2. 中国水产科学研究院 农业农村部水生动物基因组学重点实验室 北京 100141;
3. 中国水产科学研究院黑龙江水产研究所 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150070;
4. 厦门大学海洋与地球学院 福建省海洋生物资源开发利用协同创新中心 福建 厦门 361102
2. Key Laboratory of Aquatic Genomics, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Beijing 100141, China;
3. Heilongjiang River Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Harbin, Heilongjiang 150070, China;
4. College of Ocean and Earth Sciences, Xiamen University, Fujian Collaborative Innovation Center for Exploitation and Utilization of Marine Biological Resources, Xiamen, Fujian 361102, China
鲤(Cyprinus carpio)是驯化历史较为悠久的物种,出土的新石器时代早期鱼骨比较分析显示,我国鲤鱼养殖历史可追溯到距今8000年以前(Nakajima et al, 2019)。如今,鲤已成为世界性的养殖品种,养殖地域遍布欧亚大陆,年产量达418.95万t (FAO, 2020),为保障人类粮食安全和营养安全发挥了重要作用。在水生环境中,氧饱和浓度仅为同体积空气中的1/30,且扩散速度缓慢,空间分布不均匀,为适应聚集性养殖条件下的氧供应不足,低氧成为鱼类驯化过程中的高强度选择压力之一,如何从遗传角度解析鲤低氧适应驯化的机制,对于基础研究和育种应用都有重要的意义。
近年来,研究者对多种鱼类开展了低氧适应性状相关研究,从表观遗传、基因表达差异等角度揭示了鱼类在低氧胁迫下的不同应答模式,以及低氧对鱼类生长、发育、繁殖、免疫等生理过程的影响(肖武汉, 2014; Abdel-Tawwab et al, 2019)。多种不同成因和程度的低氧均可导致摄食下降、生长停滞和疾病易感(Fitzgibbon et al, 2007; Portner, 2010; Abdel-Tawwab et al, 2014; Araújo-Luna et al, 2018)。以海洋青鳉(Oryzias melastigma)为对象的研究显示,低氧通过甲基化调控造成跨世代的生殖损伤,即使子代及其生殖细胞从未暴露于低氧环境下,也会因亲代的低氧暴露史而出现性腺发育迟缓(Wang et al, 2016; Lai et al, 2019)。在低氧胁迫下,鱼类鳃丝原有的规则形态发生改变,板层排列紊乱和扭曲,细胞异常增生和坏死并存,同时,伴随着渗透压调节的紊乱,离子平衡和酸碱平衡均被打破,进而导致一系列血液生化指标的波动(Cadiz et al, 2017; Araújo-Luna et al, 2018; Abdel-Tawwab et al, 2019)。大量转录组研究(Zhang et al, 2017; Qi et al, 2018; Ding et al, 2020; Qi et al, 2020)表明,低氧诱导因子(hypoxia inducible factor, hif)通路是最主要的低氧应答信号通路,典型的差异表达基因还包括促红细胞生成素(erythropoietin, epo),血红素加氧酶(heme oxygenase, ho)属于负责氧分子转运的珠蛋白家族,参与糖酵解/糖异生、乳酸代谢、丙酮酸代谢、三羧酸循环以及活性氧(reactive oxygen species, ROS)清除等。
为将低氧适应的研究结果应用于分子辅助育种,需要在全基因组层面筛选性状差异群体的特异性分子标记和基因。全基因组关联分析(genome wide association study, GWAS)是近年来对性状的遗传机制进行解析的重要方法,其基本原理是利用逻辑或线性回归方法,筛选出与目标性状关联的单核苷酸多态性位点(single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP),并对这些遗传变异和目标性状的关系进行验证及相关功能研究。近年来,已有许多水生生物的GWAS研究报道,刘占江团队应用斑点叉尾

本研究聚焦于解析鲤低氧适应性状驯化的遗传机制,应用鲤250K高通量SNP芯片(Xu J et al, 2014; Xu P et al, 2014),对鲤养殖群体低氧适应性状开展GWAS分析,定位性状关联位点及其效应基因,旨在为培育鱼类耐低氧品种提供参考。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验用鱼松荷鲤(C. carpio Songhe)实验群体来源于中国水产科学研究院黑龙江水产研究所呼兰试验场。实验个体同批孵化、同池饲养至3月龄[平均体重(107±20) g,平均体长(16.5±2.3) cm],移入室内暂养缸中,25℃暂养7 d使之适应环境。暂养期间,气泵充氧,控制溶解氧浓度 > 6.0 mg/L,每天早、中、晚各投饵1次。
1.2 低氧胁迫实验暂养结束后,选取体质健康、体重相近、无外伤、无感染、能够正常游泳和摄食的个体用于低氧胁迫实验。实验鱼分5组,分别置于500 L的塑料缸中,每组260尾个体。实验开始前使用气泵充氧,控制溶解氧浓度 > 6.0 mg/L,禁食24 h后停止充氧,使溶解氧浓度持续自然下降。使用ORION STAR A223型溶解氧测量仪(Thermo Scientific, 美国),每隔15 min记录溶解氧浓度值,实验开始3 h后,溶解氧浓度降至0.43 mg/L,个体陆续缺氧昏迷,按昏迷顺序对实验个体进行编号,移出实验缸。实验开始5 h后,溶解氧浓度稳定在0.27 mg/L,将剩余个体移入50 L封闭玻璃缸,通过调节水量控制溶解氧浓度继续缓慢下降。实验开始10 h后,实验鱼全部昏迷,溶解氧浓度降至0.12 mg/L。
