2. 中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所 青岛海洋科学与技术试点国家实验室海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程功能实验室 山东 青岛 266071;
3. 山东师范大学 山东 济南 250014
2. Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), Qingdao 266071, China;
3. Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
Rho相关GTP结合蛋白Rho6 (Rho-related GTP-binding protein Rho6),又名Rnd1,为分子量只有20~30 kDa的小分子蛋白。作为小G蛋白家族的非典型成员,Rnd分子与GTP结合后,不能水解GTP,以持续与GTP结合的模式发挥生物功能(Nobes et al, 1998; Shutes et al, 2004; Dong et al, 2019; Wennerberg et al, 2005)。Rho-GTP酶家族基因参与许多重要的细胞过程,如细胞骨架构建、囊泡运输、细胞黏附、细胞增殖、分化、吞噬、凋亡和NADPH氧化酶的激活等,并在抵御病原体感染过程中起到一定作用(Kwon et al, 2004; Xiu et al, 2019)。
鱼类中Rnd1研究很少,仅有斑马鱼(Danio rerio) Rnd1等基因序列的报道(Salas-Vidal et al, 2005)。与Rnd1同属Rho-GTP酶超家族的Rac亚家族基因在鱼类免疫抗病中的研究较多。Rac1和Rac2基因陆续在草鱼(Ctenopharyngodon idella)、大菱鲆(Scophthalmus maximus)、斑马鱼、大黄鱼(Pseudosciaena crocea)、半滑舌鳎(Cynoglossus semilaevis)等鱼类中被鉴定出来。细菌感染后Rac1和Rac2在主要免疫组织中的表达量有明显升高,说明Rho-GTP酶家族参与了鱼体的免疫防御过程(Han et al, 2011; Hu et al, 2016; Jia et al, 2009; Liu et al, 2017; Salas-Vidal et al, 2005; Xiu et al, 2019)。
牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)是一种重要的海水养殖鱼类,广泛养殖于中国、日本和韩国等亚洲国家。近年来,随着牙鲆养殖业的不断壮大,各类疾病频繁暴发,从苗种到养成阶段均有病害发生,造成了巨大的经济损失。其中,迟缓爱德华氏菌(Edwardsiella tarda)感染引起的腹水病是牙鲆的主要病害。
本研究以牙鲆rnd1基因为对象,首次对Pornd1基因进行克隆鉴定和抗病性状关联分析。分析该基因在牙鲆健康组织中的表达量以及在迟缓爱德华氏菌感染后的表达变化,通过检测Pornd1基因在抗病家系和易感家系中的表达水平,分析该基因与抗病力的关系。进一步通过抑菌活性实验,检测PoRnd1重组蛋白的抑菌活性,从而为系统解析牙鲆抗病性状遗传机制提供基础资料。
1 材料与方法 1.1 正常牙鲆及细菌感染实验在中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所海阳实验基地(下称海阳基地)随机选取6尾健康牙鲆,麻醉后取肝、脾、肾、肠、鳃、肌肉、皮肤、心脏、脑及血液等10种组织,放入冻存管中,立即投入液氮中速冻,随后转移到–80 ℃冰箱,用于RNA的提取。
根据本实验室前期建立的方法(Wang et al, 2017),对牙鲆进行迟缓爱德华氏菌感染,感染后分别取5个时间点(0、6、12、24和48 h)的牙鲆各6条。以PBS组为对照,在相同时间点各取6条。麻醉后解剖取肝脏、脾脏和肾脏等组织,分别放入装有RNA保存液的1.5 mL离心管中保存,随后转移到–80 ℃冰箱,用于RNA的提取。
1.2 抗病家系及易感家系筛选及样品采集2014年9—10月在海阳基地实验隔离区进行的牙鲆感染实验,筛选牙鲆抗病家系F1421和易感家系F1441,2个家系的感染存活率分别为47.06%和11.11% (孙何军等, 2015)。2015年筛选牙鲆抗病家系F1501和易感家系F1544,2个家系的感染存活率分别为80.72%和8.54% (郑卫卫等, 2016)。每年在感染实验后,采集抗病家系和易感家系未经感染的鱼苗各5条,麻醉后取肝脏组织,在液氮中速冻后放入–80 ℃冰箱中保存,用于提取RNA。同时,采集鱼苗的鳍条,放入酒精中保存,用于提取DNA。
1.3 DNA、RNA提取及cDNA第一链合成DNA提取使用海洋动物组织基因组提取试剂盒(天根生化科技有限公司, 北京)进行,实验方法参照说明书。RNA提取使用Trizol法(TaKaRa, 大连),实验方法参照说明书。使用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳观察各组织RNA条带,检测其完整度,使用DNA/Proteins Analyzer P100测定RNA浓度及相关比值,选择质量较好、条带完整的RNA用于后续cDNA的合成。
