2. 上海海洋大学水产与生命学院 上海 201306;
3. 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(湛江) 广东省名特优鱼类生殖调控与繁育技术工程中心 广东海洋大学 广东 湛江 524088
2. College of Fisheries and Life Science, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306;
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhanjiang), Guangdong Research Centre on Reproductive Control and Breeding Technology of Indigenous Valuable Fish Species, Fisheries College, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang, Guangdong 524088, China
干扰素(interferons, IFNs)是一种在脊椎动物的抗病毒防御(Coccia et al, 2015; Skaug et al, 2010)、免疫激活(Lin et al, 2014; Blomstrom et al, 1986)和细胞增长调节(Lenschow et al, 2007; Cunha et al, 1996)过程中起着重要作用的细胞因子(Yoo et al, 2014; Zhao et al, 2005)。目前,已知的Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型ifn基因在鱼类对病毒感染的先天免疫和适应性免疫中起关键的抗病毒防御作用(Zou et al, 2011; Liu et al, 2010; Baeck et al, 2008)。被病毒感染的细胞识别病毒的dsRNA,且触发IFNs基因与其同源受体结合,进而启动JAK/STAT信号联系,导致干扰素刺激基因(interferon stimulated genes, ISGs)的转录诱导过程(Robertsen et al, 2006; Liu et al, 2002; Loeb et al, 1992)。干扰素刺激基因是先天免疫系统的主要部分,对限制细胞内和细胞间的病毒复制和传播非常重要,ISGs的作用机制对靶向目标有效的抗病毒感染起着至关重要的作用(Hubel et al, 2019; Yasuike et al, 2011; Giannakopoulos et al, 2009)。ISG15是一种可以作用于细胞内的抗病毒蛋白(Daniel et al, 2017; Ozato et al, 2008),它可以通过病毒与细胞蛋白结合在细胞内发挥作用,或者可以作为细胞因子作用于细胞外(Moreno et al, 2018; Okumura et al, 2007)。鱼类中,ISG15是鱼体被病毒感染后经干扰素诱导最早表达且表达量最高的蛋白之一(Álvarez et al, 2018; Zhang et al, 2007)。Liu等(2010)研究报道,美国红鱼(Sciaenops ocellatus)的ISG15同源物能够直接表现出免疫调节的特性。鳕(Gadus morhua) (Røkenes et al, 2007)、鲑(Salmo salar) (Seppola et al, 2007)和鲫(Carassius auratus) (Furnes et al, 2009)的ISG15同源物能够与细胞蛋白形成复合物发挥抗病毒的作用。因此,isg15不仅能够调节免疫反应,还具有直接的抗病毒作用,研究鱼类isg15对于解析鱼类抗病毒分子的免疫机制具有重要意义。
鞍带石斑鱼(Epinephelus lanceolatus)是一种名贵的海水养殖品种,随着消费需求的增长,养殖密度不断增加,病害问题已成为制约石斑鱼类养殖业健康可持续发展的主要瓶颈。目前,虹彩病毒(iridovirus)是海水和淡水养殖鱼类最严重的病毒性病原之一,在世界各地已从100多种鱼类中分离鉴定出虹彩病毒(Gray et al, 2015)。虹彩病毒是危害石斑鱼类最大的传染病之一(Ohta et al, 2011),但关于鞍带石斑鱼干扰素刺激基因15的克隆及功能研究尚未见报道。
本研究以鞍带石斑鱼为研究对象,对其isg15基因进行全长cDNA克隆并初步分析其结构特征,采用实时荧光定量PCR (qRT-PCR)技术检测了该基因在鞍带石斑鱼不同组织中的表达模式,以及感染虹彩病毒后主要免疫组织的表达特征,旨在为探究isg15基因在鞍带石斑鱼免疫应答中的作用机制提供数据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料 1.1.1 正常组织本实验所用的鞍带石斑鱼取自海南晨海水产有限公司,采集18月龄健康鞍带石斑鱼,麻醉后用注射器对心脏取血,然后解剖取其心脏、肝脏、鳃、肠、皮肤、肾脏、脾脏、脑等组织,将组织样品立即放入RNA保存液中,存放于-80℃冰箱,用于提取正常组织RNA。
1.1.2 虹彩病毒感染及样品收集将18月龄的健康鞍带石斑鱼腹腔注射虹彩病毒(由华南农业大学的秦启伟教授提供)进行感染,每尾100 μL (109拷贝数)。在感染后的0、12、24、72和96 h共5个时间点,以磷酸缓冲液(PBS)作为对照,分别取5尾鞍带石斑鱼,将活鱼麻醉后迅速采集脾脏和肾脏组织,放入RNA保存液中,存放于-80℃冰箱。
1.2 鞍带石斑鱼总RNA提取及cDNA第一链的合成用于全长克隆的总RNA提取按照RNAiso Plus Total RNA (TaKaRa)提取试剂说明书进行操作,提取的RNA经琼脂糖凝胶电泳检查完整性,并利用NanoDrop2000超微量分光光度计测定RNA浓度及纯度,判断核酸和蛋白质的污染情况。选取质量良好的RNA,按照PrimeScript Ⅱ 1st strand cDNA synthesis kit (TaKaRa)和SMARTer RACE 5′/3′ kit的操作说明书进行反转录,分别得到cDNA、5'RACE cDNA及3'RACE cDNA,保存至-20℃冰箱,分别用于isg15基因中间片段的克隆以及5′RACE和3′RACE扩增。