1.3 样本采集与处理实验鱼按缺氧昏迷顺序编号,记录个体信息并采集静脉血样本,剔除出现外伤或感染的个体,共采集到1243尾有效个体样本。使用动物基因组DNA提取试剂盒(天根DP324-03,中国),提取100尾极端性状个体的血液DNA。其中,每组最早昏迷的10尾个体归为低氧敏感组,5组共计50尾;最晚昏迷的10尾个体归为低氧耐受组,5组共计50尾。
1.4 基因分型和数据质控挑选电泳条带清晰无拖尾、A260 nm/A280 nm在1.8~2.0之间、浓度大于100 ng/μL的高质量DNA样本用于SNP分型,满足要求的样本共91个,包括低氧敏感样本43个,低氧耐受样本48个。使用鲤250K高通量SNP芯片(赛默飞世尔Axiom™ carp genotyping array, 美国)进行分型检测,分型实验由纽勤生物科技(上海)有限公司完成,使用Affymetrix Power Tools和SNPolisher软件读取分型数据。分型数据质控标准设置为探针质量≥0.85,SNP分型成功率≥95%,样本分型成功率≥90%,最小等位基因频率≥5%。
1.5 全基因组关联分析使用PLINK软件进行鲤低氧适应性状GWAS分析,使用“--logistic”和“--adjust”参数,显著性关联位点标准为FDR校正后的P < 0.05,提示性关联位点标准为0.05≤FDR校正后P < 0.1。对相关SNP位点的50 kb侧翼区域进行基因注释。使用R语言的CMplot软件包绘制曼哈顿图和Q-Q图。
2 结果 2.1 SNP分型应用鲤鱼250K高通量分型芯片进行SNP分型,分型及质控结果见表 1。基因分型结果显示,91个样本中共获得199 577个SNPs原始分型数据,通过质控的样本共90个,包括低氧耐受样本48个,低氧敏感样本42个。质控后得到90个样本的87 222个SNPs位点的分型数据进行后续GWAS分析。
|
|
表 1 基因分型和数据质控结果 Tab.1 Genotyping and data quality control |
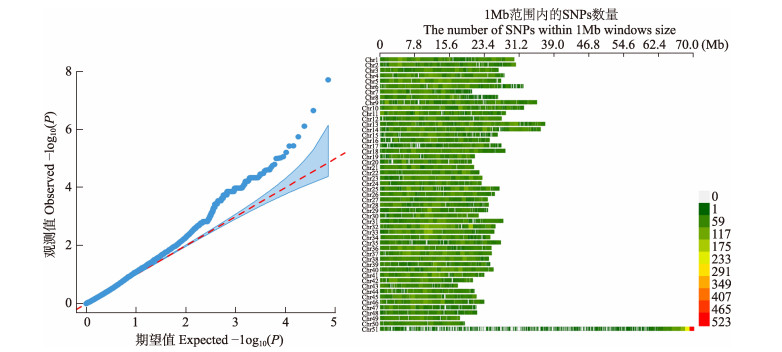
考虑到群体分层因素对GWAS的影响,首先对低氧敏感和耐受样本进行主成分分析(图 1),可以看出,实验样本中不存在显著的群体分层,群体分层对本研究的影响很小,并在后续关联分析中引入了主成分分析结果进行校正。通过PLINK进行GWAS分析,关联分析结果见表 2和表 3,包括4个关联位点(carp229220、carp195901、carp001519和carp063890)和7个提示性关联位点(carp000442、carp088568、carp195897、carp188137、carp110811、carp001038和carp051623)。使用R语言的CMplot软件包生成鲤低氧适应性状GWAS分析的Q-Q图和曼哈顿图(图 2和图 3),比较Q-Q图观测值和期望值的一致性,散点分布与趋势线吻合度较高,可以推测关联分析结果较可靠。从图 3可以看出,4个显著性关联位点与7个提示性关联位点成簇分布,大部分位于41号染色体上,表明该基因组区域可能存在与低氧适应性状密切关联的基因。

|
图 1 鲤实验群体主成分分析 Fig.1 Principal component analysis of experimental population of common carp |
|
|
表 2 低氧性状关联位点与基因 Tab.2 Associated SNPs and genes for hypoxia adaptation |
|
|
表 3 低氧性状提示性关联位点与基因 Tab.3 Suggestively associated SNPs and genes for hypoxia adaptation |
|
图 2 鲤低氧适应性状GWAS关联分析的Q-Q图和密度图 Fig.2 Q-Q plot and SNP-density plot of genome-wide association of hypoxia adaptation trait of common carp |

|
图 3 鲤低氧适应性状GWAS关联分析的曼哈顿图 Fig.3 Manhattan plot of the genome-wide association analysis for hypoxia adaptation trait of common carp |
为了定位低氧适应性状相关的基因,针对筛选的4个显著关联的SNP位点carp229220、carp195901、carp001519和carp063890,在每个SNP位点的50 kb上下游区域进行基因注释,筛选出23个候选基因(prdx5、tsc1、nxf1、vtn、gtf3c4、barhl1、cpd、cryba1、unc119、slc13a2、aldh3a2、traf4、kcnk4、hcea、esrrg、bscl2、gng3、banf1、slc3a2、calm1、pyc、tapbp和1a36)。
3 讨论本研究应用鲤250K高通量SNP芯片对鲤养殖群体低氧适应性状开展GWAS分析,筛查低氧适应性状的显著性关联SNP位点,定位低氧适应性状的关联基因。该芯片是本课题组于2014年开发完成的,是鲤的第一个高通量基因分型平台。经过鲤的多个品系的评估,25万个SNP位点中有近3/4 (199 577个)被证明在鲤中是多态性的。此外,鲤SNP芯片还在近缘物种中进行了验证,获得了2万~5万个多态性位点。该SNP芯片对鲤及其近缘物种的性状解析和多态性评估等研究具有重要价值(Xu J et al, 2014)。