使用TaKaRa Prime Script RT reagent kit with gDNA eraser合成cDNA第一链,首先去除基因组DNA,PCR体系:gDNA clean reagent 1 μL,5×gDNA clean buffer 2 μL,总RNA 1 mg,RNase-free水补足10 μL体系;反应条件42 ℃ 2 min。再进行反转录反应,PCR体系:上一步反应液10 μL,Evo M-MLVRTase enzyme mix 1 μL,RT primer mix 1 μL,5×RTase reaction buffer mixⅠ4 μL,RNase-free水4 μL;反应条件37 ℃ 15 min,85 ℃ 5 s。合成的cDNA使用β-actin内参基因引物进行PCR验证质量(表 1),PCR体系:cDNA 1 μL,TaKaRa Ex Taq 10 μL,正反引物各1 μL,ddH2O 7 μL;反应34个循环:94 ℃ 30 s,58 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 30 s;72 ℃ 5 min。经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,观察条带,选择质量好的cDNA用于后续基因克隆及荧光定量实验。
|
|
表 1 本实验所用到的引物 Tab.1 Primers used in this study |
使用DNAstar 7.0和DNAman软件进行序列合成,得到Pornd1基因cDNA序列,NCBI ORF Finder (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/)确定其开放阅读框并预测氨基酸序列,从NCBI上检索不同生物的Rnd和Rac家族蛋白序列,使用BLAST (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)进行同源性比对,使用BioEdit软件进行氨基酸序列比对,运用MEGA 7软件、采用邻位相接法(NJ法)构建氨基酸系统发育树,并设置bootstrap重复1 000次,计算各分支的置信度。
1.5 Pornd1基因中抗病相关SNP位点的定位和多态性分析实验室前期对连续多年建立的牙鲆家系进行迟缓爱德华氏菌感染实验,挑选感染后的931个个体进行全基因组重测序,开展了GWAS分析,得到一个定位在Pornd1基因上的SNP位点(Lu et al, 2020)。本实验设计引物,利用PCR方法扩增SNP位点所在区域,进行测序验证。利用2014年牙鲆抗病家系和易感家系DNA样品,进行SNP位点验证和SNP位点与抗病力的关联性分析。
1.6 荧光定量PCR 1.6.1 正常牙鲆组织中Pornd1的表达模式根据Pornd1基因的ORF序列,合成qRT-PCR引物(表 1),以牙鲆β-Actin基因为内参基因,使用TaKaRa TB Green® Premix Ex Taq™,采用染料法在ABI 7500 fast荧光定量PCR仪上荧光定量实验,测定Pornd1基因在脾、肝、肾、头肾、肠、心、鳃、皮肤、肌肉和血液中的相对表达量,PCR体系:cDNA 1 μL,TB Green Premix Ex Taq 10 μL,Rox reference DyeⅡ 0.4 μL,正反引物各0.8 μL,ddH2O 7 μL;反应程序:95 ℃ 30 s;95 ℃ 5 s,60 ℃ 34 s,40个循环。每个组织设置5个生物重复,采用2–ΔΔCt方法计算Pornd1的相对表达量,利用Origin软件绘制各组织相对表达量图,利用SPSS软件Duncan法进行显著性检验。
1.6.2 迟缓爱德华氏菌感染后Pornd1的表达模式以牙鲆β-Actin为内参基因,采用1.6.1的方法测定Pornd1基因在PBS注射、迟缓爱德华氏菌感染处理后0、6、12、24、48 h肝、脾和肾中的相对表达量,反应体系同1.6.1。每组设置5个生物重复,采用2–ΔΔCt方法计算Pornd1的相对表达量,利用Origin软件绘制不同时间点相对表达量对比图,使用SPSS软件独立样本T检验进行显著性分析。
1.6.3 Pornd1在2个家系肝脏中的表达以牙鲆β-Actin为内参基因,使用1.6.1的方法测定Pornd1在抗病及易感家系肝中的表达量,反应体系同1.6.1。每组设置6个生物重复,采用2–ΔΔCt方法计算Pornd1的相对表达量,绘制2个家系相对表达量对比图,使用SPSS软件独立样本T检验进行显著性分析。
1.7 Pornd1基因原核表达及抑菌活性实验 1.7.1 重组质粒构建及蛋白表达对Pornd1基因编码的蛋白进行结构分析,设计引物,以牙鲆肝脏cDNA为模板扩增rnd1编码区全长序列696 bp,将PCR产物纯化后连入pET-T1载体,送擎科生物(青岛)测序,将测序正确的阳性质粒(pET-T1-rnd1)进行扩增和纯化,双酶切后连入同样酶切的pET-his载体。将pET-his-rnd1转化大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli) Rosetta2 (DE3),挑取单克隆测序。将阳性单克隆扩大培养,在菌液OD600 nm=0.6时加入终浓度为1 mmol/L的IPTG,18 ℃振荡培养18 h,诱导蛋白表达。确定培养温度和培养时间后,使用200 mL菌液进行蛋白大量表达和纯化,采用镍柱法纯化重组蛋白,测定蛋白浓度为1 mg/mL。使用SDS-PAGE检测蛋白表达。
