Worm Sipunculus nudus
热休克蛋白热休克蛋白(Heat shock proteins, Hsps)是目前研究最为广泛的应激蛋白之一,可在各种环境胁迫下诱导大量表达;在正常环境条件下,细胞内也存在丰富的Hsps;根据分子量大小,Hsps可以分为Hsp110s、Hsp90s、Hsp70s、Hsp60s和小分子量Hsps等多个家族(Lindquist et al, 1988)。其中,Hsp90是一类进化上高度保守的重要细胞内伴侣蛋白,在正常情况约占细胞溶质蛋白总量的1%~2%(Lai et al, 1984),具有辅助蛋白质正确折叠、胞内物质运输、细胞增殖调控等重要功能(McClellan et al, 2007)。此外,Hsp90在配子发生中也具有重要功能。例如,非洲爪蟾(Xenopus laevis)卵母细胞的Hsp90可通过磷酸化稳定c-Mos蛋白,并依赖丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(Mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK)途径影响成熟促进因子(Maturation-promoting Factor, MPF)的合成(朱建安, 2007)。在刀额新对虾(Metapenaeus ensis)卵母细胞中,Hsp90与雌激素受体(Estrogen receptor, ER)共同作用,激活或增强卵黄蛋白原(Vitellogenin, Vg)等靶基因的转录(Wu et al, 2008)。
光裸星虫(Sipunculus nudus)又名裸体方格星虫,俗称沙虫,主要栖息于暖水性海滨潮间带,在我国华南沿海资源量较为丰富(李凤鲁等, 1990; Li et al, 2017),其味道鲜美,含有大量谷氨酸、天冬氨酸等呈味氨基酸,具有很高的市场价值(罗少杰等, 2016)。近年来,光裸星虫逐渐成为广东湛江、广西北海等北部湾沿岸地区养殖新热点,但苗种短缺制约了产业发展。目前,关于光裸星虫繁殖生物学研究主要在形态学方面,尚未开展分子机制研究。如,王庆恒等(2017)报道了光裸星虫卵子发生的超微结构,建立了卵母细胞粒径、超微结构和发育阶段的对应关系;张家炜等(2018a)观察了光裸星虫胚胎和幼体发育的超微结构。光裸星虫体腔液中有大量生殖细胞游离发育,但直接解剖获取的卵母细胞不具备受精能力。解析卵母细胞成熟机制,有助于建立卵母细胞体外促熟技术,从而提高光裸星虫苗种产量,促进产业发展。作者所在课题组已构建了不同发育阶段卵子的转录组文库,分析表明,Hsp90在卵母细胞中表达量较高,可能在卵母细胞发育过程中起着重要作用(未发表)。
本研究通过RACE技术获得SnHsp90的cDNA全长,并对其序列结构、不同组织及不同卵子发育时期的表达模式进行分析,以探究SnHsp90在光裸星虫卵母细胞发育中的作用,为认识光裸星虫卵母细胞发育的分子机制积累基础资料。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料实验所用光裸星虫于2018年6月采集自广东省湛江市草潭镇潮间带,取钻沙有力、体壁无伤的雌性虫体用于实验,体重为(12.92±1.68) g。
灭菌海水清洗虫体表面砂砾后,用2 ml注射器抽取少量体腔液,镜检分辨雌雄。取30尾雌虫,每尾抽取2 ml体腔液,分别置于5 ml离心管中冰浴静置5 min,卵母细胞沉降到管底,上层悬浮液中则含有各类血细胞、卵原细胞等。弃悬浮液,在沉淀中加入RNA Later吹打混匀,冰浴静置5 min,弃上清液,再次加入RNA Later吹打混匀。将获得的卵母细胞悬浮液全部置于50 ml烧杯中混合,逐次使用100、150和300目的细胞筛进行分级分离,结合王庆恒等(2017)工作,获得的各级卵母细胞的直径及发育时期分别为:Egg1 (< 48 μm,卵黄形成初期)、Egg2 (48~108 μm,卵黄旺盛合成前期)、Egg3 (108~150 μm,卵黄旺盛合成后期)和Egg4 (> 150 μm,成熟期)(图 1)。

|
图 1 光裸星虫不同时期卵母细胞形态 Fig.1 Oocytes of S. nudus at different developmental stages A:卵黄形成初期(Egg1);B:卵黄旺盛合成前期(Egg2);C:卵黄旺盛合成后期(Egg3);D:成熟期(Egg4);E:肾管发育时期(Egg5);F:外排卵母细胞(Egg6)。图 8同 A: Oocyte in beginning of yolk synthesis; B: Oocyte in early stage of vigorous yolk synthesis; C: Oocyte in late stage of vigorous yolk synthesis; D: Oocyte in mature stage; E: Oocytes in the nephridioduct; F: Excretive oocyte. The same as Fig. 8 |
解剖雌虫,如果肾管充盈,即用过滤海水清洗肾管表面,将肾管游离端轻轻放入2 ml离心管中,用解剖针刺破肾管收集卵母细胞,加入RNA Later吹打混匀。本研究共获得30尾雌虫肾管中的卵母细胞,混合后作为样品Egg5 (肾管发育时期)。另取30尾雌虫,阴干刺激后放入过滤海水中促使排卵,用100目筛绢网捞取水体中的外排卵母细胞,加入RNA Later吹打混匀作为样品Egg6 (外排卵母细胞)。
