2. 中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所 青岛海洋科技中心海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程功能实验室 山东 青岛 266237
2. Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Qingdao Marine Science and Technology Center, Qingdao 266237, China
鱼皮是鱼体中具有保护、感知或激素代谢等重要功能的多用途组织(Rakers et al, 2010)。鱼皮主要由表皮层、鳞片层、真皮层及皮下组织层构成,不同鱼类由于生活环境和习性的不同,其鱼皮的组织结构也不同(Hawkes, 1974; Whitear et al, 1980)。此外,鱼皮中含有丰富的胶原蛋白(Blanco et al, 2017; De Souza et al, 2022),利用组织学技术可直观地分辨鱼皮具体的组织结构(Bancroft et al, 2008),有助于了解鱼皮结构与功能之间的关系(Mittal et al, 1976)、提供生理学和病理学研究背景(Natasha et al, 2015)、设计与鱼皮相关产品的工艺等(Alla et al, 2017; Oslan et al, 2022)。目前,国内外仅有部分鱼皮组织结构的研究报道(李芳等, 2012; Pittman et al, 2013; Kucukakin et al, 2016; Al-Halani, 2018; Sadi et al, 2021)。
绿鳍马面鲀(Thamnaconus septentrionalis)具有高蛋白、低脂肪等特点,富含多种必需氨基酸,营养丰富,是深受人们喜爱的海洋经济性鱼类(王晓然等, 2023; 晋怀远等, 2023),在日本、朝鲜、我国渤海、黄海和东海一带均有分布,其中,东海曾是我国绿鳍马面鲀捕捞的主要海区(李凤辉等, 2019)。由于绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮质地较硬、食用性差、易于剥离,常剥去鱼皮食用,俗称剥皮鱼、橡皮鱼等(徐大凤等, 2018)。近些年,绿鳍马面鲀人工繁育及养殖技术得到突破,在我国沿海地区已陆续开展网箱养殖,产业规模越来越大(刘琨等, 2019)。据估算,绿鳍马面鲀养殖年产量有望达到100多万t,其鱼皮约占鱼重的6%~7%,可产鱼皮约6~7万t。因此,如何利用绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮资源是一个重要课题。目前,国内外对绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮资源的研究主要为提取胶原蛋白、多肽,制备鱼皮革、明胶、脱细胞基质等。Kim等(2002)研究了从绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮和内脏中提取胶原酶;楚水晶等(2010)和宋正规等(2018)使用酶法从绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮中提取胶原蛋白;夏姗姗等(2014)优化了绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮胶原蛋白的提取工艺;周存山等(2015)制备了绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮蛋白抗氧化肽,模拟了胃肠道消化过程;Hatab等(2017)利用胰蛋白酶从绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮等副产物中处理得到的水解物(hydrolysis of filefish byproduct-trypsin, HFBP-T),可作为食品中的天然抗菌剂;蔡金秀等(2022)从绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮中制备血管紧张素转化酶(angiotensin-converting enzyme, ACE)抑制肽作为食品中的天然抗菌素;靳挺等(2021)优化了绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮明胶制备工艺。此外,杨雨滋等(1995)和刘勋勋等(2016)利用绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮制备了鱼皮革;Cai等(2014)根据绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮的鳞片结构特点制备了仿生材料。
绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮具有特殊的鳞片结构(苏锦祥等, 1988; Cai et al, 2014),但除鳞片以外的具体结构还未有报道。本研究通过扫描电镜(SEM)、冰冻切片和组织学染色等方法对绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮的表皮层、鳞片层、真皮层和皮下组织层进行观察,并绘制结构模式图,旨在为开发利用绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮资源提供基础资料。
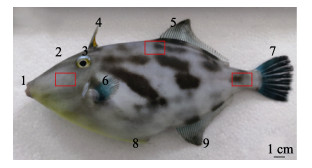
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料实验用鱼选自山东省烟台天源水产有限公司人工养殖的绿鳍马面鲀,共计6尾,平均体长为(24.49± 2.56) cm,体重为(321.47±77.19) g。头部位置选取胸鳍左上部组织为取样处,中部位置选取靠近第2背鳍处的组织作为取样处,尾部位置取尾鳍附近的组织作为取样处(图 1)。
|
图 1 绿鳍马面鲀体表各部位示意 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of each part of the T. septentrionalis 1:口;2:鼻孔;3:眼;4:第1背鳍棘;5:第2背鳍;6:胸鳍;7:尾鳍;8:短鳍棘;9:臀鳍。红色方框内为取样范围。 1: Mouth; 2: Nostril; 3: Eyes; 4: The first dorsal fin spine; 5: The second dorsal fin; 6: Pectoral fin; 7: Caudal fin; 8: Short fin spine; 9: Anal fin. The sampling sites are in the red boxes. |