1.7.2 PoRnd1重组蛋白的体外抑菌实验采用牛津杯法,检测PoRnd1重组蛋白对金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)、大肠杆菌、迟缓爱德华氏菌、哈维氏弧菌(Vibrio harveyi)的抑菌活性。取1 mL菌液加入到200 mL LB液体培养基中进行活化,37 ℃ 180 r/min恒温振荡培养6 h。取2 mL菌液用PBS缓冲液洗涤,使用分光光度计测定菌液OD600 nm值。将菌液稀释1 000倍,取100 μL均匀涂布到TSB固体培养基上。用无菌镊子将灭菌干燥后的牛津杯置于平板表面,轻轻按压固定。吸取100 μL PoRnd1蛋白(0.5 mg/mL)加入牛津杯中,阴性对照组为100 μL PBS;迟缓爱德华氏菌、哈维氏弧菌组阳性对照组为100 μL氨苄青霉素(1.0 mg/mL);金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌组阳性对照组为50 μL卡那霉素(1.0 mg/mL)。恒温培养箱37 ℃培养12 h,观察细菌生长状况及有无抑菌圈出现。
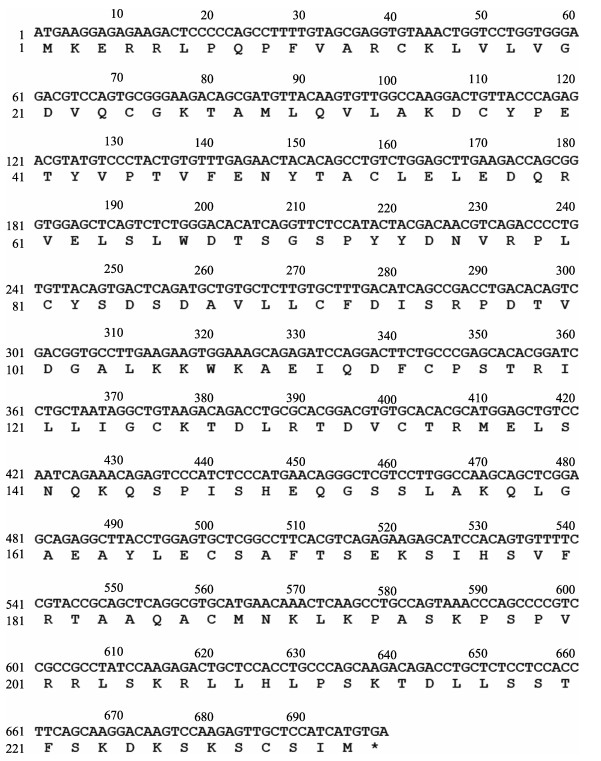
2 结果 2.1 Pornd1基因序列Pornd1 cDNA的开放阅读框为699 bp,编码232个氨基酸(图 1)。预测蛋白分子量为26 kDa。根据结构分析,牙鲆Rnd1蛋白和人类(Homo sapiens) Rnd1具有相似的结构域,包括GTP/Mg2+结合位点(22~28位、70~73位、125~126位和168~170位);Switch Ⅰ region和Switch Ⅱ region (48~50位、69~70位和86~87位),以及G1 box、G2 box、G3 box、G4 box和G5 box位点(20~27位、45~47位、67~70位、125~128位和168~170位)(图 2)。
|
图 1 Pornd1 cDNA序列和推测的氨基酸序列 Fig.1 Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of Pornd1 |
|
图 2 人类Rnd1蛋白(A)和预测的牙鲆Rnd1蛋白(B)的结构图 Fig.2 Protein structure of human rnd1 (A) and Pornd1 protein (B) |
使用NCBI BLAST (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)对Pornd1基因编码的氨基酸序列与其他物种rnd1基因编码的氨基酸序列进行同源性比较,结果显示,其与大西洋庸鲽(Hippoglossus hippoglossus)同源性最高,达到了98.28%。使用ClustalX对牙鲆Rnd1氨基酸序列与其他物种进行多重比对,可见Rnd1氨基酸序列在不同物种间的保守性非常高,尤其是在N端90个氨基酸的相似度达到90%以上(图 3)。

|
图 3 牙鲆与其他物种Rnd1氨基酸序列多重比对 Fig.3 Multiple alignment of the deduced amino acids of Rnd1 among P. olivaceus and other different species 黑色区域表示氨基酸位点同源性为100%,粉色区域表示氨基酸位点同源性至少为75%,蓝色区域表示氨基酸位点同源性至少为50%。 The black region indicates that the homology of amino acid locus is 100%. The pink region indicates that the homology of amino acid locus is at least 75%. The blue region indicates that the homology of amino acid locus is at least 50%. |
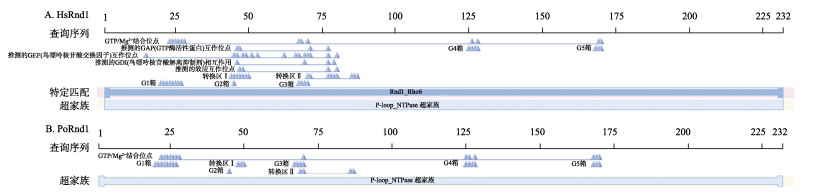
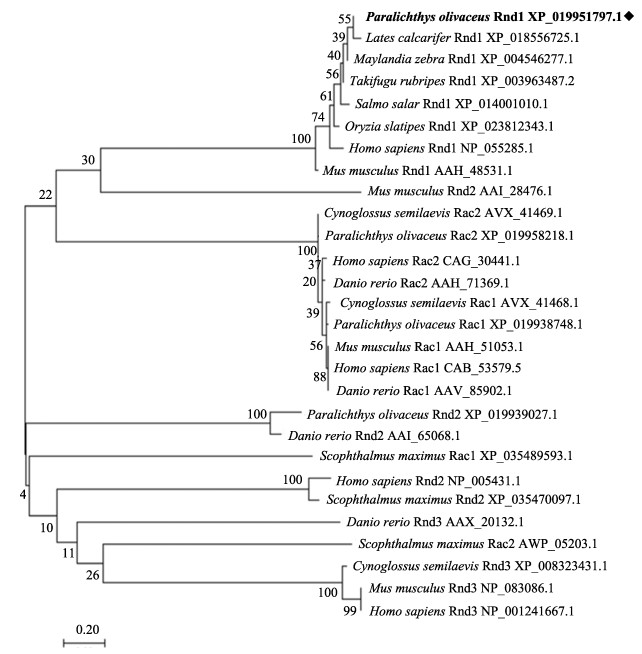
利用ClustalX多对个物种Rnd1及同家族Rnd2、Rnd3、Rac1、Rac2氨基酸序列进行比对,利用MEGA7软件进行系统进化分析,并构建NJ系统进化树,结果显示,牙鲆Rnd1氨基酸序列与其他生物Rnd1聚为一簇,Rnd2、Rnd3和Rac分别单独成为一簇(图 4)。
|
图 4 Rnd1氨基酸序列NJ系统进化树 Fig.4 Phylogenetic tree based on Rnd1 amino acid sequences by neighbor-joining method |