1.3 isg15基因的全长cDNA的克隆 1.3.1 中间片段的克隆验证中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所陈松林团队主导完成了鞍带石斑鱼全基因组测序和精细图谱绘制(Zhou et al, 2019),首先,根据鞍带石斑鱼基因组数据库中的部分isg15序列,使用Primer Premier 5.0软件设计引物(isg15-F1/ isg15-R1)(表 1),以cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增:Mix 7.5 μL,isg15-F1 0.6 μL,isg15-R1 0.6 μL,ddH2O 5.3 μL,模板cDNA 1 μL。程序:95℃预变性5 min;95℃ 30 s,58℃退火30 s,72℃延伸55 s,35个循环;72℃延伸10 min;4℃保存。扩增产物经1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,并用凝胶回收试剂盒回收、纯化,再利用T-A克隆方法克隆到pEAZY-T1载体上,转化至大肠杆菌感受态细胞中,涂板于含氨苄西林的固体培养基,37℃过夜培养12~16 h,挑取单菌落于1 mL含氨苄西林的液体培养基中,37℃ 200 r/min震荡培养6 h,进行菌液PCR检测,挑取阳性克隆。将含有目的片段的阳性菌落交由北京睿博兴科生物技术有限公司(青岛区)进行测序(王双艳等, 2019)。
|
|
表 1 本研究所用到的引物 Tab.1 Primers used in this study |
根据克隆得到的isg15基因片段序列,分别设计5′RACE和3'RACE的特异性扩增引物(5′-RACE-GSP/5′-RACE-NGSP和3′-RACE-GSP/3′-RACE-NGSP)(表 1)。分别以5′RACE cDNA和3′RACE cDNA为模板进行5′RACE和3′RACE扩增,第1轮反应体系为10 μL,根据TaKaRa TaqTM Hot Start Version说明书介绍的体系比例加样混合,进行Touch down PCR程序反应。第1轮PCR反应产物稀释50倍作为第2轮普通PCR扩增反应的模板,反应体系为50 μL,同上按比例加样混合后进行PCR反应,将得到的PCR产物根据中间片段的克隆的验证方法处理并测序。
根据基因测序获得的isg15基因5′和3′及中间片段序列,利用DNAman软件进行拼接,获得isg15基因全长序列。
1.4 isg15基因的序列分析及进化树的构建利用在线软件ExPASy (http:www.au.expasy.org)对isg15基因的cDNA序列进行蛋白翻译、分子量及等电点预测;使用SMART (http://smart.emblheidel-berg.de/)预测保守结构域。在NCBI上下载同源序列,利用DNAman进行同源序列比对分析(王杉等, 2020),利用MEGA5.1软件以邻位法(Neighbor- joining, NJ)构建系统发育树。
1.5 鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因的表达模式检测使用qRT-PCR检测健康的鞍带石斑鱼不同组织中的表达量;使用qRT-PCR检测鞍带石斑鱼经过虹彩病毒感染刺激后5个时间点的脾脏和肾脏的表达情况。根据isg15基因全长序列,设计qRT-PCR正反向引物(isg15-RT-F/isg15-RT-R)(表 1),并以(ACTIN- RT-F/ACTIN-RT-R)(表 1)作为内参基因。以鞍带石斑鱼在感染虹彩病毒后不同时间的脾脏和肾脏cDNA为模板,在7500 Fast Real-time PCR仪上进行qRT-PCR。20 μL体系:10 μL SYBR,上、下游引物(10.0 μmol/L)各0.8 μL,0.4 μL ROX reference dye Ⅱ,cDNA 1.0 μL,ddH2O 7.0 μL。每次反应均设阴性对照和无模板对照,每个反应设3个重复。扩增程序:95℃ 5 min,95℃ 5 s,60℃ 34 s,40个循环。所得实验数据采用相对CT法(2-ΔΔCt)进行isg15基因mRNA的表达量计算,实验得到的数据采用SPSS软件进行方差分析,设定P < 0.05为差异显著。
2 结果与分析 2.1 鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因的克隆及序列分析鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因序列全长为910 bp,其中,5′-非编码区为64 bp,开放阅读框为468 bp,3′-非编码区为378 bp,预测分子量为17.09 kDa,理论等电点为9.33(图 1)。SMART软件预测鞍带石斑鱼ISG15含有2个类泛素结构域UBQ(ubiquitin-like domain),分别在1~76和86~156位置,其中,C端结构域含有泛素C末端具有的LRLRGG结构域(图 1)。

|
图 1 鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因的cDNA序列及其编码序列 Fig.1 The cDNA and deduced amino acid sequences of E. lanceolatus isg15 推导的氨基酸序列显示在核苷酸序列下方,用大写字母表示。蓝色区域表示isg15基因的2个类似泛素结构域UBQ (Ubiquitin-like domain)序列特征;方框所示为起始密码子(ATG)和终止密码子(TGA),下划线(—)所示为polyA结构 The deduced amino acid sequence is shown below the nucleotide sequence and expressed in capital letters. Blue boxes represent sequences of isg15 two ubiquitin-like domain. Start codon (ATG) and termination codon (TGA) are shown in the box, and the underline (—) shows the polyA structure |
鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因编码的氨基酸序列经BLAST比对发现,与其他硬骨鱼类的isg15基因有较高的同源性,与斜带石斑鱼(Epinephelus coioides)的相似性为88.24%,与大菱鲆(Scophthalmus maximus)、大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea)和条石鲷(Oplegnathus fasciatus)的相似性为61.18%、60.59%和60.00%,与爬行动物陆龟(Gopherus evgoodei)的相似性为33.53%,与2种哺乳动物小鼠(Mus musculus)和人(Homo sapiens)的相似性为32.94%和31.18% (表 2)。
|
|
表 2 鞍带石斑鱼和其他物种的ISG15的氨基酸相似性 Tab.2 Degree of homology similarity between ISG15 of E. lanceolatus and other vertebrates |
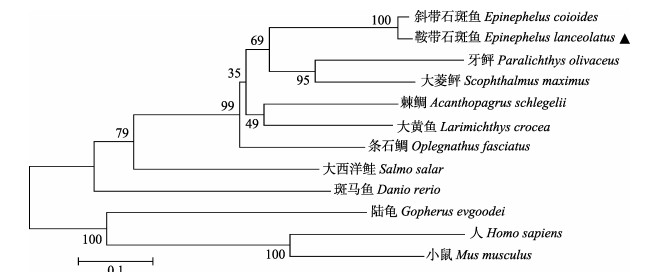
使用DNAman进行氨基酸多重序列比对,结果显示,不同物种间的ISG15序列非常保守(图 2)。为了确定isg15的系统进化关系,通过MEGA 5.1软件,采用Neighbor-joining法构建了脊椎动物isg15系统进化树(图 3)。系统发育分析显示,9种鱼类的isg15聚为一簇,爬行动物陆龟分为一支,2种哺乳动物的isg15聚为一簇。

|
图 2 ISG15的氨基酸序列多重序列比对结果 Fig.2 The multiple sequence alignment of the ISG15 amino acid 黑色区域: 相似性100%; 粉红区域: 相似性≥75; 蓝色区域: 相似性≥50% Black area: Similarity 100%; Pink area: Similarity ≥75%; Blue area: Similarity ≥50% |
|
图 3 鞍带石斑鱼isg15与其他物种isg15系统进化树分析 Fig.3 Phylogenetic analysis of isg15 sequence of E. lanceolatus with other vertebrate isg15 |
为研究isg15基因在健康鱼类中的表达模式,采用荧光定量PCR技术检测isg15基因在鞍带石斑鱼健康个体的不同组织内基因相对表达水平变化。结果显示,isg15基因主要在血液中表达,肝脏、肾脏中的mRNA水平较高,其次是鳃、肠、心脏、脾脏、皮肤、大脑和肌肉(图 4)。

|
图 4 鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因在不同组织的表达分布 Fig.4 Expression profile of isg15 in different tissues of E. lanceolatus 字母“a、b、c、d”表示SPSS 17.0软件使用Duncan算法计算的子集分组。不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05) Letters of "a, b, c, d" indicate the Duncan grouping in SPSS 17.0. Different letters indicate significant difference (P < 0.05) |
本研究采用荧光定量PCR技术检测isg15基因在鱼体注射虹彩病毒的处理下,脾脏在不同时间(0、12、24、72和96 h)基因相对表达水平变化。isg15基因在鱼体注射虹彩病毒后脾脏中相对表达变化的检测结果显示,与0 h相比,各组脾脏内isg15基因的相对表达量在感染后72 h显著上调至8.3倍,在感染后96 h降低为6.6倍(图 5)。

|
图 5 虹彩病毒感染后鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因在脾脏中的表达分布 Fig.5 The expression of E. lanceolatus isg15 in spleen after iridovirus infection 数据分析采用t检验方法验证,**代表P < 0.01。下同 Data analysis was verified by t-test, ** represented P < 0.01. The same as below |
isg15基因在鱼体注射虹彩病毒后肾脏中相对表达变化的检测结果显示,isg15基因的相对表达量在肾脏中的表达变化更为剧烈,72 h时其转录水平上调约11倍,96 h时下降至6.5倍(图 6)。

|
图 6 虹彩病毒感染后鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因在肾脏中的表达分布 Fig.6 The expression of E. lanceolatus isg15 in kidney after iridovirus infection |
