2. 中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所 青岛海洋科学与技术试点国家实验室海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程功能实验室 青岛 266071
2. Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Qingdao 266071)
脊椎动物的性别通常由基因型决定,其性别一旦形成就很难发生改变,这种性别决定方式称为遗传型性别决定(Genetic sex determination, GSD)。但在一些爬行类、两栖类、鱼类等相对低等的脊椎动物中,外界环境因素,诸如温度、pH、密度及社会性等都有可能影响性别,而这种性别决定方式称为环境型性别决定(Environmental sex determination, ESD) (Francis 1984; Rubin, 1985; Francis et al, 1993; Tabata, 1995)。前期研究发现,皮质醇在ESD型物种响应外界环境压力方面起到重要作用(Sadoul et al, 2019)。在鱼类中,温度是主要的外界压力源,外界温度的变化会显著增加机体或细胞的皮质醇水平,从而对鱼类生殖生长、性别分化等产生影响(Wendelaar Bonga, 1997; Mommsen et al, 1999)。在大西洋鲑(Salmo salar)幼鱼时期,注射皮质醇后发现,雄鱼的比例增加并且卵巢生长受到抑制(van den Hurk et al, 1985)。在牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)性别决定时期,高温引起皮质醇的增加,进而导致雄性比例升高(Yamaguchi et al, 2010)。截至目前,皮质醇介导温度进而影响性别决定的机制尚不完全清楚。
羟基类固醇11β脱氢酶(Hydroxysteroid 11-beta dehydrogenase, HSD11β)属于氧化还原酶家族,调控活性和无活性皮质酮间的相互转化,同时,还参与类固醇代谢的生理过程(Krozowski, 1999)。在哺乳动物中,羟基类固醇11β脱氢酶存在2个亚型,分别为11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (hsd11b1)和hsd11b2。hsd11b1的功能是将无活性的皮质酮转化为有活性的皮质醇,hsd11b2的功能则相反(Albiston et al, 1994; Hu et al, 2019)。鱼类不存在hsd11b1基因,而存在其同源基因Hydroxysteroid 11-beta dehydrogenase 1 like (hsd11b1l)(Tsachaki et al, 2017)。在斑马鱼(Danio rerio)和虱目鱼(Chanos chanos)中,hsd11b1l可以增加皮质醇的水平,这与哺乳动物中hsd11b1的功能相似(Baker, 2010; Hu et al, 2019)。hsd11b2可以降低鱼类组织皮质醇水平,从而保护组织免受皮质醇的伤害,并参与雄激素的合成(Alderman et al, 2012; Tokarz et al, 2013)。研究表明,高水平的雄激素可以直接影响鱼类的性别决定和分化(Miura et al, 2008; Hattori et al, 2009; Blasco et al, 2010)。牙汉鱼(Odontesthes bonariensis)高温诱导雄性化过程中,皮质醇通过调节hsd11b2高表达促进雄激素生成,从而驱动精巢发生(Fernandino et al, 2012)。
半滑舌鳎(Cynoglossus semilaevis)是我国重要的经济鱼类。研究表明,半滑舌鳎的性别决定类型是ZZ/ZW型,但其性别分化也受到外界环境的直接影响。在半滑舌鳎性别决定和分化的关键时期,高温可以诱导遗传雌性向表型雄性逆转(Chen et al, 2014)。因此,半滑舌鳎是理解温度与性别分化关系的理想模型。在本研究中,通过RACE克隆获得半滑舌鳎hsd11b1l和hsd11b2的cDNA全长,并对序列特征进行生物信息学分析,进而通过荧光定量PCR技术,分析其时空表达特征及温度响应的表达规律,可为后续深入探究温度与性别分化的关系提供基础信息。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料本实验用半滑舌鳎均取自山东海阳黄海水产有限公司。随机选取3龄半滑舌鳎雌鱼和雄鱼各3条,解剖后取脑、心脏、肠、鳃、脾脏、肾脏、肝脏、皮肤、精巢及卵巢。此外,取不同发育时期(30日龄、50日龄、3月龄、6月龄、2龄和3龄)半滑舌鳎性腺或性腺区域。将280尾30日龄的半滑舌鳎鱼苗随机等分为2组,分别采用高温(28℃)及常温(22℃)处理2个月,并在3月龄时解剖取性腺组织样品;另取140尾3月龄半滑舌鳎鱼苗,随机等分为2组,分别进行高温(28℃)与常温(22℃)处理,48 h后解剖取性腺组织样品。将上述样品液氮速冻后放入超低温冰箱保存。所有半滑舌鳎同时取尾鳍组织保存于酒精中,通过实验室前期建立的性别特异分子标记方法进行遗传性别鉴定(Jiang et al, 2017; Cui et al, 2018),对于3月龄半滑舌鳎,进一步结合dmrt1基因的相对表达量剔除伪雄鱼(Cui et al, 2017)。