解剖取9尾雌虫取体壁(M)、肠道(I)、收吻肌(Rm)、肾管(Ne)组织以及体腔液细胞(Co),液氮速冻,并转移至–80℃冰箱保存,用于RNA提取。
1.2 SnHsp90基因全长cDNA克隆总RNA提取及第一链cDNA合成参照赖卓欣等(2019)的方法进行。根据本课题组前期光裸星虫转录组数据中Hsp90的部分序列,利用Primer premier 6.0软件设计引物(表 1)。
|
|
表 1 SnHsp90基因克隆及荧光定量的引物序列 Tab.1 Primer sequence used in the cloning and real-time PCR of SnHsp90 gene |
采用巢式PCR扩增SnHsp90 3´UTR和5´UTR,PCR产物利用1%琼脂糖电泳检测,产物与载体pMD18-T连接,连接产物转化至DH5α感受态细胞,并在固体氨苄选择培养基上培养12 h。挑取阳性单克隆菌落进行PCR检测,合格后送至生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司测序。
1.3 SnHsp90序列分析利用DNAman 8对测序结果进行拼接,获得SnHsp90全长。采用ORF Finder (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder)预测SnHsp90的开放阅读框(Open Reading Frame, ORF)以及蛋白质氨基酸序列。利用ProtParam(https://web.expasy.org/protparam/)进行理化性质及二级结构预测。ProtComp 9.0(http://linux1.softberry.com/berry.phtml?topic=protcompan&group=programs&subgroup=proloc)进行蛋白亚细胞定位。NCBI Blast在线分析工具(https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)进行序列同源性、一致性性分析。Phyer2 (http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/~phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index)预测蛋白三级结构。smart进行保守结构域预测(http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/)。MEME (http://meme-suite.org/index.html)进行motif挖掘。使用Mega X构建生物系统进化树。
1.4 SnHsp90差异表达分析分别以TBP(张家炜等, 2018b)和60s-L7(筛选过程未发表)基因作为内参基因,检测SnHsp90在成体不同组织及在不同发育时期卵母细胞的表达水平。反应体系:上下游引物各0.4 μl,SYBR® Select Master Mix 5 μl,cDNA模板0.4 μl,灭菌水3.8 μl。反应条件:95℃预变性2 min,95℃变性15 s,60℃退火延伸1 min,共40个循环。采用2–ΔΔCt法计算SnHsp90的相对表达量。通过IBM SPSS Statistics 22进行显著性分析(置信水平取95%)。
2 结果与分析 2.1 SnHsp90基因克隆及氨基酸序列本研究利用RACE技术克隆获得光裸星虫SnHsp90基因cDNA序列,全长3110 bp,其中,5′ UTR为72 bp;3′ UTR为582 bp,开放式阅读框(ORF)长度为2456 bp,编码818个氨基酸。SnHsp90同时具有B型Hsp90(Hsp90B)的3个特征序列(FLREL、IGQFGVGFYS、LPLNVSRE)以及保守模块“GxxGxG” (图 2)。

|
图 2 SnHsp90 cDNA序列全长及推导的氨基酸序列 Fig.2 The full length and deduced amino acid sequence of SnHsp90 cDNA 黄色背景为Hsp90B蛋白家族的特征序列;GxxGxG以红色字体突出;5′和3′ UTR用小写字母表示;编码区以及推导的氨基酸序列用大写字母表示;信号肽以灰色阴影突出;HATPase_c结构域以黑框框出;Hsp90结构域以蓝色字体突出 The yellow background is the characteristic sequence of the Hsp90B protein family; the GxxGxG motif is highlighted in red; 5' UTR and 3' UTR are indicated with small letters; open reading fragment and the deduced amino acid sequences are indicated with capital letters; the signal peptide is highlighted by a gray shadow; the HATPase_c domain is outlined in black box; the Hsp90 domain is highlighted in blue |
