近年来,鱼粉价格不断攀升,配合饲料成本高居不下,为降低饲料成本,豆粕等产量稳定、价格低廉的植物蛋白源在水产饲料中的用量逐渐增加,但由于豆粕中含有大豆凝集素、植酸和皂甙等抗营养因子,过量替代会引起鱼类肠道损伤,诱发豆粕型肠炎(soybean meal-induced enteritis, SBMIE)(Gu et al, 2016)。对斜带石斑鱼(Epinephelus coioides)(Wang et al, 2017)、大菱鲆(Scophthalmus maximus)(Gu et al, 2016)、虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss)(Merrifield et al, 2009)等鱼的研究均报道了豆粕过量替代鱼粉后豆粕型肠炎的发生。为缓解豆粕对鱼类肠道的损伤,提高其在饲料中的利用,Gu等(2017)验证了谷氨酰胺、精氨酸等功能性氨基酸在肠道修复方面的积极作用。精氨酸(Arginine,Arg)是鱼类的必需氨基酸,又是一种功能性氨基酸,不仅参与蛋白质和嘧啶合成、激素释放,还是合成尿素、谷氨酸、肌酸、多胺和一氧化氮(NO)等生物活性物质的前体(万军利等, 2006),参与机体生长、免疫、肠道屏障、内分泌等多种代谢调节,在免疫调节及维持和保护肠道黏膜结构和功能等方面起着重要作用(Wang et al, 2009)。在畜禽(姜海龙等, 2015)和淡水鱼(Cheng et al, 2011; Jiang et al, 2015)中均报道了Arg有利于肠道黏膜损伤后的修复。陈娇娇(2017)离体培养草鱼(Ctenopharyngodon idella)肠道黏膜细胞发现,Arg能促进草鱼细胞间紧密连接蛋白基因的表达;Jiang等(2015)对建鲤(Cyprinus carpiovar. Jian)的研究发现,Arg能够调节脂多糖诱导的肠道炎症反应,抑制炎症因子的表达,促进抗炎因子的表达,但作用机制尚不清楚。
许氏平鲉(Sebastes schlegelii)是我国北方网箱养殖和增殖放流的理想种类(李宝山等, 2019),作为肉食性经济鱼类,其对鱼粉需求较高,豆粕等植物蛋白过量添加易损伤肠道健康。本研究的前期实验诱导了许氏平鲉肠炎的发生,实验鱼均出现黏膜皱襞高度降低、细胞核排列紊乱、杯状细胞明显增多等SBMIE的典型症状。基于以上实验,本研究以诱导出豆粕型肠炎的许氏平鲉[(54.97±0.12) g]为研究对象,从生长性能、Arg代谢、肠道组织结构、紧密连接蛋白基因(occludin、clnd15和zo-1)、炎症因子基因(il-1β、il-8、il-15和tlr8)和抗炎因子基因(il-12b)表达等多方面探讨Arg对豆粕型肠炎的修复作用及其机理,以期为Arg维护鱼类肠道健康方面的应用提供科学依据,为植物蛋白在肉食性经济鱼类许氏平鲉配合饲料中的应用提供参考。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验饲料以白鱼粉、豆粕和酪蛋白为主要蛋白源,鱼油为主要脂肪源,Arg 0添加为对照组(D0),Arg (L型,纯度98%,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司)添加1%、2%和3%为处理组(D1、D2和D3),用甘氨酸(L型,纯度98%,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司)配平饲料总氨基酸水平,配制4组等氮等能的实验饲料,饲料配方、营养组成及饲料Arg实测值见表 1。
|
|
表 1 饲料配方及营养组成 Tab.1 Composition and nutrient levels of the experimental diets/% |
养殖实验在山东省海洋资源与环境研究院(东营)试验基地车间的水泥池进行,实验用许氏平鲉购自威海泰丰海水育苗有限公司,选用同一批次的许氏平鲉,预实验设置30%、40%和50%的豆粕添加量,分别于实验的第14、21和28天取样,观察肠道的炎症程度,以所有样品均出现明显的肠道炎症为标准决定豆粕添加量及诱导周期,诱导实验最终使用40%豆粕饲料喂养28 d,诱导豆粕型肠炎的发生。修复实验开始前,挑选480尾初体重(initial body weight, IBW)为(54.97±1.12) g、已被诱导出豆粕型肠炎的许氏平鲉,随机分为4组,每组3个重复,每个重复40尾鱼,随机置于12个自制网箱(60 cm×60 cm×90 cm)中。修复实验进行6周,每天定时(08:00和17:00)定量投喂2次,初始投喂量为体重的1%,根据摄食情况调整投喂量并记录死鱼数量和重量。驯养及实验期间每天清底并加注新水,控制水温为18~22 ℃,pH值为7.6~8.2,溶氧 > 6 mg/L,氨氮和亚硝酸盐浓度 < 0.05 mg/L,光照周期为自然光周期。
1.3 样品采集实验结束后禁食24 h,每桶鱼计数并称末体重(final body weight, FBW)。每桶随机取10尾鱼,麻醉后测量体长和体重,尾静脉采血后分离内脏,所有操作均在冰盘内完成。血液于4 ℃静置4 h后离心(4 000 r/min, 10 min),血清保存于–20 ℃,用于酶活性及代谢产物测定。每桶取3尾鱼中后肠,生理盐水匀浆后离心(2 500 r/min, 10 min),上清液保存于–20 ℃,用于酶活性测定。每桶取3尾鱼后肠(0.8 cm)固定于Bouin’s液中,24 h后转移到70%酒精中,经脱水、透明、浸蜡、包埋后,进行常规石蜡连续切片(厚度7.0 μm),HE染色后,中性树胶封片,徕卡高清摄像系统(LEICAICC50HD)下观察并拍照。每桶取6尾鱼后肠(1 cm)于液氮中,转移至–80 ℃冰箱保存,用于基因表达量测定。
1.4 计算公式与实验方法增重率(weight gain rate, WGR, %)=[FBW(g)– IBW(g)]×100/IBW(g);
肝体比(hepatosomatic index, HSI, %)=肝脏质量(g)×100/FBW(g);
脏体比(viscerosomatic index, VSI, %)=内脏质量(g)×100/FBW(g);
肥满度(condition factor, CF)=FBW(g)×100/体长(cm)3;
存活率(survival rate, SR, %)=成活尾数×100/总尾数。
