2. 浙江海洋大学海洋工程装备学院 浙江 舟山 316000
2. Zhejiang Ocean University, School of Marine Engineering Equipment, Zhoushan, Zhejiang 316000, China
桩柱式围网(周文博等, 2018)主要由桩柱和网片组成,是典型的浅海围网养殖形式,与传统近岸网箱养殖相比具有养殖密度低、养殖水体大、养殖产品品质更近自然生态等特点。近几年该生态养殖模式已经于浙江台州、舟山、温州、山东烟台等沿海地区陆续出现并投入工程应用。由于围网养殖模式处于起步阶段,仍存在需要解决的实际工程问题,还有较大的发展空间。由于桩柱式围网设施尺度大,结构会对海域波浪场产生较大的影响,从而影响到海水中溶氧、饵料等物质输运;围网的建设也会对区域的N、P及重金属等物质的含量有影响(廖润华等, 2021),进而影响鱼类的生长(钱辰颖等, 2021)。同时,波浪扰动也会对海底沉积物产生影响(丁艳青等, 2011)。因此,研究桩柱式围网对波浪场的影响,对整个桩柱式围网的结构设计、环境分析和工程选址均具有较大意义。
目前,国内外学者对网衣系统的水动力特性进行了较多的研究。王敏法(2011)以有限元理论为基础,采用集中质量法对金枪鱼围网网具系统建立了三维动力学模型,并模拟了围网包围、收绞和沉降过程中网具的空间运动和形态,再通过围网模型实验和海上实测数据验证了数值模拟的有效性。Tsukrov等(2003)通过有限元法对波浪和水流环境负荷下的网片水动力学特性进行了数值模拟,其结果在张力腿网箱波浪力计算中具有重要应用。Bi等(2015a、b)采用物理模型实验对网箱波浪的阻尼作用进行了研究,之后建立了数值模型进行了研究,并与物理模型实验进行比对。董国海等(2014)通过建立非线性波浪场和重力式网箱数学模型,对波浪逆向和波浪同向作用下重力式网箱的受力、运动和网衣变形进行了数值模拟研究,并通过模型实验进行了验证,指出波浪同向对重力式网箱的破坏比波浪逆向严重。崔勇等(2019)根据有限单元法建立了波浪作用下双层网底网箱的受力运动模型,发现双层网底网箱的水动力特性。叶卫富等(2011)使用模型实验的方式对浮绳式围网的水动力特性进行了初步研究。陈天华等(2017、2018)发现了波浪高度对桩柱式围网养殖系统受力有较大的影响,对桩柱式围网养殖系统的网片在不同波浪和固定方式条件下的水动力特性进行了详细研究;桂福坤等(2020)研究了纲绳对桩柱式围网网片波浪力学特性的影响,分析了不同纲绳直径、形状和大小工况下,纲绳和网线的受力和变形以及网片系缚点的受力特性。目前,国内外学者对海洋养殖设施水动力特性的研究主要集中在结构受力及运动变形方面,但对大型生态围网等养殖设施周围波浪场的相关研究尚未见报道。
本研究采用数值模拟的方法对桩柱式围网的波浪场进行模拟,采用一些典型的算例对模型的合理性和有效性进行验证,并设计部分工况,进一步探讨围网对于波浪场的影响。
1 材料与方法 1.1 控制方程FUNWAVE-TVD是开源Bousinessq波浪模型FUNWAVE的进一步改进的版本,应用较为广泛,其控制方程是基于Chen等(2000)提出的完全非线性Bousinessq方程,对于网衣这种孔隙率较大的结构,由拖曳力产生的二阶项远大于由粘性作用产生的线性项,则可忽略其线性力,只考虑网衣的拖曳力作用。考虑网衣存在的控制方程表述如下:
| $ {\eta _t} + \nabla M = 0 $ | (1) |
| $ {u_{\alpha, t}} + ({u_\alpha } \times \nabla) \times {u_\alpha } + g\nabla \eta + {V_1} + {V_2} + {V_3} + R + {S_{{\text{net}}}} = 0 $ | (2) |
式中,η为波面升高,V1,V2,V3为色散项,t为对时间积分;
| $ M = h + \eta \{ {u_\alpha } + \overline {{u_2}} \} $ | (3) |
式中,h为静水深,
| $ {u_2}(z) = ({z_\alpha } - z) \times \nabla A + \frac{1}{2}(z_\alpha ^2 - {z^2}) \times \nabla B $ | (4) |
| $ {u_2} = \left({\frac{{z_\alpha ^2}}{2} - \frac{1}{6}({h^2} - h\eta + {\eta ^2})} \right) \times \nabla B + \left({{z_\alpha } + \frac{1}{2}(h - \eta)} \right) \times \nabla A $ | (5) |
| $ A = \nabla \times (h{u_\alpha }) $ | (6) |
