2. 中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所青岛海洋科学与技术试点国家实验室深蓝渔业工程联合实验室 山东 青岛 266071
2. Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Joint Laboratory for Deep Blue Fishery Engineering, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), Qingdao 266071, China
胰岛素样生长因子(insulin-like growth factor, IGF)在脊椎动物的生长发育和代谢调节中起着重要作用,主要包括IGFs (IGF-1、IGF-2和IGF-3)、细胞表面受体(IGF-1R和IGF-2R)和IGF结合蛋白(IGFBP)等关键因子。IGFBP是一个由6个成员组成的蛋白质家族(IGFBP1~6) (Hwa et al, 1999; Duan et al, 2005),对IGF有高度的亲和力。IGFBP通过与IGF及其受体之间的相互作用影响IGF的分布、稳定性、生物学活性以及在体循环中的流通、转运,从而实现对脊椎动物生长的调控。目前,在哺乳动物中已发现有6种类型的igfbp,每一种通常都有一个等位基因形式,而在斑马鱼(Danio rerio)、大西洋鲑(Salmo salar)等硬骨鱼中每个igfbp则有2个或4个亚型,它们虽然在结构上高度同源,但各有不同的结构功能和组织表达特性(Allard et al, 2018)。研究显示,肝脏是硬骨鱼类igfbp主要的合成场所(钱焜等, 2014)。igfbp-1被认为是硬骨鱼生长、繁殖和发育的重要调控因子(Wood et al, 2005a; Garcia de la Serrana et al, 2018),如在大西洋鲑幼鱼中,igfbp-1可以与皮质醇相互作用来调控生长(Breves et al, 2020)。在斜带石斑鱼(Epinephelus coioides)体外孵育的原代肝细胞中,igfbp-1可通过与胰岛素的互作进而实现对细胞代谢和生长的调控(Yang et al, 2019)。在硬骨鱼中,igfbp-2具有广泛组织表达特性,对igf的调控可能通过自分泌或者旁分泌的通路进行。如在斑马鱼中,长期禁食诱导了肝脏中igfbp-2表达量增加(Duan et al, 1999)。另外,igfbp-2会通过与igf的高亲和力来抑制igf配体的活性从而对斑马鱼生长过程起抑制调控作用(Wood et al, 2005b)。Chen等(2014)在金鱼(Carassius auratus) igfbp-2的克隆、分子表征及表达分析中发现,禁食后金鱼肝脏中igfbp-2表达量显著上调,并在饲养后迅速恢复到正常水平,表明igfbp-2的表达可能与金鱼的合成和分解代谢有关,且受到代谢因子的调控。
黄条鰤(Seriola aureovittata)是一种具有长距离洄游特性的暖温性大洋性经济鱼类,分布于全球海洋中上层,具有较高的经济价值和营养价值(徐永江等, 2019),适宜在陆基工厂化循环水、深水网箱、围栏以及养殖工船等多种模式下养殖(崔爱君等, 2022)。黄条鰤体型大、生长速度快,我们前期陆海接力养殖的研究表明,鱼类的生长受到多种环境因素的影响,如养殖密度、温度等(Ndandala et al, 2022; 倪嘉豪等, 2020),同时受到内源性生长激素–胰岛素样生长因子(GH-IGFs)轴的调控。igfbp-1和igfbp-2是硬骨鱼类生长轴的重要调控因子,它们通过与igfs及其受体协同作用调控鱼类的生长发育和营养代谢,但其在黄条鰤生长调控中的功能与作用目前尚未见报道。
本实验室前期已开展黄条鰤快速生长的调控机制相关研究,克隆了gh、igf-1、igf-2、ghr等生长相关功能基因,并揭示了其在早期生长发育中的分子调控功能(Wang et al, 2019、Wang et al, 2020)。为进一步揭示生长轴在黄条鰤生长中的调控作用,本研究克隆得到黄条鰤igfbp-1、igfbp-2a和igfbp-2b基因开放阅读框(ORF)区域,解析其结构特征及表达特性,并探究肝脏中igfbp-1、igfbp-2与生长轴关键因子igf-1、igf-2对不同养殖密度下黄条鰤生长的调控作用,为进一步阐释黄条鰤生长调控机制与开发养殖关键技术提供支撑。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料实验用黄条鰤取自大连富谷食品有限公司工厂化养殖车间,在6个容积约3 m3的圆形玻璃缸水槽中随机投放实验用鱼,采用流水养殖的方式,日换水率400%以上。养殖水温保持在22~27 ℃,盐度为29~32,溶解氧 > 6 mg/L。按鱼体重的3%~5%投喂冰鲜玉筋鱼(Ammodytes personatus),均饱食投喂。每天投喂后1 h清理养殖水槽,保持底部清洁。实验开始之前,将实验鱼在玻璃缸水槽中暂养适应14 d。将筛选后体质健康的1龄鱼[平均体长为(33.12±0.83) cm,平均体重为(565.83±70.22) g)]重新随机分布,并开始正式实验,设置低密度组(10尾/m3)、中密度组(20尾/m3)和高密度组(30尾/m3) 3个实验组,每个实验组设2个平行。实验鱼在不同养殖密度下60 d后取样。暂养结束时随机取雌雄鱼各3尾,用120 mg/L的MS222麻醉处理,在冰盘上快速取脑、垂体、鳃、心脏、肝脏、脾脏、肾脏、头肾、胃、肌肉、性腺等组织于1.5 mL无酶灭菌离心管中,置于液氮中保存,后转入–80℃冰箱中保存,用于igfbp-1、igfbp-2a和igfbp-2b基因克隆与组织分布分析。实验结束时,每个密度组分别采集6条实验鱼的肝脏组织于1.5 mL无酶灭菌离心管中,置于液氮中保存后转入–80 ℃中保存,用于检测不同养殖密度下肝脏组织中igfbp-1、igfbp-2a、igfbp-2b、igf-1和igf-2基因对黄条鰤生长的表达调控作用分析。
1.2 黄条鰤igfbp-1、igfbp-2基因克隆提取肝脏组织总RNA,使用RNAiso Plus试剂盒(TaKaRa);琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测RNA完整性,以NanoDrop2000C分光光度计(Thermo, 美国)测定RNA的质量。用PrimeScript™ RT reagent kit with gDNAEraser (Perfect Real-Time)反转录试剂盒(TaKaRa)合成cDNA第一链。
根据GenBank数据库中黄条鰤igfbp基因的预测序列设计引物(表 1),按照表 2中的PCR体系及程序扩增igfbp-1、igfbp-2a、igfbp-2b 3个基因的ORF区。
|
|
表 1 基因克隆及定量表达分析用的引物序列 Tab.1 Primer sequences used for gene cloning and quantitative expression analysis |
|
|
表 2 黄条鰤igfbp-1、igfbp-2a、igfbp-2b PCR体系及扩增程序 Tab.2 PCR system and amplification procedure for Seriola aureovittata igfbp-1, igfbp-2a and igfbp-2b |
