2. 山东师范大学 山东 济南 250014
2. Shandong Normal University, Jinan, Shandong 250014, China
干扰素调节因子(interferon regulatory factors, irfs)是一类转录因子家族,能够调控干扰素(interferon, IFN)的转录过程。在机体受到感染时,irfs能结合IFN启动子并诱导调节IFN而得名(Veals et al, 1992, Zhang et al, 2012)。在哺乳动物irfs家族已发现9个irf成员(irf1~irf9)(Barnes et al, 2002; Nguyen et al, 1997),随后在鸟类和鱼类中鉴定出irf10基因。通过解析鱼类基因组发现,鱼类中存在11个irf家族成员,其中,irf11为硬骨鱼类所特有(Stein et al, 2007)。所有的IRFs N端都有一个由115个氨基酸组成的结构域,称为DNA结合域(DNA binding domain, DBD)。DBD含有5个色氨酸重复序列,其中3个重复序列可识别干扰素刺激反应元件(IFN-sensitive response elements, ISRE)正调控序列区域DNA的GAAA和AANNNGAA序列(Escalante et al, 1998)。IRFs通过C末端的IAD结构域(IRF-associated domain),与其他转录因子相互作用来激活信号通路,实现其转录调控作用(Taniguchi et al, 2001)。IRFs是模式识别受体信号转导、促炎症因子与趋化因子转录及激活免疫应答反应过程中的重要分子,不仅参与IFN的信号通路,还在防御病毒与应激反应的过程中具有重要作用(Honda et al, 2006, Tanaka et al, 2000)。干扰素调节因子7 (irf7)是诱导Ⅰ型干扰素表达的关键因子,于1997年首次报道(Zhang et al, 1997),其最重要功能是诱导IFNα/β产生,从而诱导机体抗病毒功能(Fitzgerald et al, 2003)。目前,已在斑马鱼(Danio rerio) (Xiang et al, 2010)、鳜鱼(Siniperca chuatsi) (Sun et al, 2007)、牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus) (Hu et al, 2010)等鱼类中被鉴定,并揭示了鱼类irf7在先天免疫中的作用,。
斑石鲷(Oplegnathus punctatus)具有外形美观、肉质细嫩、生长速度快、成活率高等优点,深受消费者喜爱。2014年以来,随着斑石鲷人工繁育和养殖取得成功,斑石鲷已成为我国名贵海水养殖品种之一。但随着国内水产养殖业集约化水平不断提高,病毒病成为制约斑石鲷健康养殖的主要问题。本研究通过克隆斑石鲷irf7基因,分析在虹彩病毒(Iridovirus)刺激后各免疫组织的表达模式,有助于研究斑石鲷抗病毒及细菌免疫应答中的功能,旨在为阐述斑石鲷免疫机制提供理论基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料本实验所用斑石鲷购自山东莱州明波水产有限公司,体重为(150±15) g,健康无病。实验前在水箱中暂养1周,水温维持在25℃左右。每日投喂饲料,保持溶氧充足,每日用清洁海水换水1次。
1.2 样品处理和采集 1.2.1 健康斑石鲷组织样品采集随机选取4条健康斑石鲷,经MS-222麻醉后抽取血液,解剖后取肝、脾、肾、头肾、心脏、肠、鳃、脑、皮肤和肌肉等组织,将所取组织迅速置于液氮中,随后转移至–80℃冰箱中保存,用于提取总RNA。
1.2.2 虹彩病毒感染斑石鲷及组织样品采集选取15条健康斑石鲷用于斑石鲷虹彩病毒感染实验。本实验所用斑石鲷虹彩病毒由华南农业大学秦启伟教授提供。将斑石鲷虹彩病毒液用PBS稀释至1×109 copies/mL。将斑石鲷麻醉后腹腔注射病毒液,每尾注射100 µL。分别在0、1、4、7和10 d共5个时间点取样,每个时间点取3条鱼,每条鱼取肝脏、脾脏、肾脏3个组织。将组织立即放入液氮中冷冻,并随后放入–80℃冰箱,用于后续提取RNA。
1.2.3 poly I: C刺激斑石鲷脑细胞系将单层培养、生长状态良好的斑石鲷脑细胞系铺到12孔板上,24 h后细胞覆盖率达到90%左右。将12孔板中的旧培养基吸弃,使用无菌PBS (0.01 mmol/L, pH 7.2)洗涤3次。使用无菌PBS (0.01 mmol/L, pH 7.2)配制poly I: C (上海源叶生物科技有限公司)母液,浓度为25 mg/ml。按照低、中、高浓度(50、100、200 µg/mL),配制含有poly I: C的L-15培养基(北京索莱宝宝科技有限公司),加入培养板中,每个浓度3个重复。对照组加入与高浓度组相同体积的PBS。在刺激6 h后,吸出培养基,加入Trizol (TaKaRa)收集细胞,保存于–80℃冰箱待用。细胞实验重复3次。
1.3 总RNA提取与cDNA合成使用Trizol对所有健康以及感染后样品提取总RNA,提取后使用Pultton核酸浓度仪测定浓度及A260 nm/ A280 nm比值,使用琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测所提RNA的质量。利用合格的RNA,使用PrimeScript™ Ⅱ 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis试剂盒(TaKaRa)合成cDNA。
1.4 Opirf7基因ORF区验证根据测序结果,获得Opirf7基因的ORF区序列,使用Primer 5.0软件设计引物Opirf7-F/Opirf7-R,使用不同组织混合cDNA模板进行PCR扩增。总体系为15 µL:PCR Mix (TaKaRa) 7.5 µL,Opirf7-F 1 µL,Opirf7-R 1 µL,cDNA模板1 µL,ddH2O 4.5 µL。PCR扩增程序:95.8℃预变性5 min;95℃变性30 s,59℃退火30 s,72℃延伸30 s,35个循环;72℃延伸7 min,4℃保存。
