,水肿和中性粒细胞浸润,以及与炎症相关基因的表达,如环氧酶-2和肿瘤坏死因子-α (TNF-α) (Wang et al, 1999);研究指出,PKCα参与干扰素调节因子3的激活和I型干扰素β的合成(Johnson et al, 2007),还可以通过核因子kappa-B (NF-κB)抑制蛋白(IKB)负调节NF-κB诱导的参与各种炎症反应的基因的表达(Han et al, 1999)。
另外,Christina等(2013)研究指出,PKCα与PKCβ在多数情况下协同行使功能,如调节T细胞中的白介素-2的表达;使用PKCα/β抑制剂预处理嗜中性粒细胞可以减少NF-κB的核转位和促炎细胞因子TNF-α的产生,抑制PKCα/β可以阻止LPS或肽聚糖(PGN)诱导的NF-kB激酶抑制剂alpha/beta(IKKα/β)磷酸化被激活,IKB alpha的磷酸化和降解,以及NF-κB的p65亚基的磷酸化(Asehnoune et al, 2005)。
半滑舌鳎(Cynoglossus semilaevis)属鲽形目,俗称“龙脷”,是我国重要的海水养殖鱼类。近年来,半滑舌鳎养殖过程中细菌性疾病日益严重,其导致的鱼苗死亡造成了较高的经济损失,而哈维氏弧菌(Vibrio harveyi)是其病害发生的主要病原体之一。对于半滑舌鳎免疫相关功能研究和细菌防控手段展开深入研究将有助于半滑舌鳎产业的发展。目前,PKCα免疫相关的研究主要集中在哺乳动物(Wang et al, 1999),而在鱼类中鲜有报道。为了研究CsPKCα在免疫过程中的功能,本研究对PKCα进行了克隆,并对基因结构、组织分布以及响应哈维氏弧菌刺激后的基因表达变化进行了研究,发现CsPKCα基因参与免疫反应,为其后续相关功能的研究提供基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验用鱼本实验所用的半滑舌鳎均来源于山东省黄海水产有限公司。
1.2 样品采集3条15月龄健康半滑舌鳎成鱼,体长为(22.8± 1.8) cm,体重为(85.6±6.5) g,麻醉后分别取肝脏、脾脏、肾脏、鳃、肠、肌肉、心脏、脑、性腺、皮肤等组织,迅速放入RNA保存液中,置于-20℃冰箱中保存。
使用10月龄的60条健康半滑舌鳎进行哈维氏弧菌感染实验,具体实施方案参照先前的操作步骤(Wei et al, 2017; 王双艳等, 2019),腹腔注射的细菌浓度为1.0×104 CFU/ml。将鱼麻醉后采集肝脏、脾脏、肾脏、肠、鳃和皮肤6个免疫相关组织,分别在感染前0 h和注射后12、24、48和72 h进行样品采集并以感染前0 h作为对照,每个时间点分别随机采集3条鱼,采集的样品迅速放入RNA保存液中,置于-20℃冰箱中保存。
1.3 RNA提取及cDNA合成采用Trizol法(Invitrogen)提取半滑舌鳎各组织中的总RNA,琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测RNA的完整性,Gene Quant Pro RNA/DNA分光光度计检测其纯度与浓度。RNA鉴定合格后,使用cDNA反转试剂盒(TaKaRa)合成cDNA,RACE(TaKaRa)试剂盒合成RACE- Ready-cDNA。
1.4 PKCα基因全长cDNA的克隆根据已发表的半滑舌鳎全基因组序列(Chen et al, 2014),获得PKCα基因部分cDNA序列,使用Primer Premier 5.0软件设计引物(表 1),以肝、脾、肾、肠和鳃的混合cDNA为模板进行普通PCR扩增验证,PCR反应体系:ExTaq(TaKaRa) Mix 25 μl,上下游引物各2 μl,ddH2O 19 μl,模板cDNA 2 μl;程序为:95℃预变性2 min,35个循环(95℃变性30 s,56℃退火30 s,72℃延伸时间90 s),72℃延伸10 min,4℃保存。利用胶回收试剂盒(OMEGA)对PCR产物进行回收纯化,连接到pEASY-T1载体后,按照该载体说明书进行后续基因克隆实验,最终挑取阳性克隆送华大基因有限公司测序。
|
|
表 1 本研究所用的引物 Tab.1 Primers used in this study |
根据Smart RACE cDNA扩增试剂盒(TaKaRa)说明书进行5'-RACE和3'-RACE,通过巢式PCR进行扩增。以上述验证得到的cDNA序列为基础设计5'-RACE和3'-RACE的引物。用通用引物UPM和通用引物NUP进行巢式PCR。本研究中使用的所有引物信息见表 1。为了确保扩增的特异性,进行Touchdown PCR反应,所用程序参照之前的方法(Guo et al, 2017)。
