2. 中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所 山东 青岛 266071;
3. 上海海洋大学水产与生命学院 上海 201306
2. Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Qingdao, Shandong 266071, China;
3. College of Fisheries and Life Science, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China
血液是鱼类血液学研究及诊断的重要材料,由于鱼体血液中血小板含量高,极易凝结,因此,抗凝剂在研究过程中起到不可或缺的作用(Gholipourkanani et al, 2018)。鱼类血液会因不同抗凝剂的处理对抗凝效果和后续血液指标检测产生不同的影响,而正确使用抗凝剂会将影响降到最小(Weinert et al, 2015)。柠檬酸盐、乙二胺四乙酸盐、草酸盐和肝素等是目前鱼类血液学研究中通常采用的抗凝剂(Walencik et al, 2007)。鱼类种属多样,血液抗凝剂选择也不尽相同,研究表明,肝素是鲤鱼(Cyprinus carpio)、褐鳟(Salmo trutta)的血液抗凝剂优选(Walencik et al, 2007; Ciepliński et al, 2019);也有研究表明,乙二胺四乙酸盐对褐鳟、白斑狗鱼(Esox lucius)和鲻鱼(Mugil cephalus)血液抗凝效果更佳(Blaxhall et al, 1973; Mulcahy, 2010; Faggio et al, 2014)。张峰等(2006)研究发现,不同浓度的肝素钠、乙二胺四乙酸二钠、柠檬酸钠和草酸钠4种抗凝剂中,1.0~1.5 mg/mL的乙二胺四乙酸二钠对刺参(Stichopus japonicus)体腔细胞的抗凝效果最好,即使长时间作用,仍能使细胞保持伸展状态。Ahmed等(2014)和Sheikh等(2020)认为,肝素钠和乙二胺四乙酸二钾2种抗凝剂中,肝素钠对全唇裂腹鱼(Schizothorax labiatus)和雪鳟(Schizopyge plagiostomus)的血液生理指标、血细胞形态影响最小,推荐其作为首选抗凝剂。因此,抗凝剂对不同鱼类血液抗性效果存在显著种属间差异(Walencik et al, 2007)。
大菱鲆(Scophthalmus maximus)属鲽形目(Pleuronectiformes)、菱鲆科(Scophthalmidae)、菱鲆属(Scophthalmus),是冷水性深海底层鱼类,原产于欧洲,自1992年引进中国以来,经过近30年发展,养殖年产量稳定在5万t左右,占世界养殖大菱鲆产量80%以上,同时,形成较为完善的上下游产业链,成为我国海水鱼类养殖的重要优良品种之一(雷霁霖等, 2012)。国内外在大菱鲆苗种繁育、养殖模式、饲料营养、疾病防控、产品质量安全与加工技术等方面进行了较为系统性的研究(Qiang et al, 2004; 马爱军等, 2003; Pyanov, 2021)。目前,陆基工厂化循环水养殖是大菱鲆主要养殖模式,养殖水体温度和溶解氧是养殖过程中2个重要环境因子,特别是在高密度养殖条件下,保证养殖水体中充足的溶解氧是维持大菱鲆正常生理代谢的关键(吴志昊, 2011; 乔玮, 2014)。低氧环境对大菱鲆生理状态产生显著影响,已有研究表明,低氧环境可导致大菱鲆血液RBC、Hb和Hct显著上调,而不同抗凝剂下血液抗凝效果也会产生显著不同(刘伟东, 2009; Jia et al, 2021),上述研究过程中都涉及到对大菱鲆相关生理生化指标检测,特别是对血液样品采集和检测更是广泛应用,但急性低氧胁迫下使用抗凝剂对大菱鲆血液产生的影响还未可知。刘伟东等(2009)使用乙二胺四乙酸作为抗凝剂,研究了低温条件下大菱鲆保活过程中血液生理生化变化,发现抽血过程中血液较正常状态黏稠,流动性也不如正常状态好。纪利芹(2014)使用肝素钠作为血液抗凝剂,研究了连续降温对大菱鲆血液生理生化指标的影响。目前涉及大菱鲆血液生理生化指标检测的研究中,抗凝剂选择上存在显著不同。本研究通过选用柠檬酸钠、肝素钠、乙二胺四乙酸二钾3种常用抗凝剂,对正常溶解氧和急性低氧胁迫条件下,上述抗凝剂的抗凝效果进行对比分析,以期筛选出急性低氧胁迫条件下大菱鲆血液研究的最适抗凝剂,为急性低氧环境中大菱鲆血液学研究及健康养殖提供技术支撑。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料实验鱼由山东省烟台市经济开发区天源水产有限公司提供,共54尾,体质健康活泼,外观无损伤,平均体质量为(200.21±23.17) g,平均体长为(14.25± 3.75) cm,实验前将全部实验鱼在循环水养殖系统中暂养2周,保持水温范围为(18.0±0.5)℃,水中溶解氧浓度为(8.5±0.5) mg/L,pH为7.6±0.4,NH3-N < 0.1 mg/L,每日饱食投喂商品饲料(海童,潍坊三通生物工程有限公司) 2次,实验前24 h禁食。实验中所用3种一次性负压静脉采血管购于山东鸿海医疗器械有限公司,抗凝管内添加剂浓度分别为肝素钠12~30 IU,柠檬酸钠105~109 mmol/L,乙二胺四乙酸二钾15~22 mg/mL。