与牙鲆抗迟缓爱德华氏菌相关的位点位于牙鲆14号染色体的4 575 720 bp处,该位点的信息为C/T,在所检测的抗病家系和易感家系中,等位基因T和等位基因C出现的频率存在显著差异(P < 0.05),抗病家系中等位基因T出现的频率(freqT=0.92)高于易感家系(freqT=0.20)。利用牙鲆基因组进行SNP位点的精细定位,该位点定位在Pornd1基因的4 157 bp处(Lu et al, 2020)。经过基因结构分析和序列比对发现,Pornd1基因包含5个外显子,分别为123、87、108、136和245 bp;4个内含子分别为647、3 700、201和126 bp,SNP位点位于内含子2上(图 5)。在SNP位点上、下游设计引物,以牙鲆2014年抗病和易感家系DNA为模板,进行了SNP位点区域扩增,确定了SNP位点的位于第2内含子上。

|
图 5 Pornd1基因中抗病相关SNP位点的定位 Fig.5 Location of SNPs related to disease resistance in Pornd1 黑色区域表示外显子区域,白色区域表示内含子区域。 The black region represents the expressed region, and the white region represents the intron region. |
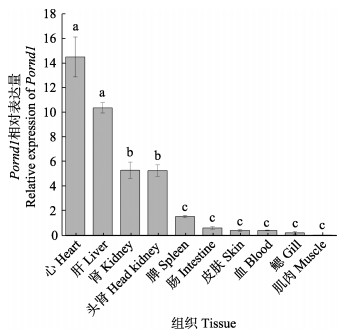
利用qRT-PCR测定Pornd1基因在不同组织中的相对表达量,分析组织表达特异性,发现Pornd1在牙鲆的心脏表达最高,在肝、肾和头肾中表达量较高,在皮肤、血液、鳃和肌肉中表达量较低(图 6)。
|
图 6 Pornd1在健康牙鲆组织中的相对表达量 Fig.6 Relative expression of Pornd1 in normal tissues of P. olivaceus 以脾中Pornd1的表达量为标准值1;数值用平均值±标准差表示(n=5);相同字母的表达水平无显著性差异(P < 0.05)。 Take the expression level of Pornd1 in the spleen as 1; Values are indicated as Mean±SD (n=5). The expression levels with the same letter are not significantly different (P < 0.05). |
利用qRT-PCR法,检测迟缓爱德华氏菌感染前和感染后不同时间,Pornd1基因在肝、肾和脾中的相对表达量。在肝、肾和脾中,PBS对照组与0 h组表达量无明显差异。细菌感染6 h后Pornd1基因的表达量显著低于0 h组(P < 0.05),之后表达量逐渐升高;在肾和脾中细菌感染48 h后Pornd1表达量极显著高于6 h、12 h时(P < 0.01) (图 7)。
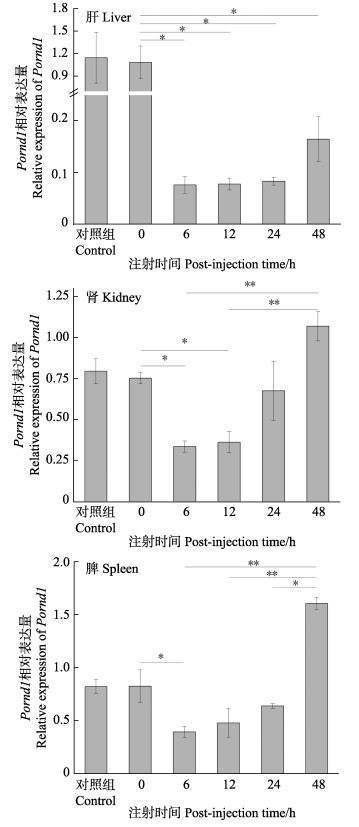
|
图 7 牙鲆感染迟缓爱德华氏菌后肝、肾和脾中Pornd1相对表达量 Fig.7 Relative expression of Pornd in liver, kidney, spleen of P. olivaceus at different time points after E. tarda infection 以各组织对照组Pornd1的表达量为标准值1;数值用平均数±标准差来表示(n=5);*为显著差异(P < 0.05);**为极显著差异(P < 0.01)。 Take the expression level of Pornd1 in PBS as 1.Values are indicated as Mean±SD (n=5). Significant difference between different groups was indicated with the asterisks ("*"P < 0.05; "**"P < 0.01)。 |
利用qRT-PCR法,分别检测2014和2015年牙鲆抗病家系和易感家系肝中Pornd1基因的表达,分析Pornd1基因在2014和2015年抗病和易感家系肝组织中的表达水平,发现该基因在抗病家系中的表达量均显著高于易感家系(P < 0.05),在抗病家系中的表达量是易感家系的3~5倍(图 8)。
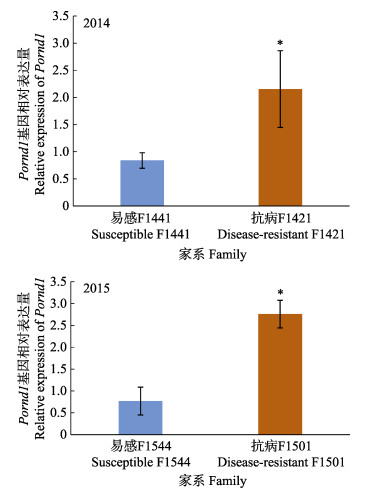
|
图 8 Pornd1在2014年和2015年抗病和易感家系肝脏中的表达差异 Fig.8 Difference of Pornd1 expression in liver between resistant and susceptible families of year 2014 and 2015 数值用平均数±标准差来表示(n=6);*为显著差异(P < 0.05)。 Values are indicated as Mean±SD (n=6); Significant difference was indicated with the asterisks (*P < 0.05). |
经1 mmol/L的IPTG诱导,在18 ℃振荡培养18 h后,对培养基上清液和菌体进行蛋白检测,结果表明,重组蛋白在上清液中表达。重组蛋白大小为32 kDa,与预期大小一致。根据重组蛋白中的His标签,进行Ni柱纯化,得到PoRnd1重组蛋白,纯化后PoRnd1重组蛋白调整浓度为1 mg/mL,分别用4、2和1 μL纯化PoRnd1蛋白溶液进行SDS-PAGE电泳检测,在32 kDa的位置有明显的蛋白条带(图 9)。
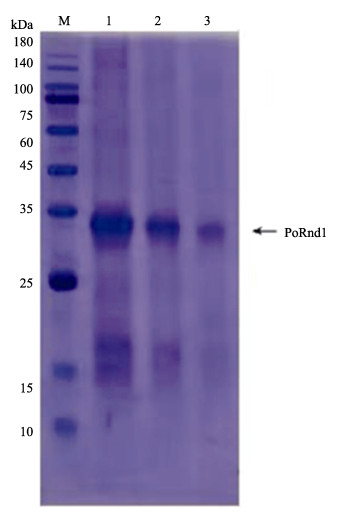