在GWAS分析中,如果样本中存在不同的群体分层结构,会对关联分析的结果产生显著影响,造成基因组膨胀系数(genomic inflation factor, GIF)的增加和假阳性的出现。主成分分析可以通过对群体的基因分型结果降维,提取主要的几个主成分,并直观地观察到群体内部的分层现象。本研究中主成分分析结果显示,群体分层对关联分析结果影响很小。使用PLINK软件进行GWAS分析时,由于本研究的低氧适应性状为二项式性状(敏感和耐受),所以,采用逻辑(logistic)回归分析,并将主成分分析的结果(前5个主成分)作为辅因子,进行结果的校正。对于GWAS分析后原始P值的分布,通过绘制Q-Q图分析P值的观测值和期望值的一致性,如果偏离趋势线太多,则提示可能有群体分层等因素影响分析的准确性,本研究的Q-Q图提示研究的可靠性较高,SNP密度图也显示分析用的8万多个位点较均匀地分布在50个染色体上。
在自然群体数量性状GWAS的研究报道中,通常会筛选到几十个到数百个关联位点,而本研究只定位到4个SNP位点,这与所采用的实验群体有关。实验用鱼为松荷鲤养殖群体,这一品种是利用多元杂交选育技术培育的鲤鱼品种,选育亲本来源包括镜鲤(C. carpio var. specularis)、荷包红鲤(C. carpio Red var vuyuanensis)和黑龙江野鲤(C. carpio haematopterus Tem.etSchl),主要选育目标为抗寒和生长(石连玉等, 2012)。由于其亲本品种间存在低氧适应性状的明显差异,特别是历经长期高强度驯化的镜鲤为低氧耐受品种,而荷包红鲤为地方原种,低氧耐受能力相对较弱(赵紫霞等, 2014),在新品种松荷鲤个体间存在低氧适应性状的显著差异,其遗传基础为来源于镜鲤基因组的少量低氧适应驯化位点。
在已发表的有限几项养殖鱼类低氧GWAS研究结果中,也呈现出类似的特点,即显著性关联位点较少,可能起源于家养驯化选择。Wang等(2017)利用斑点叉尾


通过全基因组关联分析筛查到的4个显著性关联位点中,carp229220和carp001519为同义突变,carp195901为非编码区突变,carp063890位于一个抗原提呈相关转运蛋白Tapasin编码序列内,可能并非真正的效应位点。目前,在显著性关联位点附近注释到23个功能基因,肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子(TNF receptor associated factors, trafs)编码一类具有胞内信号转导功能的蛋白,它们介导了多种生物学功能,包括先天性和获得性免疫应答、胚胎发育、应激反应和骨代谢(胡宸曦, 2020)。肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子4 (TNF receptor associated factor 4, traf4)是trafs家族中比较特殊的一员,生物学功能多且复杂,参与调控nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)、c-Jun氨基末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase, JNK)和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinases, MAPK)等低氧相关信号通路(王沂等, 2015)。韩雪晴等(2019)通过亚细胞定位和双荧光素酶报告基因研究发现,traf4在293T细胞中主要定位于细胞质,可增强NF-κB活性。过氧化物氧化还原酶(peroxiredoxin, prdx)基因家族编码具有过氧化氢酶活性的抗氧化蛋白,在生物体中参与多个与活性氧相关的信号通路,参与氧活性物质清除和细胞保护(丁婷婷等, 2020)。朱珍珍(2017)利用CRISPR/Cas9技术对斑马鱼(Danio rerio) prdx家族进行敲除,分别获得prdx1、prdx5和prdx6缺陷突变体,使用15 mmol/L的H2O2处理发现,斑马鱼prdx5缺陷的胚胎耐受胁迫能力降低。此外,脂肪醛脱氢酶(fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase, aldh3a2)基因产物参与无氧代谢,候选基因中还包含多个具体功能未知的信号转导分子(如esrrg、eng3和gpr12)和转录调控因子(如gtf3c4、sox30和tcerg1l),均与低氧应答或低氧损伤修复相关,可能贡献于低氧适应表型。此外,除了carp063890位于scaffold1133,未能装配至特定染色体,其余3个位点均定位于41号染色体,表明该染色体区域存在与低氧适应性状密切关联的基因。
本研究初步筛选了低氧适应性状的关联位点,注释了这些位点附近可能参与低氧适应调控通路的基因,为下一步开展区域内效应基因精细定位、基因表达和功能分析等研究奠定了基础,后续将通过低氧转录组分析、QTL定位等手段,筛查导致性状差异的效应基因及基因型,开展深入功能分析,为探索鲤低氧适应性状的分子机理和鱼类耐低氧品种选育提供借鉴。
ABDEL-TAWWAB M, HAGRAS A E, ELBAGHDADY H M, et al. Dissolved oxygen level and stocking density effects on growth, feed utilization, physiology, and innate immunity of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Journal of Applied Aquaculture, 2014, 26(4): 340-355 DOI:10.1080/10454438.2014.959830 |
ABDEL-TAWWAB M, MONIER M N, HOSEINIFAR S H, et al. Fish response to hypoxia stress: Growth, physiological, and immunological biomarkers. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 2019, 45(3): 997-1013 DOI:10.1007/s10695-019-00614-9 |