饲料粗蛋白采用凯氏定氮法(GB/T 6432-2006)测定;粗脂肪采用索氏抽提法(GB/T 6433-2006)测定;粗灰分采用550 ℃失重法(GB/T 6438-2007)测定;饲料Arg使用氨基酸分析仪(HITACHI L-8900)测定。
肠道总抗氧化能力(total antioxidant capacity, T-AOC)、丙二醛(malondialdehyde, MDA)含量,血清二胺氧化酶(diamine oxidase, DAO)、总一氧化氮合酶(T-NOS)、诱导型一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)活性及一氧化氮(NO)含量均采用南京建成生物工程研究所试剂盒测定。
1.5 实时荧光定量PCR检测使用山东思科捷生物技术有限公司试剂盒(SPARKeasy Improved Tissue/Cell RNA Kit)进行总RNA提取,NanoDrop®2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 美国)检测RNA浓度及纯度,1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测RNA完整性及基因组污染情况,使用SPARKscript Ⅱ RT Plus Kit (with gDNA Eraser)反转录试剂盒去除基因组DNA并反转录成cDNA。使用2× SYBR Green qPCR Mix (with ROX)进行实时荧光定量PCR (LightCycler® 480Ⅱ)分析。以核糖体蛋白L17 (rpl17)为内参,按照2–∆∆Ct计算目的基因相对表达量,引物序列见表 2。
|
|
表 2 许氏平鲉肠道相关基因引物序列 Tab.2 Sequence of primers for gut related genes of S. schlegelii |
所有数据采用SPSS 18.0进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),用Duncan’s检验进行多重比较,P < 0.05认为差异显著,P > 0.05认为差异不显著。统计数据以平均值±标准误(Mean±SE)表示。
2 结果 2.1 精氨酸对SBMIE-许氏平鲉生长性能和形体指标的影响由表 3可见,Arg对SBMIE-许氏平鲉生长性能及形体指标具有显著影响。D2和D3组许氏平鲉的末体重和增重率显著高于D0组(P < 0.05),D1组与其他各组差异均不显著(P > 0.05);D1、D2和D3组肝体比和脏体比均显著低于D0组(P < 0.05);D2组肥满度显著高于其他各组(P < 0.05),D1和D3组显著高于D0组(P < 0.05);各组间存活率差异不显著(P > 0.05)。
|
|
表 3 精氨酸对SBMIE-许氏平鲉生长性能和形体指标的影响 Tab.3 Effects of arginine on growth performance and body indexes of SBMIE-S. schlegelii |
由表 4可见,添加Arg的各组许氏平鲉血清DAO活性、NO含量及iNOS活性均显著低于D0组(P < 0.05),各处理组间无显著性差异(P > 0.05);D2和D3组血清T-NOS活性显著低于D0组(P < 0.05),D1组与其他各组间无显著性差异(P > 0.05)。
|
|
表 4 精氨酸对SBMIE-许氏平鲉血清精氨酸代谢相关酶活性及代谢产物的影响 Tab.4 Effects of arginine on metabolism-related enzymes and arginine metabolites of SBMIE-S. schlegelii |
由表 5可见,各处理组间皱襞数目和肌层厚度无显著性差异(P > 0.05),添加Arg的各组,皱襞高度显著高于D0组(P < 0.05),以D2组最高,D3组与D1、D2组无显著性差异(P > 0.05)。由图 1可见,D0组肠道黏膜受到损伤,固有层增宽(图 1-1),杯状细胞数量增加,细胞核向单层柱状上皮细胞顶端移位,排列不规则(图 1-5),添加Arg的各组,肠道黏膜结构完整,固有层增宽(图 1-3)和杯状细胞增多现象明显改善(图 1-2~4),单层柱状上皮细胞排列规整,且细胞核整齐排列于细胞中下部(图 1-6~8)。
|
|
表 5 精氨酸对SBMIE-许氏平鲉肠道组织结构的影响 Tab.5 Effects of arginine on intestinal structure of SBMIE-S. schlegelii |
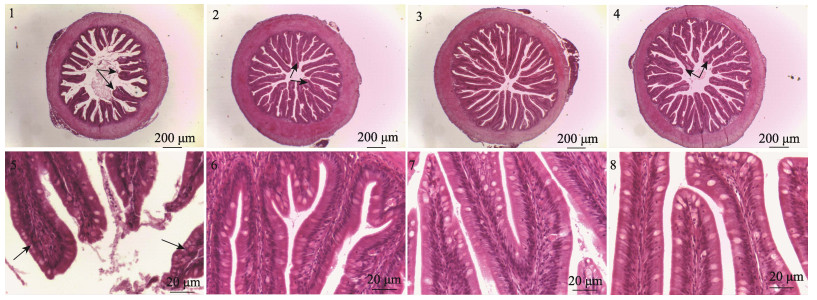
|
图 1 SBMIE-许氏平鲉肠道组织结构 Fig.1 Intestinal structure of SBMIE-S. schlegelii 图中1~4分别代表 40×下D0、D1、D2、D3组实验鱼肠道整体结构;5~8分别代表400×下D0、D1、D2、D3组肠道皱襞结构;1、2、4中箭头所示固有层增宽,5中箭头所示杯状细胞数量增加。 1~4 represent the overall structure of intestinal tract under 40× in group D0, D1, D2, and D3, respectively; 5~8 represent the intestinal fold structure under 400× in group D0, D1, D2 and D3, respectively. The arrows in figure 1, 2 and 4 indicated lamina propria widening, while the arrows in figure 5 show an increase in goblet cells. |
由表 6可见,各处理组肠道T-AOC显著高于D0组(P < 0.05),D2组显著高于其他各组(P < 0.05),D1和D3组与对照组差异不显著(P > 0.05);随着Arg添加量的升高,肠道MDA含量呈先降低后升高的趋势,D2和D3组显著低于D0组(P < 0.05),D1组与其他各组差异不显著(P > 0.05)。
|
|
表 6 精氨酸对SBMIE-许氏平鲉肠道抗氧化能力的影响 Tab.6 Effects of arginine on intestinal antioxidant capacity of SBMIE-S. schlegelii |
