2. 东营市康华海洋科技有限公司 山东 东营 257599
2. Dongying Kanghua Ocean Technology Co., LTD, Dongying, Shandong 257599, China
开拓离岸深远海养殖空间,发展大型基站式深远海养殖装备技术,是中国水产养殖发展的战略需求和未来走向。2016年,我国承建了国际首例半潜式深远海养殖网箱“Ocean Farm 1”,也是目前世界上最大的单体深海养殖网箱,该平台总高70 m,直径110 m,箱体总容量25万m3,结构总重6000多t。可以预计,深远海养殖作为鱼类工业化养殖与可持续发展的重要支撑,面临着前所未有的良好发展机遇。其中,深远海养殖网箱的研发将极大推动我国水产养殖空间的拓展和生产方式的转变,提升我国深远海水域及渔业资源的利用能力(黄一心等, 2016; 闫国琦等, 2018)。
目前,离岸网箱养殖采用最为广泛的结构形式主要为高密度聚乙烯(high density polyethylene, HDPE)深水网箱(黄小华等, 2019),国内外学者针对此类网箱的水动力特性开展了大量的研究工作。其中有利用波流循环水槽开展物理模型实验(Lader et al, 2005; 桂福坤, 2006; Decew et al, 2010; Bi et al, 2013; 黄六一等, 2007; Zhao et al, 2015; 崔勇等, 2015),也有通过建立数值模型分析网箱在波流作用下的动力响应(黄小华等, 2018; 桂福坤等, 2020; Cui et al, 2013; Lee et al, 2008; Tsukrov et al, 2003; Yao et al, 2016; Tang et al, 2017; 崔勇等, 2019)。此外,还有部分学者对网箱系统的受力情况进行了海上实测(Fredriksson et al, 2007; Gansel et al, 2018)。上述研究针对传统深水网箱的浮框受力、网衣变形、锚泊系统优化等进行了较为全面的阐述,为深水网箱的工程设计提供了理论依据。近些年来,随着我国为挪威承建的“Ocean Farm 1”投入使用,国内的大型深远海网箱养殖也进入了探索阶段,如“深蓝1号”、“德海1号”、“长鲸1号”等先后建成并开展养殖生产。与传统深水网箱不同,这些大型网箱设施通常布置于深远海域,与近海相比更容易受到强水流、巨浪和台风的影响。由于此类网箱在恶劣的海洋环境载荷作用下会产生摇荡和漂移运动,因此,对其开展水动力特性分析具有重要意义。
本文以Zhao等(2019)所描述的一种半潜式深远海网箱为研究对象,该网箱主体为桁架式钢结构,可通过调节底部储水仓以实现半潜的工作状态,从而可有效避免强风浪的影响。基于有限元方法建立该网箱实际尺寸对应的数值模型,分析波浪作用下半潜式网箱的锚绳受力与运动特性,研究结果可为此类深远海网箱设计优化提供理论参考。
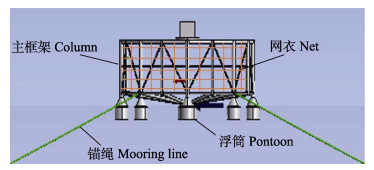
1 研究方法 1.1 基本理论半潜式网箱结构由主框架、网衣、浮筒和锚泊系统组成(图 1)。网箱在静水自由表面上做6个自由度摇荡运动时,一阶不定常速度势Φ满足以下条件可使联立方程得到定解:
| $ 在自由表面:\frac{{{\partial ^2}\mathit{\Phi} }}{{\partial {t^2}}} + g\frac{{\partial \mathit{\Phi} }}{{\partial z}} = 0 $ | (1) |
| $ 湿表面条件:\text{ }\frac{\partial \mathit{\Phi} }{\partial n}=\overrightarrow{{U}_{j}}\cdot \overrightarrow{{n}_{j}} $ | (2) |
| $ 海底边界条件:\left. {\frac{{\partial \mathit{\Phi} }}{{\partial n}}} \right|Z = - H=0 $ | (3) |
| $ 无穷远处边界条件:\mathop {\lim }\limits_{R \to \infty } \sqrt R \left({\frac{{\partial \mathit{\Phi} }}{{\partial R}} - ik\mathit{\Phi} } \right) = 0 $ | (4) |
|
图 1 半潜式网箱结构 Fig.1 Main structure of the semisubmersible deep-sea cage |
式中,g为重力加速度,t为时间;U为湿表面某处速度,n为湿表面某处法线方向;H为海底距水平面距离;R为空间一点到分析处的距离,k为波数。
总速度势可以认为是由入射波速度势、绕射速度势和幅射速度势组成:
| $ \phi = {\phi _I} + {\phi _D} - i\omega \mathop \sum \limits_{j = 1}^6 {\xi _j}{\phi _{Rj}} $ | (5) |
