海洋围网养殖是一种典型的海洋设施养殖模式,以其养殖面积大、养殖环境更近自然、养殖对象品质更近生态而备受青睐,是现代海洋养殖发展的一种新模式。近年来,由于养殖企业的急功近利,以及网衣随意安装与加固等不规范的措施,导致网衣在恶劣天气下极易被撕裂破坏,造成很多企业损失严重,缺乏有效的结构安全理论和设计规范。桩网连接模式的研究对网衣的保护有着重要作用。
近年来,国内外有关学者针对网衣水动力特性进行了很多相关研究。例如,通过数值模拟的方法对柔性渔网的表面波散射进行研究,研究结果揭示了柔性渗透屏障对波浪传播的影响(Chan et al, 2001)。Tsukrov等(2003)通过有限元法将网片在波浪和水流环境负荷下的水动力学特性进行了数值模拟,研究结果给张力腿网箱设计和管理提供重要依据。黄滨等(2009)通过大量的海上网箱沉浮实验和分析,阐述了国产HDPE升降式网箱在自然海洋环境状态中,受风、浪和流等客观因素的作用和影响,研究结果得出升降式网箱不能沉入水底的原因。刘莉莉等(2013)采用有限元方法和集中参数法对张网渔具在波流联合作用下的水动力学特性进行了数值模拟,并将数值计算结果与水槽模型实验结果进行比较,预测效果理想。董国海等(2014)通过集中质量点法和刚体运动学原理,建立非线性波流场和重力式网箱数学模型,对波流逆向和波流同向作用下,重力式网箱的受力、运动和网衣变形进行了数值模拟,并通过模型实验进行了验证,得出波流同向对重力式网箱的破坏比波流逆向严重。Fredriksson等(2003)通过采用物理模型实验和数值模拟对网箱及其系泊系统的现场勘测,再利用随机法分析了网箱及其锚绳的动态响应特性,并且在物模实验中清楚地观察到网箱的倾斜共振,充分说明数值模拟很好地预测了其系缆的张力。王敏法(2011)和周成(2015)以有限元理论为基础,采用集中质量法对金枪鱼围网网具系统建立了三维动力学模型,并模拟了围网包围、收绞和沉降过程中网具的空间运动和形态,再通过围网模型实验和海上实测数据进行修正和验证。崔勇等(2019)根据有限元法建立波浪作用下双层网底网箱的受力运动模型,计算出网底的位移和倾角。桂福坤等(2017、2020)和陈天华等(2017)采用集中质量点法数值模拟了固定方式、波浪高度及方向和纲绳相关参数选择对桩柱式围网网片水动力特性的影响。邵振宇(2020)采用集中质量点法研究桩网分离式围网网衣系统力学特性的影响,分析得出其纲绳和网线最大受力与波高、桩间距、纲绳直径、网线直径等因素的关系。刘彦等(2020)为探求人工鱼礁水平波浪受力的非线性影响因素、获取更接近实际水平波浪力的数值计算方法,采用二阶Stokes波浪理论,借助无量纲化方法对计算水平波浪力的Morison方程进行非线性因素分析,以校核验证鱼礁在海底的力学稳定性,研究得出非线性波对于求解鱼礁水平波浪的具有较好的准确性。
本文针对已有研究中的并未考虑连接方式对桩柱式围网网衣受力的研究,采用集中质量点法,StokesⅢ阶波波浪理论,研究波浪作用下2种连接方式的围网网衣纲绳和网线最大受力、最大偏移、系缚点最大受力特性,为围网工程连接方式的选择和安全评估提供技术支撑。
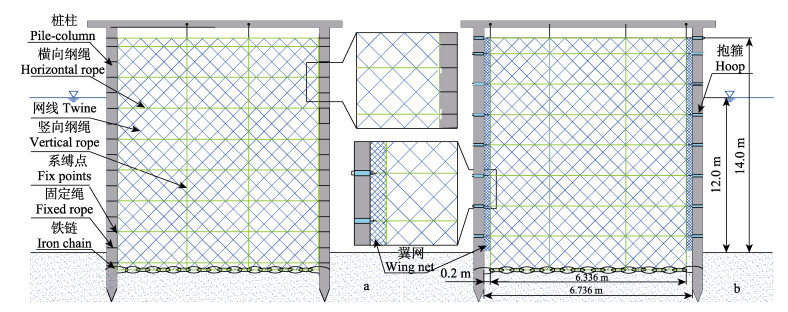
1 材料与方法 1.1 桩柱式围网的桩网连接方式桩柱式围网主要由桩柱、网衣、纲绳等结构组成,根据网衣和桩柱的连接方式可以分为桩网直接连接模式和桩网间接连接模式。桩网直接连接模式是指将网衣的左右边缘直接系缚在桩柱上(图 1a),此模式下左右边缘处网线直接固定在桩柱上,是目前常见的连接方式。桩网间接连接模式是指网衣的左右边缘不直接系缚在桩柱上(图 1b),而是通过横纲与桩柱连接,此模式下左右边缘处网线不与桩柱直接连接,利用力在网线和纲绳的传导性将网衣所受的波浪力传给纲绳,从而减轻边缘网线所受的力,防止该处网线断裂,起到保护网衣的作用,是一种新型的桩网连接模式。此外,在桩网间接连接模式下,为防止鱼类从网衣与桩柱之间的空隙逃逸,在其中间单独加装翼网,此网具有比间隙宽更宽的距离,缝合和固定在纲绳和桩柱上,在边缘处不产生对整体网衣的影响。为防止养殖鱼类从网衣底部逃逸,将铁链加装在底部纲绳上并嵌入海底。
|