本研究通过PCR及RACE方法成功获得了鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因cDNA的全长序列。SMART在线软件预测鞍带石斑鱼ISG15含有2个类泛素结构域UBQ,然而与泛素相比,ISG15与目的蛋白结合并不会导致靶蛋白的降解,而是发挥生理信号功能,与基因转录调控、蛋白质翻译以及机体应激反应等生理过程有密切联系(Liu et al, 2014)。鞍带石斑鱼ISG15的C端结构域也含有泛素C末端相同的LRLRGG结构域,其对ISG15与细胞内靶蛋白分子的连接极其重要(图 1)。大多数泛素或类泛素样蛋白通过在LRLRGG结构域的末端加上几个氨基酸,从而使其处于失活状态,而类泛素样蛋白的活化则通过蛋白酶释放有活性的尾部(Dao et al, 2005)。isg15基因是ISGs家族的重要成员之一,各个物种中的isg15基因均具有一定的保守性和保守功能(Moreno et al, 2018)。序列分析显示,克隆获得的鞍带石斑鱼isg15与斜带石斑鱼上的isg15相似度最高,达到88.24%,与大菱鲆、大黄鱼和条石鲷的相似性高于60%,与哺乳动物人和小鼠的相似性高于30%(图 2),这说明了亲缘关系越相近的物种,同源性越高。鞍带石斑鱼和其他几种已报道的鱼类,如斜带石斑鱼、条石鲷、棘鲷等的ISG15蛋白C端LRLRGG结构域之后没有末端氨基酸,说明其处于天然活化状态,推测鞍带石斑鱼的ISG15具有天然的抗病毒作用。
最初研究证明,鱼类中的Ⅰ型IFN具有抗病毒活性,对包括斑马鱼(Danio rerio)中的蛇头横纹肌病毒(Altmann et al, 2003)、鲑中的传染性胰腺疾病(IPNV) (Robertsen et al, 2003)和斜带石斑鱼中的神经坏死病毒(NNV) (Ohta et al, 2011)都有抑制作用。后期研究发现,IFN还能够诱导ISG15的表达。ISG15通过与JAK1和STAT1等重要干扰素信号通路成员的结合,调控细胞对干扰素信号的反应(Malakhov et al, 2003)。最新研究证明,isg15具有直接的抗病毒能力,其中,Wang等(2012)研究发现,半滑舌鳎的isg15基因具有非结合形式的抗病毒能力;Langevin等(2013)研究发现,斑马鱼isg15在EPC细胞中过表达后能够抑制虹彩病毒等病毒的感染。因此,isg15是抗病毒防御体系的重要部分,可以在动物机体抗病毒方面发挥重要作用,但isg15在石斑鱼类抗病毒反应中的作用机制和调控通路需要进一步研究。
本研究对isg15基因在健康鞍带石斑鱼各个组织中的表达模式进行了探究,发现isg15基因在鞍带石斑鱼的各个组织中均有表达,在血液中表达量最高,在肝脏、肾脏中的表达水平较高,说明isg15主要在免疫组织中表达。鱼类免疫相关的基因在血液中表达较高的现象也早有报道,如牙鲆的efhd2和tbcld25基因在血液中表达量最高(侯吉伦等, 2019)。血液也是鱼体重要的免疫器官,是各类免疫细胞和免疫因子的天然携带者,在鱼体免疫应答过程中发挥重要的生理和生化作用。血液也是鱼体内各个器官间物质运输的载体,机体受到感染时,血液中的细胞因子能够快速到达病区。因此,推测在病毒感染后,鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因在血液中快速表达,随着血液流动运输到病毒攻击的部位,发挥抗病毒的免疫作用。本研究对虹彩病毒感染后鞍带石斑鱼isg15的表达变化检测发现,在脾脏和肾脏中,isg15的相对表达量呈现先升高后下降的趋势,在感染虹彩病毒72 h出现峰值,其中,在脾脏中升高了8倍,在肾脏中升高了近11倍,说明鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因在对抗虹彩病毒感染的过程中响应快速,在脾脏和肾脏中发挥着重要的防御作用。
综上所述,本研究首次对鞍带石斑鱼isg15基因进行了cDNA全长克隆、进化分析及表达模式研究,同时,证明isg15基因在鱼体血液中的相对表达量远高于其他内脏组织,在脾脏和肾脏中发挥着防御病毒的作用,可为进一步研究isg15在抗病分子育种中的作用机制提供理论基础。
ALTMANN S M, MELLON M T, DISTEL D L, et al. Molecular and functional analysis of an interferon gene from the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Journal of Virology, 2003, 77(3): 1992-2002 DOI:10.1128/JVI.77.3.1992-2002.2003 |
ÁLVAREZ-TORRES D, GÓMEZ A V, ARIZCUN M, et al. Identification of an interferon-stimulated gene, isg15, involved in host immune defense against viral infections in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2018, 73: 220-227 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2017.12.027 |
ÁLVAREZ-TORRES D, PODADERA A M, ALONSO M C, et al. Molecular characterization and expression analyses of the Solea senegalensis interferon-stimulated gene 15 (isg15) following NNV infections. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2017, 66(1): 423-432 |
BAECK G W, KIM J W, PARK C I. Identification and expression analysis of an interferon stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) from black rockfish, Sebastes schlegeli. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2008, 25(5): 679-681 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2008.08.005 |