式中,ω为入射角频率,ξj为任意处的波形方程,ϕRj为任意处的速度势。
利用源汇法得到网箱水动力湿表面上每一个水动力网格上的速度势(张浩建, 2017):
| $ {\phi _i} = \mathop \sum \limits_{j = 1}^N {\beta _{ij}}{\sigma _j}\;\;\;\;\;j=1, 2, 3, …, N $ | (6) |
式中,βij为影响系数,σj为分布源密度。
求得网箱湿表面上的速度势,可运用动量方程得到作用在网箱表面上的动压力值:
| $ P({x_i}, {y_i}, {z_i}, t) = \rho \frac{{\partial \phi }}{{\partial t}} $ | (7) |
沿湿表面上的压力积分便可得到作用在网箱结构上的波浪力的水平、垂直及力矩:
| $ \left\{ \begin{array}{l} {F_x} = \iint_S {P\left({x, y, z} \right){n_x}dS} \hfill \\ {F_y} = \iint_S {P\left({x, y, z} \right){n_y}dS} \hfill \\ {M_z} = \iint_S {P\left({x, y, z} \right)\left({x{n_y} - z{n_x}} \right){n_x}dS} \hfill \\ \end{array} \right. $ | (8) |
式中,Ρ为流体密度,nx为某处法线方向沿x轴的分量,ny为某处法线方向沿y轴的分量,S为任意曲面。
1.2 网箱模型的建立网箱模型通过三维建模软件Creo Elements/Pro进行建模。本文所研究的半潜式网箱主要由浮筒、立柱、弧管组成,在通过Creo进行建模时,先建立网箱的各个浮筒和立柱单元,再以各个浮筒和立柱为基础,补齐网箱的弧管和其他构件。模型完成后导入ANSYS中进行模型前处理。由于ANSYS进行水动力计算前需要确定网箱的回转半径、质心等,所以建模完成后需先打开Creo的模型属性模块,通过查看质量属性可以得到网箱的回转半径、质心等相关参数。将网箱结构简化模型导入Workbench中进行网格划分,只需建立其湿表面模型,即可分析网箱结构的水动力响应等数据。网箱模型单元选择Shell63等Panel单元,网格划分按照以下原则:1)划分的网格单元一般为四边形,单元尺寸小于入射波波长;2)单元的纵横比统一且大于1/3;3)网格单元覆盖结构湿表面;4)一个波长最少覆盖模型的7个最大单元尺寸(唐文献等, 2017; 朱玲等, 2018; 李秀娟等, 2015)。网箱网格划分后有限元模型如图 2所示。模型网格划分完毕后,通过AQWA求解器进行求解。

|
图 2 网箱有限元模型 Fig.2 Meshing of the cage model |
模型网格划分完毕后,通过AQWA求解器进行求解。由于在AQWA中无法较好地对网衣系统进行建模,故本文先通过流体软件Star-ccm+计算出有网衣和无网衣网箱在不同流速下的压差,再将压差换算为阻力系数输入到AQWA中,从而模拟网箱装配网衣时的水动力情况。
1.3 网箱模型参数本文计算所采用的半潜式网箱的具体尺度参数如表 1所示。
|
|
表 1 网箱主要参数 Tab.1 Structure parameters of the fish cage |
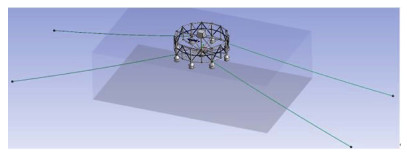
本文数值模拟计算的海域水深为120 m,海水密度为1025 kg/m3。频域分析中,波浪周期范围为8.87~ 19.72 s,浪向角为0°。时域分析中时间步长设为1 s,时长为500 s。网箱采用4点锚泊形式,锚绳长度为360 m,锚绳连接方式如图 3所示。
|
图 3 网箱锚泊方式 Fig.3 Mooring mode of cage |
本文计算设置12种波浪工况,如表 2所示。该网箱平台可通过调节底部储水仓以实现半潜的工作状态,为比较不同吃水条件下网箱的动力响应特性,共设定半潜式网箱3种不同工作状态,分别为空载(吃水深度为8.4 m)、半载(吃水深度为33.6 m)和满载(吃水深度为43.2 m)。
|
|
表 2 仿真分析工况 Tab.2 The wave condition of the simulation |
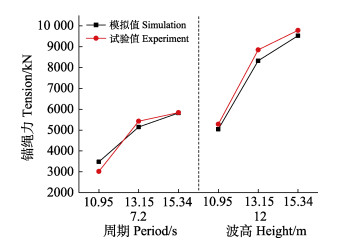
为验证本文所建立的半潜式网箱有限元数值模型的准确性,将计算结果与Zhao等(2019)中的水槽模型试验结果进行比较分析。根据水槽试验中所描述的半潜式网箱模型采用1∶120的比尺,实验模型制作主要保证几何相似、重力相似与弹性相似。因此,可根据所采用的相似准则把物理模型试验结果数据换算为原型实物网箱所对应数据,然后与本文所针对原型网箱的仿真结果来进行对比。图 4为6种波浪工况条件下,半潜式网箱迎浪侧锚绳受力计算机模拟值与试验值的比较情况。其中,网箱的吃水条件为半载状态。从图 4可以看出,采用本文有限元模型的计算结果与试验值基本吻合,锚绳受力的相对误差在5%左右,由此可见,采用本数值模型可以对半潜式网箱的水动力特性进行分析。
