2. 青岛农业大学海洋科学与工程学院 山东 青岛 266109;
3. 淮阴工学院 江苏省益生制剂重点建设实验室 江苏 淮安 223003
2. School of Marine Science and Engineering, Qingdao Agricultural University, Qingdao, Shandong 266109, China;
3. Jiangsu Provincial Key Construction Laboratory of Probiotics Preparation, Huaiyin Institute of Technology, Huaian, Jiangsu 223003, China
半乳糖凝集素(galectins)是一种能够体外结合β-半乳糖苷的可溶性凝集素,其家族成员按分子结构特征可分为原型、嵌合型和串联重复型(Thijssen et al, 2015)。半乳糖凝集素广泛存在于动物中,目前,共有15种半乳糖凝集素被分离、鉴定并命名,其相关功能已在许多物种中被广泛研究,包括真菌(Butschi et al, 2010)、刺胞动物门(Hwang et al, 2010)、昆虫(Rao et al, 2016)、线虫(Takeuchi et al, 2016)、软体动物(Bai et al, 2018)、头索动物(Yu et al, 2007)和尾索动物(Vizzini et al, 2012)等。研究发现,半乳糖凝集素在生物体的许多生物过程中发挥作用,如细胞粘附(Ferragut et al, 2019)、细胞凋亡(Liu et al, 2011)、炎症反应(Nita-Lazar et al, 2015)和肿瘤转移(Shatz-Azoulay et al, 2020)等。
半乳糖凝集素6 (Galectin-6)是一种典型的串联重复型半乳糖凝集素,Galectin-6在动物体内的功能研究尚不全面。研究发现,埃及伊蚊(Aedes aegypti)体内的Galectin-6能阻碍cry11aa [苏云金芽孢杆菌(Bacillus thuringiensis)产生的一种晶体毒素,对埃及伊蚊有致命毒性]与碱性磷酸酶1 (ALP1)和氨肽酶N (APN2)结合,对埃及伊蚊体起到保护作用(Hu et al, 2020)。对小鼠(Mus musculus) Galectin-6 (Lgals6)研究发现,Lgals6是一种新型的抗菌蛋白(antimicrobial proteins, AMPs),可能起到调节皮肤纤维化的作用,其表达水平受皮肤微生物组的影响(Natsuga et al, 2016)。此外,Gitt等(1998)研究发现,Lgals6和小鼠Galectin-4 (Lgals4)具有高度的同源性,在小鼠消化道中,Lgals6与Lgals4的表达模式几乎相同,且Lgals6和Lgals4在核酸水平和氨基酸水平的一致性分别高达93%和83%,暗示它们在小鼠体内可能具备相似的功能。研究表明,Galectin-4参与炎症反应、肠上皮伤口愈合(Paclik et al, 2008)和肠道中表达人类血型抗原的大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)杀灭过程(Stowell et al, 2010),但Galectin-6是否具有类似功能,还需要进一步验证。事实上,Galectin-6可能有一些尚未证实的潜在功能。Houzelstein等(2013)推测,Galectin-6的潜在功能并不是由其表达模式的改变引起的,而可能是由其特异性结合新配体的独特蛋白结构引起的。
目前,有关Galectin-6的报道主要集中在哺乳动物中,而在硬骨鱼类中缺乏相关研究。本研究在牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)中发现一种Galectin-6 (PoGalectin-6),对PoGalectin-6的基因序列和氨基酸序列进行分析鉴定,构建PoGalectin-6与串联重复型galectins (Galectin-6、Galectin-4、Galectin-8和Galectin-9)的系统进化树,验证PoGalectin-6在免疫组织中的分布和表达水平,表达纯化重组PoGalectin-6蛋白用于细菌结合和凝集实验,可为进一步研究PoGalectin-6的相关功能奠定理论基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料牙鲆购自山东烟台,平均体重为(120±10) g,平均体长为(22±3) cm。健康牙鲆在15℃水温海水循环养殖系统中暂养7 d。迟缓爱德华氏菌(Edwardsiella tarda)为本实验室保存菌种,经16S rRNA测序进行菌种鉴定。
1.2 样品处理和采集随机取9条健康牙鲆进行组织取样,每3条鱼的肝、脾、肾、脑、鳃、肠、皮肤和肌肉组织混合作为1个生物学重复,样品在液氮中快速冷冻后转移至–80℃保存,用于总RNA提取。
采用浸泡法对健康牙鲆进行迟缓爱德华氏菌(6×107 CFU/mL)感染实验,感染2 h后转入海水循环养殖系统正常养殖。在感染之前,随机抽取9条健康牙鲆的肠组织作为对照(0 h),恢复养殖后的2、8、12、24、48和72 h分别取9条鱼的肠组织,按上述方法冷冻保存,留待实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)分析。
1.3 RNA提取和cDNA制备根据TRIzol试剂盒(Invitrogen, 美国)的说明书,进行组织的总RNA提取,利用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测所提取RNA的完整性,用超微量分光光度计(Thermo Scientific, 中国)检测其纯度和浓度。用PrimeScript™ RT reagent kit (TaKaRa,日本)反转录合成cDNA,反应体系:2 µL 5× PrimeScript Buffer,0.5 µL PrimeScript RT Enzyme Mix Ⅰ,0.5 µL Oligo dT Primer,0.5 µL Random 6 mers,Total RNA用量为500 µg,补充RNase Free dH2O至10 µL。上述反应体系在37℃条件下反转录15 min,然后,于85℃反应5 s,使反转录酶失活。将cDNA在–20℃冰箱保存备用。