1.5 生物学分析及进化树构建使用DNAstar软件对克隆得到的序列进行拼接分析,得到CsPKCα全长cDNA序列,并查找ORF以及氨基酸序列,预测蛋白分子量及等电点;PKCα同源性分析使用BioEdit软件和NCBI数据库中Blast程序进行物种间的氨基酸序列比对;利用SMART在线软件分析其蛋白结构域;通过MEGA 7.0软件邻接法(NJ)完成生物系统进化树构建(Kumar et al, 2016)。
1.6 PKCα基因表达模式检测实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)检测PKCα基因在正常生理条件下,半滑舌鳎不同组织中的表达水平和哈维氏弧菌感染后不同时间点免疫相关组织中的表达模式。每个样品设置3个重复。根据得到的ORF区序列设计实时荧光定量引物(表 1),以β-actin基因为内参。qRT-PCR的反应体系参照SYBR®Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ(TaKaRa)试剂盒说明书,使用ABI 7500 Fast Real-time (Applied Biosystems, 美国)程序下进行PKCα基因的定量分析。本实验釆取2-ΔΔCt法计算PKCα基因的相对表达量,采用SPSS 16.0软件对PKCα基因的表达量进行单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)。设定P < 0.05为差异显著。
2 结果 2.1 cDNA序列分析CsPKCα cDNA全长为2315 bp,其中,ORF为2013 bp,编码670个氨基酸,5'UTR为218 bp,3'UTR为84 bp,预测蛋白相对分子质量为76.37 kDa,理论等电点为6.44。该基因的氨基酸序列337~595aa区段为典型的丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶催化结构域(图 1)。
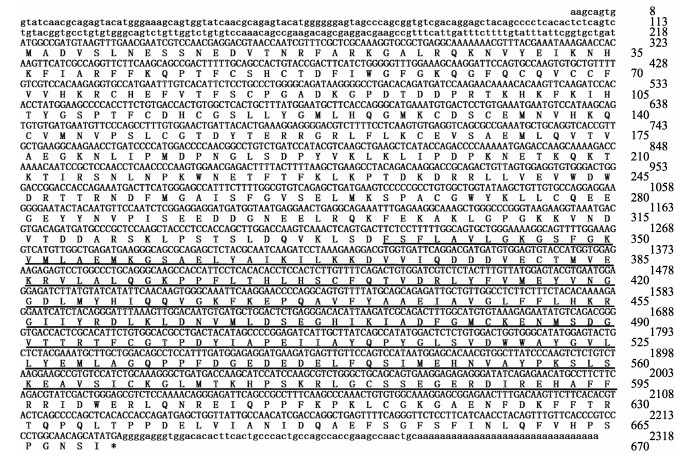
|
图 1 CsPKCα cDNA全长和推导的氨基酸序列 Fig.1 The full-length cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of CsPKCα |
如图 2所示,在CsPKCα中鉴定了保守结构域。N末端含有2个蛋白激酶C保守区1(C1)结构域和1个蛋白激酶C保守区2(C2)结构域。C1结构域具有以磷脂和锌依赖的方式结合二酰基甘油和佛波醇酯的功能,而C2结构域则负责Ca2+依赖性膜蛋白质的结合,从而进行细胞信号转导(Davletov et al, 1993; Medkova et al, 1999)。C末端具有1个丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶催化结构域(S_TKc)和1个丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶延伸结构域(S_TK_X),两者均可以与ATP结合,行使蛋白激酶活性(Knighton et al, 1991)。
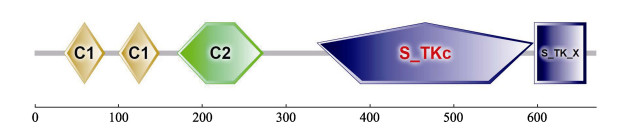
|
图 2 CsPKCα保守结构域 Fig.2 The conserved domains of CsPKCα 水平灰条表示预测没有功能域的氨基酸序列,而彩色框则表示预测有功能域的区域。注释结构域:C1,蛋白激酶C保守区1(C1)结构域;C2,蛋白激酶C保守区2(C2)结构域;S_TKc,丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶催化结构域;S_TK_X,丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶延伸结构域。