由图 2可见,相较于D0组,添加Arg的各组occludin mRNA相对表达量显著上调(P < 0.05),D1和D3组显著高于对照D0组(P < 0.05),D2组与其他各组均无显著差异(P > 0.05);D2组显著高于D0和D1组(P < 0.05),D1和D3组clnd15 mRNA相对表达量与D0组差异不显著(P > 0.05),D3组与D0和D2组差异不显著(P > 0.05);D1组zo-1 mRNA相对表达量显著高于其他各组(P < 0.05),D2和D3组与D0组差异不显著(P > 0.05)。
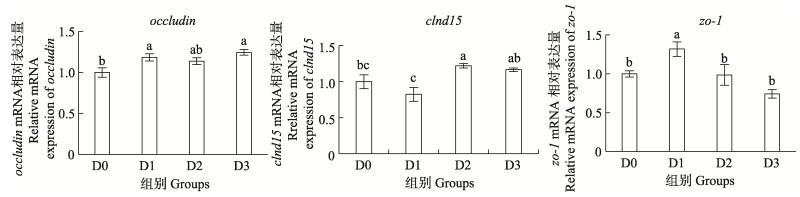
|
图 2 精氨酸对SBMIE-许氏平鲉肠道紧密连接蛋白基因表达量的影响 Fig.2 Effects of arginine on intestinal tight junction protein gene expression of SBMIE-S. schlegelii |
由图 3可见,添加Arg各组许氏平鲉肠道il-1β mRNA相对表达量下调,D1和D2组显著低于D0组(P < 0.05),D3组与其他各组间无显著差异(P > 0.05);Arg对IL-8 mRNA相对表达量无显著影响(P > 0.05);各处理组il-15和tlr8的mRNA相对表达量显著低于D0组(P < 0.05),且各处理组间差异不显著(P > 0.05);D1和D2组il-12b mRNA相对表达量显著高于D0组(P < 0.05),D3组与其他各组差异不显著(P > 0.05)。
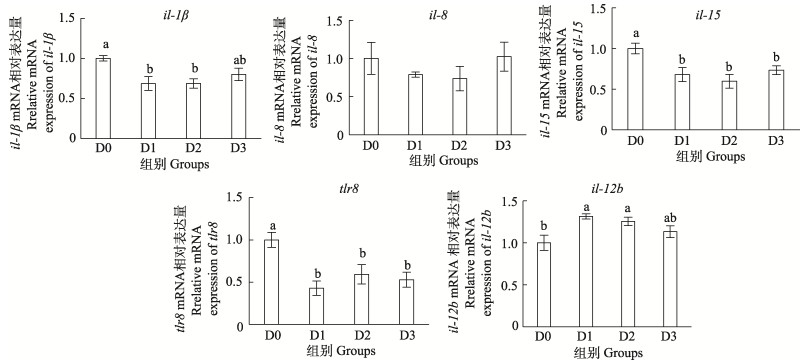
|
图 3 精氨酸对SBMIE-许氏平鲉肠道炎症因子和抗炎因子基因表达量的影响 Fig.3 Effects of arginine on intestinal inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors gene expression of SBMIE-S. schlegelii |
对斜带石斑鱼(王彦飞, 2019)、花鲈(Lateolabrax japonicus)(王亚如, 2017)、黄金鲈(Perca flavescens) (吴莉芳等, 2017)等的研究均表明,长期摄食高豆粕饲料会影响生长性能。豆粕中含有大豆抗原蛋白、皂甙、植酸、非淀粉多糖等抗营养因子(Gu et al, 2016),会降低饲料蛋白质的利用,增加内源蛋白质的分泌,最终导致粪氮增加(孙泽威等, 2005)。正常饮食情况下,健康许氏平鲉对Arg的最适需求量为2.78% (沈钰博等, 2022),本研究D0组饲料Arg水平为2.799%,满足正常许氏平鲉的基本营养需求,但SBMIE-许氏平鲉的肠道受到损伤,肠道功能的完整性直接影响鱼类生长性能,而在大菱鲆(Gu et al, 2017)、眼斑拟石首鱼(Sciaenops ocellatus)(Cheng et al, 2011)等的研究均已证明,Arg通过改善肠道功能,进而影响实验鱼生长性能。本研究在基础配方Arg水平上额外添加Arg,对许氏平鲉的增重率产生了显著的影响,2%的Arg (D2)显著提高了SBMIE-许氏平鲉的增重率,并且Arg的添加改善了肝体比、脏体比,提高了肥满度,推测Arg对SBMIE-许氏平鲉的肠道产生了积极影响,从而提高了生长性能。
二胺氧化酶(DAO)是反映肠道机械屏障受损伤程度的细胞内酶,在小肠黏膜上皮细胞绒毛中含量高、活性强,若肠黏膜细胞受损、通透性增加,细胞内DAO会通过肠道屏障释放到细胞外进入血液(卓丽欣等, 2018)。本研究Arg显著降低了血清DAO活性,提示D0组肠道细胞膜通透性增加,而Arg显著降低了DAO的释放,保护了肠黏膜屏障的完整性。诱导型NOS (iNOS)主要分布于巨噬细胞,一经产生就会催化生成大量NO (Wang et al, 2009)。NO参与上皮细胞迁移,形成新的上皮细胞,促进肠黏膜修复;在炎症反应中,致炎物可诱导局部NO合成与释放(孙红暖等, 2014),过量NO会与体内氧自由基结合生成ONOO–和NO2–,导致肠黏膜损伤(Upperman et al, 2005)。大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea)日粮添加Arg显著提高鱼血清T-NOS和肝脏T-NOS、iNOS活性,NO显著升高(Zhou et al, 2012);沈钰博等(2022)在许氏平鲉中也获得相同趋势,血清NO从对照组4.82 μmol/L提高到19.26 μmol/L。本研究Arg添加组血清T-NOS和iNOS活性显著降低,血清NO从D0组27.02 umol/L降至18.39~19.09 umol/L,与上述研究趋势相反,但Arg添加组的数值相符,原因可能是上述研究的实验鱼处于健康状态,适当添加Arg可提高NOS活性,从而增加NO的产生,而本研究D0组许氏平鲉肠道受到严重损伤,炎症反应激活了巨噬细胞iNOS的合成,增强了NO合成与释放,导致血清NO过量,而Arg可有效修复肠黏膜损伤,降低炎症反应,从而将NO的合成与释放控制在正常范围。
肠道结构的完整性与肠道吸收能力密切相关。对大西洋鳕鱼(Gadus morhua)(Refstie et al, 2006)、大菱鲆(Sun et al, 2022)、黄金鲈(吴莉芳等, 2017)等鱼的研究均表明,饲料中大量使用豆粕会导致肠道黏膜病理变化,且随着饲料豆粕比例升高及饲喂时间延长而越发严重。豆粕中含有较多的植物凝集素,与蛋白质和碳水化合物等有很强的结合能力,可作用于肠黏膜刷状缘,引起黏膜结构破坏及通透性增加(周红蕾等, 2006)。本研究D0组出现了皱襞高度降低、上皮细胞脱落、固有层增宽、杯状细胞数量增加等明显的SBMIE症状,添加Arg后肠炎症状明显改善,以D2组皱襞高度最高。在红鱼(Sciaenops ocellatus)(Cheng et al, 2011)和杂交条纹鲈鱼(Morone chrysops×Morone saxatilis)(Cheng et al, 2012)研究中也观察到类似结果:饲料添加1% Arg (豆粕提供40%饲料蛋白质),鱼的皱襞高度、肠细胞高度和微绒毛高度均有所提高。以上均表明,Arg在维护肠道黏膜结构完整性方面的积极作用。