1.2 实验方法 1.2.1 实验设计和样品采集实验分为对照组和处理组(急性低氧胁迫),每组设置3个平行,每个平行选用9尾大菱鲆。对照组将所需实验鱼(循环水中暂养)放入含有200 mg/L MS-222的海水溶液中,至深度麻醉后迅速捞起,将含有3种抗凝剂(肝素钠、柠檬酸钠和乙二胺四乙酸二钾)的一次性负压静脉采血管连接一次性静脉采血针从大菱鲆尾静脉处抽取5 mL静脉血后,将采血管静置。处理组则将实验鱼放入预先充入氮气实验桶中溶解氧含量为(1.2± 0.3) mg/L,实验期间使用溶氧仪(AZ8603型台湾衡欣)实时监测水体溶解氧变化,维持2 h后进行麻醉采血,采血方法同对照组。
1.2.2 凝血观察与血涂片制作自血液注入采血管内开始计时,将采血管静置6 h和12 h后,观察采血管内血液凝结程度,记录管内血液凝结物比例。血涂片的制作采用姬姆萨染色法,姬姆萨原液购于北京索莱宝科技有限公司(G1015),使用方法参照说明书。血涂片制作时,先将载玻片清洗干净,用移液枪取5 µL血液滴在载玻片一侧,将盖玻片一端接触血液,匀速推出,晾干后,甲醇固定10~15 min,再放入充满染色液的染色缸中着色15~30 min,着色完毕取出载玻片用蒸馏水洗净后晾干,显微镜下观察血细胞形态。
1.2.3 血液生理生化指标测定将血液样本分为2份,置于1.5 mL离心管中,1份在4℃、3500 r/min条件下离心10 min,取上清液,保存于–80℃,用于检测血浆葡萄糖和皮质醇浓度,另1份于4℃冰箱保存,使用迈瑞全自动血液细胞分析仪(BC-2800 vet)检测血液红细胞数目(1012/L)、白细胞数目(109/L)、血红蛋白含量(g/L)和红细胞积压(%)。血浆皮质醇含量采用放射性同位素免疫法(RIA),试剂盒(KIPI28000)购自北京北方生物技术研究所;血浆葡萄糖含量测定试剂盒(F006-1-1)购于南京建成生物工程研究所,操作步骤参见说明书。
1.3 数据处理实验结果用平均值±标准差(Mean±SD)表示,采用SPSS 18.0软件进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),使用Duncan多重比较分析3种抗凝剂在两种状态下的组间差异,P < 0.05为差异显著。
2 结果与分析 2.1 3种抗凝剂对大菱鲆血液抗凝效果的影响由图 1可见,正常溶解氧状态下乙二胺四乙酸二钾抗凝效果显著,急性低氧胁迫下静置6 h和12 h后,抗凝效果显著,抗凝剂分别为乙二胺四乙酸二钾和肝素钠。
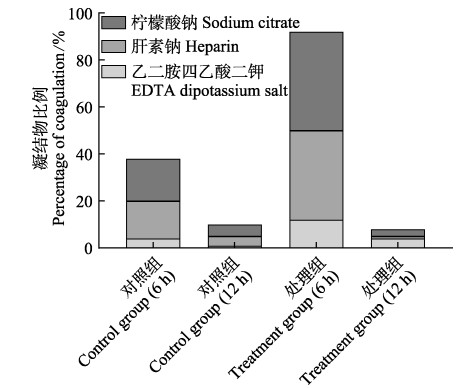
|
图 1 不同作用时间下3种抗凝剂对大菱鲆血液抗凝效果的影响 Fig.1 Effects of three anticoagulants on turbot blood cells during different treatment time |
图 2中为对照组和处理组乙二胺四乙酸二钾、肝素钠、柠檬酸钠3种抗凝剂下细胞显微图。对照组在3种抗凝剂作用下,分别出现嗜碱性粒细胞(图 2A),中性粒细胞和双核细胞(图 2B),嗜碱性粒细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞、单核细胞和淋巴细胞(图 2C)。处理组3种抗凝剂(图 2D、E、F)作用下均出现双核细胞,处理组肝素钠(图 2E)和柠檬酸钠(图 2F)抗凝作用下还分别出现微核细胞和无核红细胞。
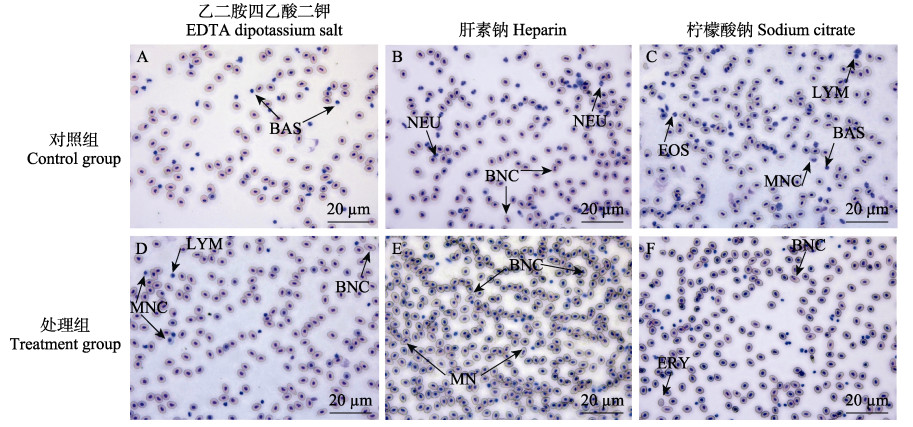
|
图 2 不同抗凝剂下大菱鲆血细胞显微结构 Fig.2 Microstructure of blood cells of turbot under different anticoagulants A:嗜碱性粒细胞(BAS);B:中性粒细胞(NEU);C:嗜酸性粒细胞(EOS),淋巴细胞(LYM),单核细胞(MNC),嗜碱性粒细胞(BAS);D:单核细胞(MNC),淋巴细胞(LYM),双核细胞(BNC);E:双核细胞(BNC),微核细胞(MN);F:双核细胞(BNC),无核细胞(ERY)。 A: Basophil (BAS); B: Neutrophils (NEU); C: Eosinophils (EOS), Lymphocytes (LYM), Monocytes (MNC), Basophil (BAS); D: Monocytes (MNC), Lymphocytes (LYM), Binucleate cells (BNC); E: Binucleate cells (BNC), Micronucleus cells (MN); F: Binucleate cells (BNC), Erythroplastid (ERY). |
急性低氧胁迫处理后,3种抗凝剂作用下大菱鲆血液白细胞数目均显著增多(图 3A) (P < 0.05),肝素钠和乙二胺四乙酸二钾抗凝作用下,大菱鲆血液红细胞数目(图 3B)和血红蛋白含量显著增加(图 3D),但柠檬酸钠抗凝作用下大菱鲆红细胞数目和血红蛋白含量显著降低(P < 0.05)。处理组中3种抗凝剂作用下大菱鲆红细胞积压变化均不显著(图 3C) (P > 0.05)。
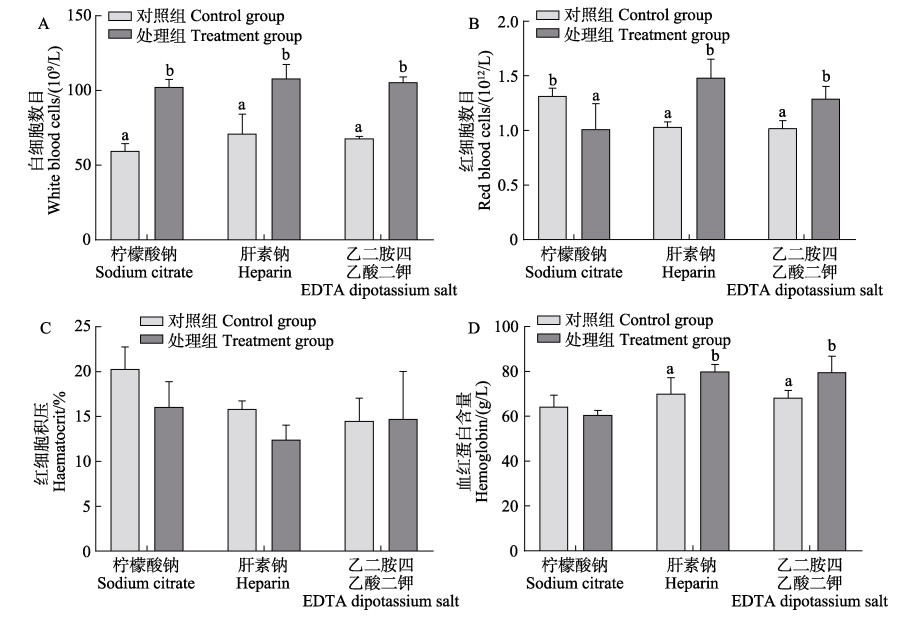
|
图 3 3种抗凝剂对急性低氧胁迫下大菱鲆白细胞数目、红细胞数目、红细胞积压和血红蛋白含量的影响 Fig.3 Effects of three anticoagulants on white blood cell numbers, red blood cell numbers, hematocrit and hemoglobin content under acute hypoxia stress in turbot 不同字母表示组间差异显著,P < 0.05。下同。 Different letters indicate significant differences, P < 0.05. The same as below. |