相对于氨基酸序列的长度和位置显示蛋白质结构域 The horizontal gray bars represent amino acid sequences without predicted functional domains, whereas the colored boxes represent the regions with confidently predicted domains. Annotated domains: C1, Protein kinase C conserved region 1 (C1) domain; C2, Protein kinase C conserved region 2 (C2) domain; S_TKc, Serine/Threonine protein kinases, catalytic domain; S_TK_X, Extension to Ser/Thr-type protein kinases domain. Protein domains are shown relative to the length of and the position in the amino acid sequences |
为了评估脊椎动物PKCα氨基酸的相似性/差异,对半滑舌鳎和其他脊椎动物的PKCα进行了多序列比对。结果显示,CsPKCα编码的氨基酸序列与其他物种PKCα编码氨基酸序列具有不同程度的相似度(81%~92%),其中,与尖吻鲈(Lates calcarifer)的相似度为92%,与牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)相似度为88%,与人(Homo sapiens)相似度为81%,氨基酸序列比对信息见图 3。
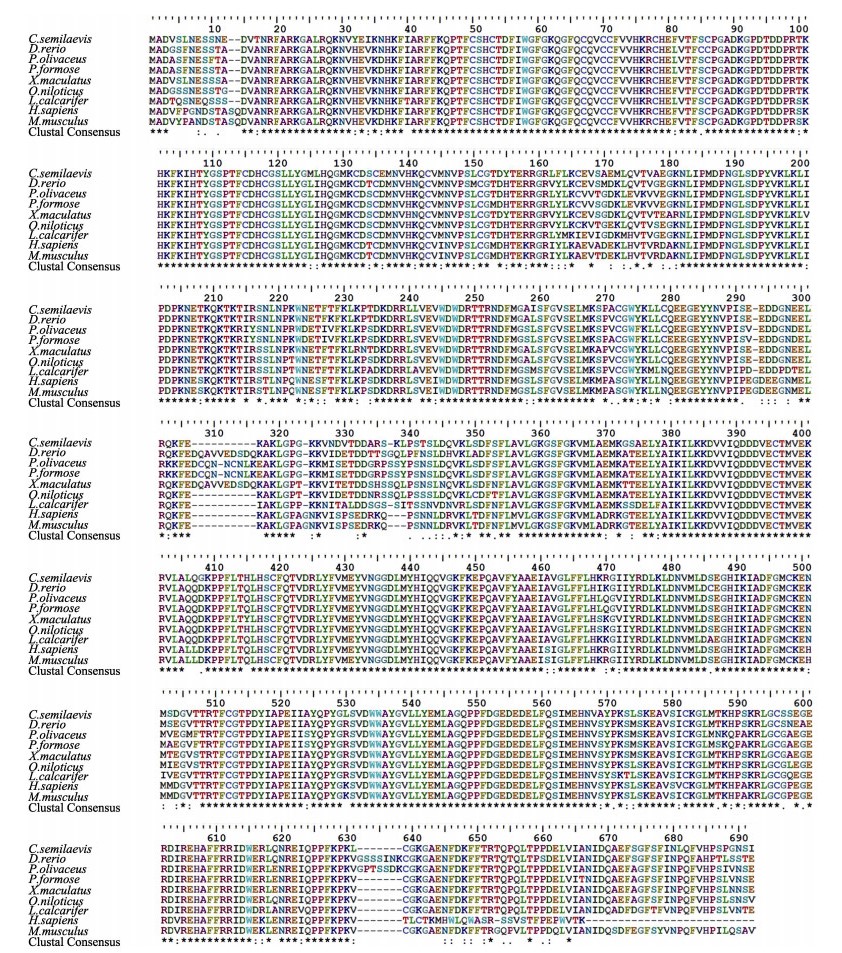
|
图 3 不同物种PKCα氨基酸序列比对 Fig.3 Multiple sequence alignment of PKCα amino acid sequences 氨基酸序列GenBank号:人(XP_016880325.1);小家鼠(NP_035231.2);斑马鱼(NP_001243170.1);牙鲆(XP_019939809.1);剑尾鱼(XP_023190086.1);罗非鱼(XP_019215250.1);亚马逊花鳉(XP_016534709.1);尖吻鲈(XP_018520387.1);半滑舌鳎(XP_008315545.1) The GenBank accession numbers of amino acid sequences used for multiple sequence alignment are as follows: Homo sapiens (XP_016880325.1); Mus musculus (NP_035231.2); Danio rerio (NP_001243170.1); Paralichthys olivaceus (XP_019939809.1); Xiphophorus maculates (XP_023190086.1); Oreochromis niloticus (XP_019215250.1); Poecilia formosa (XP_016534709.1); Lates calcarifer (XP_018520387.1); Cynoglossus semilaevis (XP_008315545.1) |
为了解PKCα在不同物种中的进化关系,使用Mega 7.0的NJ程序对来自18个物种的PKCα的氨基酸序列进行了系统发育分析(10种硬骨鱼,8种其他脊椎动物)。系统进化树显示,硬骨鱼聚为一支,其中,半滑舌鳎与牙鲆、亚马逊花鳉(Poecilia formosa)、剑尾鱼(Xiphophorus maculates)等进化地位较为接近,其他脊椎动物(鸟类、爬行类、两栖类和哺乳类)聚为一支,其中,属于两栖类的热带爪蟾(Xenopus tropicalis)、鸟类中的原鸡(Gallus gallus)和爬行类的扬子鳄(Alligator sinensis)产生分支,与哺乳动物进化地位较远(图 4)。
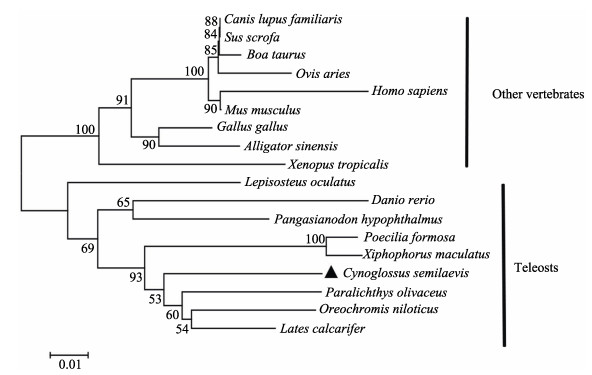
|
图 4 基于半滑舌鳎等硬骨鱼和其他脊椎动物PKCα的系统进化树 Fig.4 Phylogenetic analysis of PKCα from C. semilaevis and other vertebrates 氨基酸序列GenBank号:人(XP_016880325.1);小家鼠(NP_035231.2);原牛(NP_776860.1);原鸡(NP_001012822.1);家犬(XP_022278565.1);野猪(XP_020922399.1);扬子鳄(XP_025052051.1);绵羊(XP_014954487.1);热带爪蟾(NP_001072752.1);斑马鱼(NP_001243170.1);牙鲆(XP_019939809.1);剑尾鱼(XP_023190086.1);雀鳝(XP_015211748.1);罗非鱼(XP_019215250.1);低眼无齿鷶(XP_026789328.1);亚马逊花鳉(XP_016534709.1);尖吻鲈(XP_018520387.1);半滑舌鳎(XP_008315545.1) The