T-AOC高低体现机体清除活性氧自由基、保护细胞膜和细胞内核酸抵御自由基氧化损伤能力的高低(卓丽欣等, 2018)。MDA是生物体内脂质氧化的终产物,具有细胞毒性,能间接反映机体是否存在氧化损伤。对大黄鱼(吴钊, 2016)、奥尼罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus ×O. aureus)(Lin et al, 2011)、黄金鲫(Carassius auratus)(王婧瑶等, 2022)等的研究均表明,豆粕过量替代鱼粉会降低鱼体抗氧化能力。本研究D0组肠道T-AOC最低而MDA含量最高,与上述结果一致。可能是D0组许氏平鲉长期大量摄入豆粕造成了肠道黏膜损伤,机体过量自由基得不到及时清除,产生大量脂质过氧化产物MDA (李学丽等, 2017)。而添加Arg各组肠道T-AOC显著升高,MDA显著降低,表明Arg可以改善由高剂量豆粕引起的机体氧化损伤,在草鱼(陈娇娇, 2017)、黄颡鱼(Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) (陈启明, 2016)上也得到了类似结论。Tan等(2010)研究表明,Arg能刺激细胞增殖并预防内毒素引起的肠细胞死亡,可能是Arg修复了受损的肠道黏膜,保护肠道细胞免受损伤,从而恢复了机体抗氧化能力。
肠道紧密连接通透性决定肠道黏膜屏障的功能,跨膜蛋白[如闭锁蛋白(occludin)和闭合蛋白(claudin,CLND)]以及胞质蛋白(如zo-1)构成紧密连接的复杂蛋白质结构,zo-1通过氨基端的PDZ结构域和occludin、claudin直接连接,在紧密连接的结构组成中发挥重要作用(孔瑶瑶等, 2020)。对珍珠龙胆石斑鱼(Epinephelus fuscoguttatus ♀× Epinephelus lanceolatus ♂)的研究表明,紧密连接相关基因occludin、clnd15a、zo-1在前、中、后肠表达量都较高,提示三者在维护肠道黏膜屏障功能上的关键作用(陈东鸿等, 2021)。zo-1表达量在相当程度上受饲料营养素的影响和调节(孔瑶瑶等, 2020),在Arg (Chen et al, 2018)、谷氨酸(Jiang et al, 2017)、缬氨酸(Luo et al, 2014)上均得到证实。对大菱鲆的研究表明,40%豆粕显著降低了大菱鲆肠道紧密连接蛋白相关基因表达量而引发肠道炎症(Chen et al, 2018)。Arg作为功能性氨基酸,可能主要通过改善肠道黏膜屏障功能来减轻肠道疾病,对珍珠龙胆石斑鱼(陈东鸿等, 2021)和草鱼(陈娇娇, 2017)的研究表明,Arg可能通过增加occludin和clnd15a基因表达水平,加强与ZOs对紧密连接“锁扣”结构的“闭合”调控,从而保障肠黏膜屏障的功能。建鲤幼鱼饲料中Arg缺乏导致肠道紧密连接蛋白表达异常(Wang et al, 2016)。本研究D0组30%的豆粕添加量肠道occludin、clnd15、zo-1三种紧密连接蛋白基因的相对表达量均受到影响,Arg的添加显著上调了3个基因的相对表达量,与上述研究结果一致,表明Arg在修复肠黏膜屏障方面具有一定作用。
鱼类肠黏膜免疫状态与炎症反应密切相关,肠黏膜受损会引起通透性增加,细菌、毒素等会激活肠黏膜淋巴组织,引发免疫反应并释放大量促炎因子,影响肠上皮细胞对营养物质的吸收和对离子的转运(王亚如, 2017)。SBMIE通常与白细胞介素(il)、TLRs等促炎细胞因子基因的高表达有关(Zhao et al, 2019),il-1β、IL-8、il-12b、il-15和tlr8是肠道免疫的重要调节因子,在黏膜损伤或感染反应中起着关键作用(Wang et al, 2017)。il-1β主要由活化的巨噬细胞和单核细胞产生,对肠上皮通透性有刺激作用(Planchon et al, 1994)。TLRs能够识别肠道病原体相关分子,转化为参与肠道炎症控制的信号,使炎症处于控制之下(Zhao et al, 2019)。大菱鲆(Zhao et al, 2019)和斜带石斑鱼(Wang et al, 2017)摄食高剂量豆粕,肠道il-1β和TLRs相关分子基因表达上调,肠黏膜受损,而饲料中添加1%Arg显著抑制了大菱鲆肠道促炎因子的表达,提高了抗炎因子在后肠的表达(Chen et al, 2018);在培养基中添加Arg,显著降低了脂多糖诱导处理的细胞TLR4的表达(Tan et al, 2010)。本研究Arg添加组肠道炎症程度较D0组显著降低,与il-1β、IL-8、il-15和tlr8表达水平呈正相关,与il-12b表达水平呈负相关,提示Arg可通过降低促炎因子水平和提高抗炎因子水平缓解肠道炎症。另有研究表明,il-1β等促炎因子能够抑制紧密连接蛋白基因的表达(石丹等, 2015),推测Arg通过抑制促炎因子的表达,从而促进细胞间紧密连接蛋白合成,增强鱼类上皮细胞间物理屏障功能。
4 结论本实验条件下,高豆粕饲料中添加Arg能显著提高SBMIE-许氏平鲉的生长性能和抗氧化性能,改善Arg代谢和肠道组织结构,上调肠道紧密连接蛋白和抗炎因子相关基因的表达,下调炎症因子相关基因的表达。因此,Arg (以2%最佳)对许氏平鲉豆粕型肠炎具有修复作用。
CHEN D H, CUI X, LI G, et al. Clone of zonula occluden-1, occludin and claudin-15a genes from hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus ♀×Epinephelus lanceolatus ♂) and its expression in intestinal tissue under intervention of arginine. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(8): 4645-4661 [陈东鸿, 崔晓, 李广, 等. 珍珠龙胆石斑鱼闭锁小带蛋白-1、闭锁蛋白和跨膜蛋白-15a基因的克隆及其在精氨酸干预下的肠道组织表达. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(8): 4645-4661 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.08.044] |
