翘嘴鲌(Culter alburnus)俗称白鱼、翘嘴白等,隶属于鲤形目(Cypriniformes)、鲤科(Cyprinidae)、鲌亚科(Culterinae)、鲌属(Culter),主要分布于我国黑龙江、黄河和长江流域(Tian et al, 2020)。其肉质细嫩、营养丰富,具有高蛋白、低脂肪的特点,是我国重要的名优淡水养殖鱼类之一(张燕萍等, 2015)。随着翘嘴鲌配合饲料及人工繁殖技术的突破,其养殖规模逐年增大,现已在我国安徽、湖北、江苏、浙江及重庆等10多个省市大量养殖。然而,随着翘嘴鲌养殖规模的增大和密度的提高,养殖水环境日益恶化,其免疫力逐渐降低,病害也呈暴发趋势,表现为各种细菌性、真菌性疾病和寄生虫病频发,造成经济损失巨大,严重制约了翘嘴鲌养殖业的可持续发展。其中,细菌性疾病对翘嘴鲌的危害最为严重,目前已报道常见病原菌包含嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)、肠型点状气单胞菌(A. punotata f. intestinalis)和柱状屈桡杆菌(Flexibacter columnaris)等(黄爱华等, 2010; 杨长宏, 2017)。
2020年8月,重庆市荣昌区某养殖场的翘嘴鲌连续多日死亡,累计死亡率达20%,其临床症状主要表现为鳞片疏松、鳍条基部出血,解剖发现腹腔内有大量腹水,肝脏、脾脏肿大等。本研究针对该疫病采集病鱼,从患病濒死翘嘴鲌肝脏中分离出一株优势菌CQ200825,对优势菌进行人工感染实验来验证这株菌的致病性,结合细菌的形态学观察、理化特性鉴定、16S rRNA序列及gyrB序列分析等数据对菌种类型准确鉴定,并进行了毒力基因检测和组织病理观察,探究其毒力因子及感染后造成的组织病理变化,最后通过药敏试验筛选出敏感药物,以期为该病的诊断和防控提供科学依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料采自重庆市荣昌区某养殖场的患病翘嘴鲌5尾,本地繁育和养成,体质量为200~300 g,发病养殖场采用池塘养殖模式,占地约为50 m×667 m,养殖水温为24~28℃。健康翘嘴鲌购自重庆市永川区某养殖场,平均体长为(13.5±1.2) cm,平均体质量为(21.6± 1.5) g,共150尾,暂养于室内水族缸中,养殖期间水温为25~27℃,pH为7.1~7.6,溶解氧为8.5~9.2 mg/L,每2 d换水1次,每次换水量为总体积的1/3。健康翘嘴鲌暂养2周后用于后续的人工感染实验。
1.2 主要试剂与仪器试剂:PCR检测试剂盒和pMD19-T载体购自TaKaRa公司;基因组DNA提取试剂盒购自天根生化科技(北京)有限公司;脑心浸出液肉汤(BHI)培养基、细菌微量生化反应管和药敏纸片购自杭州微生物科技有限公司。
仪器:光学显微镜(OLYMPUS,日本)、HM325型转轮式切片机(Thermo Scientific,美国)、PCR扩增仪(Bio-Rad,美国)、电泳仪(北京市六一仪器厂)和凝胶成像系统(Bio-Rad,美国)等。
1.3 病原菌的分离纯化选择具有典型患病症状的5尾濒死翘嘴鲌于超净工作台中,75%酒精擦拭病鱼体表进行消毒,用接种环蘸取病灶明显的脏器组织及腹水,划线接种于BHI培养基上,28℃倒置培养24 h,再挑选优势单菌落进行纯化培养,肉眼观察菌落形态、大小、隆起度等,4℃保存备用。
1.4 理化特性鉴定挑取纯化培养的分离菌进行革兰氏染色,光学显微镜下观察菌体形态特征。挑取纯化的单菌落接种于BHI液体培养基,然后,将培养物接种于细菌微量生化反应管中,28℃培养24 h,鉴定结果参考《常见细菌系统鉴定手册》(东秀珠等, 2001)和《伯杰细菌鉴定手册》(Holt et al, 1994)的标准判断细菌种类。
1.5 16S rRNA和gyrB基因序列的扩增及系统发育分析利用基因组DNA提取试剂盒提取菌株CQ200825的基因组DNA作为PCR模板。PCR反应体系(50 μL):10×PCR Buffer 5 μL,16S rRNA、gyrB基因上下游引物各1 μL (引物见表 1) (Li et al, 2019; Soler et al, 2004),模板1 μL,rTaq酶0.5 μL,dNTPs 4 μL,用ddH2O补足至50 μL。PCR反应程序:94℃预变性5 min;94℃变性30 s,56℃退火30 s,72℃延伸80 s,33个循环;最后72℃终延伸10 min。反应产物用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测。用凝胶回收试剂盒进行PCR产物回收纯化,与pMD19-T载体4℃连接过夜,第2天转化DH5α感受态细胞,取反应物在氨苄青霉素固体培养物平板上涂布,倒置于37℃恒温培养箱中12~16 h,挑选阳性单克隆菌落送华大基因公司测序。将所得序列使用Blast软件与已知序列进行比对分析,并使用MEGA 5.05软件,选用NJ方法构建系统发育树。
|
|
表 1 菌株CQ200825管家基因及部分毒力基因引物 Tab.1 Primers of housekeeping genes and some virulence genes of strain CQ200825 |