BLOMSTROM D C, FAHEY D, KUTNY R, et al. Molecular characterization of the interferon-induced 15-kDa protein: Molecular cloning and nucleotide and amino acid sequence. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1986, 261(19): 8811-8816 DOI:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)84453-8 |
Coccia E M, Battistini A. Early IFN type I response: Learning from microbial evasion strategies. Seminars in Immunology, 2015, 27(2): 85-101 DOI:10.1016/j.smim.2015.03.005 |
CUNHA J D, RAMANUJAM S, WAGNER R J, et al. In vitro and in vivo secretion of human isg15, an IFN-induced immunomodulatory cytokine. Journal of Immunology, 1996, 157(9): 4100-4108 |
DAO C T. ISG15: A ubiquitin-like enigma. Frontiers in Bioscience, 2005, 10(1): 2701-2722 |
FURNES C, KILENG Ø, RINALDO C H, et al. Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) possesses three homologues of ISG15 with different expression kinetics and conjugation properties. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 2009, 33(12): 1239-1246 DOI:10.1016/j.dci.2009.07.005 |
GIANNAKOPOULOS N V, ARUTYUNOVA E, LAI C, et al. ISG15 Arg151 and the ISG15-conjugating enzyme UbE1L are important for innate immune control of Sindbis virus. Journal of Virology, 2009, 83: 1602-1610 DOI:10.1128/JVI.01590-08 |
GRAY M J, CHINCHAR V G. Ranaviruses: Lethal pathogens of ectothermic vertebrates. New York, USA: Springer, 2015, 9-57
|
HOU J L, GUO Y N, FU Y S, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of efhd2 and tbcld25 gene in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2019, 40(3): 57-68 [侯吉伦, 郭亚男, 付元帅, 等. 牙鲆efhd2和tbc1d25基因的克隆和表达分析. 渔业科学进展, 2019, 40(3): 57-68] |
HUBEL P, URBAN C, BERGANT V, et al. A protein-interaction network of interferon-stimulated genes extends the innate immune system landscape. Nature Immunology, 2019, 20(4): 493-502 DOI:10.1038/s41590-019-0323-3 |
LANGEVIN C, AA L M V D, HOUEL A, et al. Zebrafish ISG15 exerts a strong antiviral activity against RNA and DNA viruses and regulates the interferon response. Journal of Virology, 2013, 87(18): 10025-10036 DOI:10.1128/JVI.01294-12 |
LENSCHOW D J, LAI C, FRIAS-STAHELI N, et al. IFN-stimulated gene 15 functions as a critical antiviral molecule against influenza, herpes, and Sindbis viruses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(4): 6-1371 |
LIN F C, YOUNG H A. Interferons: Success in anti-viral immunotherapy. Cytokine and Growth Factor Reviews, 2014, 25(4): 369-376 DOI:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.07.015 |
LIU C S, SUN Y, ZHANG M, et al. Identification and analysis of a Sciaenops ocellatus ISG15 homologue that is involved in host immune defense against bacterial infection. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2010, 29(1): 167-174 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2010.03.012 |