1.4 PoGalectin-6基因序列分析利用NCBI网站Blast程序(https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)对PoGalectin-6基因序列进行核苷酸同源性比对;利用Open Reading Frame Finder (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/)查找ORF;使用SMART (simple modular architecture research tool)在线软件分析PoGalectin-6蛋白结构域。
1.5 PoGalectin-6同源序列比对与系统进化树构建利用NCBI网站查询不同物种的串联重复型galectins (Galectin-6、Galectin-4、Galectin-8和Galectin-9)的氨基酸序列。采用DNAMAN软件对PoGalectin-6 (XP_019943943.1)与硬骨鱼类Galectin-6和Galectin-4的氨基酸序列进行多重序列比对,包括斑马拟丽鱼(Maylandia zebra) Galectin-6 (XP_023009370. 2)、白斑狗鱼(Esox lucius) Galectin-6 (XP_019900129.1)、秀美花鳉(Poecilia formosa) Galectin-6 (XP_016527155. 1)、大菱鲆(Scophthalmus maximus) Galectin-4 (AXR99075.1)、乌鳢(Channa argus) Galectin-4 (KAF3693285.1)和尼罗罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus) Galectin-4 (XP_025753881.1)。
利用MEGA 5.0软件中的Neighbor-joining法构建PoGalectin-6与其他硬骨鱼类串联重复型galectins的系统进化树,包括上述硬骨鱼类Galectin-6和Galectin-4以及半滑舌鳎(Cynoglossus semilaevis) Galectin-4 (XP_008307038.1)、眼斑双锯鱼(Amphiprion ocellaris) Galectin-8 (XP_023152887.1)、条石鲷(Oplegnathus fasciatus) Galectin-8 (ANN46245.1)、斑马拟丽鱼Galectin-8 (XP_004561164.1)、大西洋鲑(Salmo salar) Galectin-8 (NP_001133778.1)、虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss) Galectin-9 (ACO08221.1)、斑点叉尾
根据PoGalectin-6基因序列,利用Primer Premier 5.0软件设计PoGalectin-6特异性引物(PoGalectin-6-qF和PoGalectin-6-qR),以牙鲆EF1α基因作为内参,引物序列见表 1。使用TB Green® Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ(TaKaRa, 日本)试剂盒,qRT-PCR按照说明书于BioRad CFX96荧光定量PCR仪上进行。反应体系为10 µL:5 µL TB Green Premix Ex TaqⅡ(2×),0.4 µL上游引物,0.4 µL下游引物,0.8 µL模板cDNA,3.4 µL ddH2O。反应程序:预变性95℃ 30 s;95℃ 5 s,65℃ 1 min,扩增35个循环;熔解曲线95℃ 10 s,65℃ 5 s,95℃ 0.5℃/cycle。采用2-ΔΔCt方法计算PoGalectin-6基因的相对表达量,每个样品设置3个重复。使用SigmaPlot 11.0软件作图以及单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),P < 0.05为具有显著性差异。
|
|
表 1 PoGalectin-6基因克隆和荧光定量所用引物 Tab.1 Primers for PCR and qRT-PCR of PoGalectin-6 gene |
根据PoGalectin-6基因序列合成一对引物PoGalectin-6-eF和PoGalectin-6-eF (表 1),用于扩增PoGalectin-6基因。PCR扩增体系为25 µL:12.5 µL 2×Taq PCR Mix,0.5 µL上游引物,0.5 µL下游引物,2 µL模板cDNA,9.5 µL ddH2O。反应程序:预变性94℃ 5 min;变性94℃ 30 s,退火55℃ 30 s,延伸72℃ 1 min,扩增34个循环;延伸72℃ 1 min,4℃冷却。采用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳对PCR结果进行检测,检测结果无误后,将PCR产物回收,并利用超微量分光光度计检测其纯度和浓度。使用相同的限制性内切酶(EcoRⅠ和HandⅢ)对PCR产物和pet32a质粒进行处理,使用T4 DNA连接酶将PCR产物与pet32a质粒连接,构建pet32a-PoGalectin-6重组质粒。将重组质粒转化E. coli BL21 (DE3)表达感受态细胞,使用0.5 mmol/L IPTG于37℃条件下培养4 h诱导蛋白表达,同时,以未加IPTG诱导的细胞作为对照组,通过超声破碎法提取PoGalectin-6重组蛋白(rPoGalectin-6)。将破碎后的菌液于12 000 r/min、4℃离心10 min后,收集沉淀进行变性及复性,然后经Ni-NTA树脂纯化,并利用12%十二烷基硫酸钠聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)鉴定。rPoGalectin-6蛋白浓度通过Bradford法进行测定。