急性低氧胁迫处理后大菱鲆血浆葡萄糖浓度均显著增加(图 4A) (P < 0.05),但肝素钠抗凝作用下,葡萄糖浓度显著低于柠檬酸钠和乙二胺四乙酸二钾(P < 0.05)。同时,大菱鲆血浆皮质醇浓度也出现类似变化趋势,急性低氧胁迫处理后,其浓度均显著增加,肝素钠抗凝作用下,皮质醇浓度显著低于柠檬酸钠和乙二胺四乙酸二钾(图 4B) (P < 0.05)。
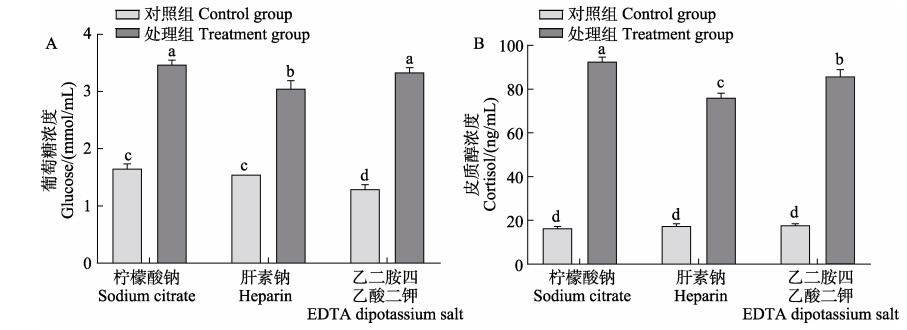
|
图 4 3种抗凝剂对急性低氧胁迫下大菱鲆血浆葡萄糖和皮质醇浓度的影响 Fig.4 Effects of three anticoagulants on turbot plasma glucose and cortisol content under acute hypoxia stress |
鱼类血液采集经抗凝剂作用后可分离出血浆,用于后续指标检测。其中,肝素钠主要是通过结合血浆中的抗凝蛋白阻止血液凝固,而柠檬酸钠和乙二胺四乙酸二钾能抑制血小板聚集和螯合Ca2+形成不易解离但可溶解的络合物,从而减少血液中Ca2+浓度,阻止血液凝固(Faggio et al, 2014)。刘凯等(2017)研究发现,肝素钠、柠檬酸钠、草酸钾和乙二胺四乙酸二钾均可延长鲫鱼(Carassius auratus)外周血的凝固时间。本研究中,柠檬酸钠和肝素钠在短时间内抗凝效果不显著,可能是柠檬酸钠与大菱鲆血液中Ca2+存在特异性结合,而肝素钠可能无法与大菱鲆血浆中的抗凝蛋白结合,从而不能减轻血液凝固现象,这种现象在鲻鱼、刺参中也有类似报道(张峰等, 2006; Faggio et al, 2014)。
目前,鱼类血细胞涂片制作是通过尾静脉采血后加入抗凝剂,抗凝剂可抑制血小板聚集,选用正确的抗凝剂对血细胞形态影响较小(曹文芝等, 2014)。周雪莹等(2007)研究表明,大菱鲆血细胞分为红细胞、淋巴细胞、单核细胞、嗜中性粒细胞和血栓细胞5种类型,未发现嗜酸性和嗜碱性粒细胞。本研究中,对照组柠檬酸钠抗凝作用下出现嗜酸性和嗜碱性粒细胞,乙二胺四乙酸二钾抗凝剂下未出现嗜酸性粒细胞,这与上述大菱鲆血细胞类型研究相悖。吴志昊等(2011)研究表明,高氧可导致大菱鲆出现核异常现象,极低氧则因大菱鲆在较短时间内死亡,无法观察到核异常情况出现。核异常现象包括核质外凸、核质内凹、双核等。此外,制药工厂及医院排放的污水、银和铜的氧化物毒性等不利因素也会导致尖齿胡鲶(Clarias gariepinus)出现核异常细胞(Alimba et al, 2017、2019; Ogunsuyi et al, 2019)。在本研究中,对照组肝素钠抗凝作用下血涂片中出现双核细胞,可能是肝素钠作为一种不利因子参与大菱鲆血液抗凝。急性低氧胁迫处理后,乙二胺四乙酸二钾、肝素钠和柠檬酸钠抗凝剂下均观察到双核血细胞,其中,肝素钠和柠檬酸钠抗凝剂下还分别出现微核和无核血细胞。
血液白细胞是鱼类机体细胞免疫和体液免疫的主要组成部分,主要功能是保护机体免受内外因素的侵害(常志成等, 2018);红细胞是鱼类血液中最多的细胞,同哺乳动物类似,主要功能就是运输O2和CO2 (高泽霞等, 2008);血红蛋白的主要功能是储存和运输O2 (王跃群等, 1998)。影响全血黏度的因子为红细胞压积和血红蛋白(Bao et al, 2018)。因此,上述血液指标可以反映鱼类在不同状况下的生理状态,也经常作为评价鱼类生理状态的重要血液学参数(Ahmed et al, 2019)。所以,本研究将正常和低氧胁迫条件下抗凝剂对大菱鲆血液指标的影响进行对比分析发现,低氧胁迫条件下白细胞数目均显著增高(P < 0.05),在吉富罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus)、花鲈(Lateolabrax maculatus)幼鱼中均有发现(陈德举等, 2019; 常志成等, 2018)。低氧胁迫条件下,肝素钠、乙二胺四乙酸二钾抗凝剂作用下大菱鲆红细胞数目显著增多(P < 0.05),在暗纹东方鲀(Takifugu fasciatus)、鲫鱼幼鱼、西伯利亚鲟(Acipenser baerii)中均有研究(李欣茹, 2018; 王晓雯等, 2016; 张曦等, 2011)。张国松(2017)研究表明,在低氧条件下,鱼类会通过增加红细胞数目从而增加血红蛋白含量来提高携氧能力,使机体应对低氧环境下的应激反应。但在本研究中,柠檬酸钠抗凝作用下红细胞数目和血红蛋白含量显著降低(P < 0.05),这可能是由于柠檬酸钠会导致红细胞出现溶血,从而造成红细胞减少(李双安等, 2005)。研究表明,乙二胺四乙酸二钾和肝素对褐鳟、横口裂腹鱼(Schizopyge plagiostomus)、全唇裂腹鱼(Schizothorax labiatus)血红蛋白含量无影响(Ciepliński et al, 2019; Sheikh et al, 2020; Ahmed et al, 2014),与对照组结果相似。上述报道中,乙二胺四乙酸二钾与肝素钠相比,横口裂腹鱼、全唇裂腹鱼血液红细胞数目较低,但在本研究中,二者红细胞数目无显著差异。研究发现,乙二胺四乙酸和肝素会使横口裂腹鱼、波斯鲟(Persian sturgeon)血液红细胞积压较高(Sheikh et al, 2020; Gholipourkanani et al, 2018)。本研究表明,柠檬酸钠与乙二胺四乙酸二钾相比红细胞积压显著升高(P < 0.05),这可能与柠檬酸钠会导致红细胞肿胀有关(Faggio et al, 2014),上述报道与本研究结果不一致。