将分离纯化的CQ200825划线接种于BHI培养基上,28℃倒置培养24 h复苏。挑取单菌落接种于BHI液体培养基,28℃、220 r/min震荡培养12~14 h,离心收集菌体并用0.65%生理盐水洗脱,参照麦氏比浊法调整菌悬液浓度为1.0×108、1.0×107、1.0×106和1.0×105 CFU/mL (马秀玲等, 2014),实验组腹腔注射菌悬液0.2 mL/尾,对照组注射相同体积的0.65%无菌生理盐水,每组实验鱼30尾,连续观察7 d。在人工感染期间,正常充气换水,水温保持在24~25℃。每天观察实验翘嘴鲌的活动情况并记录其发病与死亡情况,将濒死病鱼病症与原始病症进行对比,并再次进行病原菌的分离与鉴定。使用累积法(Reed-Muench)计算菌株的半数致死量(LD50)(杨昆明等, 2018)。
1.7 毒力基因检测以菌株CQ200825的DNA为模板,对外膜蛋白(ompA)、溶血素(hlyA)、热稳定性肠毒素(ast)和细胞毒性肠毒素(act)进行PCR扩增(李芳, 2019; 朱大玲等, 2006; 刘小芳等, 2021; 龙波等, 2016)。引物序列、退火温度和产物片段见表 1。PCR扩增产物用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测。凝胶回收试剂盒纯化,克隆经PCR验证后送至华大基因公司进行测序。
1.8 组织病理观察采用组织切片技术(胡骞等, 2020),取自然患病濒死翘嘴鲌和健康翘嘴鲌的肝、脾、肾和肠组织,用Bouinxs液固定24 h,经乙醇脱水、二甲苯透明、石蜡包埋、切片等步骤处理,切片厚度为5 μm,经HE染色、中性树胶封片,置于光学显微镜下观察拍照。
1.9 药敏试验采用纸片扩散法检测分离菌株对33种抗菌药物的敏感性(李雅军等, 2006),用无菌生理盐水稀释分离菌株成1.5×108 CFU/mL,取100 μL的菌液均匀涂布于平板表面,用无菌镊子夹取药敏纸片贴于培养基表面,28℃恒温倒置培养24 h后用游标卡尺测量抑菌圈的直径,最后根据美国临床实验室标准化研究所(CLSI)抗菌药物敏感性实验执行标准(CLSI-M100-S19)判断菌株对各药物的敏感程度(Martinez et al, 2016)。
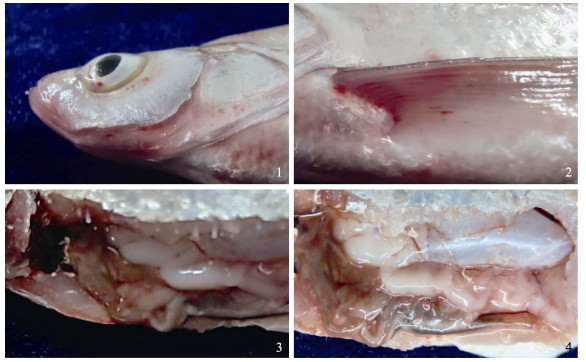
2 结果 2.1 自然发病情况自然发病的翘嘴鲌游动缓慢,食欲降低或不摄食,鳞片部分脱落,眼球突出(图 1-1),在眼眶周围、鳃盖及鳍条基部可见明显的充血、出血(图 1-1)。剖检可见腹腔内有大量腹水(图 1-3),肝脏、脾脏肿大(图 1-4),有的个体肠道充血,内无食物。
|
图 1 自然发病翘嘴鲌的临床症状 Fig.1 The clinical signs of naturally diseased C. alburnus 1:眼球突出;2:鳍条基部充血、出血;3:有腹水;4:肝脾肿大 1: Exophthalmos; 2: Hyperemia and bleeding at the base of the fin; 3: Ascites; 4: Hepatosplenomegaly |
从5尾濒死病鱼肝脏中均分离得到均一的优势菌,将其命名为CQ200825。在BHI培养基上28℃培养24 h,形成圆形、表面光滑、边缘圆整、直径为1.0~1.5 mm的菌落,革兰氏染色呈阴性,细菌形态为短杆状,多数单个排列。
2.3 病原菌的理化特性菌株CQ200825能产生吲哚,不能产生H2S。M.R试验和V-P试验阳性;赖氨酸脱羧酶和氧化酶阳性,精氨酸双水解酶、苯丙氨酸脱氨酶、鸟氨酸脱羧酶和脲酶阴性;能利用D-甘露醇、D-葡萄糖和纤维二糖,不能利用阿拉伯糖、水杨苷、山梨醇和肌醇,具体生理生化特性见表 2。根据生化特性鉴定结果,并参照《常见细菌系统鉴定手册》和《伯杰细菌鉴定手册》可初步确定分离菌株CQ200825为维氏气单胞菌(Aeromonas veronii)。
|
|
表 2 CQ200825的生理生化鉴定结果 Tab.2 Biochemical and physiological identification of strain CQ200825 |
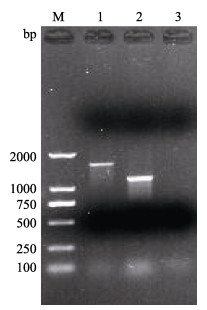
以分离菌株CQ200825基因组DNA为模板,分别用16S rRNA和gyrB基因的引物进行PCR扩增,其长度约为1500 bp和1100 bp (图 2)。对目的条带进行割胶回收、纯化、与pMD19-T载体连接、转化DH5α感受态细胞、挑选阳性克隆测序,发现菌株CQ200825所获得的16S rRNA和gyrB基因序列片段大小分别为1513和1051 bp。
|
图 2 CQ200825的16S rRNA和gyrB基因PCR扩增结果 Fig.2 PCR amplification results of 16S rRNA and gyrB genes of CQ200825 M:DL-2000 DNA marker;1:16S rRNA;2:gyrB;3:阴性对照Negative control |
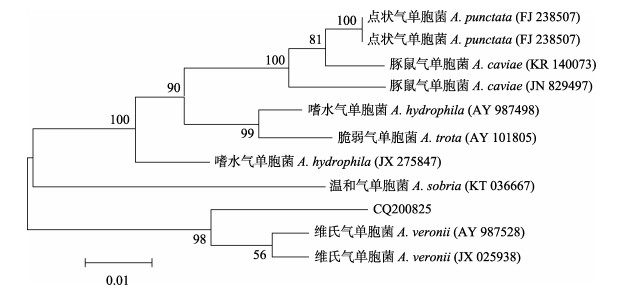