1.2 半滑舌鳎hsd11b1l和hsd11b2的全长克隆使用RNAprep pure Tissue Kit (Tiangen, 中国)提取3龄半滑舌鳎的精巢组织总RNA,并使用PrimeScriptTM Ⅱ 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (TaKaRa, 日本)完成cDNA反转录。根据半滑舌鳎基因组中的hsd11b1l (GenBank ID: XM_025065042)和hsd11b2 (GenBank ID: XM_008310169)基因序列,利用Primer 6.0设计引物(hsd11b1l-F/R和hsd11b2-F/R) (表 1)。利用SMARTTM RACE cDNA Amplification Kit (Clontech, 美国)进行5′和3′RACE克隆。RACE引物如表 1所示。PCR产物经纯化,克隆到pEasy-T1载体(TransGen, 中国)并进行测序。
|
|
表 1 实验所用到的引物 Tab.1 Primers used in the experiments |
通过在线工具SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/)预测了hsd11b1l和hsd11b2的蛋白质结构。使用AliBaba2.1(http://gene-regulation.com/pub/programs/alibaba2/index.html)对hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因启动子区域(转录起始位点上游500 bp和5'UTR区域)进行转录因子结合位点预测。从NCBI下载不同物种的蛋白质序列,然用根据软件MEGAX使用Neighbor- Joining (NJ)法构建系统进化树(Bootstrap=1000)。
1.4 半滑舌鳎hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因的表达分析选取各样本高质量的RNA 1 μg,利用PrimeScript RT reagent Kit (Takara, 日本)试剂盒反转录生成cDNA。设计hsd11b1l和hsd11b2的荧光定量检测引物(表 1),进行实时荧光定量PCR (Real-time PCR)表达分析。使用QuantiNovaTM SYBR Green PCR Kit (Qiagen, 德国)试剂盒,反应体系为20 μl,分别包含1 μl cDNA模板、10 μl SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (2×)、2 μl QN ROX Reference Dye及0.7 μmol/L的正向和反向引物。反应在ABI StepOnePlus_Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, 美国)进行,程序为95℃ 2 min;95℃ 5 s, 60℃ 10 s,共40个循环;95℃ 5 s, 60℃ 1 min, +1℃/min, 95℃ 15 s。内参用β-actin基因片段(β-actin-qF/R,表 1)。每个反应体系设置3个技术重复。使用2–ΔΔCt方法分析hsd11b1l以及hsd11b2基因在半滑舌鳎雌雄各组织、不同发育时期及温度处理样品中的表达水平(Livak et al, 2001; Li et al, 2010)。利用T-检验分析显著性,P < 0.05表示差异显著。
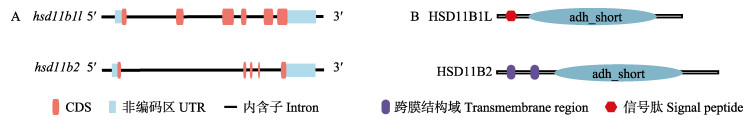
2 结果与分析 2.1 hsd11b1l和hsd11b2克隆和序列分析通过RACE克隆获得半滑舌鳎hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因的cDNA全长。hsd11b1l的cDNA全长为1650 bp,包含97 bp的5'UTR和689 bp的3'UTR,开放性阅读框(Open Reading Frame, ORF)为864 bp,编码287个氨基酸,蛋白质的分子量为31.79 kDa,预测理论等电点(pI)为7.65(图 1)。启动子区域转录因子结合位点预测分析显示,hsd11b1l启动子区域存在NF-kappaB、AP-1、E2、GATA-1、GR、PR、C/EBPalp、C/EBPbeta、TBP、HNF1、HNF3等转录因子结合位点。hsd11b2基因的cDNA全长为4526 bp,包括1209 bp的ORF,5′UTR和3′UTR长度分别为403 bp和2914 bp,编码402个氨基酸,预测分子量为44.5 kDa,理论等电点为8.38(图 2)。启动子区域转录因子结合位点预测分析显示,hsd11b2启动子区域包含GR、TBP、Sp1、Ahr、PR、Sox-2、C/EBPalp、Elk-1、HNF-3、COUP、GATA-1等转录结合位点。将hsd11b1l和hsd11b2 mRNA比对到对应DNA序列,显示hsd11b1l包含6个外显子,hsd11b2包含5个外显子(图 3A)。

|