由于绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮质地较硬,采用常规石蜡切片,鱼皮极易卷曲,成片效果不好,所以本研究采用冰冻切片,并使用OCT (optimal cutting temperature compound)包埋剂(Servicebio)进行包埋。取新鲜的绿鳍马面鲀的鱼皮组织样本(1 cm3, n=6),使用PBS溶液冲洗3次后放入带有编号的4%多聚甲醛固定液中,固定24 h后,将鱼皮从固定液中取出,分别置于15%和30%的蔗糖溶液于4 ℃下梯度脱水沉底。将脱水的鱼皮取出,使用滤纸将表面水分稍吸干后,将鱼皮组织的横切面、纵切面分别朝上,置于包埋台上,并在鱼皮组织周围滴入OCT包埋剂。将包埋台放在冰冻切片机(Thermo, CryoStar NX50,美国)的速冻台上速冻包埋,待OCT变白、变硬后,将样本托固定于切片机上进行切片(8~10 μm),将组织贴于载玻片上后风干,–20 ℃保存。
1.2.2 组织切片染色方法 1.2.2.1 苏木精–伊红染色(HE染色)苏木精–伊红染色法(hematoxylin-eosin staining),简称HE染色,是组织学中最基础且使用最广泛的技术方法之一(Feldman et al, 2014),鱼皮组织可以被苏木精–伊红染料附着不同的颜色,从而帮助分辨细胞核、胶原纤维和肌肉等。将绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮冰冻切片恢复至室温,经固定液固定、水洗后,使用HE染液套装(Servicebio)进行常规染色,切片经彻底脱水透明后,滴加中性树胶封片。
1.2.2.2 过碘酸–雪夫染色(PAS染色)过碘酸–雪夫染色法(Periodic acid-Schiff),简称PAS染色,可染色组织中糖原、黏液细胞、网状膜和基底膜、某些弹性组织、纤维蛋白和各种成分不明的物质(Wislocki et al, 1949)。将绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮冰冻切片恢复至室温,经固定液固定、水洗后,使用PAS染液套装(Servicebio)进行常规染色,切片经HCl水溶液分化、氨水返蓝、流水冲洗、彻底脱水透明后,滴加中性树胶封片。
1.2.2.3 马森三色染色(Masson染色)马森三色染色(Masson's trichrome staining),简称Masson染色,是显示动物组织中胶原纤维的常用染色方法之一,利用不同大小分子量的阴离子生物染料在结缔组织中的渗透性,可使不同的组织成分呈现不同的颜色(Calvi et al, 2012)。为探究绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮各个部位胶原纤维的分布情况,选取鱼体头部、中部、尾部位置的鱼皮进行切片,冰冻切片恢复至室温水洗后,采用Masson染液套装(Servicebio)对其进行染色,切片经1%醋酸漂洗分化、彻底脱水透明后,滴加中性树胶封片。
1.2.2.4 Van Gieson染色(VG染色)VG染色(Van Gieson staining)是利用2种不同分子量大小的阴离子染料对胶原纤维进行鉴别染色(Prentø, 1993)。为辅助HE和Masson染色观察鱼皮的胶原纤维分布情况,冰冻切片恢复至室温水洗后,使用VG染液套装(Servicebio)对其进行快速染色、水洗,经彻底脱水透明后,滴加中性树胶封片。
1.2.3 鳞片染色参照盖珊珊等(2020)的方法进行染色,使用0.5% KOH和足量的茜素红配制染色液,取新鲜的绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮第2背鳍附近的鱼皮组织进行染色,直至染为紫红色后,移至0.5% KOH溶液中浸泡48~72 h,待稍微颜色变浅、透明后,在体试镜(Nikon, SMZ1000,日本) 40×条件下进行观察染色后的骨质鳞片形态。
1.2.4 SEM观察快速取新鲜的绿鳍马面鲀第2背鳍附近的鱼皮组织(3 mm2),放入2.5%戊二醛溶液中,在4 ℃条件下固定24 h后,将组织取出。使用30%~100%酒精梯度脱水后,在临界点干燥仪(Quorum, K850, 英国)中干燥,将干燥后的组织紧贴于导电碳膜双面胶上,并放入离子溅射仪(Hitachi, MC1000, 日本)的样品台上进行喷金30 s,采用扫描电子显微镜(Hitachi, SU8100, 日本)摄片,观察绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮的层次分布和鳞片结构。
1.3 数据处理将所得的切片放置在数字扫描仪(Pannoramic MIDI, 3D Histech, 日本)的切片载盘上,在40×条件下选择手动扫描,扫描得到的图像使用SlideViewer (3DHISTECH)、ImageJ和Photoshop软件进行分析;扫描电镜图像采用ImageJ和Photoshop软件进行分析。
所测量的实验数据均通过SPSS 25.0统计软件计算平均值±标准差(Mean±SD)。
2 结果与分析切片染色和SEM的结果表明,绿鳍马面鲀同其他硬骨鱼类的鱼皮结构类似,是由表皮层[(26.81± 7.44) μm]、鳞片层[(279.62±12.83) μm]、真皮层[(188.77±15.99) μm]和皮下组织层组成,皮肤总厚度为(0.60±0.04) mm。
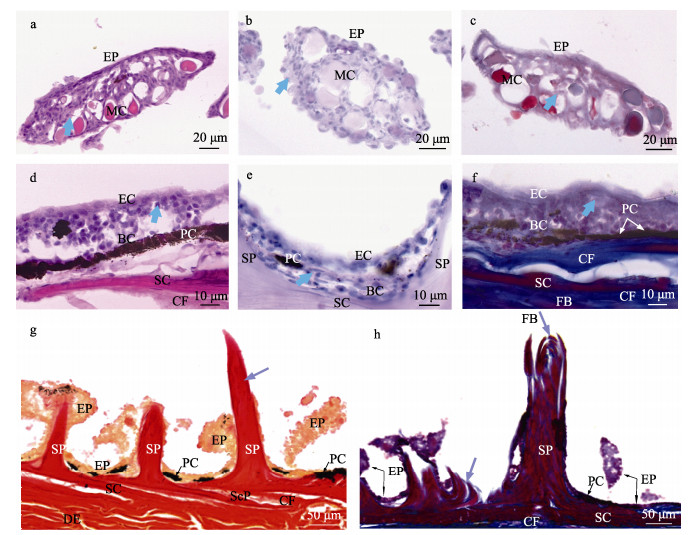
2.1 鱼皮表皮层特征绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮上分布的锥状骨质凸起外围被厚度约为(10.41±1.04) μm (n=90)的上皮细胞包围。靠近鳞片基板处的表皮厚度为(26.81±7.48) μm (n= 90),包括基底细胞和上皮细胞,基底细胞为表皮的最下层细胞,整齐地排列在基底膜上(图 2e),上皮细胞呈多边形状,紧密排列,覆盖着与细胞边缘不平行、为环状结构的微嵴(图 4b)。对锥状骨质凸起的表皮进行HE、PAS和Masson染色,在不同染色条件下,均可见形态、大小相似,细胞核体积较小的上皮细胞和体积较大的卵圆形或椭圆形的黏液细胞。
|