GenBank accession numbers of the amino acid sequences used for phylogenetic analysis are as follows: Homo sapiens (XP_016880325.1); Mus musculus (NP_035231.2); Bos Taurus (NP_776860.1); Gallus gallus (NP_001012822.1); Canis lupus familiaris (XP_022278565.1); Sus scrofa (XP_020922399.1); Alligator sinensis (XP_025052051.1); Ovis aries (XP_014954487.1); Xenopus tropicalis (NP_001072752.1); Danio rerio (NP_001243170.1); Paralichthys olivaceus (XP_019939809.1); Xiphophorus maculates (XP_023190086.1); Lepisosteus oculatus (XP_015211748.1); Oreochromis niloticus (XP_019215250.1); Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (XP_026789328.1); Poecilia formosa (XP_016534709.1); Lates calcarifer (XP_018520387.1); Cynoglossus semilaevis (XP_008315545.1) |
为了评估PKCα在半滑舌鳎不同组织中的表达模式,通过qRT-PCR检测了其在肝脏、脾脏、肾脏、鳃、肠、肌肉、心脏、脑、性腺、皮肤等组织等10种组织中的mRNA表达水平。结果显示,PKCα基因在半滑舌鳎各个组织中均有表达,其中,在免疫相关组织鳃、肠、皮肤和肝脏中表达量相对较高(图 5)。
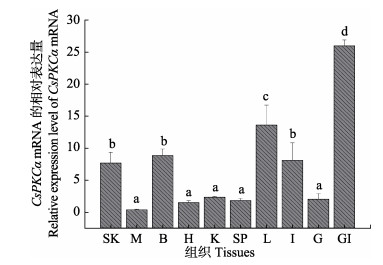
|
图 5 CsPKCα mRNA在不同组织中的表达水平 Fig.5 Relative expression levels of CsPKCα mRNA in various tissues SK:皮肤;M:肌肉;B:脑;H:心脏;K:肾脏;SP:脾脏;L:肝脏;I:肠;G:性腺;GI:鳃。显示数值为平均值±标准差(n=3),不同字母间表示差异显著(P < 0.05),下同< SK: Skin; M: Muscle; B: Brain; H: Heart; K: Kidney; SP: Spleen; L: Liver; I: Intestine; G: Gonad; GI: Gill. Values are indicated as Mean±SE (n=3). The expression levels with the same letter are not significantly different (P < 0.05). The same as below |
为了初步探究PKCα在半滑舌鳎免疫反应中的作用,结合上述组织表达结果,使用qRT-PCR测定哈维氏弧菌感染后6种免疫相关组织(鳃、肠、皮肤、脾、肝和肾)中PKCα基因的表达水平。将不同采样时间点的PKCα表达水平与0 h时的表达水平进行比较。检测结果显示,哈维氏弧菌感染后,PKCα基因在鳃、肾脏、肝脏、脾脏、皮肤中均有显著性差异表达,分别在鳃48 h、肾脏24 h、脾脏48 h和皮肤48 h时出现显著性上调,在肝脏12 h时检测到显著性下调。然而,肠中感染后未出现显著性变化(图 6)。
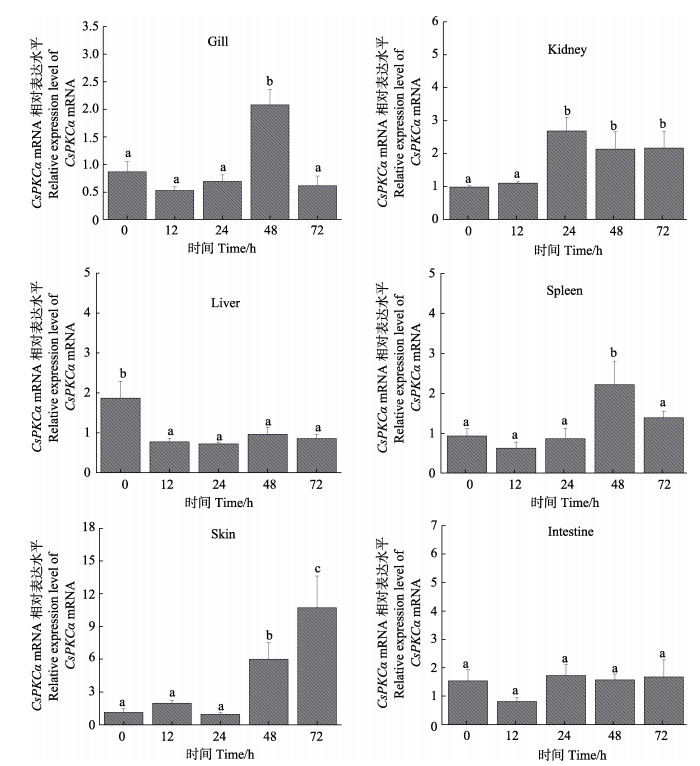
|
图 6 CsPKCα mRNA在哈维氏弧菌感染后鳃、肾脏、肝脏、脾脏、皮肤和肠中的表达水平 Fig.6 Relative expression levels of CsPKCα mRNA in the gill, kidney, liver, spleen, skin and intestine at different time points after V. harveyi infection |