分别将菌株CQ200825的16S rRNA和gyrB基因序列与NCBI基因库中的序列进行比对,结果显示,菌株CQ200825 16S rRNA基因与GenBank登录的维氏气单胞菌(登录号:NR044845)的相似性达到99.60%;菌株CQ200825 gyrB基因与GenBank登录的维氏气单胞菌(登录号:KR537456)的相似性达到99.63%。同时,使用MEGA5.05软件构建系统发育树,结果显示,菌株CQ200825均与维氏气单胞菌聚为一支(图 3、图 4)。根据以上结果可进一步确定菌株CQ200825为维氏气单胞菌。

|
图 3 基于16S rRNA序列构建的系统发育树 Fig.3 Phylogenetic tree analysis based on 16S rRNA sequence |
|
图 4 基于gyrB基因序列构建的系统发育树 Fig.4 Phylogenetic tree analysis based on gyrB sequences |
对健康翘嘴鲌腹腔注射分离菌株CQ200825,感染结果见图 5。结果显示,1.0×108 CFU/mL实验组翘嘴鲌2 d内全部死亡;1.0×107、1.0×106和1.0×105 CFU/mL实验组翘嘴鲌7 d内死亡率分别为76.7%、23.3%和6.7%;对照组未出现死亡现象,表明菌株CQ200825有较强的致病性。人工感染造成翘嘴鲌鳍条基部充血、出血,解剖发现腹腔内有大量腹水,肝脾肿大,与自然发病翘嘴鲌症状基本一致。同时,从濒死鱼体内分离到一株优势菌株,经理化特性和分子特征鉴定与菌株CQ200825一致,这表明菌株CQ200825为自然发病翘嘴鲌的病原菌。根据累积法计算得到菌株CQ200825对翘嘴鲌的7 d LD50为2.7×106 CFU/mL。

|
图 5 菌株CQ200825人工感染实验结果 Fig.5 The artificial infection experiment results of the strain CQ200825 |
根据已报道的维氏气单胞菌ompA、hlyA、ast、act基因设计引物进行PCR扩增,经测序分别获得大小为903、592、504和249 bp的DNA片段(图 6)。

|
图 6 CQ200825的毒力基因PCR扩增结果 Fig.6 PCR amplification results of virulence genes of CQ200825 M:DL-2000 DNA marker;1、3、5、7分别为ompA、hlyA、ast、act;2、4、6、8分别为ompA、hlyA、ast、act的阴性对照 M: DL-2000 DNA marker; 1, 3, 5 and 7 were ompA, hlyA, ast, and act, respectively; 2, 4, 6 and 8 were negative controls of ompA, hlyA, ast, and act, respectively |
组织病理学观察表明,患病翘嘴鲌的肝、脾、肾和肠均发生了不同程度的病变。健康鱼肝细胞呈圆形或多角形,排列整齐(图 7-1);患病鱼肝细胞肿胀、坏死,血管中血细胞凝集(图 7-2)。健康鱼脾脏红白髓分明,结构清晰(图 7-3);患病鱼脾组织坏死,细胞排列紊乱,红白髓界限不清,胞核有轻微肿胀(图 7-4)。健康鱼肾小管结构清晰,肾小囊腔体积正常(图 7-5);患病鱼肾小管上皮细胞发生颗粒变性,肾小球萎缩(图 7-6)。健康鱼肠道各部分结构清晰、完整(图 7-7);患病鱼肠道结构遭到严重破坏,浆膜脱落,肠绒毛大部分坏死脱落,杯状细胞和上皮细胞坏死(图 7-8)。

|
图 7 健康翘嘴鲌和患病翘嘴鲌组织病理学观察 Fig.7 Histopathological observation of healthy C. alburnus and diseased C. alburnus 1:健康鱼肝细胞呈圆形或多角形,排列整齐(箭头);2:患病鱼肝细胞肿胀、坏死,血管中血细胞凝集(箭头);3:健康鱼脾脏红髓和白髓结构清晰,淋巴细胞排列整齐;4:患病鱼脾脏组织坏死,胞核有轻微肿胀(箭头);5:健康鱼肾小管结构清晰(箭头);6:患病鱼肾小管上皮细胞发生颗粒变性(箭头);7:健康鱼肠道各部分结构完整;8:患病鱼肠绒毛大部分坏死脱落,杯状细胞坏死(箭头) 1: Liver cells of healthy fish were round or polygonal and arranged neatly (arrow); 2: Liver cells of diseased fish were swollen and necrotic, and hemocytes agglutinated in blood vessels (arrow); 3: The structure of red pulp and white pulp in spleen was clear and the lymphocytes were arranged neatly in healthy fish; 4: Spleen tissue of diseased fish necrosis and the nucleus had slight swelling (arrow); 5: Renal tubules of healthy fish were clear (arrow); 6: The epithelial cells of renal tubules showed granulosa degeneration in diseased fish (arrow); 7: Parts of intestines were structurally intact in healthy fish; 8: Most of the intestinal villus were necrotic and exfoliated, and goblet cells were necrotic in diseased fish (arrow) |