LIU C, ZHAO Q N, LI X Q, et al. Progress on ubiquitin-like protein ISG15. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2014, 35(11): 92-97 [刘诚, 赵倩楠, 李晓泉, 等. 类泛素蛋白ISG15研究进展. 动物医学进展, 2014, 35(11): 92-97 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5038.2014.11.021] |
LIU M J, REIMSCHUESSEL R, HASSEL B A. Molecular cloning of the fish interferon stimulated gene, 15 kDa (ISG15) orthologue: A ubiquitin-like gene induced by nephrotoxic damage. Gene, 2002, 298(2): 129-139 DOI:10.1016/S0378-1119(02)00932-0 |
LOEB K R, HAAS A L. The interferon inducible 15 kDa ubiquitin homolog conjugates to intracellar proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1992, 267(11): 7806-7813 DOI:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)42585-9 |
MALAKHOV M P, KIM K I, MALAKHOVA O A, et al. High-throughput immunoblotting: Ubiquitin-like protein ISG15 modifies key regulators of signal transduction. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003, 278(19): 16608-16613 DOI:10.1074/jbc.M208435200 |
MORENO P, ALVAREZ-TORRES D, GARCIA-ROSADO E, et al. Differential antiviral activity of European sea bass interferon-stimulated 15 protein (ISG15) against RGNNV and SJNNV betanodaviruses. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2018, 83(1): 148-157 |
OHTA T, UEDA Y, ITO K, et al. Anti-viral effects of interferon administration on sevenband grouper, Epinephelus septemfasciatus. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2011, 30(4/5): 1064-1071 |
OKUMURA F, ZOU W, ZHANG D E. ISG15 modification of the eIF4E cognate 4EHP enhances cap structure-binding activity of 4EHP. Genes and Development, 2007, 21(3): 255-260 DOI:10.1101/gad.1521607 |
OZATO K, SHIN D M, CHANG T H, et al. TRIM family proteins and their emerging roles in innate immunity. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2008, 8(11): 849-860 DOI:10.1038/nri2413 |
ROBERTSEN B. The interferon system of teleost fish. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2006, 20(2): 172-191 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2005.01.010 |
ROBERTSEN B, BERGAN V, RØKENES T, et al. Atlantic salmon interferon genes: Cloning, sequence analysis, expression, and biological activity. Journal of Interferon and Cytokine Research, 2003, 23(10): 601-612 DOI:10.1089/107999003322485107 |
RØKENES T P, LARSEN R, ROBERTSEN B. Atlantic salmon ISG15: Expression and conjugation to cellular proteins in response to interferon, double-stranded RNA and virus infections. Molecular Immunology, 2007, 44(5): 950-959 DOI:10.1016/j.molimm.2006.03.016 |