PCR扩增产物经1.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳后,将目的条带切胶、回收,将胶回收产物用pEASY-T1 Simple载体(TransGene Biotech,中国)、Trans1-T1Phage Resistant感受态细胞(TransGene Biotech, 中国)进行连接转化。之后挑取阳性克隆,送至生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司测序。
1.3 序列分析利用BLAST程序比对所得cDNA及其氨基酸序列;利用DNAMAN进行多序列比对及预测蛋白分子量和等电点;利用SignalP 5.0 Server (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?SignalP-5.0)在线软件预测蛋白的信号肽;利用NetPhos 3.1 Server软件(https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?NetPhos-3.1)预测磷酸化位点;利用NCBI数据库(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi)分析预测结构域;利用SWISS-MODEL软件(https://swissmodel.expasy.org/interactive)预测蛋白3D结构,建立模型;利用MEGA 7软件构建系统进化树。
1.4 基因表达特性分析检测了igfbp-1、igfbp-2a和igfbp-2b基因的组织表达特性,以及工厂化不同养殖密度下实验鱼肝脏中igfbp-1、igfbp-2a、igfbp-2b、igf-1和igf-2基因mRNA的相对表达量。引物序列见表 1。
基因定量检测使用SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM(TaKaRa)试剂盒,定量PCR体系为10 μL:cDNA模板1 μL,TB Green Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ (TaKaRa) 5 μL,上下游引物各0.4 μL,灭菌水3.2 μL。运用LightCycler480荧光定量PCR仪(美国)进行qRT-PCR。采用两步法反应,PCR扩增条件:95 ℃预变性30 s,95 ℃ 5 s, 60 ℃ 20 s,共40个循环。每个样品设3个重复,使用2–ΔΔCt法计算基因的相对表达量。黄条鰤arp基因作为内参(表 1)。
1.5 统计分析数据表示为平均值±标准误(Mean±SE),用SPSS 26.0软件对基因在不同组织间、不同性别间的表达水平差异进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),运用Duncan多重比较进行显著性检验。采用Pearson法进行基因表达量与不同养殖密度下生长的相关性分析。以P < 0.05作为差异显著性标准。
2 结果 2.1 黄条鰤igfbp-1和igfbp-2的基因结构特征黄条鰤igfbp-1基因ORF长度为741 bp,共编码246个氨基酸,其编码蛋白预测分子量为26.558 kDa,等电点为6.55;预测信号肽为23个氨基酸,整个编码序列包含18个半胱氨酸残基,聚集在N末端和C末端结构域(图 1)。
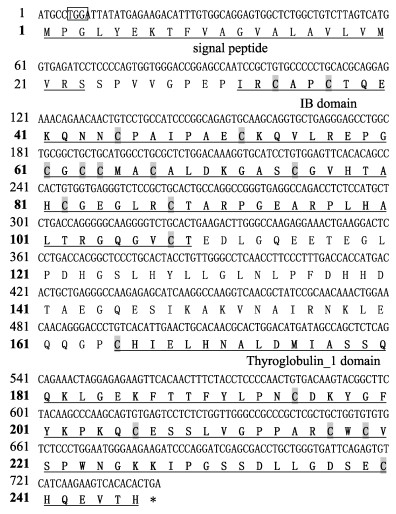
|
图 1 黄条鰤igfbp-1基因ORF序列和推导的氨基酸序列 Fig.1 ORF sequence and the deduced amino acid sequence of igfbp-1 gene from Seriola aureovittata ORF区用大写字母表示。起始密码子加框。信号肽加下划线。下划线和加粗的氨基酸序列表示保守结构域(IB结构域和Ty_1结构域)。灰色阴影表示半胱氨酸残基;*表示终止密码子。下同。 The ORF domain is indicated by capital letters. The start codon is boxed. The signal peptide is underlined. The underlined and bold amino acid sequence represent the conserved domains (IB domain and Ty_1 domain). The gray shadow shows cysteine residues. The stop codon is indicated by an asterisk. The same as below. |
igfbp-2a基因ORF长度为882 bp,编码293个氨基酸,预测信号肽为33个氨基酸,其编码的蛋白预测分子量为32.850 kDa,等电点为7.42,成熟蛋白在其N末端和C末端含有18个半胱氨酸残基(图 2)。
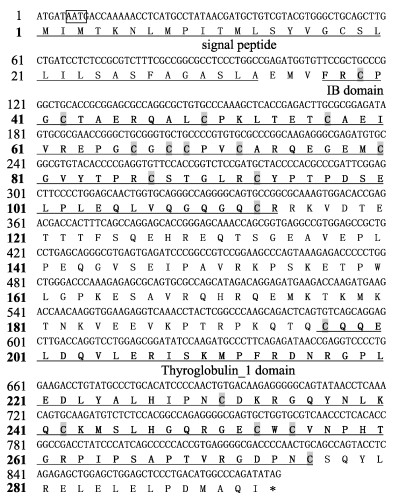
|
图 2 黄条鰤igfbp-2a基因ORF序列和推导的氨基酸序列 Fig.2 ORF sequence and the deduced amino acid sequence of igfbp-2a gene from Seriola aureovittata |
igfbp-2b基因ORF长度为810 bp,编码269个氨基酸,预测信号肽为23个氨基酸,其编码的蛋白预测分子量为29.774 kDa,等电点为7.19,成熟蛋白在其N末端和C末端含有18个半胱氨酸残基(图 3)。

|
图 3 黄条鰤igfbp-2b基因ORF序列和推导的氨基酸序列 Fig.3 ORF sequence and the deduced amino acid sequence of igfbp-2b gene from Seriola aureovittata |
3个基因编码的蛋白3D空间结构如图 4所示:IGFBP空间结构N末端均存在胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白同源物(IB)保守结构域,C末端均含有甲状腺球蛋白Ⅰ型重复(Ty-1)保守结构域,且均具有蛋白激酶A和C、酪蛋白激酶和细胞周期素依赖蛋白激酶5磷酸化位点。IGFBP-1的N端结构域位于32~109,C端结构域位于165~240,该域具有3个二硫键,分别位于165~195、206~217、219~240;具有DNA依赖性蛋白激酶磷酸化位点;α-螺旋占26.83%,延伸链占7.72%。IGFBP-2A的N端结构域位于37~114,C端结构域位于197~276,该域中,3个二硫键分别位于197~231、242~253、255~276,还存在一个N-糖基化位点位于275,以及P38蛋白激酶、DNA依赖性蛋白激酶、丝氨酸-苏氨酸蛋白激酶、细胞分裂周期激酶2、蛋白激酶G磷酸化位点;α-螺旋占29.69%,延伸链占6.83%。IGFBP-2B的N端结构域位于26~102,C端结构域位于173~252,该域中,3个二硫键分别位于173~207、218~229、231~252,还存在糖原合成酶激酶-3磷酸化位点;α-螺旋占25.65%,延伸链占9.67%。
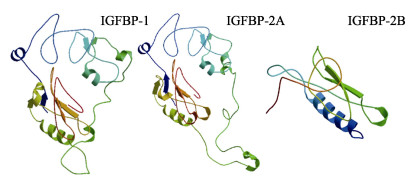