图 1 半滑舌鳎hsd11b1l基因核苷酸序列及推测的氨基酸序列 Fig.1 Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of Cynoglossus semilaevis hsd11b1l 方框内为起始密码子和终止密码子,黑色下划线表示polyA信号,红色下划线表示信号肽位置,蓝色下划线表示保守结构域 Frames indicate the start codon and stop codon, respectively. Black underline indicates the PolyA tail sequence, red underline indicates signal peptide, and blue underline indicates conserved domain |

|
图 2 半滑舌鳎hsd11b2基因核苷酸序列及推测的氨基酸序列 Fig.2 Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of C. semilaevis hsd11b2 方框内为起始密码子和终止密码子,黑色下划线表示polyA信号,紫色下划线表示跨膜结构域,蓝色下划线表示保守结构域 Frames indicate the start codon and stop codon, respectively. Black underline indicates the PolyA tail sequence, violet underline indicates transmembrane region, blue underline indicates conserved domain |
|
图 3 半滑舌鳎hsd11b1l和hsd11b2的基因结构分析及蛋白结构域预测 Fig.3 The gene structure analysis and protein domain prediction of C. semilaevis hsd11b1l and hsd11b2 A:基因结构示意图,外显子用红色框表示,DNA序列用黑线表示,UTR用蓝框表示;B:HSD11B1L和HSD11B2保守结构域 A: Schematic representation of genomic structure. The exons were represented by red boxes, DNA sequences were indicated by lines, and UTRs were shown as blues boxes; B: The predicted conserved domain of HSD11B1L and HSD11B2 |
利用SMART预测了半滑舌鳎HSD11B1L和HSD11B2的蛋白结构。结果显示,这2个蛋白都存在1个保守的结构域,为短链脱氢酶(adh_short),其中,HSD11B1L还具有信号肽,HSD11B2包含2个跨膜结构域(图 3B)。根据ExPASy (https://www.expasy.org/)的GOR Ⅳ工具预测HSD11B1L和HSD11B2蛋白的二级结构,结果表明,HSD11B2蛋白的α-螺旋和无规卷曲含量比HSD11B1L高,而延伸链的比例少。
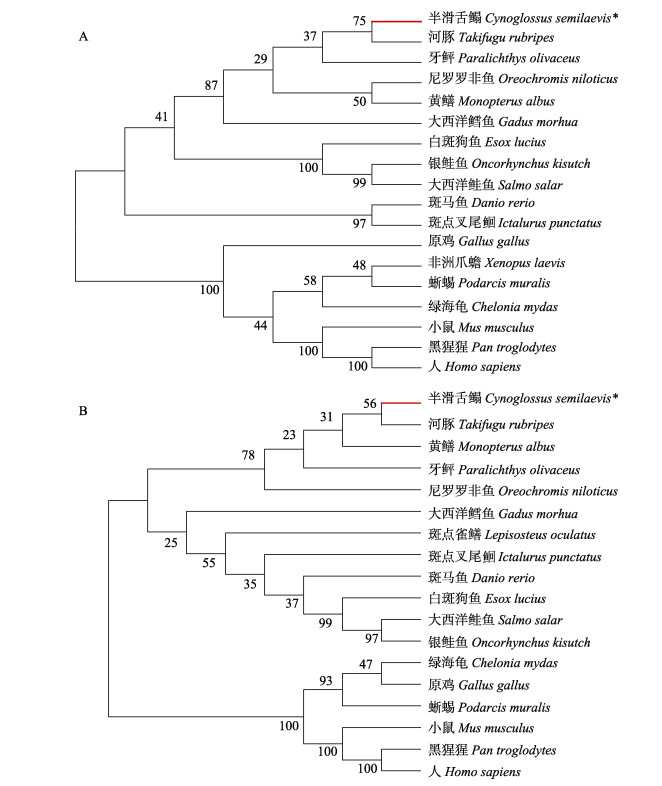
半滑舌鳎HSD11B1L和HSD11B2蛋白序列与其他物种同源性分析显示,HSD11B1L与河豚(Takifugu rubripes, XP_029684148.1)、牙鲆(XP_019936361.1)和斑马鱼(NP_ 956617.2) HSD11B1L蛋白的相似性分别为77.04%、73.08%和66.89%。HSD11B2蛋白与河豚(XP_029702217.1)、罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus, NP_001266686.1)和斑马鱼(NP_997885.2) HSD11B2蛋白的序列相似性分别为77.08%、75.33%和69.40%。进化树分析结果表明,HSD11B1L和HSD11B2均聚成了两支,一支是哺乳动物、鸟类、两栖动物和爬行动物,另一支是鱼类(图 4A、B)。
|
图 4 HSD11B1L和HSD11B2蛋白系统发育树 Fig.4 Phylogenetic analysis of HSD11B1L and HSD11B2 proteins A: HSD11B1L; B: HSD11B2 |
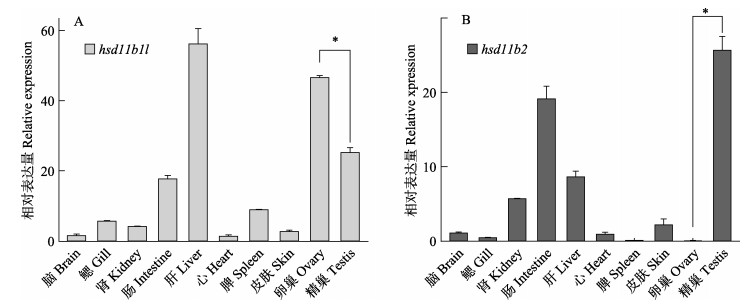
hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因在3龄半滑舌鳎不同组织的表达分析结果显示,hsd11b1l主要在肝脏、卵巢、精巢和肠中表达,并且卵巢中的表达量显著高于精巢(P < 0.05)。hsd11b2在精巢、肠、肝脏和肾脏中广泛表达,而在卵巢中几乎不表达(图 5)。
|
图 5 hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因在半滑舌鳎中的组织表达模式 Fig.5 Tissue expression analysis of hsd11b1l and hsd11b2 in C. semilaevis 数据用3个独立个体的Mean±SE表示(n=3)。*表示显著差异。下同 The mean±SE values from three separate individuals (n=3) are shown. Asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.05). The same as below |