将PCR扩增产物进行凝胶电泳检测,条带大小与目的片段相一致。将正确目的片段切下,使用胶回收试剂盒(诺唯赞)对目的片段进行回收纯化。将纯化后的产物连接到T载体中,转化Trans1-T1感受态细胞(全式金)中,冰浴30 min后42℃热激30 s,置于冰上2 min后加入500 µL无抗LB培养基,37℃摇床摇菌1 h,取200 µL菌液于超净工作台中涂板,培养过夜。次日,挑取单克隆并进行菌液PCR验证。将条带大小正确的样品送青岛擎科生物技术有限公司测序。
1.5 生物信息学分析及构建系统发育树使用DNAstar软件的Editseq分析Opirf7 ORF区,预测氨基酸序列,并推测分子量和等电点。使用网站(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/)预测其信号肽,使用网站(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/)进行跨膜结构分析。使用SMART(http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/)进行结构域预测。通过DNAMAN 8软件进行氨基酸同源比对。检索不同生物irf7序列(表 2),导入MEGA X软件进行氨基酸多重比对,采用邻接法(neighbor-joining, NJ)构建进化树。
1.6 Opirf7实时荧光定量检测使用实时荧光定量(qRT-PCR)检测斑石鲷健康个体、虹彩病毒感染及poly I: C感染细胞后Opirf7的表达模式。根据测序所获得的ORF序列设计Opirf7和内参基因的引物(表 1)。实验步骤参照TaKaRa荧光定量试剂盒,采用两步法,反应程序:95℃预变性30 s, 95℃ 5 s, 58℃ 30 s,共40个循环;60℃ 30 s,72℃ 30s,溶解曲线温度55~95℃。以β-actin为内参进行qRT-PCR分析。利用2–ΔΔCt方法计算Opirf7基因的相对表达量。实验数据采用SPSS软件进行方差分析(one-way ANOVA),设定P值< 0.05时为差异显著。使用GraphPad Prism作图。
|
|
表 1 本研究中所使用的引物 Tab.1 Primers used in this study |
以斑石鲷组织cDNA为模板,获得斑石鲷Opirf7基因ORF区全长为1332 bp,编码443个氨基酸。通过氨基酸序列分析,预测其分子量为50.5 kDa,等电点为5.546 (图 1)。通过蛋白结构域预测,发现其含有IRF家族保守结构域,包括DNA结合域(DNA binding domain, DBD)、IRF相关结构域(IRF-associated domain, IAD)和SRD结构域(Serine-rich domain, SRD) (图 2)。其中,DBD位于多肽N末端,由第4~112个氨基酸组成,该区域包含4个色氨酸重复区域;IAD位于多肽中间部分(第222~395个氨基酸);丝氨酸富含区位于多肽末端。

|
图 1 Opirf7核苷酸序列及推导的氨基酸序列 Fig.1 Opirf7 nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acid sequence 氨基酸序列在核苷酸序列下方,起始密码子“ATG”用红色标明,终止密码子“TAG”用星号标明。DBD结构域用灰色阴影标识,IAD结构域用黄色阴影标识。 The amino acid sequence is below the nucleotide sequence, the start codon "ATG" is marked with red, and the stop codon "TAG" is marked with an asterisk. The IRF domain is indicated by gray shading, and the IRF3 domain is indicated by yellow shading. |

|
图 2 斑石鲷Opirf7蛋白结构域预测 Fig.2 Protein domain prediction of Opirf7 in O. punctatus |
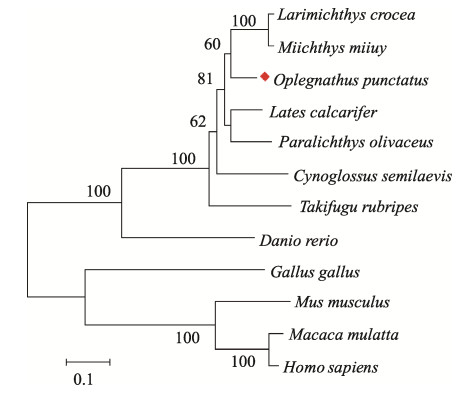
经BLAST比对发现,斑石鲷irf7氨基酸序列与其他硬骨鱼类的irf7具有较高同源性。斑石鲷irf7与尖吻鲈(Lates calcarifer)的相似性为82.92%,与大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea)、牙鲆、半滑舌鳎(Cynoglossus semilaevis)的相似性分别为81.99%、79.95%、73.74%,与哺乳动物小鼠(Mus musculus)和人(Homo sapiens)的相似性较低,分别为31.00%和30.00%(图 3)。

|
图 3 斑石鲷与其他物种irf7氨基酸序列多重比对 Fig.3 Multiple alignment of the deduced amino acids of irf7 among O. punctatus and other different species 物种间氨基酸相似度100%、75%以上和50%以上分别用黑色、玫红色和蓝色阴影表示。 The color scheme for amino acid similarity among species: black, 100%; rock red, > 75%; blue, > 50%. |