鱼类血液中的葡萄糖主要为机体提供能量,以确保各组织器官的正常运行。葡萄糖浓度会因环境因素应激而发生改变,军曹鱼(Rachycentron canadum)经急性低氧胁迫后,血浆葡萄糖浓度明显升高(黄建盛等, 2019)。在本研究中,急性低氧胁迫处理后,葡萄糖浓度显著增高(P < 0.05),肝素钠与其他2种抗凝剂相比,葡萄糖浓度显著降低(P < 0.05)。研究表明,血液离体后,常温下血液中的葡萄糖会被分解代谢,从而导致葡萄糖含量降低(代胜奇, 2012)。鱼类的应激反应类似于高等脊椎动物,快速释放儿茶酚胺,随后释放皮质醇(Clauss et al, 2008)。皮质醇为一种稳定的应激激素,在低氧条件下,刺参的皮质醇浓度显著增加(周晓梦等, 2018)。Vijayan等(1997)研究表明,皮质醇浓度会随葡萄糖浓度的增加而增加。本研究中,急性低氧胁迫处理后,肝素钠抗凝剂作用下皮质醇含量与其他2种抗凝剂相比显著降低(P < 0.05),同上述结果描述一致。
综上,本研究发现,体质量为(200.21±23.17) g的大菱鲆在乙二胺四乙酸二钾、肝素钠和柠檬酸钠3种抗凝剂作用下,正常溶解氧状态下乙二胺四乙酸二钾抗凝效果显著,急性低氧胁迫下静置6 h和12 h后,抗凝效果显著的抗凝剂分别为为乙二胺四乙酸二钾和肝素钠。肝素钠抗凝剂下出现双核血细胞,柠檬酸钠和乙二胺四乙酸二钾抗凝剂下分别出现嗜酸性、嗜碱性粒细胞和嗜碱性粒细胞。急性低氧胁迫处理后,肝素钠、柠檬酸钠抗凝剂下出现微核和无核血细胞,同时,肝素钠抗凝作用下葡萄糖和皮质醇浓度显著低于柠檬酸钠和乙二胺四乙酸二钾。此外,柠檬酸钠在急性低氧条件下红细胞数目和血红蛋白含量显著降低。综上,乙二胺四乙酸二钾可作为急性低氧胁迫条件下大菱鲆血液学分析的首选抗凝剂。
AHMED I, MAQBOOL A. Effects of sodium-heparin and dipotassium EDTA on the haematological parameters and blood cell morphology of freshwater fish Schizothorax labiatus (McClelland, 1842). Journal of Ecophysiology and Occupational Health, 2014, 14(3): 121-126 |
AHMED I, SHEIKH Z A. Hematological and serum biochemical parameters of five freshwater snow trout fish species from river Jhelum of Kashmir Himalaya, India. Comparative Clinical Pathology, 2019, 28(3): 771-782 DOI:10.1007/s00580-019-02909-y |
ALIMBA C G, ADEKOYA K O, SOYINKA O O. Exposure to effluent from pharmaceutical industry induced cytogenotoxicity, hematological and histopathological alterations in Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). EXCLI Journal, 2019, 18: 63-78 |
ALIMBA C G, AJIBOYE R D, FAGBENRO O S. Dietary ascorbic acid reduced micronucleus and nuclear abnormalities in Clarias gariepinus (Burchell 1822) exposed to hospital effluent. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 2017, 43(5): 1325-1335 DOI:10.1007/s10695-017-0375-y |
BAO J W, QIANG J, TAO Y F, et al. Responses of blood biochemistry, fatty acid composition and expression of microRNAs to heat stress in genetically improved farmed tilapia. Journal of Thermal Biology, 2018, 73: 91-97 DOI:10.1016/j.jtherbio.2018.02.007 |
BLAXHALL P C, DAISLEY K W. Routine haematological methods for use with fish blood. Journal of Fish Biology, 1973, 5(6): 771-781 DOI:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1973.tb04510.x |