|
图 4 网箱锚绳力比较 Fig.4 Comparison of mooring line tension |
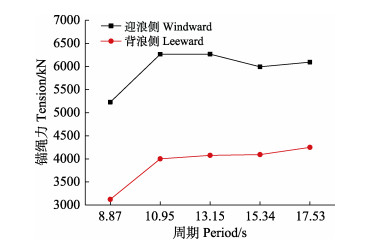
当半潜式网箱底部的浮筒空载时,网箱整体吃水为8.4 m,网箱结构大部分位于水平面之上,此时可对网箱构件和网衣部分进行必要的检查和清理。图 5和图 6为网箱处于空载状态下波浪要素对网箱锚绳受力的影响,其中锚绳受力均取计算周期内的最大值。图 5为波高保持7.2 m不变时,网箱迎浪侧和背浪测锚绳受力最大值随波浪周期的变化规律。从图 5可以看出,随着波浪周期的增大,迎浪侧锚绳受力的变化趋势不明显,背浪测锚绳受力逐渐增大。迎浪侧和背浪侧锚绳力的峰值分别在T=10.95 s、T=17.53 s时取得,分别为6275 kN和4254 kN。图 6为波浪周期取10.95 s时,网箱两侧锚绳受力的最大值随波高的变化规律。由图 6可知,当网箱空载时,两侧锚绳受力均随波高的增加而增大。其中,迎浪侧锚绳力在波高为12 m时取得最大值7032 kN,背浪侧锚绳力在波高为12 m时取得最大值5244 kN。
|
图 5 锚绳力随周期变化 Fig.5 Mooring line tension in different wave periods |

|
图 6 锚绳力随波高变化 Fig.6 Mooring line tension in different wave heights |
半潜式网箱主体为刚性结构,在波浪作用下其自身结构的变形较小,因此,其水动力特性分析主要从运动响应方面开展。由于半潜式网箱为圆形中心对称结构,运动分析主要从垂荡、纵荡及纵摇3个方面进行。图 7为不同波浪工况条件下3种不同压载状态对网箱运动幅值的影响。从图 7a可以看出,网箱的垂荡值与波高、周期均呈正相关。当波浪工况相同时,网箱空载、半载、满载状态下的垂荡值基本呈依次递减的趋势。当波高为12 m、周期为15.34 s时,网箱空载状态下最大垂荡值为12.67 m,半载和满载时为8.54 m和8.12 m,分别衰减33%和36%。图 7b为各波况下纵荡值的比较。当波周期相同时,3种压载条件下网箱的纵荡值均随着波高的增加而增大;当波高相同时,空载状态下网箱纵荡值与周期变化无关联,半载和满载状态下纵荡值与周期呈正相关。网箱空载状态下最大纵荡值为10.59 m,半载和满载时为9.17 m和7.75 m,分别衰减13%和27%。图 7c为各波况下网箱纵摇的比较。当波高相同时,纵摇值与周期变化无明显关联。3种压载状态下纵摇的变化规律与垂荡、纵荡基本相似,即空载时最大,而满载时最小。其中,当波高为12 m、周期为13.15 s时,网箱空载状态下最大纵摇值为14.6°。由此可知,网箱平台具有较好的稳定性。由以上分析可以得出,随着半潜式网箱吃水的增加,作用在网箱结构上的波浪力逐渐减小。因此,可以适当增加吃水,以保持网箱结构稳定及减轻开放海域波浪载荷所带来的不利影响。
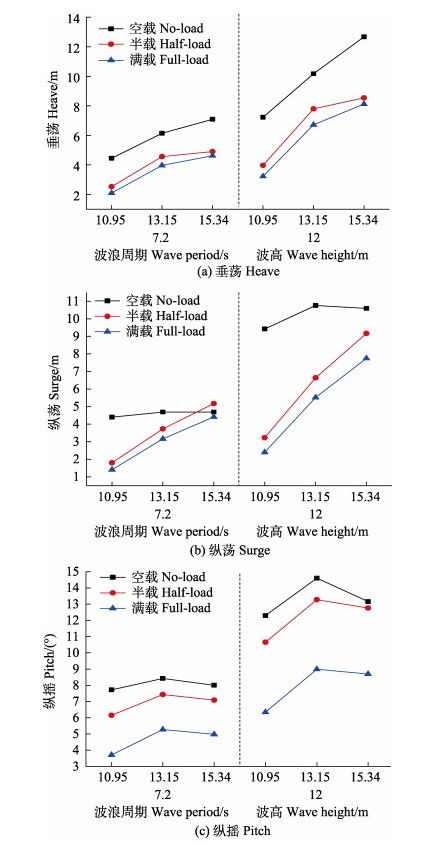
|
图 7 不同压载状态下网箱运动峰值比较 Fig.7 Comparison of maximum motion of fish cage under various ballast status |
本研究利用有限元方法对一种半潜式深远海网箱建立数值模型,首先验证了数模的准确性,然后对网箱结构在不同波浪工况下的水动力进行分析,比较了不同波高、周期及压载状态下的锚绳受力与运动响应,得出如下几点结论:
1) 将数值模拟的计算结果与实验室物理水槽结果进行比较,对比了6种波浪工况条件下,半潜式网箱锚绳受力情况。结果显示,计算值与试验值基本吻合,锚绳受力的相对误差在5%左右,因此,可通过本文所提出的有限元模型对半潜式网箱水动力特性进行分析。
2) 当波高一定时,在空载状态下,网箱锚绳受力与波浪周期改变无明显关联,迎浪侧和背浪侧锚绳力的峰值分别在T=10.95 s、T=17.53 s时取得,依次为6275 kN和4254 kN;周期一定时,两侧锚绳受力均随波高的增加而增大。其中,迎浪侧锚绳力在波高为12 m时取得最大值7032 kN,背浪侧锚绳力在波高为12 m时取得最大值5244 kN。
3) 网箱的垂荡、纵荡及纵摇值均与波高呈正相关;随着网箱吃水的增加,网箱的垂荡、纵荡及纵摇值基本呈减小趋势。其中,当波高为12 m、周期为13.15 s时,网箱空载状态下最大纵摇值≤15°,网箱整体结构可保持一定的稳定性。
本文对波浪作用下半潜式网箱的水动力响应进行了研究和分析。在实际的海况中,波浪和水流总是同时存在的,尤其是在开放海域,高流速对网箱结构安全影响巨大。因此,在今后的研究中将进一步分析波浪和水流共同作用下网箱的动力特性,以期为网箱实际工程应用提供理论依据。