ARAÚJO-LUNA R, RIBEIRO L, BERGHEIM A, et al. The impact of different rearing condition on gilthead seabream welfare: Dissolved oxygen levels and stocking densities. Aquaculture Research, 2018, 49(12): 3845-3855 DOI:10.1111/are.13851 |
CADIZ L, ZAMBONINO-INFANTE J L, QUAZUGUEL P, et al. Metabolic response to hypoxia in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) displays developmental plasticity. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2017, 215: 1-9 |
CHEN L, PENG W Z, KONG S N, et al. Genetic mapping of head size related traits in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Frontiers in Genetics, 2018, 9: 448 DOI:10.3389/fgene.2018.00448 |
CUI A J, XU Y J, WANG B, et al. Genome-wide association analysis of growth traits in yellow tail kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2020, 41(2): 71-79 [崔爱君, 徐永江, 王滨, 等. 黄条  生长性状全基因组关联分析. 渔业科学进展, 2020, 41(2): 71-79] 生长性状全基因组关联分析. 渔业科学进展, 2020, 41(2): 71-79] |
DING J, LIU C, LUO S, et al. Transcriptome and physiology analysis identify key metabolic changes in the liver of the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in response to acute hypoxia. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 189: 109957 DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109957 |
DING T T, ZHANG H, FENG J H, et al. Advances in research on mechanism of action of PRDXs family in colorectal cancer. Chinese Journal of Immunology, 2020, 36(23): 2938-2942 [丁婷婷, 张红, 冯继红, 等. PRDXs家族在结直肠癌中作用机制的研究进展. 中国免疫学杂志, 2020, 36(23): 2938-2942 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2020.23.024] |
FITZGIBBON Q P, STRAWBRIDGE A, SEYMOUR R S. Metabolic scope, swimming performance and the effects of hypoxia in the mulloway, Argyrosomus japonicus (Pisces: Scianeidae). Aquaculture, 2007, 270(1): 358-368 |
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture, 2020
|
GAO J, YANG R Q. Joint genome-wide association study of body mass and morphological traits in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2021, 42(2): 63-70 [高进, 杨润清. 大菱鲆体重和体尺性状联合GWAS分析. 渔业科学进展, 2021, 42(2): 63-70] |
GENG X, SHA J, LIU S K, et al. A genome-wide association study in catfish reveals the presence of functional hubs of related genes within QTLs for columnaris disease resistance. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16(1): 196 DOI:10.1186/s12864-015-1409-4 |
HAN X Q, GAO F Y, LU M X, et al. Cloning, expression and functional analysis of TRAF4 gene in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2019, 27(3): 381-392 [韩雪晴, 高风英, 卢迈新, 等. 尼罗罗非鱼TRAF4基因的克隆、表达及功能分析. 农业生物技术学报, 2019, 27(3): 381-392] |