|
图 9 PoRnd1重组蛋白电泳 Fig.9 SDS-PAGE analysis of PoRnd1 protein M:蛋白分子marker;1~3分别为4、2和1 μL纯化PoRnd1蛋白溶液。 M: Protein marker; 1~3: Purified PoRnd1 protein (4 μL, 2 μL and 1 μL). |
观察牛津杯法重组蛋白体外抑菌实验中细菌生长状况,发现PoRnd1重组蛋白对培养的金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、迟缓爱德华氏菌、哈维氏弧菌均有一定的抑菌活性(图 10)。

|
图 10 牛津杯法PoRnd1蛋白抑菌实验
Fig.10 Bacteriostatic experiment of Rnd1 protein of Oxford cup French flounder
A:金黄色葡萄球菌;B:大肠杆菌;C:迟缓爱德华氏菌;D:哈维氏弧菌 R:Rnd1蛋白;P:PBS阴性对照;K:卡那霉素阳性对照;A:氨苄青霉素阳性对照 A: S. aureus; B: E. coli; C: E. tarda; D: V. harveyi R: PoRnd1 protein; P: PBS negative control; K: Positive control (kanamycin); A: Positive control (ampicillin) |
Rho-GTP酶属于小G蛋白超家族,在哺乳动物中已发现大约20种,分为5个亚家族,包括Rho亚家族、Rac亚家族、Cdc42亚家族、Rnd亚家族和Rho BTB亚家族。Rho-GTP酶家族成员均具有GTP结合功能区,按作用形式可分为典型成员与非典型成员(Bustelo et al, 2007; Bustelo, 2018)。典型成员如Cdc42、Rac和Rho,在与GTP结合的活性状态和与GDP结合的非活性状态之间循环(Boettner et al, 2002);非典型成员如Rnd,主要以持续GTP结合状态存在(Nobes et al, 1998)。与人类Rnd1蛋白结构类似,PoRnd1也具有GTP结合结构域、Switch Ⅰ region、Switch Ⅱ region和多个G box,推测与人类Rnd1具有类似的功能。
在哺乳动物的研究中证明,Rnd1参与细胞形态、神经细胞成熟、基因转录、细胞迁移、细胞凋亡、肿瘤发生迁移。Nobes等(1998)研究发现,Rnd1蛋白通过结合p190RhoGAP、Syx和生长因子受体结合蛋白7 (Grb7)等分子,降低RhoA活性,抑制应力纤维形成,降低肌动球蛋白的收缩性,影响细胞形态(Nobes et al, 1998; Wennerberg et al, 2003; Goh et al, 2010; Mouly et al, 2019)。在神经细胞中,Rnd1与plexinsA1、B1作用,激发其与下游蛋白R-Ras的活性,导致生长锥塌陷,影响轴突延伸(Oinuma et al, 2004; Mouly et al, 2019)。Rnd1抑制p53蛋白表达,影响p53蛋白与BCL-2/BCL-xl结合,诱导神经细胞凋亡(董慧敏等, 2019)。Rnd1蛋白表达水平受表皮生长因子(EGF)、转录生长因子β (TGFβ)、活化T细胞核因子(NFATc1)等多种生长因子及雌二醇、孕酮等激素诱导调控(Kim et al, 2005; Suehiro et al, 2014; Okada et al, 2015; Mouly et al, 2019)。目前在抗病免疫方面的研究尚未见报道。
哺乳动物rnd1基因表达具有组织特异性(Mouly et al, 2019),rnd1在胎儿脑、肺、肝和肾中表达,在成人脑组织和肝中高表达。大鼠(Rattus norvegicus) rnd1主要在大脑、肝脏和睾丸中表达,在肌肉中不表达(Nobes et al, 1998)。脾、肾均是鱼类重要的免疫器官(Zapata et al, 2006)。在本研究中,qRT-PCR结果显示,Pornd1在心、肝和肾中表达量显著高于其他组织(P < 0.05),在肌肉中表达极低,因此,推测其可能在免疫抗病方面有一定作用。
在鱼类中,对Rnd1同属Rho-GTP酶的Rac亚家族的研究较多。Xiu等(2019)利用哈维氏弧菌感染半滑舌鳎发现,感染后免疫组织中rac1和rac2基因表达量显著上调,说明这,2个基因在鱼类先天免疫中发挥作用。Jia等(2009)发现,哈维氏弧菌感染后大菱鲆肝脏中rac1基因表达量上调;Hu等(2016)发现嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)感染后,草鱼的肝和脾中rac1基因表达量上调,并证明其在草鱼先天免疫中发挥作用。本研究对牙鲆进行迟缓爱德华氏菌感染实验,分析其肝、肾和脾感染后不同时间点Pornd1的相对表达量,发现感染后细菌侵袭造成了组织Pornd1表达量先降低,推测可能是细菌侵袭造成组织损伤导致;随时间推移,Pornd1表达量上升,在48 h达到最高值。因此,推测Pornd1可能与抵抗细菌侵袭相关,但其参与免疫反应的作用通路需要进一步研究。