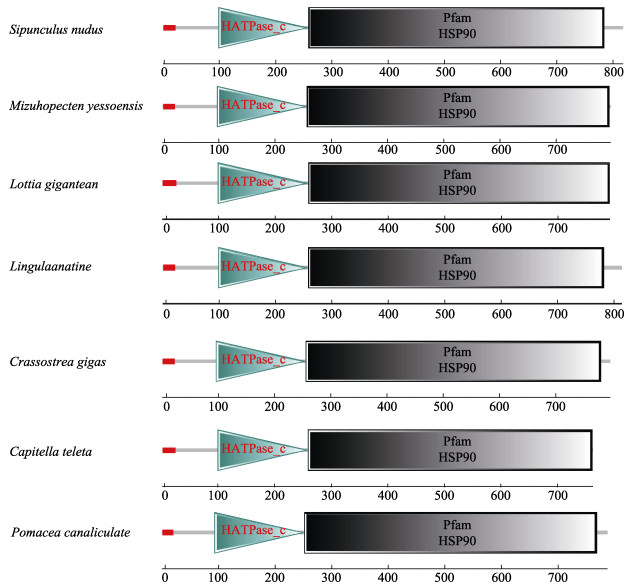
利用ProtParam预测得到SnHsp90的理论分子量为93.839 kDa,等电点为4.75,负电荷残基178个,正电荷残基114个。结果显示,其脂溶指数(Aliphatic index)为77.98,总平均亲水性(Grand average of hydropathy, GRAVY)为–0.752,属于亲水性蛋白。使用SOPMA软件对SnHsp90二级结构进行预测,发现螺旋、转角和延伸链分别占整体的55.87%、4.28%和12.59%。细胞亚定位预测结果显示,SnHsp90定位于内质网上。结构域分析显示,不同物种的Hsp90都含有信号肽、组氨酸激酶结构域(HATPase-c Domain)和热休克蛋白结构域(Hsp90 Domain)(图 3),可见Hsp90蛋白在结构域上具有高度保守性。
|
图 3 不同物种Hsp90蛋白的结构域 Fig.3 The domains of of Hsp90 proteins of different species 红色部分为信号肽;绿色三角HATPase_c结构域;黑色矩形为Hsp90结构域;各物种hsp90基因序列登录号:虾夷扇贝OWF41993.1;猫头鹰帽贝XP_009065664.1;鸭嘴海豆芽XP_023932276.1;太平洋牡蛎BAF63637.1;小头虫ELU00023.1;福寿螺XP_025107756.1 Red section is signal peptide; green triangle is HATPase_c domain; black rectangle is Hsp90 domain; The hsp90 GenBank accession numbers of each species are following: Mizuhopecten yessoensis, OWF41993.1; Lottia gigantean, XP_009065664.1; Lingula anatine, XP_023932276.1; Crassostrea gigas, BAF63637.1; Capitella teleta, ELU00023.1; Pomacea canaliculated, XP_025107756.1 |
对来源于鸭嘴海豆芽(Lingula anatine, XP_ 023932276.1)、小头虫(Capitella teleta, ELU00023.1)、福寿螺(Pomacea canaliculated, XP_025107756.1)、太平洋牡蛎(Crassostrea gigas, BAF63637.1)、水蛭(Helobdella robusta, XP_009019107.1)、猫头鹰帽贝(Lottia gigantean, XP_009065664.1)、虾夷扇贝(Mizuhopecten yessoensis, OWF41993.1)、白氏文昌鱼(Branchiostoma belcheri, XP_019627224.1)、棘冠海星(Acanthaster planci, XP_022100344.1)、斑马拟丽鱼(Maylandia zebra, XP_004567801.1)、尼罗罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus, XP_003443932.1)、杂色鳉(Cyprinodon variegatus, XP_015232211.1)、隆头蛛(Stegodyphus mimosarum, KFM57735.1)、银大马哈鱼(Oncorhynchus kisutch, XP_020311813.1)、大弹涂鱼(Boleophthalmus pectinirostris, XP_020790709.1)的Hsp90蛋白与光裸星虫Hsp90序列进行motif分析,结果表明,各物种Hsp90蛋白序列保守性较高(图 4)。其中,光裸星虫Hsp90与鸭嘴海豆芽的相似性最高,为77.72%;与大弹涂鱼的相似性最低,为69.18%。对不同物种的Hsp90蛋白序列进行Motif分析,发现这些物种均具有Motif (1~10),且相对位置一致,进一步表明Hsp90蛋白在序列上的保守性。

|
图 4 Hsp90氨基酸序列Motif分析 Fig.4 Motif analysis of amino acid sequence of Hsp90 |
对来自小头虫、鸭嘴海豆芽、水蛭的Hsp90和SnHsp90进行三级结构预测,结果发现,光裸星虫与鸭嘴海豆芽、小头虫、水蛭Hsp90在三级结果上相似性很高(图 5),说明Hsp90蛋白的三级结构非常保守。

|
图 5 光裸星虫(A)、鸭嘴海豆芽(B)、小头虫(C)和水蛭(D)Hsp90蛋白分子结构 Fig.5 The spatial structure of Hsp90 protein molecules of S. nudus (A), L. anatina (B), C. teleta(C) and H. robusta (D) |