| $ B = \nabla \times {u_\alpha } $ | (7) |
Snet为单位网衣阻力项,其表达式为:
| $ {S}_{\text{net}}=\frac{1}{2}{c}_{ij}\left|\stackrel{\rightharpoonup }{u}\right| \stackrel{\rightharpoonup }{u} $ | (8) |
当水流以一定的流速流过网箱区域时,作用在该区域的阻力值可由下式计算(Bi et al, 2015a、b):
| $ {F_d} = {C_n}\frac{1}{2}\rho \lambda A|\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\rightharpoonup}$}} {u} |\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\rightharpoonup}$}} {u} $ | (9) |
| $ {F_l} = {C_t}\frac{1}{2}\rho \lambda A|\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\rightharpoonup}$}} {u} |\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\rightharpoonup}$}} {u} $ | (10) |
式中,
| $ {F_d} = {C_d}\frac{1}{2}\rho A{u^2} $ | (11) |
| $ {F_l} = {C_l}\frac{1}{2}\rho A{u^2} $ | (12) |
在此基础上,可通过求解平面网衣的阻力系数和升力系数得到多孔介质系数。Tsukrov等(2003)研究认为,Balash等(2009)提供的公式在预测网衣阻力系数方面具有优势,与实测数据的相对误差约为4%。Aarsnes等(1990)对平面网衣升力系数进行了研究,并建立了网衣密实度
| $ {C_d} = C_d^{cyl} \times (8.03\;S_n^2 - 0.74\;{S_n} + 0.12) $ | (13) |
| $ {C_l} = (0.57\;{S_n} - 3.54\;S_n^2 + 10.1\;S_n^3) \times {\text{sin}}(2{\alpha ^, }) $ | (14) |
式中,
由于围网桩柱的刚度较大,结构在波浪作用下的运动和变形不明显。因此,可以采用入射波浪的最大水质点速度作为特征速度来计算雷诺数(Bi et al, 2015a、b),公式如下:
| $ Re = \frac{{Ud}}{\nu } $ | (15) |
式中,U为波浪中水粒子的最大速度,在线性波理论中可近似为
数值模型采用有限体积法和有限差分法的空间离散方法,在对源项采用具有二阶精度的有限差分法,其他项采用高精度的有限体积法进行构造,时间积分上使用更为稳定Runge-Kutta法确定自适应时间步长。在计算过程中,采用HLL式黎曼问题近似求解器计算数值通量,高阶MUSCL-TVD法求解界面通量。破碎处理根据Tonelli等(2009)的方法,当波面升高同静水深比值达到0.8时,判断波浪开始破碎,将Bousinessq方程退化为非线性浅水方程,忽略Bouinessq方程中的高阶非线性项和色散项,将波浪破碎处理为激波。
2 结果 2.1 网衣模型验证采用Lader等(2007)的网衣物理模型实验进行模型验证,该物理模型实验采用活塞式造波机产生规则波,实验布置及浪高仪分布见图 1。
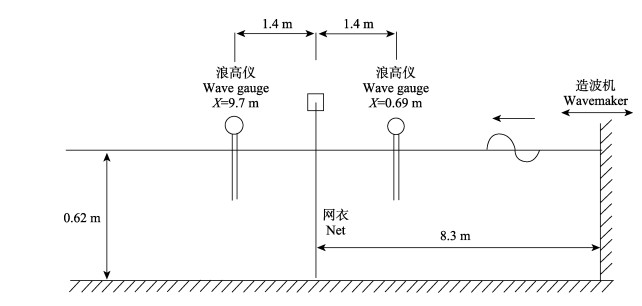
|
图 1 波浪穿过网衣传播变形的实验布置 Fig.1 Layout of model experiment for wave through the net (Lader et al, 2007) |
数值水槽的造波方式采用域内造波,入射波浪为规则波,部分工况的入射波要素见表 1。数值水槽左端和右端均设置了海绵层吸收边界,海绵层长度取1.25倍波长以上。数值水槽在13.0 m处布置网衣,网衣高度为1.0 m。数值模型采用了与物理模型相同规格的3种网衣,网衣具体规格见表 2。
|
|
表 1 入射规则波的波浪要素 Tab.1 Wave parameters of incident regular waves |
|
|
表 2 网衣模型规格 Tab.2 Net model specification |
本研究使用波高平方系数CEH作为动力响应指标,描述了由于网衣的存在而对波浪能造成的变化,具体公式如下:
| $ {C_{{\text{EH}}}} = \frac{{{H_i}^2}}{{{H_t}^2}} $ | (16) |
式中,