1.8 rPoGalectin-6与微生物的亲和力检测通过酶联免疫吸附法检测rPoGalectin-6对3株革兰氏阳性菌[枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)、蜡样芽孢杆菌(Bacillus cereus)和短小芽孢杆菌(Bacillus pumilus)]及3种革兰氏阴性菌[杀鲑气单胞菌(Aeromonas salmonicida)、迟缓爱德华氏菌和创伤弧菌(Vibrio vulnificus)]的亲和力。上述细菌均取自本实验室保存菌种,将上述细菌于磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)中重悬至1×108 CFU/mL,各取100 µL的细菌悬液置于96孔EIA/RIA板(康宁,中国),4℃下过夜培养。然后每孔加入250 µL封闭缓冲液(5%脱脂奶粉溶于PBST),继续在4℃条件下封闭1 h。用PBS将rPoGalectin-6稀释至终浓度分别为0.1、1和5 μg/mL,以PBS作为对照,各取100 µL rPoGalectin-6加入孔中,并在22℃下培养1 h,每个蛋白浓度均设置3个平行。接着将小鼠抗His抗体(全式金,中国)按照1∶2000的比例稀释至5%脱脂奶粉中,分别向每孔中加入100 µL小鼠抗His抗体,并在37℃下孵育1 h。然后,将羊抗鼠IgG (全式金,中国)按照1∶4000的比例稀释至5%脱脂奶粉中,分别向每孔中加入100 µL含HRP标签的羊抗鼠IgG,并于37℃下孵育1 h。在上述每一步结束时,均用300 µL PBST洗涤3次。以上反应结束后,分别向每孔加入100 µL TMB溶液显色5 min,最后每孔加入100 µL浓度为1 mol/L硫酸终止反应,在450 nm处测定吸光值。
1.9 rPoGalectin-6与微生物的凝集活性检测利用2株革兰氏阳性菌(短小芽孢杆菌和枯草芽孢杆菌)和2株革兰氏阴性菌(杀鲑气单胞菌和迟缓爱德华氏菌)检测rPoGalectin-6的细菌凝集活性,上述细菌均取自本实验室保存菌种。将细菌培养至对数中期后重悬于Tris缓冲盐溶液(TBS)中至终浓度为1×108 CFU/mL。实验组处理方法:将25 µL rPoGalectin-6蛋白(60 μg/mL)与25 µL各菌液在室温下混合均匀,并加入5 µL浓度为0.1 mol/L的CaCl2溶液,置于200 r/min摇床中培养1 h。同时,将rPoGalectin-6蛋白和细菌混合培养作为对照组,验证无Ca2+存在的情况下rPoGalectin-6蛋白的微生物凝集活性。在相同条件下,用相同体积和浓度的牛血清白蛋白(BSA)代替rPoGalectin-6蛋白作为空白对照组。微生物凝集实验结果均在光学显微镜下观察得到。
2 结果 2.1 PoGalectin-6基因序列分析和结构特征通过NCBI网站对PoGalectin-6的核酸序列进行鉴定发现,PoGalectin-6的ORF长1089 bp,共编码362个氨基酸(aa),预测其分子量为39.11 kDa,理论等电点(pI)为5.89。利用SMART软件对其氨基酸序列分析,显示PoGalectin-6是一个串联重复型半乳糖凝集素,在其ORF两端各有1个糖识别结构域(CRD),长度分别为127 aa和126 aa。2个CRD之间通过一个长度为65 aa的富含甘氨酸的连接区域连接。此外,PoGalectin-6的2个CRD均含有一个典型的β-半乳糖苷结合基序(HXNPR,X代表任何氨基酸) (图 1)。

|
图 1 牙鲆Galectin-6 ORF序列和推测的氨基酸序列 Fig.1 The ORF and deduced amino acid sequences of PoGalectin-6 左边的数字代表核苷酸和推测的氨基酸序列。红色字体表示起始密码子(ATG)和终止密码子(TGA)。黄色阴影的氨基酸序列代表2个CRD。红色阴影的氨基酸序列代表连接区域。黑框代表CRD中的保守基序HXNPR(X代表任何氨基酸)。 The numbers on the left represent the nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences. Red font indicates the start codon (ATG) and the stop codon (TGA). The yellow shaded amino acid sequence represents two CRDs. The red shaded amino acid sequence represents the linker. The black boxes represent the conserved motifs HXNPR (X represents any amino acid) in the CRD. |
将PoGalectin-6与其他硬骨鱼类的Galectin-6和Galectin-4进行同源比对,显示其相似性为58.10%~ 80.90%。其中,PoGalectin-6与大菱鲆Galectin-4的相似性最高,为80.90%;与尼罗罗非鱼Galectin-4的相似性最低,为58.10%。将PoGalectin-6与上述6种串联重复型galectins进行多重序列比对,结果显示,不同硬骨鱼类的Galectin-6和Galectin-4的2个CRD并不保守,但在每个CRD上都存在一段高度保守的氨基酸基序HXNPR (X代表任何氨基酸)(图 2)。

|
图 2 PoGalectin-6多序列比对 Fig.2 Multiple sequence alignment of PoGalectin-6 氨基酸序列比对采用DNAMAN软件构建。红框代表2个CRD。黄框代表CRDs中的保守基序HXNPR (X代表任何氨基酸)。 The amino acid sequence alignment was constructed by the DNAMAN. Red boxes represent two CRDs. The yellow boxes represent the conserved motifs HXNPR (X represents any amino acid) in CRDs. |