图 2 绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮切片染色 Fig.2 The skin of the T. septentrionalis by slice staining a、d:表皮纵切HE染色;b、e:表皮纵切PAS染色;c、f:表皮纵切Masson染色;g:锥状骨质突起纵切VG染色;h:锥状骨质突起纵切Masson染色。蓝色箭头指向的为上皮细胞的细胞核;紫色箭头指向为层状骨片。EP:表皮;SP:锥状骨质凸起;SC:鳞片基板;ScP:鳞囊;EC:上皮细胞;BC:基底细胞;PC:色素细胞;MC:黏液细胞;FB:成纤维细胞;CF:胶原纤维;DE:真皮层。 a, d: HE staining by longitudinal sectioning of epidermis; b, e: PAS staining by longitudinal incision of epidermis; c, f: Masson staining by longitudinal incision of epidermis; g: VG staining by longitudinal incision of spine of conical bone; h: Masson staining by longitudinal incision of spine of conical bone. Blue arrows point to the nuclei of epithelial cells; Purple arrows point to thin bone plates layered on top of each other. EP: Epidermis; SP: Spine of conical bone; SC: Scale substrate; ScP: Scale pocket; EC: Epithelial cells; BC: Basal cells; PC: Pigment cells; MC: Mucous cells; FB: Fibroblast; CF: Collagen fibers; DE: Dermis. |
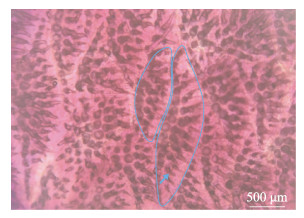
绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮表面触感如砂纸,鳞片层由成排的锥状骨质凸起和基板组成。经茜素红染色处理后,可见锥状骨质凸起,其根部牢牢固定于基板,每个基板上大致有2~4行呈放射状的锥状骨质凸起(图 3),凸起呈实心圆锥状,顶端弯曲,方向不一,露于体外,被上皮细胞所组成的褶皱状表皮所包围(图 4f),其长度为(257.13±10.41) μm (n=90)。经VG和Masson染色发现,锥状骨质凸起的主要成分为胶原基质,分别显示为红色和蓝色。结合切片染色和SEM扫描发现,锥状骨质凸起是由层状含有胶原成分的骨片形成的实心体(图 2g、h)。
|
图 3 绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮鳞片染色 Fig.3 Scale staining of the skin of the T. septentrionalis 蓝色线条为部分鳞片基板的轮廓,蓝色箭头指向锥状骨质凸起。 The blue line is the outline of part of the scale substrate, and the blue arrow is the spine of conical bone. |

|
图 4 绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮扫描电镜 Fig.4 The skin of the T. septentrionalis by SEM a、d:鱼皮俯视图;b、c、e为放大的经SEM扫描的局部位置俯视图,其中,红色箭头指向表皮,绿色箭头指向锥状骨质凸起裂开的一层一层的薄骨板;f:经SEM扫描的局部位置侧视图;黄色箭头指向鳞片基板根部裸露的形状、大小不一的小齿,白色椭圆内为2个鳞片基板呈叠瓦状排列的交界处。EP:表皮;SP:锥状骨质凸起;SC:鳞片基板;ScP:鳞囊。 a, d: Top view of fish skin; b, c, e: Enlarged top views of local positions scanned by SEM, in which the red arrow points to the epidermis and the green arrow points to the thin bone plate which is cracked by cone-shaped bone protrusion; f: Side view of local position scanned by SEM; The yellow arrow points to small teeth with different sizes, which are exposed at the root of the scale substrate, and the white ellipse is the junction of two scale substrates arranged in a shingle shape. EP: Epidermis; SP: Spine of conical bone; SC: Scale substrate; ScP: Scale pocket. |
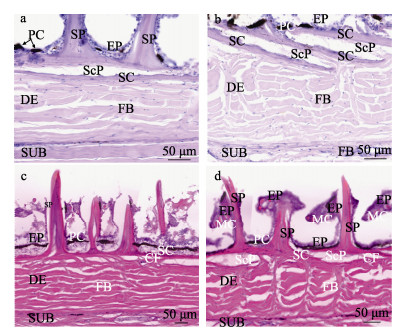
各鳞片的基板呈覆瓦状排列,鳞片基板在真皮层上方(图 4f和图 5b),鳞片基板的形状不一,呈不规则多边形,厚度为(22.49±5.19) μm (n=90)。基板根部上分布着大小、形状不一的小齿,部分基板深入真皮层上方,周围被胶原纤维所包围。
|
图 5 绿鳍马面鲀真皮层切片染色 Fig.5 Staining of dermal sections of the skin of the T. septentrionalis a:真皮层横切PAS染色;b:真皮层纵切PAS染色;c:真皮层横切HE染色;d:真皮层纵切HE染色。EP:表皮;SP:锥状骨质凸起;SC:鳞片基板;ScP:鳞囊;PC:色素细胞;MC:黏液细胞;FB:成纤维细胞;CF:胶原纤维;DE:真皮层;SUB:皮下组织层。 a: PAS staining of dermis by transect; b: PAS staining of dermis by longitudinal cut; c: HE staining of dermis by transect; d: HE staining of dermis by longitudinal cut. EP: Epidermis; SP: Spine of conical bone; SC: Scale substrate; ScP: Scale pocket; PC: Pigment cells; MC: Mucous cells; FB: Fibroblast; CF: Collagen fibers; DE: Dermis; SUB: Subcutaneous. |
绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮的真皮层位于鳞片层的下方,是绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮的主要成分,厚度约为表皮层的9倍,平均厚度为(176.97±21.11) μm (n=180),与锥状骨质凸起的高度比近似1∶1.5。HE和PAS染色显示,绿鳍马面鲀的真皮层内由纵横交错的纤维结缔组织构成,胶原纤维被HE染液染成粉色,在真皮层内未观察到脂肪细胞(图 5c、d)。从横切角度来看,真皮中散落分布着垂直于表皮层的胶原纤维束,纤维束分布较为紧密,呈“波浪”形(图 5a、c);从纵切角度来看,真皮中散落分布着较多的垂直于表皮层的胶原纤维束,整体呈“人”字形(图 5b、d)。Masson染色可以很好地分辨胶原纤维与肌纤维、胞质等在不同部位的分布情况,可看出绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮真皮层内的纤维束互相交错在一起(图 5),胶原束的方向几乎与皮面平行,并互相交织在一起,胶原纤维呈“人”字形,在一个水平面上向各方向延伸。不同部位的鱼皮真皮层测量数据见表 1。从表 1可以看出,头部的鱼皮真皮层内的纤维束在不同角度下均较为粗短,平均宽度为(13.00±2.63) μm (n=60),分布较为杂乱,真皮层厚度约为(180.84±15.35) μm (n=60) (图 6a、b);中部的鱼皮真皮层内的纤维束在横切角度下排列较为紧密,在纵切角度下排列较为疏松,纤维束整体较细长,平均宽度为(9.89±2.44) μm (n=60),真皮层的平均厚度为(188.77±15.99) μm(n=60)(图 6c、d),尾部的纤维束在不同角度的排列均较为紧密、细长,纤维束平均宽度为(9.70±2.03) μm (n=60),真皮层的平均厚度为(161.31±21.32) μm (n=60) (图 6e、f)。
|
|
表 1 绿鳍马面鲀不同部位皮肤真皮层的测量数据(平均值±标准差) (μm) Tab.1 Measurements of different parts of the dermis of T. septentrionalis (Mean±SD)(μm) |

|
图 6 绿鳍马面鲀真皮层不同部位的Masson染色 Fig.6 Masson staining of dermis in different parts of the T. septentrionalis a:头部真皮层横切;b:头部真皮层纵切;c:中部真皮层横切;d:中部真皮层纵切;e:尾部真皮层横切;f:尾部真皮层纵切。白色线段为真皮层标注;DE:真皮层。 a: Transverse section of head dermis; b: Longitudinal section of the head dermis; c: Transection of middle dermis; d: Longitudinal section of middle dermis; e: Transverse section of caudal dermis; f: Longitudinal section of caudal dermis. The white line segment marks the dermis; DE: Dermis. |
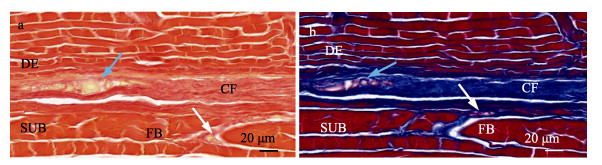
绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮的皮下组织层分布较多的结缔组织,有少量的非纤维间质(图 7)。经VG和Masson染色后,可以清晰地看到皮下组织层的主要结缔组织为胶原纤维,含有少量胞质和红细胞,皮下组织层的肌纤维被胶原纤维束所包围,且皮下组织层与真皮层界限明显。
|
图 7 绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮皮下组织切片染色 Fig.7 Staining of subcutaneous tissue sections of the skin of the T. septentrionalis a:经VG染色的皮下组织层;b:经Masson染色的皮下组织层。其中,白色箭头和蓝色箭头分别指向非纤维间质。DE:真皮层;SUB:皮下组织层;FB:纤维束;CF:胶原纤维。 a: Subcutaneous tissue stained by VG; b: Subcutaneous tissue stained by Masson. The white arrow and the blue arrow point to the non-fibrous interstitial respectively. DE: Dermis; SUB: Subcutaneous; FB: fibroblast; CF: Collagen fiber. |
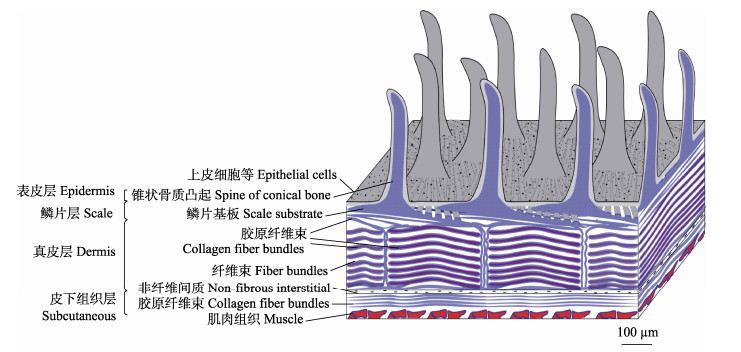
根据SEM及组织切片染色结果可以看出,绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮由表皮层、鳞片层、真皮层和皮下组织层组成,组织结构见图 8 (正面为纵切,侧面为横切)。
|
图 8 绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮组织结构模式 Fig.8 The skin structure pattern diagram of the T. septentrionalis |
表皮层的主要作用是为鱼体提供一定的保护、分泌和免疫等作用(Mittal et al, 1976),通过SEM观察,在绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮表皮层上发现了表面结构——微嵴,其可感应不同来源的压力、对创伤的机械防御,并可能有助于将黏液分泌物保持在皮肤表面,从而适应生存环境(Yamada, 1968; Hawkes, 1974)。表皮层主要由复层上皮细胞组成,细胞核分别在PAS和HE染色中显示为蓝色和蓝紫色,分布着大量游离的黏液细胞(Henrikson et al, 1967),这些黏液细胞穿插于基底层和上皮层中,有些黏液细胞在PAS染色中着色程度不一致,原因可能是有些黏液细胞处于退化阶段,在释放黏液物质后,不久黏液细胞变空(Sinha, 1975)。黏液细胞释放的黏液物质中有少量的多糖类成分,PAS染色后显示为紫色;在锥状骨质凸起附近黏液细胞分布较多,在基底层细胞附近较少。绿鳍马面鲀鱼体上还分布着肉眼可见的色素细胞(迟雯丹等, 2022),可保护鱼体免受紫外线损伤、躲避敌害等皮肤表面(Ducrest et al, 2008),色素细胞分布在表皮层和鳞片层之间的交界处,偶尔在真皮层、皮下组织层内也可看到色素细胞。