HU C X. Cloning of TRAF gene family in Hyriopsis cumingii and their interaction with β-Arrestin. Master's Thesis of Nanchang University, 2020, 99 [胡宸曦. 三角帆蚌TRAF家族基因的克隆及与β-arrestin蛋白互作. 南昌大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2020, 99]
|
LAI K P, WANG S Y, LI J W, et al. Hypoxia causes transgenerational impairment of ovarian development and hatching success in fish. Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 53(7): 3917-3928 DOI:10.1021/acs.est.8b07250 |
LI H L, GU X H, LI B J, et al. Genome-wide QTL analysis identified significant associations between hypoxia tolerance and mutations in the GPR132 and ABCG4 genes in nile tilapia. Marine Biotechnology, 2017, 19(5): 441-453 DOI:10.1007/s10126-017-9762-8 |
NAKAJIMA T, HUDSON M J, UCHIYAMA J, et al. Common carp aquaculture in Neolithic China dates back 8, 000 years. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 2019, 3(10): 1415-1418 DOI:10.1038/s41559-019-0974-3 |
PORTNER H O. Oxygen- and capacity-limitation of thermal tolerance: a matrix for integrating climate related stressor effects in marine ecosystems. Journal of Experimental Biology, 2010, 213(6): 881-893 DOI:10.1242/jeb.037523 |
QI D, CHAO Y, WU R, et al. Transcriptome analysis provides insights into the adaptive responses to hypoxia of a schizothoracine fish (Gymnocypris eckloni). Frontiers in Physiology, 2018, 9: 1326 DOI:10.3389/fphys.2018.01326 |
QI M, WU Q, LIU T, et al. Hepatopancreas transcriptome profiling analysis reveals physiological responses to acute hypoxia and reoxygenation in juvenile qingtian paddy field carp Cyprinus carpio var qingtianensis. Frontiers in Physiology, 2020, 11: 1110 DOI:10.3389/fphys.2020.01110 |
SHI L Y, LI F, JIA Z Y, et al. Study on genetic diversity and structure in songhe carp. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2012(4): 104-112 [石连玉, 李飞, 贾智英, 等. 选育品种松荷鲤遗传结构研究. 海洋湖沼通报, 2012(4): 104-112] |
WANG S Y, LAU K, LAI K P, et al. Hypoxia causes transgenerational impairments in reproduction of fish. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12114 DOI:10.1038/ncomms12114 |
WANG X Z, LIU S K, JIANG C, et al. Multiple across-strain and within-strain QTLs suggest highly complex genetic architecture for hypoxia tolerance in channel catfish. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2017, 292(1): 63-76 DOI:10.1007/s00438-016-1256-2 |
WANG Y, ZHAO J J, HAN X Y, et al. Structure and biological function of TRAF4. Life Science Research, 2015, 19(2): 169-175 [王沂, 赵俊暕, 韩晓燕, 等. TRAF4的结构与生物学功能. 生命科学研究, 2015, 19(2): 169-175] |