通过MEGA X软件采用Neighbor-joining法构建了Opirf7的系统进化树(图 4)。发育分析显示,斑石鲷Opirf7与其他硬骨鱼类的irf7聚为一支,鸡(Gallus gallus)、小鼠猕猴(Macaca mulatta)和人类的irf7聚为另一大支。斑石鲷Opirf7在进化上与大黄鱼、
|
图 4 斑石鲷Opirf7与其他物种系统进化分析 Fig.4 Phylogenetic analysis of Opirf7 and other species |
Opirf7在健康斑石鲷个体11个组织中均有表达。其中,在肝脏中表达量最高,在皮肤、肌肉、脑、肠等组织中表达量较低,在头肾中表达量最低(图 5)。
|
|
表 2 本研究用于序列比对和进化树分析的irf7蛋白信息 Tab.2 The species information used in the irf7 for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree analysis in this study |

|
图 5 Opirf7基因在健康斑石鲷组织中的相对表达量 Fig.5 The relative expression of the Opirf7 gene in different tissues of O. punctatus 不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。 Different letters indicate the significant difference (P < 0.05). |
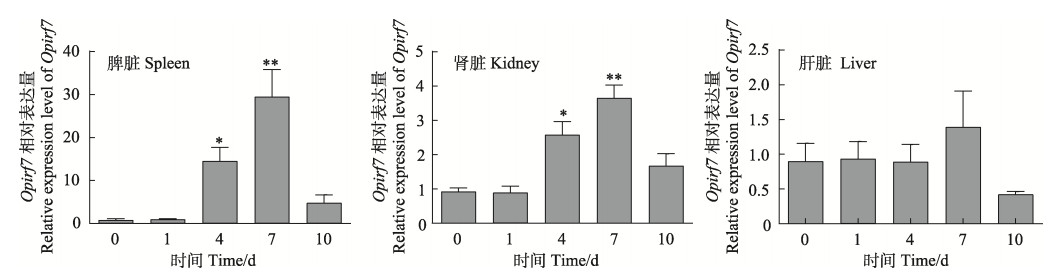
虹彩病毒刺激斑石鲷后,Opirf7的表达量在脾脏、肾脏中显著上调。脾脏中,Opirf7的表达量在第4天升高至对照组的15倍,在第7天表达量最高,约为对照组的37倍,在第10天表达量降低。在肾脏中,第4天升高2.5倍,第7天时达到表达峰值,为对照组的4倍。在肝脏组织中,Opirf7表达量稍有变化,但差异并不显著。
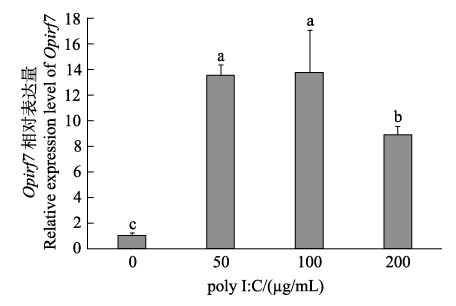
2.5 poly I: C刺激斑石鲷脑细胞系Opirf7的表达在病毒类似物poly I: C感染的斑石鲷脑细胞系中,irf7的表达呈现先升高后降低的趋势,在50 µg/mL poly I: C (低浓度)刺激时表达量显著升高(13~14倍),在100 µg/mL poly I: C (中浓度)刺激时表达量也显著升高(14~17倍),而在200 µg/mL poly I: C (高浓度)刺激时,irf7的表达量仍显著高于对照组(8~9倍),推测200 μg/mL浓度较高,对细胞造成一定的损伤,因而表达水平有所下降。
3 讨论本研究通过PCR技术获得了斑石鲷Opirf7基因CDS区序列,并对其序列进行分析。预测其编码蛋白的分子量为50.5 kDa,无信号肽及跨膜区。氨基酸序列比对结果发现,斑石鲷Opirf7基因编码的多肽具有典型的DNA结合域(DBD)、干扰素相关区(IAD)和丝氨酸富含区(SRD)。在哺乳动物中,所有IRF家族成员中的DBD通常包含一个5-色氨酸重复序列,而在硬骨鱼类的DBD则只有4个间隔的色氨酸重复序列。这些间隔的色氨酸重复序列通过形成螺旋–转角–螺旋结构与靶基因启动子中的IFN刺激反应元件(ISRE)和IRF调节元件(IRFE)共有序列结合(Escalante et al, 1998; Paun et al, 2007)。IAD是除IRF-1和IRF-2以外的所有IRF家族成员均具有的结构域。在哺乳动物中,IAD可通过形成IRF同源/异源二聚体与其他转录因子结合以激活干扰素(Eroshkin et al, 1999)。SRD仅存在于IRF-3/5/7中(Holland et al, 2009; Xu et al, 2010),与病毒诱导的磷酸化有关。通过氨基酸多重序列比对发现,斑石鲷Opirf7与哺乳类、鸟类及其他硬骨鱼类irf7的结构域特征高度保守。Opirf7与硬骨鱼类相似性较高,与尖吻鲈的相似性为82.92%,而与哺乳类、鸟类相似性较低。系统进化结果表明,斑石鲷与硬骨鱼类的irf7聚为一大支,而与鸟类、哺乳类进化关系较远。
|
图 6 斑石鲷感染虹彩病毒后Opirf7基因在免疫组织中的实时定量表达分析 Fig.6 Real-time quantitative expression analysis of Opirf7 gene in immune tissues of O. punctatus infected with Iridovirus * 表示差异显著(P < 0.05),** 表示差异极显著(P < 0.01)。 * indicates significant difference (P < 0.05), ** indicates highly significant difference (P < 0.01). |
|
图 7 斑石鲷脑细胞系感染polyI: C后Opirf7基因表达分析 Fig.7 Real-time quantitative expression analysis of Opirf7 gene in brain cell line infected with poly I: C |
在鱼类中,irf7基因在各物种中表达量最高的组织并不完全一致。在尖吻鲈中,相对表达量较高组织为鳃和后肠(Krishnan et al, 2019);在斜带石斑鱼(Epinephelus coioides)的脾和肠中表达量较高(Cui et al, 2011);在赤眼鳟(Squaliobarbus curriculus)的脾中表达量最高,而在肝脏中表达量最低(Zhao et al, 2017)。本研究中,对健康斑石鲷组织中Opirf7的相对表达量分析发现,Opirf7在肝脏中的表达量远高于其他组织,说明肝脏可能在抗病毒免疫防御中也发挥一定的作用。