|
图 4 黄条鰤IGFBP-1、IGFBP-2A、IGFBP-2B蛋白结构 Fig.4 3D structure of Seriola aureovittata IGFBP-1, IGFBP-2A, and IGFBP-2B |
同源性分析表明,黄条鰤IGFBP-1氨基酸序列与五条鰤(Seriola quinqueradiata)、斜带石斑鱼、黄金鲈(Perca flavescens)的IGFBP-1同源性分别为98.37%、84.08%、83.20%,与哺乳动物的IGFBP-1同源性为41%~46% (图 5)。IGFBP-2A与高体鰤(Seriola dumerili)、河鲈(Perca fluviatilis)、鞍带石斑鱼(Epinephelus lanceolatus)、大菱鲆(Scophthalmus maximus)的同源性分别为100%、95.90%、96.59%、93.01%,与高等脊椎动物的同源性为50%~51%。igfbp-2b氨基酸序列与牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)、斑马鱼、虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss)的同源性分别为84.39%、60.08%、56.93%,与高等脊椎动物的同源性为45%~47%。黄条鰤IGFBP-2A和IGFBP-2B的氨基酸序列同源性为55.22% (图 6)。

|
图 5 黄条鰤IGFBP-1与其他物种氨基酸序列比对 Fig.5 Amino acid sequence alignment of Seriola aureovittata IGFBP-1 with other species 红色框表示(GCGCCXXC)结构域,蓝色框表示(CWCV)结构,绿色框表示RGD结构。下同。 The red box represents the (GCGCCXXC) structure, the blue box the (CWCV) structure, and the green box the RGD structure. The same as below. |

|
图 6 黄条鰤IGFBP-2与其他物种氨基酸序列比对 Fig.6 Amino acid sequence alignment of Seriola aureovittata IGFBP-2 with other species |
系统进化分析表明,黄条鰤IGFBP-1与五条鰤IGFBP-1聚为一个小的分支,又与黄金鲈和斜带石斑鱼等鲈形目鱼类聚为一个大的分支,哺乳动物的IGFBP-1单独为一分支。IGFBP-2A与高体鰤IGFBP-2聚为一个小的分支,与河鲈和鞍带石斑鱼等鲈形目鱼类IGFBP-2A聚为一支,又与大菱鲆IGFBP-2A、牙鲆IGFBP-2A鲽形目鱼类聚为大的一支。而IGFBP-2B与牙鲆IGFBP-2B等鲽形目鱼类聚为一小支,然后与斑马鱼IGFBP-2B鲤形目鱼类聚为一支,哺乳动物IGFBP-2聚为一支,表明黄条鰤IGFBP-2B在系统进化上的保守性较低(图 7)。
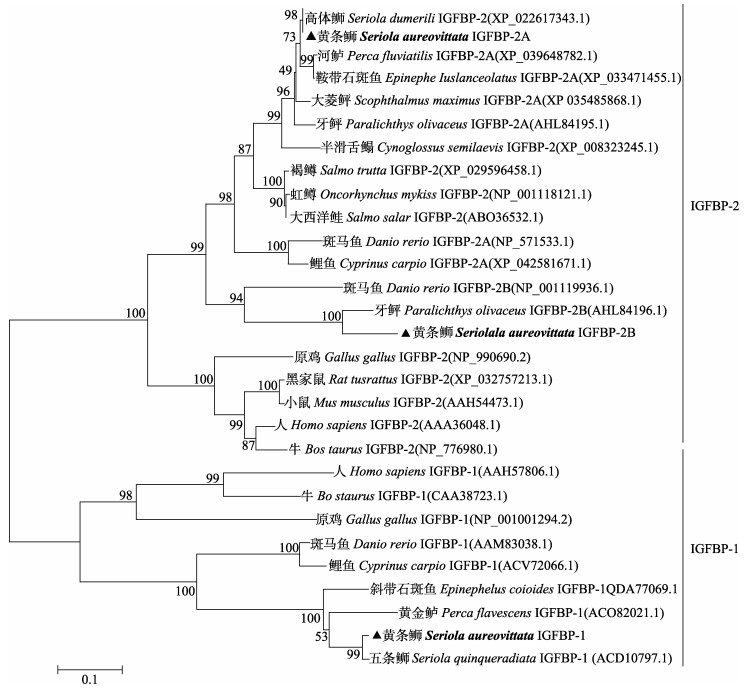
|
图 7 黄条鰤IGFBP-1和IGFBP-2氨基酸序列的系统进化树 Fig.7 Phylogenetic tree of Seriola aureovittata IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-2 amino acid sequences |
黄条鰤igfbp-1、igfbp-2a、igfbp-2b基因在所检测组织中均有分布(图 8)。igfbp-1在雌雄鱼肝脏中均表达量最高(P < 0.05),在性腺中也有高表达,且雄鱼表达量高于雌鱼(P < 0.05),其他组织间的表达量极低且无显著差异。igfbp-2a在雌雄鱼在肝脏中均表达量最高(P < 0.05),其次为性腺(P < 0.05),在其他组织中表达量相对较低,雌鱼肝脏中的表达量高于雄鱼的表达量(P < 0.05)。igfbp-2b在雌雄鱼肝脏中均表达量最高(P < 0.05),在其他组织中表达量较低且无显著性差异,雄鱼肝脏中的表达量高于雌鱼(P < 0.05)。

|
图 8 黄条鰤igfbp-1、igfbp-2a、igfbp-2b基因在不同组织中的相对表达量 Fig.8 Relative expression levels of igfbp-1, igfbp-2a, and igfbp-2b in different tissues of Seriola aureovittata 不同大写字母表示雌鱼不同组织之间差异显著(P < 0.05);不同小写字母表示雄鱼不同组织之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。*表示雌鱼和雄鱼在同一组织内存在显著差异(P < 0.05),**代表有极显著差异(P < 0.01)。 Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different tissues of female (P < 0.05), and different small letters indicate significant differences between different tissues of male (P < 0.05). * indicates significant difference within the same tissue between female and male fish (P < 0.05), and ** indicates highly significant difference within the same tissue between female and male fish (P < 0.01). |
本实验室前期研究已表明,在不同工厂化养殖密度条件下,黄条鰤的生长性能出现明显差异:低密度组实验鱼终末体质量和肥满度显著高于高密度组(P < 0.05),增重率和特定生长率显著高于中、高密度组(P < 0.05),而中、高密度组实验鱼生长差异不显著(姜燕等, 2022)。
检测了不同养殖密度组黄条鰤肝脏中igfbp-1、-2a、-2b以及igf-1和igf-2基因表达水平变化(图 9):随着密度的增加,igfbp-1、-2a、-2b的表达量呈现下降趋势,低密度组表达量最高(P < 0.05),中、高密度组表达量低且无显著性差异;igf-1和igf-2也呈现低密度组表达量最高的表达特性(P < 0.05) (图 9)。相关性分析表明,各基因表达水平均与低密度组实验鱼生长呈现显著正相关(igfbp-1 r=0.836, P < 0.05; igfbp-2a r=0.443, P < 0.05; igfbp-2b r=0.549, P < 0.05; igf-1 r=0.500, P < 0.05; igf-2 r=0.925, P < 0.05;),但与中、高密度组实验鱼生长无显著相关关系。

|