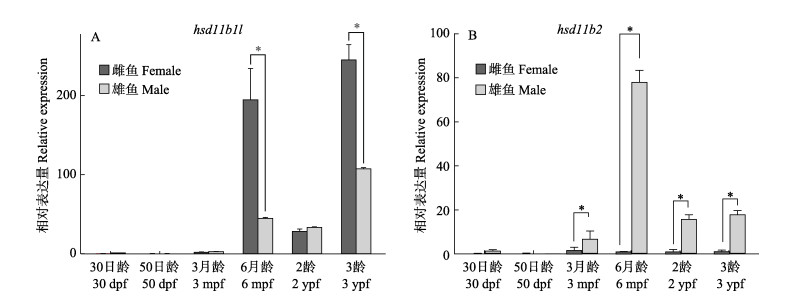
hsd11b1l在性别分化早期基本不表达,3月龄开始有微弱表达。在卵巢中,hsd11b1l在6月龄的表达量急剧升高,然后在2龄时期急剧下降,在3龄表达量重新上升并达到峰值;在精巢中,hsd11b1l表达与卵巢中类似,在6月龄表达量急剧升高,在2龄表达量略有下降,在3龄表达量重新上升并达到峰值,在6月龄及3龄中精巢的表达量均显著低于卵巢(P < 0.05) (图 5A)。
hsd11b2基因在性别分化早期基本不表达。在精巢中,hsd11b2在3月龄开始表达,6月龄达到峰值且显著高于其他时期(P < 0.05),随后在2龄表达量下降并维持较低水平至3龄;在卵巢中,各阶段均几乎无法检测到hsd11b2的表达(图 6B)。
|
图 6 hsd11b1l和hsd11b2在性腺发育阶段的表达模式 Fig.6 The hsd11b1l and hsd11b2 expression in gonad development stage |
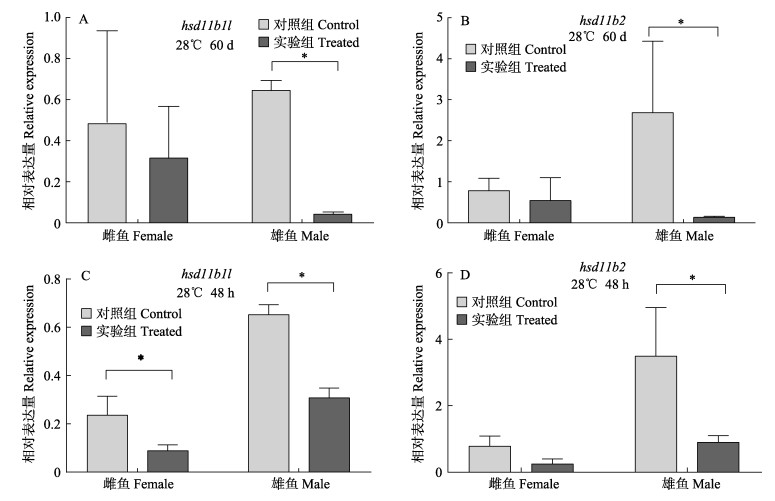
在30日龄到3月龄性别分化过程对半滑舌鳎进行高温(28℃)处理,hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因在雄鱼中的表达量均显著低于正常生长温度组(P < 0.05),在雌鱼中的表达量无显著差异(图 7A、B)。对3月龄幼鱼进行48 h的短期高温刺激后,hsd11b1l表达量在雌鱼和雄鱼中均显著下调,雌鱼为常温条件下的37.80%,雄鱼为47.18%;hsd11b2基因在雄鱼中显著下调表达,为常温对照组的25.65%(P < 0.05),在雌鱼中的表达量无显著差异(图 7C、D)。
|
图 7 高温(28℃)处理后hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因在性腺中的表达模式 Fig.7 Analysis of hsd11b1l and hsd11b2 expression after high temperature treatment (28℃) |
本研究克隆获得了半滑舌鳎hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因的cDNA全长,分析了基因序列特征。研究发现,2个基因都含有1个保守的短链脱氢酶结构域,该结构域属于链脱氢酶/还原酶家族(SDR),是一种重要的氧化还原酶家族(Ghosh et al, 1994),表明hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因在皮质醇的生理过程中具有氧化还原酶的作用。此外,hsd11b1l基因启动子序列中包含糖皮质激素受体(GR)、雌激素(E2)、TATA结合蛋白(TATA-binding protein, TBP)等转录结合位点,hsd11b2启动子区域包含糖皮质激素受体(GR)、雄激素受体(AHR)和TBP等转录结合位点。皮质醇是一种糖皮质激素,可以与糖皮质激素受体结合,在生长、生殖等生理活动中起到重要作用(Mommsen et al, 1999)。在牙鲆、青鳉(Oryzias latipes)、牙汉鱼等鱼类中,皮质醇参与高温诱导雄性化(Hattori et al, 2009; Hayashi et al, 2010; Yamaguchi et al, 2010)。雄激素和雌激素受体可以直接参与鱼类的性别发育调节。TBP则是一类可以与RNA聚合酶Ⅱ共同发挥作用的转录因子,在精子形成期过量表达,参与精细胞的形成(Schmidt et al, 1997)。
本研究分析了半滑舌鳎hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因的时空表达特征。组织表达结果显示,hsd11b1l基因主要在半滑舌鳎肝脏和性腺中表达,这与其他脊椎动物中的研究结果相似。HSD11B1是一种还原型酶,可以转化生成大量皮质醇并且增强糖皮质激素的作用,这种酶存在于人类的多种组织器官中,在肝脏、脂肪等关键的代谢组织中非常丰富(White et al, 1997; Tomlinson et al, 2004)。本研究结果显示,半滑舌鳎hsd11b1l于3月龄开始表达,在6月龄和3龄时期鱼的卵巢中显著高于其他时期和精巢。半滑舌鳎在6月龄左右开始分化形成卵母细胞,3龄已进入卵巢发育成熟期,暗示hsd11b1l可能参与半滑舌鳎卵巢发育过程(Chen et al, 2014; Li et al, 2016、2017)。前期研究表明,hsd11b2不仅催化皮质酮向皮质醇的转化过程,还可催化11-酮基雄烯二酮生成11-酮基睾酮,在雄激素的形成过程中起到至关重要的作用(Oppermann et al, 1997)。牙汉鱼hsd11b2可通过合成雄激素进而参与雄性化形成(Zhang et al, 2018)。在虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss)中,hsd11b2在调节精子发生过程中起到重要作用,其表达模式在雄鱼发育过程中发生显著变化(Liu et al, 2000; Kusakabe et al, 2002)。本研究中,半滑舌鳎hsd11b2主要在精巢中表达,在卵巢中几乎不表达,也提示该基因在精巢中发挥重要作用。对精巢各发育时期的进一步分析表明,hsd11b2在3月龄开始表达,在6月龄达到峰值,随后在成熟精巢中表达量下降,这一发现与半滑舌鳎精巢细胞分化时间吻合(Chen et al, 2014; Li et al, 2016; Chen et al, 2009),表明hsd11b2在生殖细胞分化增殖过程中起到重要作用。