利用最大似然法(Maximum likelihood),选择光裸星虫、太平洋牡蛎、福寿螺、猫头鹰帽贝、虾夷扇贝、鸭嘴海豆芽、小头虫、水蛭、白氏文昌鱼、杂色鳉、尼罗罗非鱼、斑马拟丽鱼、大弹涂鱼以及银大马哈鱼的Hsp90蛋白序列构建系统进化发育树。结果显示,Hsp90系统发育树可分为无脊椎动物和脊椎动物两大支,在无脊椎动物中,光裸星虫Hsp90与水蛭、小头虫等环节动物聚为一支,再与鸭嘴海豆芽、太平洋牡蛎、虾夷扇贝等软体动物聚为一支(图 6)。系统发育树聚类结果与传统分类学结果一致。

|
图 6 Hsp90蛋白质聚类分析 Fig.6 Protein cluster analysis of Hsp90 |
利用qRT-PCR对SnHsp90进行不同组织的表达模式分析,结果显示,SnHsp90在光裸星虫的各个组织中均有表达,且收吻肌中表达量最高,差异显著(P < 0.05) (图 7)。

|
图 7 光裸星虫SnHsp90在不同组织中的相对表达量 Fig.7 Relative expression of SnHsp90 in different tissues M:体壁;I:肠;Rm:收吻肌;Ne:肾管;Co:体腔液细胞。不同字母代表差异性显著(P < 0.05), 下同 M: Body wall; I: Intestine; Rm: Rhynchonellida muscle; Ne: Nephridioduct; Co: Coelomic cell. Different letters mean significant difference (P < 0.05). The same as below |
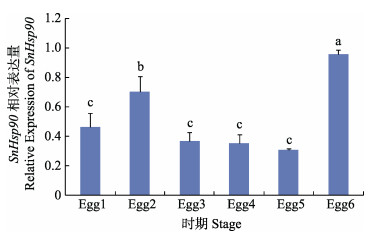
如图 8所示,SnHsp90在不同发育时期卵母细胞中均有表达。其中,在Egg6的表达量显著高于其他时期(P < 0.05),Egg2表达量显著高于Egg1和Egg3~5 (P < 0.05)。
|
图 8 SnHsp90在不同时期卵母细胞中的相对表达量 Fig.8 Relative expression of SnHsp90 in oocytes at different periods |
生殖细胞发生是水产动物繁殖生物学研究的重要内容。近年来,通过构建不同发育时期性腺的转录组文库,已发掘了大量与水产动物繁殖相关的关键基因。例如,袁静(2013)比较分析了5~180日龄尼罗罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus)性腺转录组,发现雌雄性腺特异表达的基因分别为69个和259个。林睿涓(2017)利用七彩神仙鱼(Symphysodon haraldi)性腺转录组文库,筛选出12个与性别决定、性腺发育和性激素调控相关的重要功能基因。本课题组前期构建了光裸星虫卵母细胞的转录组文库,分析发现Hsp90在各时期卵母细胞均具有较高的表达水平(未发表),暗示着其在卵母细胞或胚胎发育中承担着重要作用。本研究通过分析SnHsp90的序列特征及表达模式,探索其在卵母细胞发育中可能具有的功能。
Hsp90家族可分为Hsp90A、Hsp90B、TNF受体相关因子(TNF receptor associated factors, TRAP)、Hsp90C、高温蛋白G (High-temperature protein G, HTPG) 5个亚家族,其中,Hsp90B定位于真核生物内质网中,含有信号肽结构,序列上同时存在“FLREL”、“IGQFGVGFYS”及“LPLNVSRE” 3个标签序列(Chen et al, 2006)。本研究利用RACE方法克隆获得SnHsp90 cDNA全长序列,显示SnHsp90具有信号肽结构,且存在Hsp90B亚家族的上述3个特征序列标签,可见本研究克隆所得的SnHsp90属于Hsp90B亚家族。一般来说,Hsp90B亚家族的C末端具有内质网定位序列“KDEL”。然而,有研究指出,该序列在Hsp90B中并不保守,其K位点和D位点会发生一定的变化(Gupta, 1995; Chen et al, 2006)。这与本研究发现的SnHsp90氨基酸序列C末端序列为“HTEL”的结果一致。
对软体动物、棘皮动物、脊椎动物等16个物种进行motif搜索,发现不同物种间搜索出来的motif类型、数目以及排列顺序上均一致;光裸星虫、鸭嘴海豆芽、小头虫和水蛭同源Hsp90在三维结构上高度相似。以上结果均说明了Hsp90在二级和三级序列上均具有较高的保守性。
Hsp90B也称为葡萄糖调节的蛋白(Glucose regulated protein 94 kDa, Grp94) (Gupta, 1995; Chen et al, 2006),作为分子伴侣时,有助于蛋白质的正确折叠以及防止错误折叠蛋白的积累(Young et al, 2001; Mamipour et al, 2017; Krüger et al, 2019);参与免疫球蛋白、Toll样受体(Toll-like receptors, TLRs)和某些整联蛋白(Integrin)的折叠、组装和转运等过程(Melnick et al, 1992; Yang et al, 2007)。本研究中,SnHsp90在收吻肌、体壁、肠等组织中均有表达,提示该基因广泛参与了各组织的生理活动。在收吻肌的参与下,光裸星虫的吻可快速伸缩进行摄食和钻穴。在频繁的强力伸缩过程中,收吻肌的细胞可能发生损伤,SnHsp90在收吻肌中的表达量显著高于其他组织,推测与细胞的损伤修复有关。