图 9 不同养殖密度下黄条鰤肝脏igfbp-1、igfbp-2a、igfbp-2b、igf-1和igf-2基因的表达特性 Fig.9 Expression characteristics of liver igfbp-1, igfbp-2a, igfbp-2b, igf-1, and igf-2 of Seriola aureovittata under different stocking densities A、B、C分别代表低、中、高密度组。 A, B, and C stand for low, medium, and high density culture group, respectively. |
本研究首次获得了黄条鰤igfbp-1、igfbp-2a和igfbp-2b基因的ORF序列。结果显示,与其他硬骨鱼类基本一致,igfbp-1和igfbp-2中均存在N末端结构域中12个半胱氨酸残基和C末端结构域中6个半胱氨酸残基,这些半胱氨酸残基参与内部二硫键的形成以及帮助形成N末端和C末端结构域的球状结构,且在进化上较为保守(Hwa et al, 1999; Zhou et al, 2008)。已有研究发现,半胱氨酸残基参与了草鱼(Ctenopharyngodon idellus) igfbp-2空间结构的形成(Yang et al, 2020)。序列比对结果显示,在N末端结构域中,黄条鰤3个igfbp之间也存在一个共同的保守的基序(GCGCCXXC),五条鰤中也存在类似情况(Pedroso et al, 2009),此基序在与igf的相互作用中起着重要作用(Kamangar et al, 2006)。不同物种中igfbp的N末端和C末端具有高度的保守性。中间可变结构域保守性较低,翻译后修饰,如糖基化位点和磷酸化位点,通常在这个中间区域发现(Zhou et al, 2008)。黄条鰤igfbp-1和igfbp-2的C末端结构域高度保守,其中包含一个保守的CWCV结构,此结构被称为甲状腺球蛋白Ⅰ型重复结构域(钱焜等, 2014),可能在igfbp和igf与细胞外基质的结合中起重要作用(Bach, 2018)。先前研究表明,所有哺乳动物igfbp-1和igfbp-2的C末端都含有RGD结构(Rodgers et al, 2008),人类igfbp-1可以通过RGD结构与α5β1整合素结合来刺激细胞迁移(Feng et al, 2015),但在黄条鰤与其他硬骨鱼的igfbp-1中,其C末端区域缺失RGD结构,取而代之的结构为LGD。斑马鱼(Maures et al, 2002)、花鲈(Lateolabrax japonicus)(钱焜等, 2014)、大菱鲆(胡健等, 2012) igfbp-1中也均未发现RGD结构。而哺乳动物、鸟类和其他已知硬骨鱼igfbp-2中的RGD结构在黄条鰤igfbp-2中有发现,花鲈、大菱鲆igfbp-2中也是如此,表明igfbp-1在鱼类与硬骨鱼类中发挥生理功能的机制存在差异。
本研究从黄条鰤肝脏中克隆出2种类型的igfbp-2,分别为igfbp-2a、igfbp-2b。黄条鰤igfbp-2a和igfbp-2b基因位于不同分支。igfbp-2a与高体鰤关系最近,和斑马鱼igfbp-2a聚为一支;而igfbp-2b与牙鲆关系最近,和斑马鱼igfbp-2b聚为一支。系统进化分析结果表明黄条鰤igfbp-2a和igfbp-2b基因起源于同一祖先基因,经历了鱼类基因组的复制,是人类等其他哺乳动物igfbp-2的同源基因。在虹鳟体内也发现了2种同源的igfbp-2 (钱焜等, 2014),其中一种还被误命名为igfbp-3 (Maures et al, 2002),原因是其结构与其他的igfbp结构相似度很低。本研究也发现,黄条鰤igfbp-2b在结构上保守性较差,系统进化分析也表明其与鲽形目(Pleuronectiformes)、鲤形目(Cypriniformes)聚为一支,表明其在系统进化上保守性不高。在斑马鱼及其他鱼中也发现,igfbp-2存在类似同源性且具有不同功能,可能是由基因组复制引起并在进化过程中发生了生理功能的改变(Allard et al, 2018)。本研究虽未对其功能进行研究,但发现在黄条鰤生长调控中与igfbp-2a表达量一致,表明虽结构不保守,但功能是保守的。
3.2 组织分布特征已有研究表明,肝脏是硬骨鱼igfbp-1合成的主要场所(Pedroso et al, 2009)。本研究在黄条鰤中检测到igfbp-1 mRNA在肝脏中表达量最高,在脑和性腺中也有显著表达,但其他组织中igfbp-1 mRNA表达量极低;组织分布特征与五条鰤(Pedroso et al, 2009)、牙鲆(翟万营等, 2012)类似。但也有研究表明,陶洋等(2011)在草鱼成鱼的脾、肌、眼、鳃、胰脏、肠、脑和性腺中均未检测到igfbp-1 mRNA的表达。以上结果表明,不同鱼类igfbp-1 mRNA主要在肝脏中表达,在除肝脏以外的组织中表达分布差异较大,这可能取决于物种的特异性。
(Zhou2008)等对斑马鱼研究发现,斑马鱼基因组包含2个igfbp-2,igfbp-2a和igfbp-2b的蛋白具有类似的生物活性,但这2个基因却表现出不同的时空表达模式。本研究黄条鰤igfbp-2 mRNA在肝脏组织中显著高表达,与鲤鱼(Cyprinus carpio) (Chen et al, 2009)、斜带石斑鱼(Chen et al, 2010)、五条鰤(Pedroso et al, 2009)的研究结果一致。igfbp-2a mRNA表达量最丰富的组织是肝脏,性腺次之,在鳃、心脏、肾脏、头肾中也有较高表达但无显著差异。igfbp-2b mRNA也是在肝脏组织表达量最高,其余组织中均有分布,但表达量极低且无显著差异。这些结果表明,除了在结构和系统进化上有差别外,黄条鰤igfbp-2的2种等位基因在生理功能上可能也不同,其功能的差异特性及可能的作用通路有待于今后进一步验证。另外,本研究还发现,黄条鰤igfbp-2a mRNA在性腺中也有明显高表达,可能说明其除了调控生长之外,还有更广泛的生物功能,这在其他鱼中也有发现,如在鲤鱼(Chen et al, 2009)和虹鳟(钱焜等, 2014)性腺中也检测到有表达,表明igfbp-2对于鱼类性腺发育也可能具有重要的调控作用(Chen et al, 2010),但igfbp-2对黄条鰤性腺发育是否具有生理调控作用尚需进一步确证。
本研究还发现,雌雄鱼相同组织中同一基因的表达量之间也存在差异,比如雄鱼肝脏中基因的表达量igfbp-1和igfbp-2b显著高于雌鱼,而雌鱼肝脏igfbp-2a表达量则显著高于雄鱼。这种性别之间基因的组织差异性表达,说明igfbp发挥生理功能时可能具有性别二态性,同黄条鰤hsp70的基因表达模式相似(方璐等, 2023),但这种雌雄差异的特性具体是由什么决定以及可能的信号通路尚不清楚,值得今后深入研究。