图 1 桩柱式围网连接方式工程结构示意图 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the connection mode between pile and net of net enclosure aquaculture facility a:直接连接;b:间接连接 a: Direct connection; b: Indirect connection |
本研究采用集中质量点法模拟2种连接方式的网片在波浪条件下的受力及运动。模型的集中质量点设于每个网目目脚的两端,假设网片由有限的无质量弹簧连接的集中质量点所构成,通过计算集中质量点在波浪和边界条件下的位移,确定网的形状,如图 2所示。

|
图 2 集中质量点示意图 Fig.2 Schematic diagram of the lumped mass point |
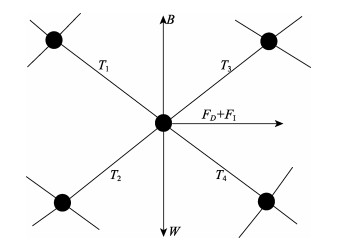
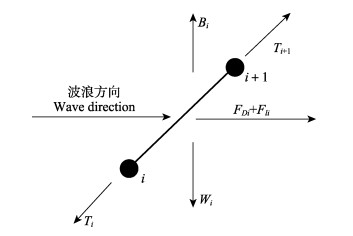
网衣集中质量点受力主要包括重力、浮力、网线张力、速度力和惯性力等,网衣受到的波浪力可根据莫里森方程来计算(王树青等, 2013)。跟据网目的结构特点,假定目脚两端的集中质量点为圆球,球由于在各个方向的投影面积都相等,故在计算波浪力时在其运动方向上水动力系数取恒定值。目脚为圆柱体杆件,杆件在运动过程中,各个方向投影不一致,故在计算波浪力时考虑波浪入射方向与网线夹角的关系,需要在目脚建立局部坐标系(ξ,η,τ),τ方向为沿目脚方向,ξ轴在τ和水质点相对速度组成的平面内与τ垂直,η轴与ξ和水质点组成的平面相垂直(赵云鹏, 2007; 陈天华等, 2017)。集中质量点的受力如图 3所示,纲绳与网线的数值模拟基本相同,取其中第i个和i+1个集中质量点之间的纲绳受力,如图 4所示,主要集中质量点运动方程如下:
| $ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {(M + \Delta M)a = T + {F_D} + {F_I} + W + B} \\ {\Delta M = {\rho _w}\forall {C_m}} \\ {T = {d^2}{C_1}{\varepsilon ^{{C_2}}}, \varepsilon = \frac{{l - {l_0}}}{{{l_0}}}} \\ {{F_D} = \frac{1}{2}{\rho _w}{C_D}A\frac{{{v_k}|{v_k}|}}{2}} \\ {{F_I} = {\rho _w}\forall {C_M}\frac{{\partial v}}{{\partial t}}} \end{array}} \right. $ | (1) |
|
图 3 集中质量点受力分析示意图 Fig.3 Schematic diagram of force analysis of the lumped mass point |
|
图 4 纲绳和网线受力分析示意图 Fig.4 Schematic diagram of force analysis of the rope and twine |
式中,ΔM、M分别为各集中质量点的附加质量和质量,单位为kg;a为各集中质量点的加速度矢量,单位为m/s2;T为集中质量点所受到的张力矢量,单位为N;FD、FI分别为集中质量点的速度力矢量和惯性力矢量,单位为N;W为集中质量点的重力矢量,单位为N;B为质点的浮力矢量,单位为N;CD为速度力项系数;A为网线沿波浪方向的投影面积,单位为m2;CM为惯性力项系数;Cm为附加的质量力项系数;d为网线直径,单位为m;l0为网线原始长度,单位为m;l为变形后的长度,单位为m;C1、C2为构件材料弹性系数;vk为水质点与集中质量点的相对速度,单位为m/s;v为水质点的速度,单位为m/s。
本研究采用欧拉法求解运动方程(王能超, 2005),网片的形状变化基于运动方程求解集中质量点速度加速度,然后根据下一步长(步长取0.000 01 s)求解位移、速度和加速度,从而确定新的网片形状,最后根据求出的集中质量点位移和速度代替上一步网片形状重复计算直到计算结束,具体的计算流程见图 5。

|
图 5 模拟流程图 Fig.5 Flow chart for simulation |
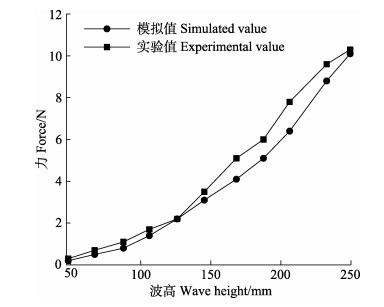