从图 2可以看出,当波浪在经过不同规格的网衣区域时,会发生不同程度的衰减。在高频规则波条件下,波高平方系数随着网衣密实度的增大呈先增大后减小的趋势;在低频规则波条件下,波高平方系数呈现一直减小的趋势。整体而言,本模型的计算结果与对应的实验数据吻合良好,结果趋势相同,误差均 < 3%,表明本模型可以有效地模拟波浪在经过网衣区域的传播过程。
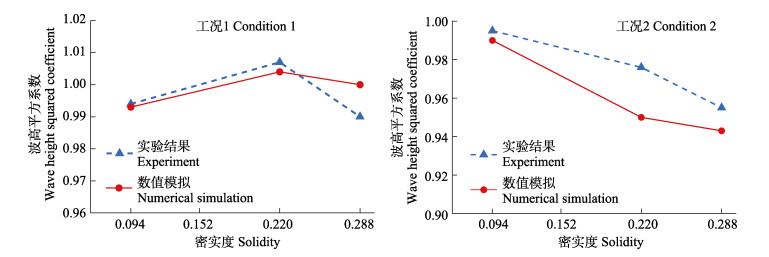
|
图 2 规则波在经过网衣后的波能变化 Fig.2 Change of wave energy of regular wave after passing through the net |
采用Bi等(2015a, b)研究的波浪穿过圆形网箱的物理模型实验对本研究数学模型进一步进行验证。该物理模型实验水槽长为22 m、宽为0.45 m、深为0.6 m,实验水深为0.4 m。该实验的模型比尺为1∶50,而网衣则是依据桂福坤等(2002)提出的变尺度模型相似准则进行设计。实验设计工况见表 3。从表 3可以看出,实验采用单体网箱测定网箱前后波浪变化,网箱的密实度为0.2。测定网箱前后波浪变化实验装置布置见图 3。
|
|
表 3 入射规则波的波浪要素 Tab.3 Wave parameters of incident regular waves |

|
图 3 网箱内外波高变化实验装置布置 Fig.3 Experimental setup for wave elevation around the net cage (Bi et al, 2015a、b) |
数值水槽长为30 m、宽为12 m,网箱布置在水槽19.3 m处。与物理模型实验采用相同的浪高仪布置方式,取测点1为网前波高,测点5为网后波高进行计算,水槽前后各布置4 m的消浪区以保证不会发生波浪反射。网箱的布置方式及规格与物理模型实验一致。
使用波浪透射系数进行分析和验证,当波浪传播经过网箱结构时,假定网箱前的波高为Hi,网箱后的波高为Ht,则根据规则波的能量计算公式,定义波浪透射系数公式如下:
| $ {C_t} = \frac{{{H_i}}}{{{H_t}}} $ | (17) |
从图 4可以看出,当波浪传播经过网箱时,由于网箱对波浪的耗散作用,波高出现了不同程度的衰减,波高最大衰减可以达到6%左右。从图 4还可以看出,波高衰减率随着波高的增加而呈减小的趋势,数值模拟和实验结果的趋势一致。同时,本模型的计算结果与网箱实验数据吻合良好,误差均<3.5%,误差相较于单片网的误差有所增加,造成误差增大的原因可能是网箱形状为圆形,相较于单片网更难以精细地模拟出其边界情况。表明本模型可以有效地模拟波浪在经过网箱结构区域的传播过程。

|
图 4 规则波在经过网箱结构后的波高变化 Fig.4 Variation of wave height of regular wave after passing through the net cage |
采用上述模型对本研究的内容进行数值模拟。模型比尺为1∶50,数值波浪水槽的有效长度为50 m,宽度为20 m,水槽前后端均设置4 m的海绵层以吸收反射波,根据表 4参数设置围网数值模型以及模拟水深。本研究中,围网为双层网结构,网衣模型厚度为0.025 m,根据Bi等(2015a、b)的研究结果,每层网衣对应的多孔介质系数按照公式(13)和公式(14)进行计算,桩柱的堵塞率为0.1,因此,将上述网衣多孔介质系数均乘以1.37,作为单层围网整体模型的多孔介质系数结果见表 6。从表 6可以看出,采用结构化网格进行划分,x方向网格和y方向网格一致。从图 5可以看出,随着网格数的增加,波高趋于收敛,造出的波浪更加稳定。在网格尺寸定义为波长的1/50时,表明波浪趋于稳定。数值求解空间步长x方向和y方向均为0.025 m。根据表 5设置了4种不同工况的规则波,用来探究围网对不同周期规则波波浪场的影响。
|
|
表 4 围网参数 Tab.4 Pile-net enclosure parameter |
|
|
表 5 波浪参数 Tab.5 Wave parameters |
|
|
表 6 多孔介质系数 Tab.6 Porous coefficients |
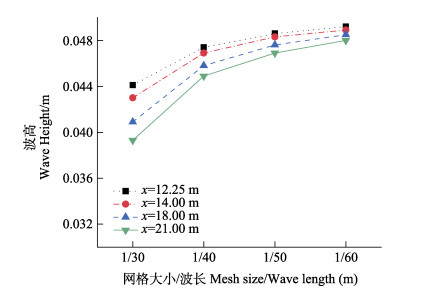
|
图 5 数值波浪水槽参数收敛性验证 Fig.5 Parameter convergence verification of numerical wave tank |
为研究不同波浪周期对波浪透射系数的影响,在水深和波高不变情况下,周期从0.9 s增加到1.5 s的波浪透射系数。不同波浪周期情况下,围网背浪侧的波浪透射系数变化趋势见图 6。本研究对有无围网存在时的2种数学模型的波浪传播演化结果进行了对比分析。结果表明,随着波浪周期的不断增大,围网背浪侧波浪衰减系数呈先减小后增大的趋势,最大波高衰减达93.3%。围网中心处的波浪衰减系数同样呈先减小后增大的趋势。同时,围网中心处的波浪透射系数均大于围网后半个波长处的波浪透射系数,说明围网后的衰减更为明显。