CAO W Z, LIU Y, LIANG B, et al. Development of haemocytes in peripheral blood and hematopoietic organs of zebra fish, Danio rerio. Fisheries Science, 2014, 33(7): 403-409 [曹文芝, 刘云, 梁冰, 等. 斑马鱼外周血液及造血器官血细胞发生的观察. 水产科学, 2014, 33(7): 403-409 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2014.07.001] |
CHANG Z C, WEN H S, ZHANG M Z, et al. Effects of dissolved oxygen levels on oxidative stress response and energy utilization of juvenile Chinese sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) and associate physiological mechanisms. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science), 2018, 48(7): 20-28 [常志成, 温海深, 张美昭, 等. 溶解氧水平对花鲈幼鱼氧化应激与能量利用的影响及生理机制. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 48(7): 20-28 DOI:10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20170296] |
CHEN D J, QIANG J, TAO Y F, et al. Effects of different dissolved oxygen levels on the growth, blood biochemistry, fatty acid composition and against Streptococcus iniae infection of GIFT juvenile (Oreochromis niloticus). Freshwater Fisheries, 2019, 49(4): 83-89 [陈德举, 强俊, 陶易凡, 等. 不同溶氧水平对吉富罗非鱼幼鱼生长、血液生化、脂肪酸组成及其抗海豚链球菌病的影响. 淡水渔业, 2019, 49(4): 83-89 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2019.04.013] |
CIEPLIŃSKI M, KASPRZAK M, GRANDTKE M, et al. The effect of dipotassium EDTA and lithium heparin on hematologic values of farmed brown trout Salmo trutta (L.) spawners. Aquaculture International, 2019, 27(1): 79-87 DOI:10.1007/s10499-018-0308-5 |
CLAUSS T M, DOVE A D, ARNOLD J E. Hematologic disorders of fish. Veterinary Clinics of North America Exotic Animal Practice, 2008, 11(3): 445-462 DOI:10.1016/j.cvex.2008.03.007 |
DAI S Q. Influence and evaluation of different anticoagulants on the assays for serum glucose. Jilin Medical Journal, 2012, 33(17): 3739-3740 [代胜奇. 不同抗凝剂对血葡萄糖测定的影响及评价. 吉林医学, 2012, 33(17): 3739-3740] |
FAGGIO C, ARFUSO F, PICCIONE G, et al. Effect of three different anticoagulants and storage time on haematological parameters of Mugil cephalus (Linneaus, 1758). Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 2014, 14: 615-621 |
GAO Z X, WANG W M. Research progress of fish peripheral blood erythrocytes. Journal of Hydroecology, 2008, 28(2): 1-3 [高泽霞, 王卫民. 鱼类外周血红细胞研究进展. 水生态学杂志, 2008, 28(2): 1-3] |
GHOLIPOURKANANI H, RANJDOOST M, JAFARYAN H, et al. Comparative study of hematological and blood chemistry of Persian sturgeon (Asipencer persicus) exposed to two common anticoagulants. Journal of the Hellenic Veterinary Medical Society, 2018, 68(2): 225-230 DOI:10.12681/jhvms.15609 |