本研究采取的数值模拟计算方法的正确性判断,在浙江海洋大学拖曳力水池实验室进行物理验证性实验,在波浪周期T=1.6 s实验条件下进行比例为1∶1的模型模拟,网衣尺寸为0.64 m × 0.20 m,计算网目数和模拟网目数保持一致,材料为PE,位于水面下0.2 m,波高为0.050~0.250 m,给出各种波高条件下网衣最大水平波浪力和水阻力(陈天华, 2017)。不同波高条件下的模拟值与实验值之间的关系见图 6,由图 6可知,网衣水平波浪力最大值与实验值吻合较好。计算可得平均误差值4.9% (< 10%),说明本研究建立的数学模型和采用的计算方法是可行的。
|
图 6 网衣水平波浪力模拟值和实验值对比 Fig.6 Comparison of horizontal wave force on net between experimental value and simulated value |
实际的围网养殖工程中,网衣顶端均高出水位2~3 m。本研究通过比较波面水质点(η)与网衣集中质量点(z)的相对位置判断网衣是否出水。当z > η时,水质点的速度和加速度都为0;当z < η时,运用StokesⅢ阶波波浪理论的水质点速度和加速度(王树青等, 2013)。
1.3 计算参数本研究采用PE材质的有结节网衣,网片宽度为6.336 m,高度为14 m,出水2 m (以桩网间接连接式围网为例,如图 1所示),计算网目数为53 760,目脚长度为0.04 m,网线直径为0.003 5 m,网衣结节直径为0.010 99 m,纲绳直径为0.018 m,水平缩结系数为0.66,垂直缩结系数为0.75,弹性系数C1=345.3×106,C2=1.012 1 (石建高, 2018)。考虑网片网目数较多,采用8×8的网目群化方法将相邻64个网目合并成一个等效大网目(刘莉莉, 2012)。根据李玉成等(2005)的研究,水动力系数取Cd=1.45。
本研究工况如表 1所示,波高变化范围为2~6 m,波长变化范围为24~72 m,波周期变化范围为3.81~7.27 s,所有工况下的波陡均为1/12,可以代表普通海况和高海况下的波浪特点。不同工况下H/(gT2)的取值如表 1所示,均满足StokesⅢ阶波波浪理论的适用范围[0.008 6 ≤H/(gT2)≤0.019 6,0.01≤d/(gT2)≤0.40] (王树青等, 2013)。因此,本研究适用StokesⅢ阶波波浪理论计算波面、水质点速度和加速度等波浪参数。
|
|
表 1 计算工况 Tab.1 Calculation conditions |
计算网片初始形状及波浪的入射方向,即波浪方向与网衣垂直(如图 7所示),网衣运动方向为yz平面。在数值模拟过程中,桩网直接连接模式在边缘处由纲绳和网线共同系缚在桩柱上;桩网间接连接模式由横向纲绳直接连接在桩柱上,没有网线系缚在桩柱上,其中网线固定在左右距离桩柱最近的纵向纲绳上。
|
图 7 模拟网片初始形状示意图 Fig.7 Schematic diagram of original shape of the simulated net panel |
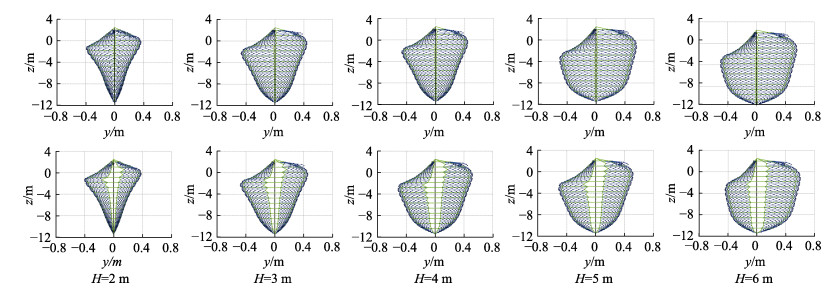
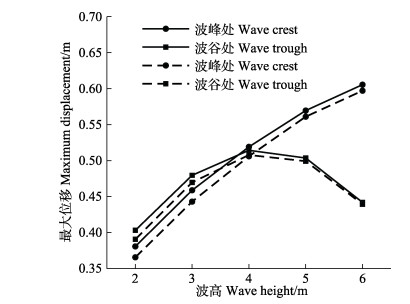
桩柱式围网网衣单元最大偏移量是指网衣变形后结节到网片初始平面的最大距离,其在不同波高条件的最大偏移见图 8 (桩网直接连接和桩网间接连接)。从图 8可以看出,网衣左右最大偏移量呈不对称状,左右最大偏移量的位置对应高度不一致。随着波高的变化,这种不对称状越来越明显,左右最大偏移的位置对应高度越来越大,水深较低的部位网衣偏移量开始逐渐变大。2种连接方式的网衣随着波高的变化,最大偏移量呈逐渐变大的趋势。为便于解释左右最大偏移量,结合波浪运动规律,定义波峰时刻偏移(图 8中右边最大偏移位置)和波谷时刻偏移(图 8中左边最大偏移位置)。网衣单元左右运动最大偏移量见图 9。由图 9可知,波峰时刻2种连接方式的网衣最大偏移量均随波高的增加而增加。波谷时刻随着波高的增加呈先增加后减小的趋势。0刻度线以上有部分网衣位移过大,主要原因是波浪从波谷运动到波峰,第1根和第2根横纲绳在波浪的作用下间距减小,波峰处速度大,波浪力大,使网衣会在波浪的作用下冲过纲绳。总体上看,间接连接的网衣最大偏移量要大于直接连接的网衣最大偏移量。
|