在动物和植物良种选育中,进行分子标记辅助育种是一项十分重要的工作。大量经济性状相关基因的单核苷酸多态性位点陆续被开发出来,但在鱼类中的研究还较少。本研究利用牙鲆抗病家系和易感家系重测序和等位基因频率分析,结合Pornd1基因扩增和测序验证,确定了Pornd1基因上定位一个抗迟缓爱德华氏菌病相关单核苷酸多态性位点,以期能够为提高牙鲆抗病育种和种质资源鉴定提供有效的基因标记。本研究还发现,Pornd1基因在抗病家系肝脏中的表达量显著高于易感家系,而且PoRnd1重组蛋白对迟缓爱德华氏菌等细菌具有明显的抑菌活性,推测PoRnd1蛋白在抗迟缓爱德华氏菌病方面发挥一定作用,但SNP位点对基因表达的影响机制、蛋白与细菌互作的作用机制等问题仍需进一步研究。
4 结论本研究首次克隆了Pornd1基因,发现Rnd1在不同生物中高度保守,发现一个抗病相关SNP位点在其内含子2上。Pornd1基因在牙鲆免疫组织中表达较高,在迟缓爱德华氏菌感染后表达量显著升高,而且在抗病家系肝脏中的表达量显著高于易感家系。进一步从蛋白水平研究发现,PoRnd1重组蛋白对迟缓爱德华氏菌等细菌具有抑菌活性。因此,本研究为阐明Pornd1基因免疫抗病功能提供了研究基础,为开展牙鲆抗病分子育种提供了一个有效标记,并为解析牙鲆抗病性状的遗传机制提供了理论基础。
BOETTNER B, VAN AELST L. The role of Rho GTPases in disease development. Gene, 2002, 286(2): 155-174 DOI:10.1016/S0378-1119(02)00426-2 |
BUSTELO X R, SAUZEAU V, BERENJENO I M. GTP-binding proteins of the Rho/Rac family: Regulation, effectors and functions in vivo. BioEssays, 2007, 29(4): 356-370 DOI:10.1002/bies.20558 |
BUSTELO X R. RHO GTPases in cancer: Known facts, open questions, and therapeutic challenges. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2018, 46(3): 741-760 DOI:10.1042/BST20170531 |
DONG H M, LIU B H, SUN Q, et al. RhoE regulated neurocytes apoptosis in PC12 cells through p53 protein. Stroke and Nervous Diseases, 2019, 26(6): 649–652, 663 [董慧敏, 刘宝辉, 孙前, 等. RND1通过p53蛋白促进PC12细胞凋亡. 卒中与神经疾病, 2019, 26(6): 649–652, 663 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-0478.2019.06.001] |
DONG X, GAO J, ZHANG C Y, et al. Neutrophil membrane-derived nanovesicles alleviate inflammation to protect mouse brain injury from ischemic stroke. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(2): 1272-1283 |
GOH L L, MANSER E, OUCHI T. The RhoA GEF Syx is a target of Rnd3 and regulated via a Raf1-like ubiquitin-related domain. PLoS One, 2010, 5(8): e12409 DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0012409 |
HAN F, WANG X Q, YANG Q L, et al. Characterization of a RacGTPase up-regulated in the large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea immunity. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2011, 30(2): 501-508 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2010.11.020 |
HU M Y, SHEN Y B, XU X Y, et al. Identification, characterization and immunological analysis of Ras related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1) from grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 2016, 54(1): 20-31 DOI:10.1016/j.dci.2015.08.010 |