CHEN J J. Studies on the regulation and the related mechanism of arginine on growth and intestinal structure of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Master's Thesis of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017 [陈娇娇. 精氨酸对草鱼幼鱼生长、肠道结构调控及机制研究. 华中农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2017]
|
CHEN Q M. Effects of dietary arginine levels on growth, immunity and intestinal health of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Masterxs Thesis of South China Agricultural University, 2016 [陈启明. 精氨酸对黄颡鱼生长、免疫及肠道健康的影响. 华南农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2016]
|
CHEN Z C, LIU Y, LI Y X, et al. Dietary arginine supplementation mitigates the soybean meal induced enteropathy in juvenile turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L. Aquaculture Research, 2018, 49(4): 1535-1545 DOI:10.1111/are.13608 |
CHENG Z Y, ALEJANDRO B, DELBERT M G. Effects of dietary arginine and glutamine on growth performance, immune responses and intestinal structure of red drum, Sciaenops ocellatus. Aquaculture, 2011, 319(1): 247-252 |
CHENG Z Y, GATLIN D M, BUENTELLO A. Dietary supplementation of arginine and/or glutamine influences growth performance, immune responses and intestinal morphology of hybrid striped bass (Morone chrysops×Morone saxatilis). Aquaculture, 2012, 362/363: 39-43 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.07.015 |
GU M, BAI N, XU B, et al. Protective effect of glutamine and arginine against soybean meal-induced enteritis in the juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2017, 70: 95-105 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2017.08.048 |
GU M, BAI N, ZHANG Y, et al. Soybean meal induces enteritis in turbot Scophthalmus maximus at high supplementation levels. Aquaculture, 2016, 464: 286-295 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.06.035 |
JIANG H L, QIN G X, CHE D S, et al. Effect of arginine on piglet intestinal mechanical barrier and related mechanism. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2015, 37(1): 83-87 [姜海龙, 秦贵信, 车东升, 等. 精氨酸对仔猪肠道机械屏障的影响及相关机理. 吉林农业大学学报, 2015, 37(1): 83-87] |
JIANG J, SHI D, ZHOU X Q, et al. In vitro and in vivo protective effect of arginine against lipopolysaccharide induced inflammatory response in the intestine of juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 42(2): 457-464 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2014.11.030 |
JIANG J, YIN L, LI J Y, et al. Glutamate attenuates lipopolysaccharide induced oxidative damage and mrna expression changes of tight junction and defensin proteins, inflammatory and apoptosis response signling molecules in the intestine of fish. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2017, 70: 473-484 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2017.09.035 |