鳞片层的主要作用为保护机体免受机械损伤、细菌侵染等(Natasha et al, 2015)。绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮的鳞片层位于表皮层之下、真皮层之上,由特化的锥状骨质凸起和基板组成。SEM及切片染色结果显示,绿鳍马面鲀的鱼鳞与其他真骨鱼类一样,同属骨鳞,但却没有一般骨鳞的鳞焦、鳞嵴及鳞沟等特征(苏锦祥等, 1988),与Cai等(2014)和李凤辉等(2019)的研究结果相一致。研究还发现,绿鳍马面鲀的鱼鳞长度为200~300 μm,大小不一;且鳞片基板的厚度不一,靠近锥状骨质凸起处的厚度为最厚点,四周的厚度则最薄,在13~30 μm之间。各个鳞片基板与真皮层之间的口袋内有胶原纤维,称为鳞囊(Whitear et al, 1980),其富有弹性,可根据鱼体的需求进行局部调整,起到保护作用,使鳞片基板具有一定的弯曲弹性。虽然,锥状骨质凸起和双斑鲀(Tetraodon steindachneri)鱼皮的刺外形类似,但不同的是绿鳍马面鲀的锥状骨质凸起为实心,且不能伸缩,鳞囊包裹性小(Hertwig et al, 1992)。绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮的锥状骨质凸起经Masson染色的纵切面和SEM的横截面是由层状骨板形成,骨板中胶原纤维分布紧密(图 2h和图 4e),该特点可作为研究鱼体生长发育规律或年龄的参考依据(Heidarsson et al, 2006; Pittman et al, 2013; Landa et al, 2015)。
绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮真皮层内分布着纵横交错的纤维束,未发现有明显的松弛层和致密层界限,胶原纤维束致密地分布在真皮层内,提供了高抗张强度,可提供机械保护、缓冲的作用(Hertwig et al, 1992),不同位置的真皮层厚度为中部>头部>尾部,纤维束宽度为头部>中部≈尾部。真皮层内有大量的成纤维细胞(Le Guellec et al, 2003)和少量的非纤维间质,在真皮层与皮下组织层交界处含有少量的色素细胞和红细胞等物质。真皮层和皮下组织层被2条相对的细胞膜致密线分开(Whitear et al, 1980),其中,PAS显示为阳性反应(图 5a、b),推测这2条致密线可能是真皮层与皮下组织层的分界处。皮下组织层内主要成分为胶原纤维,含有少量的红细胞和其他纤维间质成分,经HE染色后,未见脂肪细胞,且鱼皮脂肪含量较低(夏珊珊等, 2014),因此,皮下组织层内的脂肪细胞含量较少。绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮真皮层纤维束的分布情况和厚度观察结果可为鱼皮制革工艺提供数据参考,鳞片层特殊结构的观察可应用于生物医药和新型仿生材料开发等领域,鱼皮中胶原基质比例大,可作为食品、保健品和化妆品等相关产品的开发原料。
AL-HALANI A A. Effect of seasonal changes on physiological and histological characteristics of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) inhabited two different freshwater habitats. International Journal of Modern Biology and Medicine, 2018, 9: 9-28 |
ALLA J, RAMANATHAN G, FATHIMA N N, et al. Fish skin and exotic leathers. Journal of the American Leather Chemists Association, 2017, 112(2): 36-43 |
BANCROFT J D, GAMBLE M. Theory and practice of histological techniques. Elsevier Health Sciences, 2008 |
BLANCO M, VÁZQUEZ J A, PÉREZ-MARTÍN R I, et al. Hydrolysates of fish skin collagen: An opportunity for valorizing fish industry byproducts. Marine Drugs, 2017, 15(5): 131 DOI:10.3390/md15050131 |
CAI J X, XIA S S, MA J W, et al. Preparation, isolation and stability of collagen ACE inhibitory peptides from the skin of Navodon septentrionalis. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(3): 225-234 [蔡金秀, 夏姗姗, 马佳雯, 等. 马面鱼皮ACE抑制肽的制备、分离纯化及稳定性. 中国食品学报, 2022, 22(3): 225-234] |
CAI Y, LIN L, XUE Z, et al. Filefish-inspired surface design for anisotropic underwater oleophobicity. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(6): 809-816 DOI:10.1002/adfm.201302034 |
CALVI E N C, NAHAS F X, BARBOSA M V, et al. An experimental model for the study of collagen fibers in skeletal muscle. Acta Cirurgica Brasileira, 2012, 27(10): 681-686 DOI:10.1590/S0102-86502012001000003 |