在高温处理2个月后,hsd11b1l和hsd11b2在雄鱼中表达量均显著降低;高温处理48 h后,hsd11b1l在雌、雄鱼中表达量均显著降低,hsd11b2在雄鱼中表达量显著降低(P < 0.05),表明温度可影响皮质醇和皮质酮之间的相互转化。但在牙汉鱼中,高温处理14 d后,hsd11b2表达量升高,与本研究结果相反(Fernandino et al, 2012)。牙汉鱼分析的是hsd11b2在幼鱼躯干部位的表达变化,包括了肝、肠、性腺等多个组织。根据hsd11b2的功能及组织表达模式,肝脏也是其发挥作用的主要器官。因此,结果的不同可能反映了不同组织在应对高温时的不同表现。后续将针对hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因在肝脏和不同性腺中的作用机制展开更深入的研究。
综上所述,本研究报道了半滑舌鳎hsd11b1l和hsd11b2基因的全长序列,分析了它们在性腺发育过程以及高温胁迫后的表达规律,为进一步研究二者在温度介导半滑舌鳎性别分化过程中的机理奠定了基础。
Albiston AL, Obeyesekere VR, Smith RE, et al. Cloning and tissue distribution of the human 1lβ-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 enzyme. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 1994, 105(2): R11-R17 DOI:10.1016/0303-7207(94)90176-7 |
Alderman SL, Vijayan MM. 11-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 in zebrafish brain: A functional role in hypothalamus- pituitary-interrenal axis regulation. Journal of Endocrinology, 2012, 215(3): 393 DOI:10.1530/JOE-12-0379 |
Baker M. Evolution of 11[beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase- type 1 and 11[beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-type 3. Nature Precedings, 2010, 1 |
Blasco M, Fernandino JI, Guilgur LG, et al. Molecular characterization of cyp11a1 and cyp11b1 and their gene expression profile in pejerrey (Odontesthes bonariensis) during early gonadal development. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular and Integrative Physiology, 2010, 156(1): 110-118 DOI:10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.01.006 |
Chen SL, Tian YS, Yang JF, et al. Artificial gynogenesis and sex determination in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Marine Biotechnology, 2009, 11(2): 243-251 DOI:10.1007/s10126-008-9139-0 |
Chen SL, Zhang G, Shao CW, et al. Whole-genome sequence of a flatfish provides insights into ZW sex chromosome evolution and adaptation to a benthic lifestyle. Nature Genetics, 2014, 46(3): 253-260 DOI:10.1038/ng.2890 |
Cui Y, Wang WF, Ma LY, et al. New locus reveals the genetic architecture of sex reversal in the Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Heredity, 2018, 121(4): 319-326 DOI:10.1038/s41437-018-0126-6 |