JIA A R, ZHANG X H. cDNA cloning, characterization, and expression analysis of the Rac1 gene from Scophthalmus maximus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2009, 154(1): 80-84 DOI:10.1016/j.cbpb.2009.05.002 |
KIM Y, HORI M, YASUDA K, et al. Differences in the gestational pattern of mRNA expression of the Rnd family in rat and human myometria. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular and Integrative Physiology, 2005, 142(4): 410-415 DOI:10.1016/j.cbpa.2005.08.028 |
KWON Y S, ANN H S, NABESHIMA T, et al. Selegiline potentiates the effects of EGb 761 in response to ischemic brain injury. Neurochemistry International, 2004, 45(1): 157-170 DOI:10.1016/j.neuint.2003.10.005 |
LIU L, HUANG W W, WANG J H, et al. Anthraquinone derivative exerted hormetic effect on the apoptosis in oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced PC12 cells via ERK and Akt activated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 2017, 262: 1-11 DOI:10.1016/j.cbi.2016.12.001 |
LU S, LIU Y, YU X, et al. Prediction of genomic breeding values based on pre‑selected SNPs using ssGBLUP, WssGBLUP and BayesB for Edwardsiellosis resistance in Japanese flounder. Genetics Selection Evolution, 2020, 52: 49 DOI:10.1186/s12711-020-00566-2 |
MOULY L, GILHODES J, LEMARIÉ A, et al. The RND1 Small GTPase: Main functions and emerging role in oncogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(15): 3612 DOI:10.3390/ijms20153612 |
NOBES C D, LAURITZEN I, MATTEI M G, et al. A new member of the Rho family, Rnd1, promotes disassembly of actin filament structures and loss of cell adhesion. Journal of Cell Biology, 1998, 141(1): 187-197 DOI:10.1083/jcb.141.1.187 |
OINUMA I, ISHIKAWA Y, KATOH H, et al. The semaphorin 4D receptor Plexin-B1 is a GTPase activating protein for R-Ras. Science, 2004, 305(5685): 862-865 DOI:10.1126/science.1097545 |
OKADA T, SINHA S, ESPOSITO I, et al. The Rho GTPase Rnd1 suppresses mammary tumorigenesis and EMT by restraining Ras-MAPK signalling. Nature Cell Biology, 2015, 17(1): 81-94 DOI:10.1038/ncb3082 |
SALAS-VIDAL E, MEIJER A H, CHENG X, et al. Genomic annotation and expression analysis of the zebrafish Rho small GTPase family during development and bacterial infection. Genomics, 2005, 86(1): 25-37 DOI:10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.03.010 |