3.3 IGFBPs对黄条鰤生长的表达调控作用越来越多的研究证实,IGFBP通过生长轴(GH/ IGF-I axis)对鱼类生长代谢起着重要的生理调控作用(Reinecke, 2010)。(胡健等2012)对大菱鲆早期生长发育过程的调控机制的研究表明,IGFBP-1和IGFBP-2对细胞增殖、生长及组织器官分化发育都起着重要的生理学作用。本实验室开展的工厂化养殖密度对黄条鰤生长的影响研究发现,低密度组实验鱼生长显著快于高密度组(姜燕等, 2022)。本研究进一步发现,在工厂化低密度养殖条件下,黄条鰤肝脏中igfbp-1、igfbp-2、igf-1和igf-2 mRNA表达水平均显著高于高密度组实验鱼,同时,这些生长关键因子的表达与低养殖密度下的快速生长呈显著正相关关系,表明IGFBPs与IGFs等生长因子通过生长轴对黄条鰤的生长起着正向协同调控作用。已有研究表明,igfbp-1主要在肝脏中合成,其表达和分泌受到分解代谢因子和激素的高度调控,如肝脏igfbp-1表达水平被饥饿、缺氧和应激高度诱导(Maures et al, 2002; Kajimura et al, 2006)。Breves等(2016)的研究也表明,在饥饿条件下,大西洋鲑的肝脏igfbp1a1显著上调表达,但同时肌肉igf1则显著下调表达,表明肝脏和肌肉组织中的生长关键因子可能通过不同的途径参与了生长代谢调控。对五条鰤的研究也表明,在实验鱼饥饿并恢复投喂后生长速度加快,同时,肝脏中igfbp-1、igfbp-2、igfbp-3、igfbp-5和igf-1表达量均升高,表明生长轴关键因子igf-1与igfbps协同参与了饥饿后的代谢补偿生长调控(Pedroso et al, 2009)。另外,对若鲉杜父鱼(Scorpaenichthys marmoratus) (Strobel et al, 2020)研究也表明,实验鱼在饥饿条件下生长受到抑制,同时肝脏igf-1和igfbp-1表达水平升高,而igfbp-2b基因表达水平降低,推测是igf-1通过与igfbp的结合直接调节细胞有丝分裂和代谢过程,激活生长因子的合成和释放来调节机体生长(Qian et al, 2016; Hack et al, 2019)。在体外细胞孵育水平上,有学者研究了生长激素对鲤鱼原代培养肝细胞中igfbp-1a的表达影响,结果表明,生长激素下调了肝细胞中igfbp-1a的表达,推测通过MAPK和三碘化磷激酶信号通路实现了对细胞生长的调控(Chen et al, 2018)。本研究结果表明,高密度抑制了黄条鰤肝脏igfbps与igfs基因的表达,且它们在生长过程中起正向协同调控作用。
本实验室的前期研究还发现,工厂化低密度养殖条件下显著快速生长的黄条鰤血清中IGF-1、GH的水平均显著高于高密度组条件下生长显著迟滞的实验鱼,而血清中皮质醇含量及葡萄糖浓度显著低于高密度组(姜燕等, 2022)。本研究深入分析发现,低密度下快速生长的黄条鰤肝脏中igfbp-1、igfbp-2、igf-1和igf-2 mRNA显著高表达,且血清IGF-1、GH具有相同表达趋势,与皮质醇含量及葡萄糖浓度表达趋势相反,表明生长轴关键因子与皮质醇和葡萄糖参与了不同密度下黄条鰤的生长调控。皮质醇是指示生物应激状态程度的重要因子,而葡萄糖则是机体供能的重要来源以及应对环境胁迫的重要生理指标。已有研究表明,胰岛素可降低igfbp-1的表达,糖皮质激素可增加其表达(O'brien et al, 1995),这种调节机制有助于促进igfbp-1在饥饿和分解代谢条件下的表达,包括氨基酸短缺和缺氧(McLellan et al, 1992)。在不利生长条件下,igfbp-1的功能是通过与igf结合并抑制igf活性来降低发育和生长速率(Maures et al, 2002; Kajimura et al, 2006)。新近对大西洋鲑幼鱼的研究表明,外源皮质醇激素可以通过调节GH/IGF-I生长轴,主要是肝脏中igf-1、igf-2、igfbp-1和igfbp-2的表达来影响大西洋鲑幼鱼的生长和离子调节(Breves et al, 2020)。同时,Yang等(2020)在草鱼肝脏细胞的体外孵育研究中发现,肝细胞igfbp-2的表达受到葡萄糖、胰岛素和胰高血糖素的调控。因此,本研究发现的黄条鰤肝脏IGFBP-1、IGFBP-2、IGF-1和IGF-2等生长因子与血清皮质醇、葡萄糖之间存在的相关表达调控,是否是黄条鰤通过调整机体代谢水平以适应环境从而获得不同密度下的快速生长优势尚有待于深入研究。
ALLARD J B, DUAN C. IGF-binding proteins: Why do they exist and why are there so many? Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2018, 9: 117
|
BACH L A. What happened to the IGF binding proteins? Endocrinology, 2018, 159(2): 570–578
|
BREVES J P, PHIPPS-COSTIN S K, FUJIMOTO C K, et al. Hepatic insulin-like growth-factor binding protein (igfbp) responses to food restriction in Atlantic salmon smolts. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2016, 233: 79-87 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2016.05.015 |
BREVES J P, SPRINGER-MILLER R H, CHENOWETH D A, et al. Cortisol regulates insulin-like growth-factor binding protein (igfbp) gene expression in Atlantic salmon parr. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 2020, 518: 110989 DOI:10.1016/j.mce.2020.110989 |
CHEN W B, LI W G, ZHANG Z, et al. Cloning, molecular characterization and expression analysis of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) cDNA in goldfish, Carassius auratus. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 40(6): 1669-1681 DOI:10.1007/s10695-014-9958-z |
CHEN W B, LI W S, LIN H R. Common carp (Cyprinus carpio) insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2): Molecular cloning, expression profiles, and hormonal regulation in hepatocytes. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2009, 161(3): 390-399 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2009.02.004 |
CHEN W B, LIN H R, LI W S. Molecular cloning and expression profiles of IGFBP-1a in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and its expression regulation by growth hormone in hepatocytes. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2018, 221/222: 50-59 DOI:10.1016/j.cbpb.2018.04.005 |