CHI W D, SONG J J, GUO W, et al. Early ontogeny of chromatophores and skin color changes of modest filefish Thamnaconus septentrionalis. Fishery Science, 2022, 41(2): 218-225 [迟雯丹, 宋静静, 郭文, 等. 绿鳍马面鲀早期色素细胞发育与体色变化. 水产科学, 2022, 41(2): 218-225] |
CHU S J, NONG S Z, LIU C S, et al. Study on the extraction technology of collagen with enzyme from Navodon modestus skins. Food Science and Technology, 2010, 35(5): 234–237, 241 [楚水晶, 农绍庄, 柳春山, 等. 酶法提取马面鱼鱼皮胶原蛋白的工艺研究. 食品科技, 2010, 35(5): 234–237, 241] |
DE SOUZA A, DE ALMEIDA C M, DE ARAÚJO T A T, et al. Fish collagen for skin wound healing: A systematic review in experimental animal studies. Cell and Tissue Research, 2022, 388(3): 489-502 DOI:10.1007/s00441-022-03625-w |
DUCREST A, KWLLER L, ROULIN A. Pleiotropy in the melanocortin system coloration and behavioural syndromes. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2008, 23(9): 502-510 |
FELDMAN A T, WOLFE D. Tissue processing and hematoxylin and eosin staining. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2014, 1180: 31-43 |
GAI S S, GUAN S G, YU C Y, et al. Skeletal deformities in larvae and juveniles of hatchery-reared greenling Hexagrammos otakii. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2020, 35(4): 544-550 [盖珊珊, 官曙光, 于超勇, 等. 人工繁育大泷六线鱼仔稚鱼的骨骼畸形观察. 大连海洋大学学报, 2020, 35(4): 544-550] |
HATAB S, CHEN M L, MIAO W H, et al. Protease hydrolysates of filefish (Thamnaconus modestus) byproducts effectively inhibit foodborne pathogens. Foodborne Pathogens and Disease, 2017, 14(11): 656-666 DOI:10.1089/fpd.2017.2317 |
HAWKES J W. The structure of fish skin: Ⅰ. General organization. Cell and Tissue Research, 1974, 149(2): 147-158 DOI:10.1007/BF00222270 |
HEIDARSSON T, ANTONSSON T, SNORRASON S S. The relationship between body and scale growth proportions and validation of two back-calculation methods using individually tagged and recaptured wild Atlantic salmon. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 2006, 135(5): 1156-1164 DOI:10.1577/T05-286.1 |
HENRIKSON R C, MATOLTSY A G. The fine structure of teleost epidermis: Ⅱ. Mucous cells. Journal of Ultrastructure Research, 1967, 21(3/4): 213-221 |
HERTWIG I, EICHELBERG H, HENTSCHEL J. Light and electron microscopic studies of the skin of the Palembang puffer, Tetraodon steindachneri (Teleostei, Tetraodontidae). Zoomorphology, 1992, 111(4): 193-205 DOI:10.1007/BF01633008 |
JIN H Y, LIU Y K, GAO Y, et al. Isolation and identification of Aeromonas salmonicida from Thamnaconus septentrionalis and Sebastes schlegeli. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2023, 44(1): 191-200 [晋怀远, 刘耀宽, 高晔, 等. 绿鳍马面鲀与许氏平鲉杀鲑气单胞菌病原的分离和鉴定. 渔业科学进展, 2023, 44(1): 191-200] |
JIN T, WU Y X, BAO Z W, et al. Study on the preparation of gelatin from Navodon septentrionalis fish skin. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(12): 180-182 [靳挺, 武玉学, 包哲隈, 等. 绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮明胶的制备工艺研究. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(12): 180-182 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2021.12.046] |