KONG Y Y, MA X H, MAI K S, et al. Research progress of effects of diet nutrients on intestinal tight junction protein zonula occludens-1 of fish. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(11): 5081-5088 [孔瑶瑶, 马秀华, 麦康森, 等. 饲料营养素对鱼类肠道紧密连接蛋白闭锁小带蛋白-1影响的研究进展. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(11): 5081-5088 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.11.014] |
LI B S, WANG J Y, WANG C Q, et al. Development of formula diet and current situation of culture industry of Korean rockfish Sebastes schlegeli. Open Journal of Fisheries Research, 2019, 6(2): 1-10 [李宝山, 王际英, 王成强, 等. 许氏平鲉配合饲料的研究进展及产业发展现状. 水产研究, 2019, 6(2): 1-10] |
LI X L, WANG J Y, SONG Z D, et al. Research on partial replacement of fishmeal by two kinds of soybean meal in the feed of juvenile ♀ Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂ Epinephelus lanceolatus. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2017, 26(5): 716-725 [李学丽, 王际英, 宋志东, 等. 两种豆粕部分替代鱼粉在珍珠龙胆石斑鱼幼鱼饲料中的研究. 上海海洋大学学报, 2017, 26(5): 716-725] |
LIN S M, LUO L. Effects of different levels of soybean meal inclusion in replacement forfish meal on growth, digestive enzymes and transaminase activities inpractical diets for juvenile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus×O. Aureus. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2011, 168: 80-87 DOI:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2011.03.012 |
LUO J B, FENG L, JIANG W D, et al. The impaired intestinal mucosal immune system by valine deficiency for young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) is associated with decreasing immune status and regulating tight junction proteins transcript abundance in the intestine. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2014, 40(1): 197-207 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2014.07.003 |
MERRIFIELD D L, DIMITROGLOU A, BRADLEY G, et al. Soybean meal alters autochthonous microbial populations, microvilli morphology and compromises intestinal enterocyte integrity of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Journal of Fish Diseases, 2009, 32(9): 755-766 DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2761.2009.01052.x |
PLANCHON S M, MARTINS C, GUERRANT R L, et al. Regulation of intestinal epithelial barrier function by TGF-beta 1. Evidence for its role in abrogating the effect of a T cell cytokine. Journal of Immunology, 1994, 153(12): 5730-5739 DOI:10.4049/jimmunol.153.12.5730 |
REFSTIE S L, LANDSVERK T, BAKKE-MCKELLEP A M, et al. Digestive capacity, intestinal morphology, and microflora of 1-year and 2-year old atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) fed standard or bioprocessed soybean meal. Aquaculture, 2006, 261(1): 269-284 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.07.011 |