本研究检测了菌株CQ200825对氟苯尼考等33种抗菌药物的敏感性,包括红霉素等3种大环内酯类、头孢他啶等12种β-内酰胺类、多四环素等3种四环素、复方新诺明等2种磺胺类、庆大霉素等6种氨基糖苷类、恩诺沙星等3种喹诺酮类、氟苯尼考以及林可霉素、多黏霉素等2种其他类抗菌药物。结果显示,分离菌株对多西环素、恩诺沙星、氟苯尼考等17种抗菌药高度敏感,对红霉素、复方新诺明、磺胺异恶唑和新霉素中度敏感,对青霉素、阿莫西林、庆大霉素等12种抗菌药表现为耐药,具体结果见表 3。
|
|
表 3 CQ200825株对38种抗菌药物的耐药性分析 Tab.3 Antimicrobial susceptibility of CQ200825 isolate to 38 kinds of antibiotics |
本研究从患病翘嘴鲌肝脏中分离得到一株致病菌CQ200825,人工感染症状与自然发病鱼基本一致,7 d LD50为2.7×106 CFU/mL,表现出较高的致病力。经形态学观察和生理生化特性分析发现,菌株CQ200825与维氏气单胞菌非常相似,因为维氏气单胞菌区别于气单胞菌属其他细菌的理化特征是精氨酸双水解酶阴性、赖氨酸脱羧酶阳性(Holt et al, 1994)。为进一步确定其分类地位,本研究进行了16S rRNA基因序列分析,结果显示,该序列与已知维氏气单胞菌序列相似性达到99.60%。但由于16S rRNA基因保守性较高,无法区分亲缘关系较近的细菌类群(Martino et al, 2011),而gyrB基因较16S rRNA具有更高的替换率,适合亲缘关系较近的种属鉴定(Tancsics et al, 2014)。因此,本研究针对gyrB基因序列进行分析,结果显示,其与已知维氏气单胞菌序列相似性达到99.63%。结合形态学、生理生化特性以及16S rRNA和gyrB序列分析综合判定分离菌株CQ200825为维氏气单胞菌。
维氏气单胞菌亦被称为维罗纳气单胞菌,隶属于气单胞菌科(Aeromonadaceae)、气单胞菌属(Aeromonas),是致病性气单胞菌的代表种,普遍存在于海水、淡水及土壤等环境中,该细菌能够感染各种水产动物,尤其在水温高、水质条件恶劣、水产动物体表受伤的情况下发病率较高(凡飞等, 2015)。王兴丽等(2016)研究发现,该菌能引起虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss)体表溃疡、鳃丝和内脏出血等症状。郭莹等(2020)研究发现,该菌能引起罗氏沼虾(Macrobrachium rosenbergii)肌肉发白、游泳足和附肢发红等症状,严重时出现大量死亡。据报道,感染维氏气单胞菌患病或死亡的水产动物还有锦鲤(Cyprinus carpio var. koi)、花斑副沙鳅(Parabotia fasciata)、斑点叉尾
维氏气单胞菌致病机理较为复杂,可能是由于其携带了多种毒力因子,包括外膜蛋白、溶血素、气溶素、细胞毒性肠毒素、丝氨酸蛋白酶等(Nawaz et al, 2010)。因此,检测菌株是否携带毒力基因对了解维氏气单胞菌致病性及防治至关重要。经PCR检测并测序,菌株CQ200825携带ompA、hlyA、ast和act 4种毒力基因。这4种毒力基因作为质粒基因,是气单胞菌致病性发挥关键作用的毒力因子,一般与其感染过程中的入侵、粘附、定植、释放及损伤宿主组织等活动有关。有研究表明,hlyA是导致宿主组织广泛出血和溶血的关键毒力基因,同时也可以导致宿主肠炎(常藕琴等, 2014),ast和act是气单胞菌导致肠炎的关键毒力因子,且肠炎的严重程度与毒力因子的数量和种类有着密切联系(Nawaz et al, 2010)。Chopra等(2000)研究表明,气单胞菌属细菌对宿主的感染力较强,可能与act可刺激宿主的促炎反应有关。同时结合组织病理学研究发现,患病鱼的肝、脾、肾及肠均有不同程度的病变,其中以肝、肠损伤最为严重,表现为肝细胞肿胀、坏死,血管中血细胞凝集;肠道浆膜脱落,肠绒毛大部分坏死脱落,可以推测肝脏和肠道是该菌的主要靶器官,同时,肝、肠的感染也可能是脾、肾等器官病变的原因之一,这与大口黑鲈(Micropterus salmoides)和达氏鲟(Acipenser dabryanus)感染维氏气单胞菌引起的组织病理变化特征相一致(Pei et al, 2021; 刘亚等, 2018)。