本研究通过RACE方法获得了半滑舌鳎PKCα基因cDNA全长,并进行了基因的序列鉴定,预测出其具有典型的蛋白激酶C保守区1和保守区2,以及丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶催化结构域。丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶催化结构域是蛋白激酶最为关键的结构域,蛋白激酶C对蛋白底物的丝氨酸和苏氨酸残基的磷酸化即通过该结构域来完成,进而调节蛋白质的生物活性状态,影响细胞活动如细胞内外信号传导,细胞周期进程,细胞内运输等(Haas et al, 1992; 康涵等, 2012)。
氨基酸序列比对显示,PKCα在硬骨鱼和哺乳动物中高度保守,相似度高达81%以上(图 3),这表明PKCα可能在硬骨鱼和哺乳动物之间具有相似的功能。至今,PKCα的研究主要集中于哺乳动物,其参与T、B细胞的多种免疫反应(Volkov et al, 2001; Guo et al, 2004),并可以显著改变炎症诱导的反应以及炎症相关基因的表达(Wang et al, 1999)等,但相关免疫反应机制还需进一步阐明,在半滑舌鳎中的研究有待继续开展。
qRT-PCR检测的组织表达模式结果显示,PKCα在半滑舌鳎各个组织广泛表达,其中,在免疫相关组织鳃中表达最高,鳃是水生生物与外部水环境接触的主要组织,是防御病原体入侵的第一道防线(Li et al, 2015; 王贞杰等, 2017),另外,在免疫相关组织肝脏、皮肤和肠中也有较高的表达。为了进一步研究CsPKCα基因对哈维氏弧菌的响应模式,检测了CsPKCα基因在哈维氏弧菌感染后鳃,肾脏、脾脏、肝脏、皮肤和肠等6个组织的表达情况。结果显示,CsPKCα mRNA在鳃、肾脏、脾脏、皮肤中均出现显著性上升,其中,鳃和脾脏CsPKCα的表达量在48 h出现峰值,肾脏CsPKCα的表达量在24、48和72 h一直维持高表达,皮肤CsPKCα的表达量在24~72 h持续上升,显示后期在皮肤中一直处于应答状态。这与PKCα高表达于哺乳动物的肝脏、脾脏、肾脏和皮肤并行使免疫相关功能极为类似(Dean et al, 1994; Dorr et al, 1998)。鱼类特有的鳃,作为硬骨鱼的呼吸器官,也是其防止病原菌侵染的首要防线,哈维氏弧菌感染后CsPKCα在鳃中的表达量显著上调,显示出免疫应答反应,值得注意的是,在哺乳动物中同为呼吸器官的肺也是PKCα高表达并发挥免疫反应的重要场所(Dean et al, 1994; Lahn et al, 2004)。然而,CsPKCα的表达量在肠中一直无显著变化,表明CsPKCα可能不参与哈维氏弧菌感染后肠中的免疫相关反应,而组织分布检测到CsPKCα在肠中具有较高的表达,这可能与PKCα参与营养调节有关(Bergan et al, 2012)。另外,通过小鼠巨噬细胞的细菌响应研究发现,细菌DNA可通过活化PKCα、PKCβII和NF-κB来激活巨噬细胞(王立生等, 2007)。巨噬细胞已被广泛认知具有重要的生物学功能,参与生物机体非特异性和特异性免疫反应,通过噬菌作用清除病原体(Gordon et al, 2010)。因此,有关鱼类PKCα是否参与激活巨噬细胞来增强机体对病原菌的免疫耐受力将是未来需要解决的研究课题之一。
目前,鱼类中PKCα基因的克隆及免疫相关功能的研究鲜有报道。本研究对半滑舌鳎PKCα基因进行了cDNA全长克隆、序列鉴定、进化分析以及表达模式的研究,进行了CsPKCα响应哈维氏弧菌的免疫应答分析,为鱼类PKCα基因后续的功能研究提供了参考资料。
Alvaro V, Prévostel C, Joubert D, et al. Ectopic expression of a mutant form of PKCalpha originally found in human tumors:Aberrant subcellular translocation and effects on growth control. Oncogene, 1997, 14(6): 677 |
Asehnoune K, Strassheim D, Mitra S, et al. Involvement of PKCalpha/beta in TLR4 and TLR2 dependent activation of NF-kappaB. Cellular Signalling, 2005, 17(3): 385-394 |