卵母细胞发育过程中,核糖体、内质网、高尔基体等细胞器大量增殖,积累大量酶、蛋白质、mRNA等物质。本研究显示,SnHsp90在光裸星虫各时期卵母细胞中均有较高表达,有利于快速合成蛋白的正确折叠,与卵母细胞旺盛的转录和翻译活动相一致。有研究显示,Hsp90可与Greatwall激酶结合,影响生殖细胞的细胞周期进程(Yamamoto et al, 2014)。在刀额新对虾中,Hsp90与雌激素受体结合,介导雌激素信号转导过程,开启靶基因如卵黄蛋白原的转录(Wu et al, 2008)。光裸星虫卵母细胞Egg2处于卵黄旺盛合成前期,卵黄快速积累(王庆恒等, 2017),本研究显示,光裸星虫SnHsp90在该时期显著高表达(P < 0.05),暗示SnHsp90的表达可能与卵黄合成之间存在相关性,与刀额新对虾的研究结果相似。
Hsp90在水生生物应激和抗逆过程中具有重要作用。例如,Hsp90B在莱茵衣藻(Chlamydomonas reinhardtii)耐盐群体的细胞中表达上调,可能在盐度耐受方面起作用(Sithtisarn et al, 2017);三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)具有2个Hsp90基因,对胁迫条件可产生不同的响应,例如,热处理导致Hsp90-1的表达量显著上调,而Hsp90-2则显著下调(Zhang et al, 2009);氨氮胁迫下,中国对虾(Fenneropenaeus chinensis)鳃、肝胰腺、肌肉和血细胞的Hsp90表达量均在短时间内明显上调,有利于防止分子氨对组织细胞的损伤(王芸等, 2013)。本研究中,Egg6是经肾管排放到水体中的卵母细胞,需要应对体内外渗透压、pH、离子浓度等环境因子的重大改变,SnHsp90在Egg6时期表达量最高,暗示SnHsp90的高表达可能与卵母细胞应对环境变化密切相关。
Chen B, Zhong D, Antónia M. Comparative genomics and evolution of the Hsp90 family of genes across all kingdoms of organisms. BMC Genomics, 2006, 7(1): 156-156 DOI:10.1186/1471-2164-7-156 |
Gupta RS. Phylogenetic analysis of the 90 kD heat shock family of protein sequences and an examination of the relationship among animals, plants, and fungi species. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1995, 12(6): 1063-1073 |
Krüger K, Thomas R, Carsten Z, et al. Role of heat shock proteins 70/90 in exercise physiology, exercise immunology and their diagnostic potential in sports. Journal of Applied Physiology, 2019, 126(4): 916-927 DOI:10.1152/japplphysiol.01052.2018 |
Lai BT, Chin NW, Stanek AE, et al. Quantitation and intracellular localization of the 85K heat shock protein by using monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 1984, 4(12): 2802-2810 DOI:10.1128/MCB.4.12.2802 |
Lai ZX, Liu Y, Wang QH, et al. cDNA cloning of FBP gene in Pinctada fucata martensii and its response to temperature stress. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2019, 40(2): 106-114 [赖卓欣, 刘雅, 王庆恒, 等. 马氏珠母贝(Pinctada fucata martensii) FBP基因的克隆及其对温度胁迫的响应. 渔业科学进展, 2019, 40(2): 106-114] |
Li FL, Kong QL, Shi GT, et al. Studies on the genus Sipunculus(Sipuncula) of the China coasts. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 1990, 20(1): 93-99 [李凤鲁, 孔庆兰, 史贵田, 等. 中国沿海方格星虫属(星虫动物门)的研究. 青岛海洋大学学报, 1990, 20(1): 93-99] |