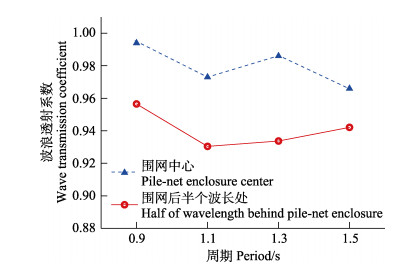
|
图 6 不同位置的波浪透射系数 Fig.6 Wave transmission coefficient at different positions |
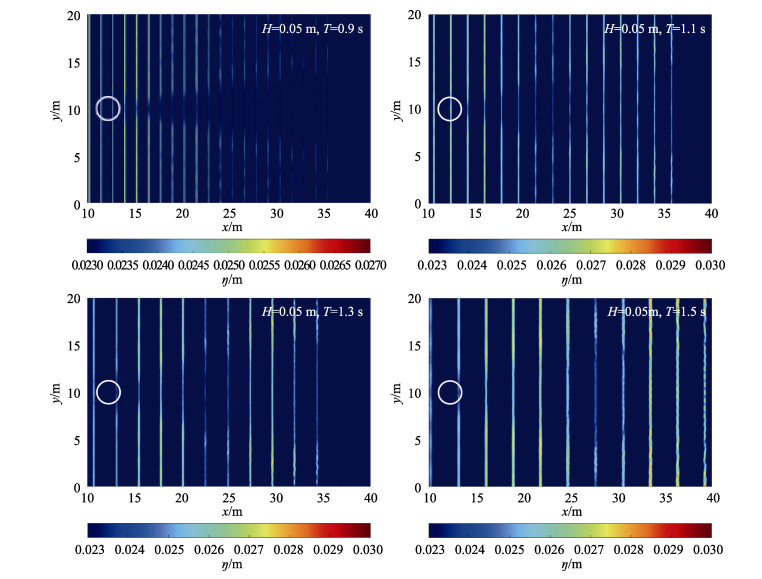
规则波波浪经过围网后波浪场的变化见图 7。从图 7可以看出,通过减小波高的展示范围可以更好地体现出围网对于波浪传播的影响。从低频规则波的波浪传播云图可以看出,围网对波浪场的影响呈锥形扩散趋势,在远离围网区域距离时,最大波高衰减位置开始向两边扩散,同时,在围网的正后方开始出现波高恢复的情况,整体的波高衰减程度越来越小。高频规则波的主要波高衰减区域集中在围网正后区域,也呈锥形区域并展开,但未出现最大衰减位置扩散情况。
|
图 7 规则波在经过围网结构后的同一时刻波浪场变化云 Fig.7 Nephogram of wave field changes of regular waves after passing through the cage structure at the same time |
为进一步研究低频规则波在受到围网的影响,选取工况为H=0.05 m、T=1.5 s时,围网后垂直波浪传播方向的波高分布见图 8。从图 8可以看出,在围网背浪侧距围网中心1.75 m处,波高主要衰减区域还是集中在围网的正后方,而到了5.75 m处,波高衰减区域开始向两侧扩散,到了8.75 m处,波高衰减的区域扩散更大,可以看出波高最大衰减部分呈对称状分布在两侧,相较于5.75 m处其最大衰减部位之间的距离更大,同时,围网正后方区域已经开始出现波高恢复的情况。说明低频波浪的波高衰减的最大位置从开始分布在中间,后逐步向两侧扩散。同时,中间部位开始逐步有恢复的趋势,而整体波高的衰减开始逐步的减小。但对于高频波浪而言,衰减主要集中在围网中心后的部位,远离围网处衰减逐步的减小。导致这一现象的原因可能是高频波浪相较于低频而言会更易透过围网使得衰减部位较为集中,而低频波浪则会发生波浪绕射的情况,因而出现扩散情况。

|
图 8 不同位置的垂直波浪传播方向波浪透射系数分布 Fig.8 Cross sectional wave height distribution at different locations |
本研究将FUNWAVE-TVD模型与多孔介质模型相结合,建立了模拟离岸养殖围网内外波浪场分布特性的数学模型,并开展了模型实验验证和模拟分析研究,取得的主要研究结论如下:
(1) 该模型可以较好地模拟网衣及围网结构对其周围波浪场的影响,误差均 < 3.5%。
(2) 在围网影响下,较低频规则波的波高衰减区域呈辐射状趋势扩散,并随着波浪进一步传播,最大波高衰减位置开始向两侧扩散,同时,围网背浪侧的波高衰减程度减小,波高有恢复趋势,而高频波浪的波高衰减区域则较为集中。
(3) 低频波浪受围网的影响较大,其背浪侧的波浪透射系数影响范围较大。
AARSNES J V, RUDI H, LØLAND G. Current forces on cage, net deflection: Engineering for offshore fish farming. Proceedings of a conference organised by the Institution of Civil Engineers, Glasgow, UK, 17–18 October 1990
|
BALASH C, COLBOURNE B, BOSE N, et al. Aquaculture net drag force and added mass. Aquacultural Engineering, 2009, 41(1): 14-21 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaeng.2009.04.003 |
BI C W, ZHAO Y P, DONG G H. Numerical study on the hydrodynamic characteristics of biofouled full-scale net cage. China Ocean Engineering, 2015a, 29(3): 401-414 DOI:10.1007/s13344-015-0028-9 |
BI C W, ZHAO Y P, DONG G H, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on the damping effect of net cages in waves. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2015b, 55: 122-138 DOI:10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2015.02.010 |