尽管免疫接种是控制水产养殖动物暴发性流行病有效的方法,但存在免疫效果不理想、免疫力持久性差等问题,使得免疫接种的开发和应用受到很大限制。目前,国内外对维氏气单胞菌病的防治仍为主要使用抗菌药物。本研究药敏试验分析了33种药物,其中,高度敏感抗菌药物17种,包括多西环素、恩诺沙星、氟苯尼考等,占比为51.52%;中度敏感药物4种,包括红霉素、复方新诺明、磺胺异恶唑和新霉素,占比为12.12%;耐药抗菌药物12种,包括青霉素、阿莫西林、庆大霉素等,占比为36.36%。维氏气单胞菌四川分离株对丁胺卡那、庆大霉素中度敏感,对四环素、环丙沙星、磺胺异恶唑等耐药(龙波等, 2016);维氏气单胞菌印度分离株对四环素、环丙沙星等高度敏感,对丁胺卡那耐药(Mallik et al, 2020)。而本研究中的CQ200825株对丁胺卡那、四环素、环丙沙星等高度敏感,对磺胺异恶唑中度敏感,对庆大霉素耐药。这可能是由于不同来源、不同地理环境中的菌株对不同抗菌药物的敏感程度存在差异。因此,在选择抗菌药物治疗时,首先应参考菌株药敏试验结果,结合无公害食品渔用药物使用准则(NY 5071-2002)及农业农村部渔业渔政管理局印发《水产养殖用药明白纸2020年1、2号》等相关规定,进行科学、规范用药。
CHANG O Q, LIU X Y, PAN H J, et al. Histopathological and pathogeny preliminary research on mulberry heart of Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baeri). Journal of Fisheries of China, 2014, 38(6): 904-911 [常藕琴, 刘晓勇, 潘厚军, 等. 西伯利亚鲟桑葚心病理组织学和病因的初步研究. 水产学报, 2014, 38(6): 904-911] |
CHOPRA A K, XU X, RIBARDO D, et al. The cytotoxic enterotoxin of Aeromonas hydrophila induces proinflammatory cytokine production and activates arachidonic acid metabolism in macrophages. Infection Immunity, 2000, 68(5): 2808-2818 DOI:10.1128/IAI.68.5.2808-2818.2000 |
DONG X Z, CAI M Y. Manual for identification of bacteriology. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 114-115 [东秀珠, 蔡妙英. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 114-115]
|
FAN F, ZHANG S W, LI L T, et al. Screening and characterization of a bacterium named 4-1-3 antagonizing Aeromonas veronii. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2015, 36(2): 146-152 [凡飞, 张生武, 李联泰, 等. 凡隆气单胞菌(Aeromonas veronii)拮抗菌4-1-3的筛选鉴定及其活性物质初探. 渔业科学进展, 2015, 36(2): 146-152] |
GAO J W, LIANG L G, WANG Y B, et al. Identification and susceptibility test of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii isolated from Siniperca chuatsi. Microbiology China, 2016, 43(12): 2686-2692 [高金伟, 梁利国, 王亚冰, 等. 鳜源致病性维氏气单胞菌的鉴定及药敏试验. 微生物学通报, 2016, 43(12): 2686-2692 DOI:10.13344/j.microbiol.china.160029] |
GAO T, WANG J, WANG K Y, et al. Isolation, identification and drug sensitivity analysis of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii from diseased Parabotia fasciata Dabry. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 42(3): 239-244 [高通, 王均, 汪开毓, 等. 花斑副沙鳅源致病性维氏气单胞菌的分离、鉴定及药物敏感性分析. 中国预防兽医学报, 2020, 42(3): 239-244] |
GUO Y, GUO Q S, ZHOU M, et al. Aeromonas veronii from Macrobrachium rosenbergii: Isolation and identification. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(36): 137-143 [郭莹, 郭青松, 周淼, 等. 罗氏沼虾维氏气单胞菌的分离鉴定. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(36): 137-143 DOI:10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb20200100027] |