HUANG J S, LU Z, CHEN G, et al. Acute hypoxia stress on blood biochemical indexes of large-sized juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 41(6): 76-84 [黄建盛, 陆枝, 陈刚, 等. 急性低氧胁迫对军曹鱼大规格幼鱼血液生化指标的影响. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(6): 76-84] |
JI L Q. Effect of continuous cooling on serum physiological, biochemical index and molecular mechanism of adult Scophthalmus maximus L. Master′s Thesis of Ocean University of China, 2014 [纪利芹. 连续降温对大菱鲆血液生理生化指标的影响及分子机制. 中国海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2014]
|
JIA Y D, WANG J W, GAO Y T, et al. Hypoxia tolerance, hematological, and biochemical response in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L). Aquaculture, 2021, 535(3): 736380 |
LEI J L, LIU X F, GUAN C T. Turbot culture in China for two decades: Achievements and prospect. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2012, 33(4): 123-130 [雷霁霖, 刘新富, 关长涛. 中国大菱鲆养殖20年成就和展望–庆祝大菱鲆引进中国20周年. 渔业科学进展, 2012, 33(4): 123-130 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2012.04.016] |
LI S A, LI Y R, GAO M, et al. Effects of different blood cells on plasma coagulation in carp Cyprinus carpio. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 2005, 51(S): 146-510 [李双安, 李玉荣, 高明, 等. 鲤鱼血细胞对血液凝固的影响. 动物学报, 2005, 51(S): 146-510] |
LI X R. Effects of hypoxic stress on energy metabolism, blood indexes and gene expression of Takifugu fasciatus. Master′s Thesis of Nanjing Normal University, 2018 [李欣茹. 低氧胁迫对暗纹东方鲀能量代谢、血液指标及基因表达的影响. 南京师范大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2018]
|
LIU K, XIE N, MA H J, et al. Study on the anticoagulation effect of different anticoagulants on peripheral blood of crucian carp. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(8): 115-116 [刘凯, 谢楠, 马恒甲, 等. 不同抗凝剂对鲫鱼外周血的抗凝效果研究. 安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(8): 115-116] |
LIU W D, XUE C H, YIN B Z, et al. Physiological and biochemical change of Scophthalmus maximus kept alive at low temperature with or without water. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2009, 30(5): 69-74 [刘伟东, 薛长湖, 殷邦忠, 等. 低温下大菱鲆有水和无水保活过程中生理生化变化的研究. 渔业科学进展, 2009, 30(5): 69-74] |