CHEN W B, WANG Y, LI W S, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) in orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides: Molecular characterization, expression profiles and regulation by 17beta-estradiol in ovary. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2010, 157(4): 336-342 DOI:10.1016/j.cbpb.2010.08.001 |
CUI A J, XU Y J, LIU X Z. Comparative analysis of digestive enzyme activities among three Seriola species. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2022, 43(6): 102-110 [崔爱君, 徐永江, 柳学周. 3种养殖鰤鱼消化相关酶活性的比较分析. 渔业科学进展, 2022, 43(6): 102-110] |
DUAN C, DING J, LI Q, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 is a growth inhibitory protein conserved in zebrafish. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(26): 15274-15279 |
DUAN C, XU Q J. Roles of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding proteins in regulating IGF actions. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2005, 142(1/2): 44-52 |
FANG L, XU Y J, CUI A J. Molecular cloning and temporal expression pattern of hsp70 gene during the early life stages of Seriola lalandi. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2023, 44(4): 00-00 [方璐, 徐永江, 崔爱君. 黄条鰤hsp70基因克隆及其在早期生长发育过程中的表达调控特性. 渔业科学进展, 2023, 44(4): 00-00] |
FENG N P, ZHANG Z, WANG Z F, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 promotes adhesion of endothelial progenitor cells to endothelial cells via integrin α5β1. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 2015, 57(3): 426-434 DOI:10.1007/s12031-015-0589-3 |
GARCIA DE LA SERRANA D, MACQUEEN D J. Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins of teleost fishes. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2018, 9: 80 DOI:10.3389/fendo.2018.00080 |
HACK N L, CORDOVA K L, GLASER F L, et al. Interactions of long-term food ration variation and short-term fasting on insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) pathways in copper rockfish (Sebastes caurinus). General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2019, 280: 168-184 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2019.04.025 |
HU J, WEN H S, GUAN J, et al. Cloning of IGFBP-1, -2 and expression analysis during adult and early developmental stages in Scophthalmus maximus. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 34(5): 139-146 [胡健, 温海深, 关健, 等. 大菱鲆2种类胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白基因克隆及在成鱼和早期发育期中的表达. 海洋学报(中文版), 2012, 34(5): 139-146] |
HWA V, OH Y, ROSENFELD R G. The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily. Endocrine Reviews, 1999, 20(6): 761-787 |
JIANG Y, WANGW X, XU Y J, et al. Effects of industrial stocking density on the growth and physiological characteristics of Seriola lalandi. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2022, 29(9): 1290-1299 [姜燕, 王维鑫, 徐永江, 等. 工厂化养殖密度对黄条鰤生长和生理特性的影响. 中国水产科学, 2022, 29(9): 1290-1299] |