HAN Z R, SUN J F, JIANG B Y, et al. Concurrent infections of Aeromonas veronii and Vibrio cholerae in koi carp (Cyprinus carpio var. koi).. Aquaculture, 2021, 535: 736395 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736395 |
HOLT J G, KRIEG N R, SNEATH P H A, et al. Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology (9th ed). Baltimore: Willians and Wilkins, 1994
|
HU Q, HU R X, JIN Y L, et al. Isolation, identification and pathohistological observation of Aeromonas veronii from Procambarus clarkii. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2020, 44(4): 811-818 [胡骞, 胡瑞雪, 金玉立, 等. 克氏原螯虾源维氏气单胞菌的分离鉴定及组织病理学观察. 水生生物学报, 2020, 44(4): 811-818] |
HUANG A H, ZHANG D Z. The diagnosis and prevention of common diseases of Erythroculter ilishaeformis. Fishery Guide to be Rich, 2010(21): 45-47 [黄爱华, 张大中. 翘嘴红鲌常见疾病的诊断与防治. 渔业致富指南, 2010(21): 45-47] |
JIANG G M, LI J L, LIU L, et al. Isolation and identification of bacterial pathogens from Procambarus clarkii and study on variations in serum immune factors. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2021 [蒋国民, 李金龙, 刘丽, 等. 克氏原螯虾(Procambarus clarkia)细菌性病原分离鉴定及血清免疫因子变化研究. 水产学报, 2021] |
LI F, WU D, GU H R, et al. Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas veronii cause motile Aeromonas septicaemia in the cultured Chinese sucker, Myxocyprinus asiaticus. Aquaculture Research, 2019, 50(5): 1515-1526 |
LI F. Motile Aeromonas septicemia and Clinostomum disease in farmed Chinese sucker, Myxocyprinus asiaticus. Doctoral Dissertation of Southwest University, 2019 [李芳. 胭脂鱼运动型气单胞菌败血症及弯口吸虫病初步研究. 西南大学博士研究生学位论文, 2019]
|
LI Y J, ZHANG B, WANG H. Update of CLSI/NCCLS drug susceptibility standards in 2006 (CLSI/NCCLS M100-S16 replace M100-S15). Jiangxi Journal of Medical Laboratory Sciences, 2006, 24(4): 355-356 [李雅军, 张斌, 王华. 2006年CLSI/NCCLS药敏标准的更新(CLSI/NCCLS M100-S16代替M100-S15). 江西医学检验, 2006, 24(4): 355-356] |
LIU X F, REN Y, ZHANG D F, et al. Detection, genotyping and pathogenicity of virulence genes in Aeromonas species isolated from diseased freshwater fish. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2021, 45(3): 462-471 [刘小芳, 任燕, 张德锋, 等. 鱼源气单胞菌的毒力基因检测、分型及致病力. 水产学报, 2021, 45(3): 462-471] |