SEPPOLA M, STENVIK J, STEIRO K, et al. Sequence and expression analysis of an interferon stimulated gene (ISG15) from Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 2007, 31(2): 156-171 DOI:10.1016/j.dci.2006.05.009 |
SKAUG B, CHEN Z J. Emerging role of ISG15 in antiviral immunity. Cell, 2010, 143(2): 187-190 DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.033 |
WANG S Y, WANG L, CHEN Z F, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) gene in the half smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2019, 40(2): 51-57 [王双艳, 王磊, 陈张帆, 等. 半滑舌鳎多聚免疫球蛋白受体(pIgR)基因的克隆和表达分析. 渔业科学进展, 2019, 40(2): 51-57] |
WANG S, XU W T, LI M, et al. Molecular cloning and expression pattern analysis of TGF-β1 in spotted knifejaw (Oplegnathus punctatus). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2020, 41(3): 78-87 [王杉, 徐文腾, 李明, 等. 斑石鲷TGF-β1基因克隆和表达分析. 渔业科学进展, 2020, 41(3): 78-87] |
WANG W, ZHANG M, XIAO Z Z, et al. Cynoglossus semilaevis ISG15: A secreted cytokine-like protein that stimulates antiviral immune response in a LRGG motif-dependent manner. PLoS One, 2012, 7(9): e44884 DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0044884 |
YASUIKE M, KONDO H, HIRONO I, et al. Identification and characterization of Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus interferon-stimulated gene 15 (Jf-ISG15). Comparative Immunology Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 2011, 34(1): 83-91 DOI:10.1016/j.cimid.2010.02.005 |
YOO J S, KATO H, FUJITA T. Sensing viral invasion by RIG-I like receptors. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2014, 20: 131-138 DOI:10.1016/j.mib.2014.05.011 |
ZOU J, SECOMBES C J. Teleost fish interferons and their role in immunity. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 2011, 35(12): 1376-1387 DOI:10.1016/j.dci.2011.07.001 |
ZHAO C, DENISON C, HUIBREGTSE J M, et al. Human ISG15 conjugation targets both IFN-induced and constitutively expressed proteins functioning in diverse cellular pathways. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(29): 10200-10205 DOI:10.1073/pnas.0504754102 |
ZHANG Y B, WANG Y L, GUI J F. Identification and characterization of two homologues of interferon-stimulated gene ISG15 in crucian carp. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2007, 23(1): 52-61 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2006.09.004 |
ZHOU Q, GAO H, ZHANG Y, et al. A chromosome-level genome assembly of the giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus) provides insights into its innate immunity and rapid growth. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2019, 19(5): 1322-1332 DOI:10.1111/1755-0998.13048 |