BI C W, ZHAO Y P, DONG G H, et al. Experimental investigation of the reduction in flow velocity downstream from a fishing net. Aquacultural Engineering, 2013, 57: 71-81 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaeng.2013.08.002 |
CUI Y, GUAN C T, HUANG B, et al. Numerical simulation of the hydrodynamic characteristics of double-bottom cage for flounder fish under waves. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2019, 40(6): 18-24 [崔勇, 关长涛, 黄滨, 等. 波浪作用下双层网底鲆鲽网箱水动力特性的数值模拟. 渔业科学进展, 2019, 40(6): 18-24] |
CUI Y, GUAN C T, WAN R, et al. Numerical simulation of a flatfish cage system in waves and currents. Aquacultural Engineering, 2013, 56: 26-33 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaeng.2013.04.001 |
CUI Y, GUAN C T, ZHAO X, et al. Analysis of two-dimension flow field of the square cage based on particle image velocimetry (PIV). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2015, 36(5): 138-144 [崔勇, 关长涛, 赵侠, 等. 基于PIV技术的方形网箱二维流场分析. 渔业科学进展, 2015, 36(5): 138-144] |
DECEW J, TSUKROV I, RISSO A, et al. Modeling of dynamic behavior of a single-point moored submersible fish cage under currents. Aquacultural Engineering, 2010, 43(2): 38-45 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaeng.2010.05.002 |
FREDRIKSSON D W, DECEW J C, TSUKROV I, et al. Development of large fish farm numerical modeling techniques with in-situ mooring tension comparisons. Aquacultural Engineering, 2007(36): 137-148 |
GANSEL L C, OPPEDAL F, BIRKEVOLD J, et al. Drag forces and deformation of aquaculture cages—Full-scale towing tests in the field. Aquacultural Engineering, 2018, 81: 46-56 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaeng.2018.02.001 |
GUI F K. Hydrodynamic behaviors of deep-water gravity cage. Doctoral Dissertation of Dalian University of Technology, 2006 [桂福坤. 深水重力式网箱水动力学特征研究. 大连理工大学博士研究生学位论文, 2006]
|
GUI F K, ZHANG B B, QU X Y, et al. Force analysis of piles in net enclosure aquaculture engineering subjected to waves and current. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(11): 31-38 [桂福坤, 张斌斌, 曲晓玉, 等. 波流作用下围网养殖工程的桩柱结构受力分析. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(11): 31-38 DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.11.004] |