研究表明,irf7在硬骨鱼类中参与细菌、病毒感染后的免疫应答。欧洲鳗鲡(Anguilla anguilla)感染迟缓爱德华氏菌(Edwardsiella tarda)后,其免疫组织中的irf7表达量显著上调;迟缓爱德华氏菌或细胞肿大虹彩病毒(Megalocytivirus)刺激都能导致半滑舌鳎各免疫组织irf7表达量显著上调(Zhang et al, 2015)。在本研究中,虹彩病毒感染斑石鲷后,脾脏、肾脏组织中Opirf7的表达量显著上调,总体趋势表现为先升高至峰值,随后逐渐恢复至正常水平。在细胞水平中也发现了相似的表达趋势,说明Opirf7对病毒刺激的响应非常迅速,有可能参与斑石鲷抗病毒感染机制。
综上所述,本研究通过对Opirf7基因克隆、序列特征及表达模式分析,初步表明Opirf7参与斑石鲷免疫应答过程,为进一步研究Opirf7在斑石鲷抗病免疫中的作用机制奠定了基础。
BARNES B, LUBYOVA B, PITHA P M. On the role of IRF in host defense. Journal of Interferon and Cytokine Research, 2002, 22(1): 59-71 DOI:10.1089/107999002753452665 |
CUI H, YANG Y, WEI J, et al. Identification and functional characterization of an interferon regulatory factor 7-like (IRF7-like) gene from orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 2011, 35(6): 672-684 DOI:10.1016/j.dci.2011.01.021 |
EROSHKIN A, MUSHEGIAN A. Conserved transactivation domain shared by interferon regulatory factors and Smad morphogens. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 1999, 77(5): 403-405 DOI:10.1007/s001090050369 |
ESCALANTE C R, YIE J, THANOS D, AGGARWAL A K. Structure of IRF-1 with bound DNA reveals determinants of interferon regulation. Nature, 1998, 391(6662): 103-106 DOI:10.1038/34224 |
FITZGERALD K A, ROWE D C, BARNES B J, et al. LPS-TLR4 signaling to IRF-3/7 and NF-κB involves the toll adapters TRAM and TRIF. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 2003, 198(7): 1043-1055 DOI:10.1084/jem.20031023 |
HOLLAND J W, BIRD S, WILLIAMSON B, et al. Molecular characterization of IRF3 and IRF7 in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss: Functional analysis and transcriptional modulation. Molecular Immunology, 2009, 46(2): 269-285 |
HONDA K, TANIGUCHI T. IRFs: Master regulators of signalling by Toll-like receptors and cytosolic pattern- recognition receptors. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2006, 6(9): 644-658 DOI:10.1038/nri1900 |
HU G, YIN X, XIA J, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of interferon regulatory factor 7 (irf7) in Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2010, 29(6): 963-971 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2010.08.002 |
KRISHNAN R, KURCHETI P P, MUSHTAQ Z, et al. Interferon-regulatory factors, IRF3 and IRF7 in Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer: Characterization, ontogeny and transcriptional modulation upon challenge with nervous necrosis virus. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2019, 89: 468-476 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2019.03.073 |
NGUYEN H, HISCOTT J, PITHA P M. The growing family of interferon regulatory factors. Cytokine and Growth Factor Reviews, 1997, 8(4): 293-312 DOI:10.1016/S1359-6101(97)00019-1 |