Li J, Xie X, Zhu C, et al. Edible peanut worm (Sipunculus nudus) in the Beibu Gulf:Resource, aquaculture, ecological impact and counterplan. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2017, 16(5): 823-830 DOI:10.1007/s11802-017-3310-z |
Lindquist S, Craig EA. The heat-shock proteins. Annual Review of Genetics, 1988, 22(3): 631-677 |
Lin RJ.Gonad transcriptome of discus fish (Symphysodon haraldi) and expression of vasa gene.Masterxs Thesis of Shanghai Ocean University, 2017 [林睿涓.七彩神仙鱼(Symphysodon haraldi)性腺转录组分析及vasa基因的时空表达.上海海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2017]
|
Luo SJ, Yang CY, Wang QH, et al. Nutrition components analysis and evaluation on four wild populations of peanut worm Sipunculus nudus. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2016, 36(1): 25-30 [罗少杰, 杨创业, 王庆恒, 等. 光裸星虫4个野生群体的营养成分分析与品质评价. 广东海洋大学学报, 2016, 36(1): 25-30] |
Mamipour M, Yousefi M, Hasanzadeh M. An overview on molecular chaperones enhancing solubility of expressed recombinant proteins with correct folding. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2017, 102: 367-375 DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.025 |
McClellan AJ, Xia Y, Deutschbauer AM, et al. Diverse cellular functions of the Hsp90 molecular chaperone uncovered using systems approaches. Cell, 2007, 131(1): 121-135 DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.036 |
Melnick J, Aviel S, Argon Y. The endoplasmic reticulum stress protein GRP94, in addition to BiP, associates with unassembled immunoglobulin chains. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1992, 267(30): 21303-21306 |
Sithtisarn S, Yokthongwattana K, Mahong B, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii control and a salinity-tolerant strain revealed a differential protein expression pattern. Planta, 2017, 246(5): 843-856 DOI:10.1007/s00425-017-2734-4 |
Wang Y, Li J, Zhang Z, et al. Effects of pH and ammonia-N stresses on HSP90 gene expression of Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2013, 34(5): 43-50 [王芸, 李健, 张喆, 等. pH、氨氮胁迫对中国对虾HSP90基因表达的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2013, 34(5): 43-50] |
Wang QH, Zhang JW, Hao RJ, et al. Ultrastructure of oogenesis in coelomic fluid of Sipunculus nudus. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(1): 57-66 [王庆恒, 张家炜, 郝瑞娟, 等. 光裸星虫体腔液中卵母细胞发生的超微结构. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(1): 57-66 DOI:10.11693/hyhz20160600123] |