SHEN Y B, WANG J Y, LI B S, et al. Dietary arginine requirement of juvenile rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2022, 43(3): 33-44 [沈钰博, 王际英, 李宝山, 等. 许氏平鲉幼鱼对饲料中精氨酸需求量的研究. 渔业科学进展, 2022, 43(3): 33-44] |
SHI D, ZHOU X Q, ZHAO Y, et al. Effects of arginine on immune function in fish and its mechanism. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2015, 27(10): 3026-3032 [石丹, 周小秋, 赵叶, 等. 精氨酸对鱼类免疫功能的影响及其机制. 动物营养学报, 2015, 27(10): 3026-3032 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2015.10.006] |
SUN H N, YANG H M, WANG Z Y, et al. Nutrition physiological and immune functions of arginine in animals. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2014, 26(1): 54-62 [孙红暖, 杨海明, 王志跃, 等. 精氨酸对动物的营养生理免疫作用. 动物营养学报, 2014, 26(1): 54-62 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2014.01.008] |
SUN H Y, ZHANG J J, WANG W T, et al. The effects of sodium propionate supplementation in the diet with high soybean meal on growth performance, intestinal health, and immune resistance to bacterial infection in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture Nutrition, 2022, 2022: 8952755 |
SUN Z W, QIN G X, ZHANG Q H. Effects of soybean antigen protein on growth performance, dietary nutrient digestibility and intestinal absorption capacity of calves. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2005, 11: 33-36 [孙泽威, 秦贵信, 张庆华. 大豆抗原蛋白对犊牛生长性能、日粮养分消化率和肠道吸收能力的影响. 中国畜牧杂志, 2005, 11: 33-36] |
TAN B, YIN Y, KONG X, et al. L-arginine stimulates proliferation and prevents endotoxin-induced death of intestinal cells. Amino Acids, 2010, 38(4): 1227-1235 DOI:10.1007/s00726-009-0334-8 |
UPPERMAN J S, POTOKA D A, GRISHIN A, et al. Mechanisms of nitric oxide-mediated intestinal barrier failure in necrotizing enterocolitis. Seminars in Pediatric Surgery, 2005, 14(3): 159-166 DOI:10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2005.05.004 |
WAN J L, MAI K S, AI Q H. The recent advance on arginine nutritional physiology in fish. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2006, 13(4): 679-685 [万军利, 麦康森, 艾庆辉. 鱼类精氨酸营养生理研究进展. 中国水产科学, 2006, 13(4): 679-685 DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2006.04.027] |
WANG B, FENG L, CHEN G F, et al. Jian carp (Cyprinus Carpio var. Jian) intestinal immune responses, antioxidant status and tight junction protein mRNA expression are modulated via Nrf2 and PKC in response to dietary arginine deficiency. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2016, 51: 116-124 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2015.10.032 |
WANG J Y, WU L F, WANG D, et al. Effects of replacing fish meal with soybean meal on growth, digestive enzyme activity and non-specific immune indexes of Carassius auratus. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2022, 44(1): 104-111 [王婧瑶, 吴莉芳, 王东, 等. 豆粕替代鱼粉对黄金鲫生长、消化酶活力及非特异性免疫指标的影响. 吉林农业大学学报, 2022, 44(1): 104-111] |