PAUN A, PITHA P M. The IRF family, revisited. Biochimie, 2007, 89(6/7): 744-753 |
STEIN C, CACCAMO M, LAIRD G, et al. Conservation and divergence of gene families encoding components of innate immune response systems in zebrafish. Genome Biology, 2007, 8(11): R251 DOI:10.1186/gb-2007-8-11-r251 |
SUN B J, CHANG M X, SONG Y, et al. Gene structure and transcription of IRF-1 and irf7 in the mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 2007, 116(1/2): 26-36 |
TANAKA N, TANIGUCHI T. The interferon regulatory factors and oncogenesis. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 2000, 10(2): 73-81 DOI:10.1006/scbi.2000.0310 |
TANIGUCHI T, OGASAWARA K, TAKAOKA A, et al. IRF family of transcription factors as regulators of host defense. Annual Review of Immunology, 2001, 19: 623-655 DOI:10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.623 |
VEALS S A, SCHINDLER C, LEONARD D, et al. Subunit of an alpha-interferon-responsive transcription factor is related to interferon regulatory factor and Myb families of DNA-binding proteins. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 1992, 12(8): 3315-3324 |
XIANG Z, DONG C, QI L, et al. Characteristics of the interferon regulatory factor pairs zfIRF5/7 and their stimulation expression by ISKNV Infection in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 2010, 34(12): 1263-1273 DOI:10.1016/j.dci.2010.07.003 |
XU Q Q, CHANG M X, XIAO F S, et al. The gene and virus-induced expression of IRF-5 in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 2010, 134(3/4): 269-278 |
ZHANG J, LI Y X, HU Y H. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of eleven interferon regulatory factors in half-smooth tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 44(1): 272-282 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2015.02.033 |
ZHANG L, PAGANO J S. IRF-7, a new interferon regulatory factor associated with Epstein-Barr virus latency. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 1997, 17(10): 5748-5757 DOI:10.1128/MCB.17.10.5748 |
ZHANG R, KANG C, PENG L, et al. Regulation of T helper cell differentiation by interferon regulatory factor family members. Immunologic Research, 2012, 54(1/2/3): 169-176 |
ZHAO X, WANG R, LI Y, et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of interferon regulatory factor 7 of the barbel chub, Squaliobarbus curriculus. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2017, 69: 185-194 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2017.08.024 |