HUANG L Y, LIANG Z L, SONG W H, et al. Experimental study on effect of reducing current velocity by square net cage structure. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2007, 14(5): 860-863 [黄六一, 梁振林, 宋伟华, 等. 方形箱网结构减流效果试验. 中国水产科学, 2007, 14(5): 860-863 DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2007.05.023] |
HUANG X H, LIU H Y, HU Y, et al. Deformation simulation and structural improvement design for floating collar of deep-water aquaculture net cage. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(15): 44-49 [黄小华, 刘海阳, 胡煜, 等. 深水养殖网箱浮架变形模拟及结构改进设计. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(15): 44-49 DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.15.006] |
HUANG X H, WANG F F, LIU H Y, et al. Effects of mooring systems and ballast status on dynamic behaviors of semi-submersible offshore fish farm. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(15): 48-53 [黄小华, 王芳芳, 刘海阳, 等. 系泊和压载方式对半潜式渔场平台动力特性的影响. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(15): 48-53 DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.15.007] |
HUANG Y X, XU H, DING J L. Research on the development of offshore aquaculture facilities and equipment in China. Fishery Modernization, 2016, 43(2): 76-81 [黄一心, 徐皓, 丁建乐. 我国离岸水产养殖设施装备发展研究. 渔业现代化, 2016, 43(2): 76-81 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9580.2016.02.014] |
LADER P F, ENERHAUG B. Experimental investigation of forces and geometry of a net cage in uniform flow. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2005, 30(1): 79-84 DOI:10.1109/JOE.2004.841390 |
LEE C W, KIM Y B, LEE G H, et al. Dynamic simulation of a fish cage system subjected to currents and wave. Ocean Engineering, 2008, 35: 1521-1532 DOI:10.1016/j.oceaneng.2008.06.009 |
LI X J, GAO Z, ZHANG K K, et al. A study on the hydrodynamic characteristics of a new semi-submersible based on AQWA. China Offshore Platform, 2015, 30(6): 91-98 [李秀娟, 高泽, 张可可, 等. 基于AQWA的新型半潜式海洋钻井平台水动力特性研究. 中国海洋平台, 2015, 30(6): 91-98 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-4500.2015.06.016] |