LIU Y, YANG R, CHEN Y Y, et al. Isolation, identification of Aeromonas veronii in Acipenser dabryanus and its histological observations. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2018, 49(6): 1235-1241 [刘亚, 杨锐, 陈叶雨, 等. 达氏鲟维氏气单胞菌的分离鉴定及病理组织学观察. 南方农业学报, 2018, 49(6): 1235-1241] |
LONG B, WANG J, HE Y, et al. Isolation, identification and pathogenicity of Aeromonas veronii isolated from Micropterus salmoides. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2016, 36(1): 48-55 [龙波, 王均, 贺扬, 等. 加州鲈源维氏气单胞菌的分离、鉴定及致病性. 中国兽医学报, 2016, 36(1): 48-55] |
MA X L, CHEN R J, WANG F, et al. Determination of bacterial suspension concentration and the scope of application using absorbance method. Journal of Microbiology, 2014, 34(4): 90-92 [马秀玲, 陈蕊君, 王飞, 等. 吸光度法快速确定菌悬液浓度及其适用范围. 微生物学杂志, 2014, 34(4): 90-92] |
MALLIK S K, JOSHI N, SHAHI N, et al. Characterization and pathogenicity of Aeromonas veronii associated with mortality in cage farmed grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (Valenciennes, 1844) from the Central Himalayan region of India. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2020, 113(12): 2063-2076 |
MARTINEZ R, ROCHA J F, BEJARANO D, et al. Identification of SNPs in growth-related genes in Colombian creole cattle. Genetics and Molecular Research, 2016, 15(3): 120-125 |
MARTINO M E, FASOLATO L, MONTEMURRO F, et al. Determination of microbial diversity of Aeromonas strains on the basis of multilocus sequence typing, phenotype, and presence of putative virulence genes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(14): 4986-5000 |
NAWAZ M, KHAN S A, KHAN A A, et al. Detection and characterization of virulence genes and integrons in Aeromonas veronii isolated from catfish. Food Microbiology, 2010, 27(3): 327-331 |
PEI C, SONG H L, ZHU L, et al. Identification of Aeromonas veronii isolated from largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides and histopathological analysis. Aquaculture, 2021, 540: 736707 |
SOLER L, YÁÑEZ M A, CHACON M R, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Aeromonas based on two housekeeping genes. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2004, 54(5): 1511-1519 |