Cui Z, Liu Y, Wang W, et al. Genome editing reveals dmrt1 as an essential male sex-determining gene in Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 42213 DOI:10.1038/srep42213 |
Fernandino JI, Hattori RS, Kishii A, et al. The cortisol and androgen pathways cross talk in high temperature-induced masculinization: The 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase as a key enzyme. Endocrinology, 2012, 153(12): 6003-6011 DOI:10.1210/en.2012-1517 |
Francis RC, Barlow GW. Social control of primary sex differentiation in the Midas cichlid. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1993, 90(22): 10673-10675 DOI:10.1073/pnas.90.22.10673 |
Francis RC. The effects of bidirectional selection for social dominance on agonistic behavior and sex ratios in the paradise fish (Macropodus opercularis). Behaviour, 1984, 90(1-3): 25-44 DOI:10.1163/156853984X00542 |
Ghosh D, Erman M, Wawrzak Z, et al. Mechanism of inhibition of 3α, 20β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase by a licorice-derived steroidal inhibitor. Structure, 1994, 2(10): 973-980 DOI:10.1016/S0969-2126(94)00099-9 |
Hattori RS, Fernandino JI, Kishii A, et al. Cortisol-induced masculinization: Does thermal stress affect gonadal fate in pejerrey, a teleost fish with temperature-dependent sex determination?. PLoS One, 2009, 4(8): e6548 DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0006548 |
Hayashi Y, Kobira H, Yamaguchi T, et al. High temperature causes masculinization of genetically female medaka by elevation of cortisol. Molecular Reproduction and Development, 2010, 77(8): 679-686 DOI:10.1002/mrd.21203 |
Hu YC, Chu KF, Hwang LY, et al. Cortisol regulation of Na+, K+-ATPase β1 subunit transcription via the pre-receptor 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1-like (11β-hsd1l) in gills of hypothermal freshwater milkfish, Chanos chanos. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2019, 192: 105381 DOI:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105381 |
Jiang L, Li H. Single locus maintains large variation of sex reversal in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics, 2017, 7(2): 583-589 |
Krozowski Z. The 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: Functions and physiological effects. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 1999, 151(1-2): 121-127 DOI:10.1016/S0303-7207(98)00256-1 |