XIAO W H. Hypoxia signal transduction pathway and fish adaptation to hypoxia. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2014, 44(12): 1227-1235 [肖武汉. 低氧信号传导途径与鱼类低氧适应. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2014, 44(12): 1227-1235] |
XU J, ZHAO Z X, ZHANG X F, et al. Development and evaluation of the first high-throughput SNP array for common carp (Cyprinus carpio). BMC Genomics, 2014, 15: 307 DOI:10.1186/1471-2164-15-307 |
XU P, ZHANG X F, WANG X M, et al. Genome sequence and genetic diversity of the common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Nature Genetics, 2014, 46(11): 1212-1219 DOI:10.1038/ng.3098 |
ZHANG G S, ZHAO C, WANG Q T, et al. Identification of HIF-1 signaling pathway in Pelteobagrus vachelli using RNA-Seq: Effects of acute hypoxia and reoxygenation on oxygen sensors, respiratory metabolism, and hematology indices. Journal of Comparative Physiology B, 2017, 187(7): 921-943 |
ZHANG H Y, XU P, JIANG Y L, et al. Genomic, transcriptomic, and epigenomic features differentiate genes that are relevant for muscular polyunsaturated fatty acids in the common carp. Frontiers in Genetics, 2019, 10: 217 DOI:10.3389/fgene.2019.00217 |
ZHAO Z X, CAO D C, KUANG Y Y, et al. Analysis of common carp neuroglobin gene sequence and hypoxia expression. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2014, 38(3): 325-332 [赵紫霞, 曹顶臣, 匡友谊, 等. 鲤神经球蛋白基因序列与低氧表达分析. 水产学报, 2014, 38(3): 325-332] |
ZHENG X H, KUANG Y Y, LÜ W H, et al. Genome-wide association study for muscle fat content and abdominal fat traits in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). PLoS One, 2016, 11(12): e0169127 DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0169127 |
ZHONG X X, WANG X Z, ZHOU T, et al. Genome-wide association study reveals multiple novel QTL associated with low oxygen tolerance in hybrid catfish. Marine Biotechnology, 2017, 19(4): 379-390 DOI:10.1007/s10126-017-9757-5 |
ZHOU Q, SU Z C, LI Y Z, et al. Genome-wide association mapping and gene expression analyses reveal genetic mechanisms of disease resistance variations in Cynoglossus semilaevis. Frontiers in Genetics, 2019, 10: 1167 DOI:10.3389/fgene.2019.01167 |
ZHOU T, LIU S K, GENG X, et al. GWAS analysis of QTL for enteric septicemia of catfish and their involved genes suggest evolutionary conservation of a molecular mechanism of disease resistance. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2017, 292(1): 231-242 DOI:10.1007/s00438-016-1269-x |
ZHU Z Z. Study on zebrafish rsph3 gene in early development and preparation of zebrafish prdx mutants. Master's Thesis of Shandong University, 2017, 87 [朱珍珍. 斑马鱼rsph3基因在早期发育中的研究及斑马鱼prdx突变体的制备. 山东大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2017, 87]
|