图 8 桩网直接连接(第1行)和间接连接(第2行)模式下网衣单元最大偏移量随波高的变化 Fig.8 Variation of the maximum displacement of the net panel related to wave height under the configurations of direct (first row) and indirect (second row) pile-net connections |
|
图 9 2种桩网连接下的网衣单元最大偏移量随波高变化(虚线:间接连接式;实线:直接连接式) Fig.9 Variation of the maximum displacement of the net panel related to wave height under the configurations of direct (solid line) and indirect (dotted line) pile-net connections |
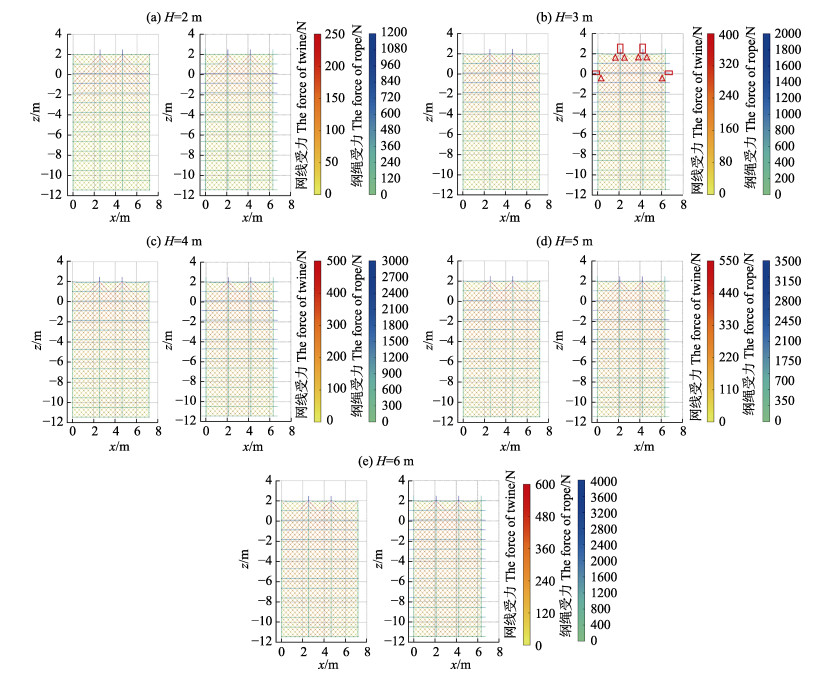
桩柱式围网网衣纲绳和网衣受力分布见图 10。图 10中的颜色代表纲绳和网线受力大小(图 10右侧给出颜色对应受力大小),横纲绳受力随着水深的增加逐渐减小,横纲绳的最大受力部位出现在水平面附近,竖纲绳和网线的最大受力部位出现在顶部连接槽钢处。连接槽钢处的2根竖纲绳受力远远大于其他部位的纲绳,其主要原因是承担了大部分网衣的受力。在数值模拟过程中,此处纲绳因受力拉伸量最大,导致周围网线在此处拉扯受力变大,受力呈现“
|
图 10 桩网直接连接(左)和间接连接(右)模式下网衣受力分布图随波高的变化 Fig.10 Variation of the force distribution map of the net panel related to wave height under the configurations of direct (left) and indirect (right) pile-net connections |
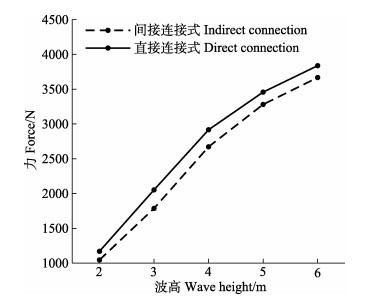
|
图 11 2种桩网连接方式纲绳最大受力随波高变化 Fig.11 Variation of the maximum force of the rope related to wave height under the configurations of direct (solid line) and indirect (dotted line) pile-net connections |
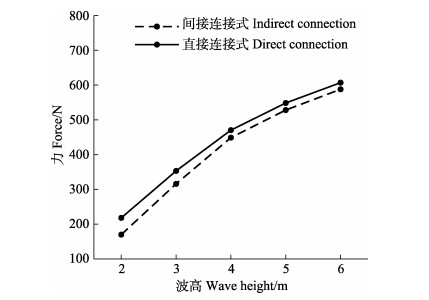
|
图 12 2种桩网连接方式网线最大受力随波高变化 Fig.12 Variation of the maximum force of the twine related to wave height under the configurations of direct and indirect pile-net connections |
由图 10可见,除了水平面上(0刻度线上)网线的最大受力之外,水平面下网线最大受力主要出现在–0.8 m处网衣左右两端。水平面上的网线短期内破坏并不会引起鱼类的出逃,而水平面之下网衣的破坏极易引起鱼类的出逃。由于波浪作用于网衣上力的分布不均匀性,所以同一水平面网衣最大受力分布不同。故研究不同桩网连接方式下的同一水平面最大网线受力分布对连接方式的选择具有重要意义。图 13给出2种连接方式下–0.8 m处(水平面下最大网线受力处横截面相交网线受力情况,从左往右1个网目取1个监测点)网衣横截面网线受力分布,总体上看,2种连接方式下水平网线受力随波高的增加而增加,间接连接的网线受力要小于直接连接的网线受力。

|
图 13 2种连接方式下的水平面下网线最大受力随波高变化(虚线:间接连接式;实线:直接连接式) Fig.13 Variation of the maximum force of twine under the water surface related to wave height under the configurations of direct (solid line) and indirect (dotted line) pile-net connections |