利用MEGA 5.0软件对PoGalectin-6与其他硬骨鱼类的串联重复型galectins (Galectin-6、Galectin-4、Galectin-8和Galectin-9)的氨基酸序列比对,构建了系统进化树(图 3)。系统进化树由两大分支组成,Galectin-6和Galectin-4聚为一支,Galectin-8和Galectin-9聚为一支。PoGalectin-6在进化上与大菱鲆Galectin-4亲缘关系最为密切,与其他物种的Galectin-8和Galectin-9亲缘关系较远。
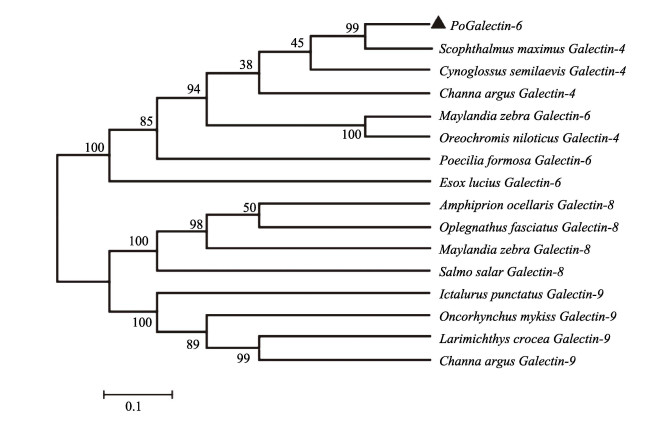
|
图 3 PoGalectin-6与其他硬骨鱼类的串联重复型galectins的系统进化树 Fig.3 The phylogenetic tree showing the relationship between PoGalectin-6 with tandem repeat galectins of other teleost 使用MEGA 5.0中的neighbor-joining方法构建系统进化树,构建了PoGalectin-6和Galectin-4、Galectin-6、Galectin-8和Galectin-9等串联重复型galectins的系统进化树。 Phylogenetic tree was constructed using a neighbor-joining algorithm in MEGA 5.0. The phylogenetic trees of PoGalectin-6 and other tandem repeats galectin was constructed, including Galectin-4, Galectin-6, Galectin-8, and Galectin-9. |
利用qRT-PCR方法分析PoGalectin-6在不同组织(肝、脾、肾、脑、肠、鳃、皮肤和肌肉)中的表达水平。结果显示,PoGalectin-6在组织中的表达具有明显的特异性(图 4),PoGalectin-6主要在牙鲆的肠组织中有大量表达。相对于肠组织中的表达量,在脑、皮肤以及肌肉组织中表达量非常低,而在肝、脾、肾和鳃组织中均不表达。
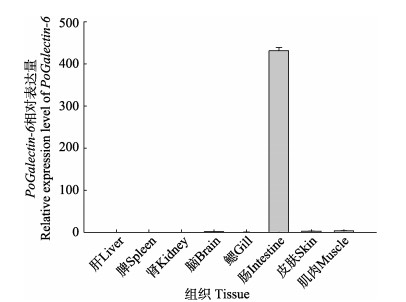
|
图 4 PoGalectin-6在牙鲆正常组织中的相对表达量 Fig.4 The relative expression of PoGalectin-6 gene in normal tissues of P. olivaceus |
迟缓爱德华氏菌感染牙鲆能够诱导PoGalectin-6在肠组织中的表达变化。在感染0、2、8、12、24、48、72 h,PoGalectin-6在肠组织中的表达水平如图 5所示,PoGalectin-6呈现出先升高后降低的表达趋势。其表达水平在感染后12 h呈现显著上调,并达到峰值,是0 h表达量的4.2倍。感染后48 h达到第2个峰值,是0 h表达量的2.4倍,随后PoGalectin-6表达水平下降,并在感染后72 h恢复至正常水平。
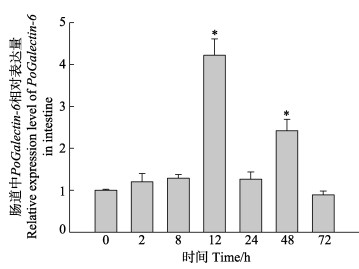
|
图 5 迟缓爱德华氏菌感染牙鲆后肠道中PoGalectin-6的表达水平 Fig.5 Expression level of PoGalectin-6 in the intestine of P. olivaceus infected E. tarda 以0 h时的表达水平为对照,不同时间点(2、8、12、24、48和72 h)的表达量通过qRT-PCR获得。*代表显著性差异(P < 0.05)。 The data determined by qRT-PCR at different time points (0, 2, 8, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h) compared with the 0 h time point respectively. The symbol * represent P < 0.05. |
以pet32a为表达载体,重组PoGalectin-6蛋白经镍柱分离纯化,纯化的rPoGalectin-6蛋白包含来自pet32a载体质粒约15 kDa的标签蛋白和39.11 kDa的PoGalectin-6蛋白。重组蛋白经12% SDS-PAGE电泳分析(图 6),在55 kDa处有条带,与预测目的条带大小基本一致。阴性对照和上清液中均未发现目的条带,说明成功表达并分离纯化了rPoGalectin-6蛋白。
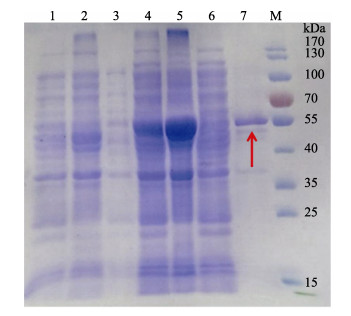
|
图 6 纯化rPoGalectin-6蛋白的SDS-PAGE分析 Fig.6 SDS-PAGE analysis of purified rPoGalectin-6 M:蛋白质Marker;1:未诱导的细菌总提取物;2:未诱导的细菌提取物沉淀;3:未诱导的细菌提取物上清液;4:诱导的细菌总提取物;5:诱导的细菌提取物沉淀;6:诱导的细菌提取物上清液;7:纯化的rPoGalectin-6蛋白 Lane M: Molecular weight marker; Lane 1: Total soluble cellular extract from negative control; Lane 2: Total precipitation cellular extract from negative control; Lane 3: total supernatant cellular extract from negative control; Lane 4: Total soluble cellular extract from the experimental group; Lane 5: Total precipitation cellular extract from the experimental group; Lane 6: Total supernatant cellular extract from the experimental group; Lane 7: Concentrated purified recombinant PoGalectin-6 |