TANG M F, XU T J, DONG G H, et al. Numerical simulation of the effects of fish behavior on flow dynamics around net cage. Applied Ocean Research, 2017, 64: 258-280 DOI:10.1016/j.apor.2017.03.006 |
TANG W X, GAO Z, ZHANG J, et al. A study on the hydrodynamic characteristics of semi-submersible offshore platform with two column structures based on AQWA. Ship Science and Technology, 2017, 39(5): 82-87 [唐文献, 高泽, 张建, 等. 基于AQWA的2种立柱结构的半潜式海洋平台水动力特性研究. 舰船科学技术, 2017, 39(5): 82-87 DOI:10.3404/j.issn.1672-7619.2017.05.016] |
TSUKROV I, EROSHKIN O, FREDRIKSSON D W, et al. Finite element modeling of net panels using a consistent net element. Ocean Engineering, 2003, 30: 251-270 DOI:10.1016/S0029-8018(02)00021-5 |
YAN G Q, NI X H, MO J S. Research status and development tendency of deep sea aquaculture equipments: A review. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2018, 33(1): 123-129 [闫国琦, 倪小辉, 莫嘉嗣. 深远海养殖装备技术研究现状与发展趋势. 大连海洋大学学报, 2018, 33(1): 123-129] |
YAO Y M, CHEN Y L, ZHOU H, et al. Numerical modeling of current loads on a net cage considering fluid-structure interaction. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2016, 62: 350-366 DOI:10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2016.01.004 |
ZHANG H J. Numerical study on trimaran heave and pitching hydrodynamics based on panel method. Master′s Thesis of Dalian Maritime University, 2017 [张浩建. 基于面元法的三体船升沉纵摇水动力数值研究. 大连海事大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2017]
|
ZHAO Y P, BI C W, CHEN C P, et al. Experimental study on flow velocity and mooring loads for multiple net cages in steady current. Aquacultural Engineering, 2015, 67: 24-31 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaeng.2015.05.005 |
ZHAO Y P, GUAN C T, BI C W, et al. Experimental investigations on hydrodynamic responses of a semi-submersible offshore fish farm in waves. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2019, 7: 238 DOI:10.3390/jmse7070238 |
ZHU L, HU J P. Analysis and optimization on the flow ability of wave buoy based on AQWA. Guangdong Ship Building, 2018, 2: 50-54 [朱玲, 胡金鹏. 基于AQWA的波浪观测浮标随波性能分析与优化研究. 广东造船, 2018, 2: 50-54] |