在工程实际使用过程中,常发现围网网片和桩柱之间的系缚点破坏,导致鱼类的逃逸。网衣的系缚点指的是网线和纲绳通过强约束固定在桩柱上,系缚点受力是指纲绳和网线作用在这一点的矢量和。系缚点可以分为顶点处(图 14中1、15、16和30号顶点)和非顶点处两类。顶点处系缚点受力=纲绳A和C的张力+网线B的张力。非顶点处系缚点受力=纲绳A、B和C的张力+网线D和E的张力。图 15表明,随着波高的增加,2种连接方式的桩柱式围网系缚点受力随波高增加而增加。系缚点最大受力出现在12号系缚点和13号系缚点,2处系缚点的位置在水平面下0~1 m左右的范围,故对2种连接方式的围网水平面下0~1 m之间系缚点的进行加固是非常重要的。总体上看,随着深度的增加系缚点受力越来越小,水面以上,随着桩高的增加而逐渐降低。间接连接的围网网衣系缚点受力要小于直接连接的围网网衣系缚点受力。
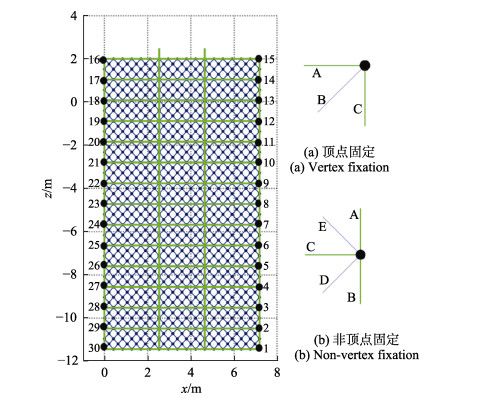
|
图 14 网片固定示意图 Fig.14 Schematic diagram of net panel fixing in the vertex (a) and non-vertex (b) |
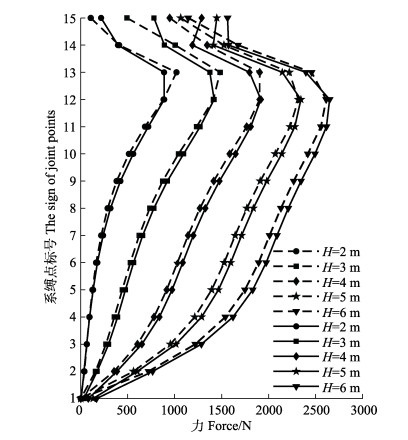
|
图 15 2种桩网连接方式下的最大系缚点受力随波高变化(虚线:间接连接式;实线:直接连接式) Fig.15 Variation of the maximum force of joint points related to wave height under the configurations of direct (solid line) and indirect (dotted line) pile-net connections |
桩柱式围网主要由桩柱、网衣、纲绳等构成,围网网衣最大偏移量的研究对于网衣编排和设备安装具有指导意义。在实际工程过程中,在最大偏移量范围内要尽量避免障碍物,否则会造成网衣的磨损破坏。研究结果表明,围网网衣的最大偏移量随着波高的增加而增加,桩网间接连接的围网网衣偏移量要大于桩网直接连接的围网网衣。在运动的形状上看,围网形状变化呈不对称状。陈天华等(2017)研究发现,偏移量随波高呈正比关系,这与本研究结果一致。在运动形状上呈现不对称状,根据波浪的运动规律,网衣出水条件下不同时刻网衣与海水接触面积不同,从而导致作用在其上的力不同,最大偏移不同,这在本研究和前人的研究中都给予了证实(杨熙等, 2020)。本研究中的2种连接方式的围网,当波高 < 4 m时,波峰和波谷处的位移几乎保持一致。当波高 > 4 m时,波浪与网片接触面积逐渐减小,在相同情况下,作用于网衣的波浪力减小。即在波谷时,随着波高的增加,网片出水部分面积越来越大,波高为4 m时,水面以上网衣高度为4 m;波高为5 m时,水面以上网衣高度为4.5 m;波高为6 m时,水面以上网衣高度为5 m。在波谷时刻带动整体网衣一起向后运动,能作用于网衣的力会减小,故位移减小。从整体的角度来看,间接连接的围网网衣和桩柱连接处没有网线连接,导致边缘处全部由纲绳承担拉力,而直接连接方式的连接处有网线和纲绳共同承担拉力,所以导致间接连接的最大偏移量大于直接连接方式的最大偏移量。
3.2 波高对2种连接方式力学特性的影响网衣纲绳受力、网线受力以及系缚点受力是研究围网网衣安全的3个重要因素。研究发现,2种连接方式的纲绳和网线的最大受力和系缚点受力以及水平网线受力是随着波高的增加而增加,这与陈天华等(2017)的研究结果一致。从网线受力和纲绳受力的角度来看,间接连接模式受力小于直接连接模式。2种连接方式的纲绳和网线最大受力的部位都保持一致,纲绳和网线最大受力均在竖纲绳连接槽钢处,横纲绳随着水深的增加受力逐渐减小,横纲绳在水平面附近受力最大(图 10显示,纲绳颜色越蓝表示受力越大),在实际建设过程中,对网线、纲绳以及系缚点的最大受力部位要进行特殊加固措施,可以选择强度大、抗破坏能力强的纲绳和网线。一方面可以有效降低纲绳和网线断裂的风险,另一方面能避免盲目加固造成的不必要的施工作业。从系缚点受力的角度看,间接连接方式的围网系缚点受力要小于直接连接方式的围网系缚点受力,二者最大系缚点受力均出现在水平面下0~1 m的范围内。在这些范围内的纲绳和网线需要选用安全系数为其受力5~6倍的纲绳和网线材料。随着水深的增加,系缚点受力和横纲绳受力都逐渐减小,可以选择价格便宜的纲绳,不仅满足使用要求,而且节约成本。从水平网线受力的角度来看,除了2个竖纲绳连接处的网线受力最大,其余网线受力最大的部位在水平面下–0.8 m左右的位置(图 10所示),此处的网衣破坏会直接引起围网养殖物种的逃逸,需要对此处围网网衣进行加固处理。故对网衣力学特性的研究,可以直接指导实际工程建设过程中的材料选取和加固部位。