rPoGalectin-6蛋白与微生物结合实验验证了对革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌的结合能力。结果如图 7所示,rPoGalectin-6与微生物的结合能力与细菌种类有关,其对枯草芽孢杆菌、蜡样芽孢杆菌、杀鲑气单胞菌、迟缓爱德华氏菌和创伤弧菌均表现出较强的结合能力,且蛋白浓度越高,其结合能力越强,而rPoGalectin-6蛋白与短小芽孢杆菌并没有表现出明显的结合能力。
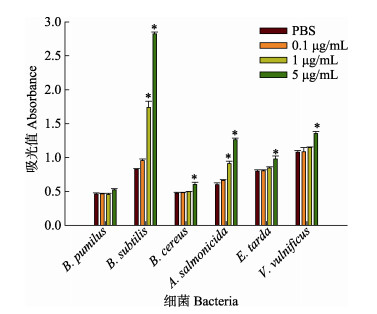
|
图 7 rPoGalectin-6蛋白与微生物结合能力验证 Fig.7 Verification of bacterial binding capacity *代表与PBS组相比具有显著性差异(P < 0.05)。 * indicates a significant difference compared with PBS (P < 0.05). |
细菌凝集实验结果如图 8所示,rPoGalectin-6蛋白均能够显著凝集短小芽孢杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、杀鲑气单胞菌和迟缓爱德华氏菌。对照组中,BSA并未展现出对细菌的凝集反应。此外,在Ca2+不存在的情况下,rPoGalectin-6蛋白未表现出明显的细菌凝集现象,这说明只有在Ca2+存在的情况下,rPoGalectin-6才能展现出较强的微生物凝集活性。
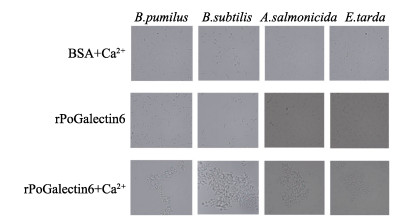
|
图 8 rPoGalectin-6蛋白与微生物的凝集活性 Fig.8 Agglutinating activity of rPoGalectin-6 with microorganisms |
半乳糖凝集素是一种具有保守CRD的可溶性凝集素,它们广泛存在于哺乳动物和昆虫体内,并在机体免疫过程中发挥重要作用。研究发现,在哺乳动物体内,半乳糖凝集素主要参与细胞粘附、生长调节和免疫等生物过程,尤其在疾病防控等方面起到关键作用(Oyanadel et al, 2018; Rao et al, 2016; Wdowiak et al, 2018)。虽然在哺乳动物中已经鉴定出Galectin-6,但在硬骨鱼中尚无Galectin-6的相关研究,因此,其应对细菌感染的免疫功能尚不清楚。本研究通过分析PoGalectin-6的分子特征,探究其在体内发挥的相关功能,旨在为硬骨鱼类中Galectin-6的功能研究奠定基础。
本研究成功从牙鲆体内分离并鉴定了Galectin-6,序列分析表明,PoGalectin-6是一种标准的串联重复型半乳糖凝集素,它拥有2个能够特异性识别并结合糖的CRD,每个CRD上都包含一个非常保守的糖结合基序(HXNPR,X代表任何氨基酸),CRD之间是由65个氨基酸编码的富含甘氨酸的结合肽组成的连接区域。同源序列比对分析表明,PoGalectin-6与大菱鲆Galectin-4相似性最高(80.90%),在系统进化树上,PoGalectin-6和Galectin-4分布在同一分支。同源序列比对和系统进化树实验结果证实,PoGalectin-6与大菱鲆Galectin-4亲缘关系上更接近,这也与Gitt等(1998a)发现Lgals4和Lgals6高度相似的结论相一致。Gitt等(1998b)是在研究小鼠Lgals4的过程中意外发现一个由8个外显子编码、具有2个CRD的新的串联重复型半乳糖凝集素,即Lgals6。随后,将Lgals6与Lgals4进行比对分析发现,二者同源性非常高,不同之处在于,Lgals6的2个CRD之间的连接区域相较于Lgals4缺少24个氨基酸。因此,Gitt等(1998b)推测,连接区域长度的差异可能会影响CRD间交联配体的功能活性,进而导致小鼠Lgals6和Lgals4存在功能上的差异。这种现象在哺乳动物的Galectin-9中已有先例,如哺乳动物肠道中的Galectin-9具有较长的连接区域,而其他组织中的Galectin-9则具有较短的连接区域,这表明连接区域的长度差异可能导致不同组织中Galectin-9的功能差异(Wada et al, 1997)。
为了明确PoGalectin-6是否在牙鲆机体免疫过程中发挥作用,在迟缓爱德华氏菌感染牙鲆72 h内,对PoGalectin-6的组织分布情况进行分析。结果显示,PoGalectin-6主要在牙鲆肠组织中大量表达,在其他组织中表达量非常低或基本不表达,这与Houzelstein等(2013)发现的小鼠体内Lgals6仅在肠胃中有表达的结果一致。鉴于肠道是硬骨鱼体内能识别微生物并促进免疫排斥的主要粘膜相关淋巴组织(MALT)之一(Fermino et al, 2011),且PoGalectin-6与Lgals6均在肠道组织中具有类似的表达分布,因此,对PoGalectin-6是否在牙鲆体内也作为抗菌蛋白在免疫中发挥重要作用进行进一步验证。攻毒实验显示,迟缓爱德华氏菌感染牙鲆后12 h内,肠组织内PoGalectin-6的表达量增加了4倍以上,说明PoGalectin-6在迟缓爱德华氏菌入侵后参与了机体的免疫应答。
半乳糖凝集素作为模式识别受体(pattern recognition receptor, PRR),可以直接与细菌和寄生虫表面的多聚糖相互作用,在抵抗微生物感染的过程中起到调节免疫应答的作用(Shi et al, 2018)。微生物结合实验表明,rPoGalectin-6能广泛识别并结合革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌,暗示PoGalectin-6可能参与牙鲆对细菌感染的先天免疫防御机制。此外,rPoGalectin-6对微生物的结合能力具有浓度依赖性,即高浓度的rPoGalectin-6对细菌的结合能力更强。虽然rPoGalectin-6与细菌的结合能力已被证实,但rPoGalectin-6与细菌的作用机制尚不清楚。Galectin-6已被证明具有β-半乳糖苷结合活性(Gitt et al, 1998a),然而,rPoGalectin-6是否通过结合细菌表面的β-半乳糖苷进而展现出与细菌的亲和力还有待进一步研究。