TANCSICS A, BENEDEK T, FARKAS M, et al. Sequence analysis of 16S rRNA, gyrB and catA genes and DNA-DNA hybridization reveal that Rhodococcus jialingiae is a later synonym of Rhodococcus qingshengii. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2014, 64(1): 298-301 |
TIAN J, PENG D, WEN H, et al. A comparative study on protein-sparing effects among juvenile Erythroculter ilishaeformis line, Ancherythroculter nigrocauda line and their hybrid F1 fed diets with different protein to carbohydrate ratios. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2020, 26(4): 993-1006 |
TIAN L, WEN G L, ZHANG S B, et al. Isolation and biological characterization of the pathogenic Aeromonas veronii from Ictalurus punctatus. China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 45(11): 3203-3210 [田浪, 温贵兰, 张升波, 等. 斑点叉尾  源致病性维氏气单胞菌的分离与生物学特性鉴定. 中国畜牧兽医, 2018, 45(11): 3203-3210] 源致病性维氏气单胞菌的分离与生物学特性鉴定. 中国畜牧兽医, 2018, 45(11): 3203-3210] |
WANG X L, WANG K Y, CHEN D F, et al. Isolation and identification of Aeromonas veronii from rainbow trout and histopathology study of the diseased fish. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2016, 38(11): 879-883 [王兴丽, 汪开毓, 陈德芳, 等. 一株虹鳟源维氏气单胞菌的分离鉴定及组织病理学观察. 中国预防兽医学报, 2016, 38(11): 879-883] |
YANG C H. Artificial propagation test of Erythroculter ilishaeformis. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 23(7): 128–129, 175 [杨长宏. 翘嘴红鲌的人工繁殖技术试验. 安徽农学通报, 2017, 23(7): 128–129, 175] |
YANG K M, GUO A M, MA J X, et al. Isolation, identification and antibiotic sensitivity of bacillary enteritis in Perca fluviatilis Linnaeus. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, 39(6): 42-51 [杨昆明, 郭爱民, 马江霞, 等. 河鲈细菌性肠炎致病菌的分离、鉴定及药敏实验. 渔业科学进展, 2018, 39(6): 42-51] |
ZHANG Y P, WU B, FANG C L, et al. The estimation of biological parameters for Culter alburnus in the waterway connecting the Poyang Lake and the Yangtze River. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2015, 36(5): 26-30 [张燕萍, 吴斌, 方春林, 等. 鄱阳湖通江水道翘嘴鲌(Culter alburnus)的生物学参数估算. 渔业科学进展, 2015, 36(5): 26-30] |
ZHU D L, LI A H, WANG J G, et al. The correlation between the distribution pattern of virulence genes and the virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila strains. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2006, 45(1): 82-85 [朱大玲, 李爱华, 汪建国, 等. 嗜水气单胞菌毒力与毒力基因分布的相关性. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 45(1): 82-85] |