CHAN A T, LEE S W C. Wave characteristics past a flexible fishnet. Ocean Engineering, 2001, 28(11): 1517-1529 DOI:10.1016/S0029-8018(00)00062-7 |
CHEN T H, MENG A, GUI F K. Effect of wave height and direction on hydraulic characteristics of net of pile-column type net enclosure aquaculture system. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(2): 245-251 [陈天华, 孟昂, 桂福坤. 波浪高度及方向对桩柱式围网养殖系统网片水力特性的影响. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(2): 245-251] |
CHEN T H. Study on hydrodynamic characteristics of pile-column type net enclosure aquaculture facility. Master´s Thesis of Zhejiang Ocean University, 2017 [陈天华. 桩柱式围网养殖系统水动力特性研究. 浙江海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2017]
|
CUI Y, GUAN C T, HUANG B, et al. Numerical simulation of the hydrodynamic characteristics of double-bottom cage for flounder fish under waves. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2019, 40(6): 18-24 [崔勇, 关长涛, 黄滨, 等. 波浪作用下双层网底鲆鲽网箱水动力特性的数值模拟. 渔业科学进展, 2019, 40(6): 18-24 DOI:10.19663/j.issn2095-9869.20180820001] |
DONG G H, MENG F B, ZHAO Y P, et al. A numerical study on dynamic properties of the gravity cages under parallel and counter wave-current conditions. Fishery Modernization, 2014, 41(2): 49-56 [董国海, 孟范兵, 赵云鹏, 等. 波流逆向和同向作用下重力式网箱水动力特性研究. 渔业现代化, 2014, 41(2): 49-56 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9580.2014.02.010] |
FREDRIKSSON D W, SWIFT M R, IRISH J D, et al. Fish cage and mooring system dynamics using physical and numerical models with field measurements. Aquacultural Engineering, 2003, 27(2): 117-146 DOI:10.1016/S0144-8609(02)00043-2 |