KAJIMURA S, AIDA K, DUAN C. Understanding hypoxia- induced gene expression in early development: in vitro and in vivo analysis of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-regulated zebra fish insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 gene expression. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 2006, 26(3): 1142-1155 DOI:10.1128/MCB.26.3.1142-1155.2006 |
KAMANGAR B B, GABILLARD J C, BOBE J. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP)-1, -2, -3, -4, -5, and -6 and IGFBP-related protein 1 during rainbow trout postvitellogenesis and oocyte maturation: Molecular characterization, expression profiles, and hormonal regulation. Endocrinology, 2006, 147(5): 2399-2410 DOI:10.1210/en.2005-1570 |
MAURES T J, DUAN C. Structure, developmental expression, and physiological regulation of zebrafish IGF binding protein-1. Endocrinology, 2002, 143(7): 2722-2731 DOI:10.1210/endo.143.7.8905 |
MCLELLAN K C, HOOPER S B, BOCKING A D, et al. Prolonged hypoxia induced by the reduction of maternal uterine blood flow alters insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) and IGFBP-2 gene expression in the ovine fetus. Endocrinology, 1992, 131(4): 1619-1628 DOI:10.1210/endo.131.4.1382958 |
NDANDALA C B, DAI M S, MUSTAPHA U F, et al. Current research and future perspectives of GH and IGFs family genes in somatic growth and reproduction of teleost fish. Aquaculture Reports, 2022, 6: 101289 |
NI J H, ZHU X J, JI Y P, et al. Effects of breeding density on the growth, metabolic enzyme activity and related gene expression level of juvenile Pampus argenteus. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 54-64 [倪嘉豪, 朱晓静, 季益平, 等. 养殖密度对银鲳幼鱼生长、代谢酶活力及其相关基因表达的影响. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(2): 54-64] |
O'BRIEN R M, NOISIN E L, SUWANICHKUL A, et al. Hepatic nuclear factor 3- and hormone-regulated expression of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 genes. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 1995, 15(3): 1747-1758 DOI:10.1128/MCB.15.3.1747 |
PEDROSO F L, FUKADA H, MASUMOTO T. Molecular characterization, tissue distribution patterns and nutritional regulation of IGFBP-1, -2, -3 and -5 in yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2009, 161(3): 344-353 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2009.01.010 |
QIAN B Y, XUE L Y. Liver transcriptome sequencing and de novo annotation of the large yellow croaker (Larimichthy crocea) under heat and cold stress. Marine Genomics, 2016, 25: 95-102 DOI:10.1016/j.margen.2015.12.001 |
QIAN K, WEN H S, CHI M L, et al. Cloning and characteristics of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1, 2 genes (igfbp-1, 2) of Japanese sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) and their expression analysis. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science), 2014, 44(9): 37-45 [钱焜, 温海深, 迟美丽, 等. 海产花鲈IGFBP-1、2基因的克隆及表达分析. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 44(9): 37-45 DOI:10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.2014.09.005] |
REINECKE M. Influences of the environment on the endocrine and paracrine fish growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor-I system. Journal of Fish Biology, 2010, 76(6): 1233-1254 DOI:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2010.02605.x |