KIM S K, PARK P J, KIM J B, et al. Purification and characterization of a collagenolytic protease from the filefish, Novoden modestrus. BMB Reports, 2002, 35(2): 165-171 DOI:10.5483/BMBRep.2002.35.2.165 |
KUCUKAKIN E, ADIGUZEL ZENGIN A C, DEVECI R, et al. Histological, histochemical and chemical study on Katsuwonus pelamis fish skins. Leather and Footwear Journal, 2016, 16(4): 299-312 DOI:10.24264/lfj.16.4.5 |
LANDA J, RODRIGUEZ-MARIN E, LUQUE P L, et al. Growth of bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) in the North-eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean based on back-calculation of dorsal fin spine annuli. Fisheries Research, 2015, 170: 190-198 DOI:10.1016/j.fishres.2015.06.002 |
LE GUELLEC D, MORVAN-DUBOIS G, SIRE J Y. Skin development in bony fish with particular emphasis on collagen deposition in the dermis of the zebrafish (Danio rerio). The International Journal of Developmental Biology, 2003, 48(2/3): 217-231 |
LI F H, LIU K, WANG P F, et al. Morphological structure and karyotype of Thamnaconus septentrionalis. South China Fisheries Science, 2019, 15(3): 104-112 [李凤辉, 刘琨, 王鹏飞, 等. 绿鳍马面鲀外部形态特征与染色体核型分析. 南方水产科学, 2019, 15(3): 104-112] |
LI F, WANG Q J, HOU L J. Histology research and application prospects of sturgeon skin in leather industry. China Leather, 2012, 41(5): 24-27 [李芳, 王全杰, 侯立杰. 鲟鱼皮的组织学研究及其在皮革中的应用. 中国皮革, 2012, 41(5): 24-27] |
LIU K, LIU G, HUANG L, et al. Experiment on cage cultivation of large-size Thamnaconus septentrionalis Günther. Fishery Modernization, 2019, 46(6): 54-60 [刘琨, 刘刚, 黄亮, 等. 绿鳍马面鲀大规格苗种网箱培育. 渔业现代化, 2019, 46(6): 54-60] |
LIU X X, QIU J S, SHAO S J, et al. Properties of Thamnaconus modestus leather made by ultrasonic method. Leather and Chemicals, 2019, 36(2): 21–24, 31 [刘勋勋, 邱纪时, 邵思佳, 等. 超声波法制备橡皮鱼皮革的性能. 皮革与化工, 2019, 36(2): 21–24, 31] |
MITTAL A K, BANERJEE T K. Functional organization of the skin of the 'Green-puffer fish' Tetraodon fluviatilis (Ham. -Buch.) (Tetraodontidae, Pisces). Zoomorphologie, 1976, 84(2): 195-209 DOI:10.1007/BF00999712 |
NATASHA FUNK, MARC V, SZEWCIW L T, et al. Bioinspired fabrication and characterization of a synthetic fish skin for the protection of soft materials. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2015, 7(10): 5972-5983 DOI:10.1021/acsami.5b00258 |
OSLAN S N H, LI C X, SHAPAWI R, et al. Extraction and characterization of bioactive fish by-product collagen as promising for potential wound healing agent in pharmaceutical applications: Current trend and future perspective. International Journal of Food Science, 2022, 1-10 |
PITTMAN K, PITTMAN A, KARLSON S, et al. Body site matters: An evaluation and application of a novel histological methodology on the quantification of mucous cells in the skin of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. Journal of Fish Diseases, 2013, 36(2): 115-127 |