SUEHIRO J, KANKI Y, MAKIHARA C, et al. Genome-wide approaches reveal functional vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-inducible nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) c1 binding to angiogenesis-related genes in the endothelium. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, 289(42): 29044-29059 DOI:10.1074/jbc.M114.555235 |
SHUTES A, BERZAT A C, COX A D, et al. Atypical mechanism of regulation of the Wrch-1 Rho family small GTPase. Current Biology, 2004, 14(22): 2052-2056 DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2004.11.011 |
SUN H J, CHEN S L, ZHENG W W, et al. Screening for resistance to Edwardsiella tarda in different families of Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2015, 22(6): 1115-1122 [孙何军, 陈松林, 郑卫卫, 等. 抗迟缓爱德华氏菌病牙鲆家系的筛选与分析. 中国水产科学, 2015, 22(6): 1115-1122] |
WANG L, SHAO C W, XU W T, et al. Proteome profiling reveals immune responses in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) infected with Edwardsiella tarda by iTRAQ analysis. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2017, 66: 325-333 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2017.05.022 |
WENNERBERG K, ROSSMAN K L, DER C J. The Ras superfamily at a glance. Journal of Cell Science, 2005, 118(Pt 5): 843-846 |
WENNERBERG K, FORGET M A, ELLERBROEK S M, et al. Rnd proteins function as RhoA antagonists by activating p190 RhoGAP. Current Biology, 2003, 13(13): 1106-1115 DOI:10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00418-4 |
XIU Y J, ZHANG H X, WANG S Y, et al. cDNA cloning, characterization, and expression analysis of the Rac1 and Rac2 genes from Cynoglossus semilaevis. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2019, 84: 998-1006 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2018.11.006 |
ZAPATA A, DIEZ B, CEJALVO T, et al. Ontogeny of the immune system of fish. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2006, 20(2): 126-136 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2004.09.005 |
ZHENG W W, CHEN S L, LI Z Y, et al. Analyzing of heritability and breeding value of disease resistance for Edwardsiella tarda in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2016, 24(8): 1181-1189 [郑卫卫, 陈松林, 李泽宇, 等. 牙鲆抗迟缓爱德华氏菌性状的遗传力和育种值分析. 农业生物技术学报, 2016, 24(8): 1181-1189] |