RODGERS B D, ROALSON E H, THOMPSON C. Phylogenetic analysis of the insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP) and IGFBP-related protein gene families. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2008, 155(1): 201-207 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.04.013 |
STROBEL J S, HACK N L, LABEL K T, et al. Effects of food deprivation on plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 (Igf1) and Igf binding protein (Igfbp) gene transcription in juvenile cabezon (Scorpaenichthys marmoratus). General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2020, 286(C): 113319 |
TAO Y, ZOU S M. cDNA cloning and expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein gene IGFBP-1 in Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2011, 20(1): 15-21 [陶洋, 邹曙明. 草鱼胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白IGFBP-1基因的全长cDNA克隆及表达. 上海海洋大学学报, 2011, 20(1): 15-21] |
WANG B, XU Y J, LIU X Z, et al. Molecular characterization and expression profiles of insulin-like growth factors in yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi) during embryonic development. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 2019, 45(1): 375-390 DOI:10.1007/s10695-018-0570-5 |
WANG B, ZHANG Y X, LIU Q, et al. Molecular identification and developmental expression patterns of growth hormone and its receptors in yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Molecular Biology Reports, 2020, 47(9): 7305-7312 DOI:10.1007/s11033-020-05729-4 |
WOOD A W, DUAN C, BERN H A. Insulin-like growth factor signaling in fish. International Review of Cytology, 2005a, 243: 215-285 |
WOOD A W, SCHLUETER P J, DUAN C. Targeted knockdown of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 disrupts cardiovascular development in zebrafish embryos. Molecular Endocrinology, 2005, b, 19(4): 1024-1034 |
XU Y J, ZHANG Z R, LIU X Z, et al. Morphometric characteristics of the embryonic and postembryonic development of yellowtail kingfish, Seriola aureovittata. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2019, 26(1): 172-182 [徐永江, 张正荣, 柳学周, 等. 黄条鰤早期生长发育特征. 中国水产科学, 2019, 26(1): 172-182] |
YANG G K, CHEN B C, SUN C Y, et al. Molecular identification of grouper Igfbp1 and its mRNA expression in primary hepatocytes under Gh and insulin. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2019, 281: 137-144 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2019.06.001 |
YANG G K, ZHAO W L, QIN C B, et al. Molecular identification of grass carp igfbp2 and the effect of glucose, insulin, and glucagon on igfbp2 mRNA expression. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 2020, 46(4): 1469-1482 |
ZHAI W Y, ZHANG J L, SHI Z Y, et al. The full-length cDNA cloning and gene expression analysis of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1) in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Journal of Fisheries of China, 2012, 36(2): 170-179 [翟万营, 张俊玲, 施志仪, 等. 牙鲆胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白IGFBP-1 cDNA全长的克隆及表达分析. 水产学报, 2012, 36(2): 170-179] |
ZHOU J F, LI W H, KAMEI H, et al. Duplication of the IGFBP-2 gene in teleost fish: Protein structure and functionality conservation and gene expression divergence. PLoS One, 2008, 3(12): 1-11 |