GUI F K, Chen T H, Zhao Y P, et al. Study of effect on wave mechanical properties for net panel of pile-column type net enclosure by fixations. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2017, 57(3): 285-292 [桂福坤, 陈天华, 赵云鹏, 等. 固定方式对桩柱式围网网片波浪力学特性影响研究. 大连理工大学学报, 2017, 57(3): 285-292] |
GUI F K, SHAO Z Y, CHEN T H, et al. Study on effect of rope on wave mechanical properties for panel of pile-column type net enclose. Journal of Hydrodynamics A, 2020, 35(4): 505-514 [桂福坤, 邵振宇, 陈天华, 等. 纲绳对桩柱式围网网片波浪力学特性影响研究. 水动力学研究与进展: A辑, 2020, 35(4): 505-514] |
HUANG B, GUAN C T, CUI Y, et al. Study on key techniques for submergence of HDPE submersible deep-sea cage. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2009, 30(5): 102-107 [黄滨, 关长涛, 崔勇, 等. 国产HDPE升降式深水网箱下沉关键技术的研究. 渔业科学进展, 2009, 30(5): 102-107] |
LI Y C, GUI F K. Experimental study and selection of the drag coefficient of knotted and knotless plane fishing net. China Ocean Platform, 2005, 20(6): 11-17 [李玉成, 桂福坤. 平面有结节和无结节网目试验及水阻力系数的选择. 中国海洋平台, 2005, 20(6): 11-17] |
LIU L L, WAN R, HUANG L Y, et al. Numerical simulation of hydrodynamic characteristics of stow net in wave and current. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science), 2013, 43(5): 24-29 [刘莉莉, 万荣, 黄六一, 等. 波流场中张网渔具水动力学特性的数值模拟. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 43(5): 24-29] |
LIU L L. Numerical simulation study on hydrodynamic characteristics of net fishing gear—Take gillnet and show net as examples. Master´s Thesis of Ocean University of China, 2012 [刘莉莉. 网渔具水动力学特性的数值模拟研究—以刺网和张网为例. 中国海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2012]
|
LIU Y, ZHAO Y P, DONG G H. Non-linear analysis of the horizontal wave force on a type of frustum cones artificial reef. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2020, 41(2): 12-19 [刘彦, 赵云鹏, 董国海. 一种圆台型人工鱼礁非线性波浪作用受力分析. 渔业科学进展, 2020, 41(2): 12-19] |