Kusakabe M, Kobayashi T, Todo T, et al. Molecular cloning and expression during spermatogenesis of a cDNA encoding testicular 11β‐hydroxylase (p45011β) in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Molecular Reproduction and Development, 2002, 62(4): 456-469 DOI:10.1002/mrd.10145 |
Li H, Xu W, Zhang N, et al. Two figla homologues have disparate functions during sex differentiation in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 1-10 DOI:10.1038/s41598-016-0001-8 |
Li H, Xu W, Zhu Y, et al. Characterization and expression pattern of r-spondin1 in Cynoglossus semilaevis. Journal of Experimental Zoology Part B: Molecular and Developmental Evolution, 2017, 328(8): 772-780 DOI:10.1002/jez.b.22774 |
Li Z, Yang L, Wang J, et al. β-actin is a useful internal control for tissue-specific gene expression studies using quantitative real-time PCR in the half-smooth tongue sole Cynoglossus semilaevis challenged with LPS or Vibrio anguillarum. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2010, 29(1): 89-93 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2010.02.021 |
Liu S, Govoroun M, D'Cotta H, et al. Expression of cytochrome p45011β (11β-hydroxylase) gene during gonadal sex differentiation and spermatogenesis in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2000, 75(4-5): 291-298 DOI:10.1016/S0960-0760(00)00186-2 |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408 DOI:10.1006/meth.2001.1262 |
Miura S, Horiguchi R, Nakamura M. Immunohistochemical evidence for 11β-hydroxylase (p45011β) and androgen production in the gonad during sex differentiation and in adults in the protandrous anemonefish Amphiprion clarkii. Zoological Science, 2008, 25(2): 212-219 DOI:10.2108/zsj.25.212 |
Mommsen TP, Vijayan MM, Moon TW. Cortisol in teleosts: Dynamics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 1999, 9(3): 211-268 DOI:10.1023/A:1008924418720 |
Oppermann UC, Persson B, Jörnvall H. The 11β‐hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase system, a determinant of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid action: Function, gene organization and protein structures of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase isoforms. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1997, 249(2): 355-360 DOI:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.t01-1-00355.x |