凝集活性是半乳糖凝集素最重要的特性,它们可以通过结合细胞表面的糖蛋白和糖复合物来凝集细胞。细菌凝集实验结果表明,rPoGalectin-6对革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌均具有凝集活性,这意味着rPoGalectin-6可能作为一种粘连相关的蛋白质,通过识别、结合以及凝集微生物,在牙鲆的先天性免疫防御过程中发挥作用。在对凝集素凝集活性的研究中,认为Ca2+是C型动物凝集素发挥凝集活性的重要因素(Su et al, 2020),相反,半乳糖凝集素曾被认为是不依赖于Ca2+的S型动物凝集素(Hughes, 2001)。然而,一些半乳糖凝集素确实表现出Ca2+依赖性的凝集活性,例如,中华绒螯蟹(Eriocheir sinensis)半乳糖凝集素Galectin (EsGal) (Wang et al, 2016)和大黄鱼Galectin-9 (LcGal9) (Zhang et al, 2016)。这些结果表明,非Ca2+依赖的凝集活性可能不是半乳糖凝集素不可或缺的特征。Ca2+在rPoGalectin-6凝集过程中的作用机制可借鉴巨噬细胞甘露糖受体第4个CRD (CRD-4)与单糖的结合机制(Mullin et al, 1997)。CRD-4与甘露糖的结合由2个Ca2+参与,其中一个Ca2+仅起到定位作用,另一个Ca2+则与CRD-4侧链的羰基氧原子形成配位键,然后与甘露糖的羟基3或4结合形成三元络合物,完成CRD-4与甘露糖的结合。因此,Ca2+是Ca2+依赖型凝集素白识别和结合碳水化合物过程中的一个重要因素,这也解释了在没有Ca2+存在的情况下,rPoGalectin-6没有表现出理想的细菌凝集活性。
本研究识别并鉴定了PoGalectin-6,它主要在肠组织中大量表达,并且经微生物刺激后,PoGalectin-6在肠组织中的表达水平显著升高。在与细菌的互作实验中发现,rPoGalectin-6具有较强的细菌结合能力和凝集活性。综上所述,PoGalectin-6参与了由迟缓爱德华氏菌感染所引起的免疫应答,为探索Galectin-6在硬骨鱼类中的免疫功能奠定了基础。
BAI Y, NIU D, BAI Y, et al. Identification of a novel galectin in Sinonovacula constricta and its role in recognition of gram-negative bacteria. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2018, 80: 1-9 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2018.05.041 |
BUTSCHI A, TITZ A, WALTI M A, et al. Caenorhabditis elegans N-glycan core beta-galactoside confers sensitivity towards nematotoxic fungal galectin CGL2. PLoS Pathogens, 2010, 6(1): e1000717 DOI:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000717 |
FERMINO M L, POLLI C D, TOLEDO K A, et al. LPS-induced galectin-3 oligomerization results in enhancement of neutrophil activation. PLoS One, 2011, 6(10): e26004 DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0026004 |
FERRAGUT F, CAGNONI A J, COLOMBO L L, et al. Dual knockdown of galectin-8 and its glycosylated ligand, the activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM/ CD166), synergistically delays in vivo breast cancer growth. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta: Molecular Cell Research, 2019, 1866(8): 1338-1352 DOI:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.03.010 |
GITT M A, COLNOT C, POIRIER F, et al. Galectin-4 and galectin-6 are two closely related lectins expressed in mouse gastrointestinal tract. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1998a, 273(5): 2954-2960 DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.5.2954 |
GITT M A, XIA Y R, ATCHISON R E, et al. Sequence, structure, and chromosomal mapping of the mouse Lgals6 gene, encoding galectin-6. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1998b, 273(5): 2961-2970 DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.5.2961 |