LIU W D. Basic research on keep-alive of tubots (Scophthalmus maximus). Master′s Thesis of Ocean University of China, 2009 [刘伟东. 大菱鲆(Scophthalmus maximus)保活的基础研究. 中国海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2009]
|
MA A J, LEI J L, CHEN S Q, et al. Proceedings on the study of nutrition requirement and feed for turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2003, 34(4): 450-459 [马爱军, 雷霁霖, 陈四清, 等. 大菱鲆营养需求与饲料研究进展. 海洋与湖沼, 2003, 34(4): 450-459] |
MULCAHY M F. Blood values in the pike Esox lucius L. Journal of Fish Biology, 2010, 2(3): 203-209 |
OGUNSUYI O I, FADOJU O M, AKANNI O O, et al. Genetic and systemic toxicity induced by silver and copper oxide nanoparticles, and their mixture in Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(26): 27470-27481 |
PYANOV D. A review of the cultivation potential of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) in the Baltic Sea region: A promising candidate species for marine aquaculture in Russia. IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 689(1): 012040 |
QIANG M, LEI J L, WANG Y G. Biology and critical breeding techniques of turbot, Scophthalmus maximus. Marine Sciences, 2004, 28(3): 1-4 |
QIAO W. Effect of stocking density on adult turbot is growth, physiology and water quality in recirculating aquaculture system. Master′s Thesis of Ocean University of China, 2014 [乔玮. 养殖密度对循环水养殖大菱鲆生长、生理特性及水质的影响研究. 中国海洋大学硕士研究生论文, 2014]
|
SHEIKH Z A, AHMED I. Comparative evaluation of two anticoagulants used for the analysis of haematological, biochemical parameters and blood cell morphology of himalayan snow trout, Schizopyge plagiostomus. Tissue Cell, 2020, 67: 101398 |
VIJAYAN M M, PEREIRA C, GRAU E G, et al. Metabolic responses associated with confinement stress in Tilapia: The role of cortisol. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part C: Comparative Pharmacology and Toxicology, 1997, 116(1): 89-95 |
WALENCIK J, WITESKA M. The effects of anticoagulants on hematological indices and blood cell morphology of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part C: Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2007, 146(3): 331-335 |
WANG X W, ZHU H, HU H X, et al. Effects of hypoxia on physiological status of Siberian sturgeon Acipenser baeri juveniles. Fisheries Science, 2016, 35(5): 459-465 [王晓雯, 朱华, 胡红霞, 等. 低氧胁迫对西伯利亚鲟幼鱼生理状态的影响. 水产科学, 2016, 35(5): 459-465] |