Baier G, Wagner J. PKC inhibitors:Potential in T cell-dependent immune diseases. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 2009, 21(2): 262-267 |
Bergan HE, Kittilson JD, Sheridan MA. Nutrition-regulated lipolysis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) is associated with alterations in the ERK, PI3K-Akt, JAK-STAT, and PKC signaling pathways. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2012, 176(3): 367-376 |
Chen SL, Zhang G, Shao CW, et al. Whole-genome sequence of a flatfish provides insights into ZW sex chromosome evolution and adaptation to a benthic lifestyle. Nature Genetics, 2014, 46(3): 253 |
Christina LN, Nikolaus T, Katarzyna W, et al. PKCα and PKCβ cooperate functionally in CD3-induced de novo IL-2 mRNA transcription. Immunology Letters, 2013, 151(1-2): 31-38 |
Davletov BA, Südhof TC. A single C2 domain from synaptotagmin I is sufficient for high affinity Ca2+/phospholipid binding. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1993, 268
|
Dean NM, McKay R. Inhibition of protein kinase C-alpha expression in mice after systemic administration of phosphorothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1994, 91(24): 11762-11766 |
Dorr FA, Kisner DL. Antisense oligonucleotides to protein kinase C-α and C-raf kinase:Rationale and clinical experience in patients with solid tumors. Antisense Research and Application. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1998, 11061106: 463-476 |
Gordon S, Martinez FO. Alternative activation of macrophages:Mechanism and Functions. Immunity, 2010, 32(5): 593-604 |
Guo B, Su TT, Rawlings DJ. Protein kinase C family functions in B-cell activation. Current Opinion in Immunology, 2004, 16(3): 367-373 |
Guo H, Wei M, Liu Y, et al. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of the aqp1aa gene in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). PLoS One, 2017, 12(4): e0175033 |