HOUZELSTEIN D, REYES-GOMEZ E, MAURER M, et al. Expression patterns suggest that despite considerable functional redundancy, galectin-4 and -6 play distinct roles in normal and damaged mouse digestive tract. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 2013, 61(5): 348-361 DOI:10.1369/0022155413478612 |
HU X, CHEN H, XU J, et al. Function of Aedes aegypti galectin-6 in modulation of Cry11Aa toxicity. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2020, 162: 96-104 DOI:10.1016/j.pestbp.2019.09.010 |
HUGHES R C. Galectins as modulators of cell adhesion. Biochimie, 2001, 83(7): 667-676 DOI:10.1016/S0300-9084(01)01289-5 |
HWANG J S, TAKAKU Y, MOMOSE T, et al. Nematogalectin, a nematocyst protein with GlyXY and galectin domains, demonstrates nematocyte-specific alternative splicing in Hydra. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(43): 18539-18544 DOI:10.1073/pnas.1003256107 |
LIU F T, YANG R Y, SAEGUSA J, et al. Galectins in regulation of apoptosis. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 2011, 705: 431-442 |
MULLIN N P, HITCHEN P G, TAYLOR M E. Mechanism of Ca2+ and monosaccharide binding to a C-type carbohydrate-recognition domain of the macrophage mannose receptor. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1997, 272(9): 5668-5681 DOI:10.1074/jbc.272.9.5668 |
NATSUGA K, CIPOLAT S, WATT F M. Increased bacterial load and expression of antimicrobial peptides in skin of barrier-deficient mice with reduced cancer susceptibility. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2016, 136(1): 99-106 DOI:10.1038/JID.2015.383 |
NATSUGA K, WATT F M. Galectin-6 is a novel skin anti-microbial peptide that is modulated by the skin barrier and microbiome. Journal of Dermatological Science, 2016, 84(1): 97-99 DOI:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.06.008 |
NITA-LAZAR M, BANERJEE A, FENG C, et al. Galectins regulate the inflammatory response in airway epithelial cells exposed to microbial neuraminidase by modulating the expression of SOCS1 and RIG1. Molecular Immunology, 2015, 68(2 Pt A): 194-202 |
OYANADEL C, HOLMES C, PARDO E, et al. Galectin-8 induces partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition with invasive tumorigenic capabilities involving a FAK/EGFR/ proteasome pathway in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 2018, 29(5): 557-574 DOI:10.1091/mbc.E16-05-0301 |
PACLIK D, LOHSE K, WIEDENMANN B, et al. Galectin-2 and –4, but not galectin-1, promote intestinal epithelial wound healing in vitro through a TGF-beta-independent mechanism. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, 2008, 14(10): 1366-1372 DOI:10.1002/ibd.20499 |
RAO X J, WU P, SHAHZAD T, et al. Characterization of a dual-CRD galectin in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 2016, 60: 149-159 DOI:10.1016/j.dci.2016.03.001 |