WANG Y Q, LIU S J, WANG G, et al. Comparative hematological studies in Cyprinus carpio Xiangyunnensis and Cyprinus carpio Xiangjiangnensis. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 1998, 21(1): 71-75 [王跃群, 刘少军, 王刚, 等. 湘云鲤和湘江野鲤血液指标的比较. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 1998, 21(1): 71-75] |
WEINERT N C, VOLPATO J, COSTA Á, et al. Hematology of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) subjected to anesthesia and anticoagulation protocols. Semina Ciências Agrárias, 2015, 36(6): 4237-4250 |
WU Z H, YOU F, WANG Y F, et al. The effect of hypoxia and hyperoxia on nucleus anomaly, SOD, CAT activities and MDA content in juvenile turbot Scophthalmus maximus. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2011, 20(6): 808-813 [吴志昊, 尤锋, 王英芳, 等. 低氧和高氧对大菱鲆幼鱼红细胞核异常及氧化抗氧化平衡的影响. 上海海洋大学学报, 2011, 20(6): 808-813] |
WU Z H. Physiology effect of Fe (Ⅱ) and DO on juvenile turbot Scophthalmus maximus. Doctoral Dissertation of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011 [吴志昊. Fe(Ⅱ)、DO含量对养殖大菱鲆幼鱼生理学性状影响的研究. 中国科学院研究生院博士学位论文, 2011]
|
ZHANG F, SONG Z D, LIU H W, et al. Effects of four anticoagulants on anticoagulation of coelomocytes in sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 2006, 21(1): 87-89 [张峰, 宋志东, 刘洪伟, 等. 4种抗凝剂对刺参体腔细胞的抗凝效果. 大连海洋大学学报, 2006, 21(1): 87-89] |
ZHANG G S. Molecular mechanism of response to hypoxia stress in Pelteobagrus vachelli. Doctoral Dissertation of Nanjing Normal University, 2017 [张国松. 瓦氏黄颡鱼(Pelteobagrus vachelli)应对低氧胁迫的分子机制研究. 南京师范大学博士研究生学位论文, 2017]
|
ZHANG X, FU S J, PENG J L, et al. The effect of acute hypoxia on blood parameters of juvenile crucian carp. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science), 2011, 28(4): 19-22 [张曦, 付世建, 彭姜岚, 等. 急性低氧对鲫鱼幼鱼血液基础指标的影响. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 28(4): 19-22] |
ZHOU X M, ZHANG X M, LI W T. Effect of high temperature and hypoxia on median lethal time and physiological function in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus of two sizes. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2018, 25(1): 60-73 [周晓梦, 张秀梅, 李文涛. 高温和低氧胁迫对两种规格刺参半致死时间及生理机能的影响. 中国水产科学, 2018, 25(1): 60-73] |
ZHOU X Y, CUI L B, LIU D, et al. Studies on blood cell morphology and relevant physiological indices of Scophthanalmus maximus L. Ludong University Journal (Natural Science), 2007, 23(4): 366-370 [周雪莹, 崔龙波, 刘冬, 等. 养殖大菱鲆血细胞形态和相关生理指标的测定. 鲁东大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 23(4): 366-370] |