CUI Y, GUAN C T, HUANG B, et al. Numerical simulation of the hydrodynamic characteristics of double-bottom cage for flounder fish under waves. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2019, 40(6): 18-24 [崔勇, 关长涛, 黄滨, 等. 波浪作用下双层网底鲆鲽网箱水动力特性的数值模拟. 渔业科学进展, 2019, 40(6): 18-24] |
CHEN Q, KIRBY J T. Boussinesq modeling of wave transformation, breaking, and runup. Ⅱ: 2D. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal and Ocean Engineering, 2000, 126(1): 48-56 DOI:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(2000)126:1(48) |
CHEN T H, MENG A, GUI F K. Effect of wave height and direction on hydraulic characteristics of net of pile-column type net enclosure aquaculture system. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(2): 245-251 [陈天华, 孟昂, 桂福坤. 波浪高度及方向对桩柱式围网养殖系统网片水力特性的影响. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(2): 245-251] |
CHEN T H, PAN D, FENG D J, et al. Effect on hydrodynamics of unit net of a column-type net enclosure aquaculture engineering in current by fixations. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2018, 42(3): 452-460 [陈天华, 潘旳, 冯德军, 等. 固定方式对水流作用下桩柱式围网网片力学特性的影响. 水产学报, 2018, 42(3): 452-460] |
DONG G H, MENG F B, ZHAO Y P, et al. A numerical study on dynamic properties of the gravity cage under parallel and counter wave-current conditions. Fishery Modernization, 2014, 41(2): 49-56 [董国海, 孟范兵, 赵云鹏, 等. 波流逆向和同向作用下重力式网箱水动力特性研究. 渔业现代化, 2014, 41(2): 49-56] |
DING Y Q, ZHU G W, QIN B Q, et al. Experimental study on the effect of wave disturbances on the phosphorus dynamics in shallow lakes. Advances in Water Science, 2011, 22(2): 273-278 [丁艳青, 朱广伟, 秦伯强, 等. 波浪扰动对太湖底泥磷释放影响模拟. 水科学进展, 2011, 22(2): 273-278] |
GUI F K, LI Y C, ZHANG H H. The proportiona; criteria for model testing of force acting on fishing cage net. China Offshore Platform, 2002(5): 23-26 [桂福坤, 李玉成, 张怀慧. 网衣受力试验的模型相似条件. 中国海洋平台, 2002(5): 23-26] |