SHATZ-AZOULAY H, VINIK Y, ISAAC R, et al. The animal lectin galectin-8 promotes cytokine expression and metastatic tumor growth in mice. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 7375 DOI:10.1038/s41598-020-64371-z |
SHI W, XUE C, SU X Z, et al. The roles of galectins in parasitic infections. Acta Tropica, 2018, 177: 97-104 DOI:10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.09.027 |
STOWELL S R, ARTHUR C M, DIAS-BARUFFI M, et al. Innate immune lectins kill bacteria expressing blood group antigen. Nature Medicine, 2010, 16(3): 295-301 DOI:10.1038/nm.2103 |
SU Y, LIU Y, GAO F, et al. A novel C-type lectin with a YPD motif from Portunus trituberculatus (PtCLec1) mediating pathogen recognition and opsonization. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 2020, 106: 103609 DOI:10.1016/j.dci.2020.103609 |
TAKEUCHI T, ARATA Y, KASAI K I. Galactosebeta1-4fucose: A unique disaccharide unit found in N-glycans of invertebrates including nematodes. Proteomics, 2016, 16(24): 3137-3147 DOI:10.1002/pmic.201600001 |
THIJSSEN V L, HEUSSCHEN R, CAERS J, et al. 2015. Galectin expression in cancer diagnosis and prognosis: A systematic review. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1855(2): 235-247 |
VIZZINI A, PARRINELLO D, SANFRATELLO M A, et al. Inducible galectins are expressed in the inflamed pharynx of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2012, 32(1): 101-109 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2011.10.028 |
WADA J, KANWAR Y S. Identification and characterization of galectin-9, a novel beta-galactoside-binding mammalian lectin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1997, 272(9): 6078-6086 DOI:10.1074/jbc.272.9.6078 |
WANG M Q, WANG L L, HUANG M M, et al. A galectin from Eriocheir sinensis functions as pattern recognition receptor enhancing microbe agglutination and haemocytes encapsulation. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2016, 55: 10-20 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2016.04.019 |
WDOWIAK K, FRANCUZ T, GALLEGO-COLON E, et al. Galectin targeted therapy in oncology: Current knowledge and perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(1): 210 DOI:10.3390/ijms19010210 |
YU Y, YUAN S, YU Y, et al. Molecular and biochemical characterization of galectin from amphioxus: Primitive galectin of chordates participated in the infection processes. Glycobiology, 2007, 17(7): 774-783 DOI:10.1093/glycob/cwm044 |
ZHANG D L, LÜ C H, YU D H, et al. Characterization and functional analysis of a tandem-repeat galectin-9 in large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2016, 52: 167-178 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2016.03.032 |