Han Y, Tao M, Murray NR, et al. Interleukin-1-induced nuclear factor-κB-IκBα autoregulatory feedback loop in hepatocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1999, 274(2): 939 |
Haas DW, Hagedorn CH. Protein kinase C phosphorylates both serine and threonine residues of the mRNA cap binding protein eIF-4E. Second Messengers Phosphoproteins, 1992, 14(1-2): 55-63 |
Johnson J, Albarani V, Nguyen M, et al. Protein kinase Calpha is involved in interferon regulatory factor 3 activation and type I interferon-beta synthesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(20): 15022-15032 |
Knighton DR, Zheng JH, Eyck LT, et al. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science, 1991, 253(5018): 407-417 |
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7:Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7. 0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2016, 33(7): 1870 |
Kang H, Wu WJ. The role of serine/threonine protein kinases in Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis. Journal of Microbes and Infection, 2012, 7(1): 56-61 [康涵, 吴文娟. 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶在结核分枝杆菌致病机制中的作用. 微生物与感染, 2012, 7(1): 56-61] |
Lahn M, Su C, Li S, et al. Expression levels of protein kinase C-α in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clinical Lung Cancer, 2004, 6(3): 184-189 |
Li C, Song L, Tan F, et al. Identification and mucosal expression analysis of cathepsin B in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) following bacterial challenge. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 47(2): 751-757 |
Medkova, M. Interplay of C1 and C2 domains of protein kinase C-alpha in its membrane binding and activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1999, 274(28): 19852-19861 |
Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT, Rennert P. NF-κB activation by protein kinase C isoforms and B-cell function. Embo Reports, 2003, 4(1): 31-36 |
Nakashima S. Protein kinase Cα (PKCα):Regulation and biological function. Journal of Biochemistry, 2002, 132(5): 669-675 |