GUI F K, SHAO Z Y, CHEN T H, et al. Study on effect of rope on wave mechanical properties for net panel of pile-column type net enclosure. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2020, 35(4): 505-514 [桂福坤, 邵振宇, 陈天华, 等. 纲绳对桩柱式围网网片波浪力学特性影响研究. 水动力学研究与进展(A辑), 2020, 35(4): 505-514] |
LADER P F, OKSEN A, JENSEN A, et al. Experimental investigation of the interaction between waves and net structures—Damping mechanism. Aquacultural Engineering, 2007, 37(2): 100-114 |
LIAO R H, WU X G, WANG Z D, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment on the main nutrients and heavy metals in sediments of Lake Gehu, Taihu Basin after removing the aquaculture net. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2021, 33(5): 1436-1447 [廖润华, 吴晓刚, 王兆德, 等. 太湖流域滆湖围网拆除后沉积物营养盐和重金属空间分布特征及评价. 湖泊科学, 2021, 33(5): 1436-1447] |
QIAN C Y, ZHENG G D, CHEN J, et al. Effects of oxygen on the gill tissue and enzyme activities of each tissue in a hypoxia-tolerant new strain F5 of Megalobrama amblycephala. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2021, 42(4): 73-81 [钱辰颖, 郑国栋, 陈杰, 等. 溶解氧对团头鲂耐低氧新品系F5代的鳃组织形态及各组织酶活性的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2021, 42(4): 73-81] |
TONELLI M, PETTI M. Hybrid finite volume-finite difference scheme for 2DH improved Boussinesq equations. Coastal Engineering, 2009, 56(5/6): 609-620 |
TSUKOV I, EROSHKIN O, FREDRIKSSON D, et al. Finite element modeling of net panels using a consistent net element. Ocean Engineering, 2003, 30(2): 251-270 |
WANG M F. Development of the 3D numerical model tuna purse seine gear. Master's Thesis of Shanghai Ocean University, 2021, 63 [王敏法. 金枪鱼围网网具数值模拟初步研究, 上海海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2011, 63]
|
YE W F, WU J X, MA J Z, et al. Application and research on floating flexible seine aquaculture facility in offshore. Fishery Modernization, 2011, 38(5): 7-11 [叶卫富, 吴佳兴, 马家志, 等. 浅海浮绳式围网设施应用研究. 渔业现代化, 2011, 38(5): 7-11] |
ZHOU W B, SHI J G, YU W W, et al. Current situation and development trend of marine seine culture in China. Fishery Information and Strategy, 2018, 33(4): 259-266 [周文博, 石建高, 余雯雯, 等. 中国海水围网养殖的现状与发展趋势探析. 渔业信息与战略, 2018, 33(4): 259-266] |