Sadoul B, Geffroy B. Measuring cortisol, the major stress hormone in fishes. Journal of Fish Biology, 2019, 94(4): 540-555 DOI:10.1111/jfb.13904 |
Schmidt EE, Ohbayashi T, Makino Y, et al. Spermatid-specific overexpression of the tata-binding protein gene involves recruitment of two potent testis-specific promoters. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1997, 272(8): 5326-5334 DOI:10.1074/jbc.272.8.5326 |
Tabata K. Reduction of female proportion in lower growing fish separated from normal and feminized seedlings of hirame Paralichthys olivaceus. Fisheries Science, 1995, 61(2): 199-201 DOI:10.2331/fishsci.61.199 |
Tokarz J, Norton W, Möller G, et al. Zebrafish 20β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 is important for glucocorticoid catabolism in stress response. PLoS One, 2013, 8(1) |
Tomlinson JW, Walker EA, Bujalska IJ, et al. 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1: A tissue-specific regulator of glucocorticoid response. Endocrine Reviews, 2004, 25(5): 831-866 DOI:10.1210/er.2003-0031 |
Tsachaki M, Meyer A, Weger B, et al. Absence of 11-keto reduction of cortisone and 11-ketotestosterone in the model organism zebrafish. Journal of Endocrinology, 2017, 232: 323-335 DOI:10.1530/JOE-16-0495 |
van den Hurk R, van Oordt P. Effects of natural androgens and corticosteroids on gonad differentiation in the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 1985, 57(2): 216-222 DOI:10.1016/0016-6480(85)90266-7 |
Wendelaar Bonga SE. The stress response in fish. Physiological Reviews, 1997, 77(3): 591-625 DOI:10.1152/physrev.1997.77.3.591 |
White PC, Mune T, Agarwal AK. 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and the syndrome of apparent mineralocorticoid excess. Endocrine Reviews, 1997, 18(1): 135-156 |
Yamaguchi T, Yoshinaga N, Yazawa T, et al. Cortisol is involved in temperature-dependent sex determination in the Japanese flounder. Endocrinology, 2010, 151(8): 3900-3908 DOI:10.1210/en.2010-0228 |
Zhang Y, Hattori RS, Sarida M, et al. Expression profiles of amhy and major sex-related genes during gonadal sex differentiation and their relation with genotypic and temperature-dependent sex determination in pejerrey Odontesthes bonariensis. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2018, 265: 196-201 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2018.03.013 |