Wu LT, Chu KH. Characterization of heat shock protein 90 in the shrimp Metapenaeus ensis:Evidence for its role in the regulation of vitellogenin synthesis. Molecular Reproduction and Development, 2008, 75(5): 952-959 DOI:10.1002/mrd.20817 |
Yamamoto TM, Wang L, Fisher LA, et al. Regulation of Greatwall kinase by protein stabilization and nuclear localization. Cell Cycle, 2014, 13(22): 3565-3575 DOI:10.4161/15384101.2014.962942 |
Yang Y, Liu B, Dai J, et al. Heat shock protein gp96 is a master chaperone for Toll-like receptors and is important in the innate function of macrophages. Immunity, 2007, 26(2): 215-226 DOI:10.1016/j.immuni.2006.12.005 |
Young JC, Moarefi I, Hartl FU. Hsp90:A specialized but essential protein-folding tool. Journal of Cell Biology, 2001, 154(2): 267-273 DOI:10.1083/jcb.200104079 |
Yuan J.Characterization of gonadal transcriptomes from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and bioinformatic analysis of Fox gene family.Masterxs Thesis of Southwest University, 2013 [袁静.尼罗罗非鱼性腺发育过程的转录组学研究及Fox家族生物信息学分析.西南大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2013]
|
Zhang JW, Hao RJ, Wang QH, et al. Microscopic and ultrastructural observations of embryonic and larval development in Sipunculus nudus. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2018a, 25(5): 976-987 [张家炜, 郝瑞娟, 王庆恒, 等. 光裸星虫胚胎和幼体发育的显微和超微结构. 中国水产科学, 2018a, 25(5): 976-987] |
Zhang JW, Zheng Z, Wang QH, et al. Screening of reference genes for real-time PCR in whole tissue from Sipunculus nudus. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2018b, 38(1): 7-13 [张家炜, 郑哲, 王庆恒, 等. 光裸星虫全组织荧光定量PCR分析中内参基因的筛选. 广东海洋大学学报, 2018b, 38(1): 7-13] |
Zhang XY, Zhang MZ, Zheng CJ, et al. Identification of two hsp90 genes from the marine crab, Portunus trituberculatus and their specific expression profiles under different environmental conditions. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C:Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2009, 150(4): 465-473 DOI:10.1016/j.cbpc.2009.07.002 |
Zhu JA.The effects of injecting c-mos siRNA on maturation, fertilization and development of porcine oocyte.Institute of Biotechnology Ilan University, 2007 [朱建安.注射c-mos siRNA对猪卵母细胞成熟, 受精及发育的影响.宜兰大学生物技术研究所, 2007]
|