Newton AC. Protein kinase C: Structural and spatial regulation by phosphorylation, cofactors, and macromolecular interactions. Chemical Reviews, 2001, 101(8): 2353-64 |
Singh S, Mohamed W, Aguessy A, et al. Functional interaction of PkcA and PldB regulate aggregation and development in, Dictyostelium discoideum. Cellular Signalling, 2017, 34: 47-54 |
Volkov Y, Long A, Mcgrath S, et al. Crucial importance of PKC-beta(I) in LFA-1-mediated locomotion of activated T cells. Nature Immunology, 2001, 2(6): 508-514 |
Wang HQ, Smart RC. Overexpression of protein kinase C-alpha in the epidermis of transgenic mice results in striking alterations in phorbol ester-induced inflammation and COX-2, MIP-2 and TNF-alpha expression but not tumor promotion. Journal of Cell Science, 1999, 112(Pt 20): 3497-3506 |
Wang LS, Li YX, Zhu HM, et al. Influence of bifidobacterium DNA on PKC and NF-kappaB in murine macrophages. Chinese Journal of Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 2007, 23(1): 11-13 [王立生, 李迎雪, 朱惠明, 等. 双歧杆菌DNA对小鼠巨噬细胞中PKC和NF-κB的影响. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2007, 23(1): 11-13] |
Wang SY, Wang L, Chen ZF, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) in half smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2019, 40(2): 1-8 [王双艳, 王磊, 陈张帆, 等. 半滑舌鳎多聚免疫球蛋白受体(pIgR)基因的克隆和表达分析. 渔业科学进展, 2019, 40(2): 1-8] |
Wang ZJ, Chen SQ, Cao DZ, et al. Effects of acute ammonia nitrogen stress on histopathology of gill and liver and enzyme activities of juvenile Verasper variegatus. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2017, 38(2): 59-69 [王贞杰, 陈四清, 曹栋正, 等. 急性氨氮胁迫对圆斑星鲽(Verasper variegatus)幼鱼鳃和肝组织结构及相关酶活性的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2017, 38(2): 59-69] |
Wei M, Xu WT, Li HL, et al. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a novel r-spondin member (rspo2l) in Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2017, 72: 436-442 |