WANG W W, QIAO S Y, LI D F. Amino acids and gut function. Amino Acids, 2009, 37(1): 105-110 DOI:10.1007/s00726-008-0152-4 |
WANG Y F. Effects of fish meal replacement with extruded or common soybean meal on the growth performance and gut-barrier function of grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Masterxs Thesis of Jimei University, 2019 [王彦飞. 膨化和普通豆粕替代鱼粉对斜带石斑鱼生长性能和肠道屏障的影响. 集美大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2019]
|
WANG Y R, WANG L, ZHANG C X, et al. Effects of substituting fishmeal with soybean meal on growth performance and intestinal morphology in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Aquaculture Reports, 2017, 5(C): 52-57 |
WANG Y R. Effects of substituting fishmeal with soybean meal on growth performance and intestinal healthy in Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus). Masterxs Thesis of Jimei University, 2017 [王亚如. 豆粕替代鱼粉对花鲈生长性能和肠道健康的影响. 集美大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2017]
|
WU L F, QU Z H, ZHOU K, et al. Effects of replacing fish meal with soybean meal on growth and intestinal tissue of Perca flavescens. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(6): 1-8 [吴莉芳, 瞿子惠, 周锴, 等. 豆粕替代鱼粉对黄金鲈生长及肠道组织的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(6): 1-8] |
WU Z. Research on the partial replacement of fish meal by different processing soybean meal in the diet of Pseudosciaena crocea. Master's Thesis of Shanghai Ocean University, 2016 [吴钊. 不同工艺的豆粕部分替代鱼粉在大黄鱼饲料中的研究. 上海海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2016]
|
ZHAO S F, CHEN Z C, ZHENG J, et al. Citric acid mitigates soybean meal induced inflammatory response and tight junction disruption by altering TLR signal transduction in the intestine of turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2019, 92: 181-187 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2019.06.004 |
ZHOU H L, LI C L, WANG G P, et al. Anti-nutritional factors in soybean meal and their removal methods. Feed Industry, 2006(3): 23-26 [周红蕾, 李春玲, 王贵平, 等. 大豆中抗营养因子及其去除方法概述. 饲料工业, 2006(3): 23-26 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-991X.2006.03.007] |
ZHOU Q C, ZENG W P, WANG H L, et al. Dietary arginine requirement of juvenile yellow grouper Epinephelus awoara. Aquaculture, 2012, 350/351/352/353: 175-182 |
ZHUO L X, ZHAO H X, HUANG Y H, et al. Influence of oxidized fish oil on the intestinal health of juvenile yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) and the use of arginine as an intervention measure. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2018, 42(1): 100-111 [卓丽欣, 赵红霞, 黄燕华, 等. 氧化鱼油对黄颡鱼幼鱼肠道健康的影响及精氨酸的干预作用. 水产学报, 2018, 42(1): 100-111] |