SHAO Z Y. Study on the mechanical characteristics of the net system of pile net separation. Master´s Thesis of Zhejiang Ocean University, 2020 [邵振宇. 桩网分离式围网网衣系统力学特性研究. 浙江海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2020]
|
SHI J G. Rope net technology. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2018 [石建高. 绳网技术学. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2018]
|
TSUKROV I, EROSHKIN O, FREDRIKSSON D, et al. Finite element modeling of net panels using a consistent net element. Ocean Engineering, 2003, 30(2): 251-270 |
WANG M F. Development of the 3D numerical model tuna purse seine gear. Master´s Thesis of Shanghai Ocean University, 2011 [王敏法. 金枪鱼围网网具数值模拟初步研究. 上海海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2011]
|
WANG N C. Calculation method: Algorithm design and MATLAB implementation. Higher Education Press, 2006, 77–84 [王能超. 计算方法: 算法设计及其MATLAB实现. 高等教育出版社, 2006 77–84]
|
WANG S Q, LIANG B C. Wave mechanics for ocean engineering. Qingdao: China Ocean University Press, 2013: 63-174 [王树青, 梁丙臣. 海洋工程波浪力学. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社, 2013: 63-174]
|
YANG X, LIU C, PAN Y, et al. Effect of wave heights and water depths on hydraulic characteristics of net under out of the water surface conditions. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2020, 39(4): 347-352 [杨熙, 刘灿, 潘昀, 等. 网片出水条件下波高和水深对其水动力特性的影响. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 39(4): 347-352] |
ZHAO Y P. Numerical investigation on hydrodynamic behavior of deep-water gravity cage. Doctoral Dissertation of Dalian University of Technology, 2007 [赵云鹏. 深水重力式网箱水动力特性数值模拟研究. 大连理工大学博士研究生学位论文, 2007]
|
ZHOU C. Study of tuna purse seine performance based on numerical simulation. Doctoral Dissertation of Shanghai Ocean University, 2015 [周成. 基于数值模拟的金枪鱼围网性能的研究. 上海海洋大学博士研究生学位论文, 2015]
|