PRENTØ P. Van gieson's picrofuchsin. The staining mechanisms for collagen and cytoplasm, and an examination of the dye diffusion rate model of differential staining. Histochemistry, 1993, 99(2): 163-174 |
RAKERS S, GEBERT M, UPPALAPATI S, et al. 'Fish matters': The relevance of fish skin biology to investigative dermatology. Experimental Dermatology, 2010, 19(4): 313-324 |
SADI N H, YOGA G P. Skin characteristic of Pangasius catfish in Indonesia. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 789(1): 012026 |
SINHA G M. A histochemical study of the mucous cells in the bucco-pharyngeal region of four Indian freshwater fishes in relation to their origin, development, occurrence and probable functions. Acta Histochemica, 1975, 53(2): 217-223 |
SONG Z G, ZHU L N, ZHANG H C, et al. Extraction and structural characterization of collagen from skin of Thamnaconus modestus. Food Science, 2018, 39(20): 260-267 [宋正规, 朱丽娜, 张洪超, 等. 胃蛋白酶提取马面鱼皮胶原蛋白及结构分析. 食品科学, 2018, 39(20): 260-267] |
SU J X, ZHOU Y X. Comparative studies of the scales of filefishes (Pisces: Tetradontiformes, Aluteridae) by scanning electron microscope. Current Zoology, 1988, 34(2): 110-117 [苏锦祥, 周云昕. 革鲀科鳞片构造的扫描电镜观察和比较研究. 动物学报, 1988, 34(2): 110-117] |
WANG X R, BIAN L, HU Q, et al. Acute effects of cadmium on the antioxidant enzyme activities and histological structure of the gills and liver of juvenile Thamnaconus septentrionalis. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2023, 44(3): 74-84 [王晓然, 边力, 胡琼, 等. 镉对绿鳍马面鲀幼鱼急性毒性、肝脏抗氧化能力及组织结构的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2023, 44(3): 74-84] |
WHITEAR M, MITTAL A K, LANE E B. Endothelial layers in fish skin. Journal of Fish Biology, 1980, 17(1): 43-65 |
WISLOCKI G B, RHEINGOLD J J, DEMPSEY E W. The occurrence of the periodic acid-Schiff reaction in various normal cells of blood and connective tissue. Blood, 1949, 4(5): 562-568 |
XIA S S, CAO S Q, LIU L, et al. Composition and optimization of extraction of collagen from Navodon septentionalis skin using response surface methodology. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 28(5): 869-875 [夏珊珊, 曹少谦, 刘亮, 等. 响应面法优化马面鱼皮胶原蛋白提取工艺及胶原组成分析. 核农学报, 2014, 28(5): 869-875] |
XU D F, LIU K, WANG P F, et al. Analysis of nutritional composition in the muscle of Thamnaconus septentrionalis. Marine Sciences, 2018, 42(5): 122-129 [徐大凤, 刘琨, 王鹏飞, 等. 绿鳍马面鲀肌肉营养成分分析和营养评价. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(5): 122-129] |
YAMADA J. A study on the structure of surface cell layers in the epidermis of some teleosts. Annotationes Zoologicae Japonenses, 1968, 41(1): 1-8 |
YANG Y Z, JIAO Y R. Development the source of black scraper skins. China Leather, 1995(9): 17-18 [杨雨滋, 焦永若. 马面鲀鱼皮资源的开发利用. 中国皮革, 1995(9): 17-18] |
ZHOU C S, QIN X P, YU X J, et al. Antioxidant activity and characteristics of simulated gastrointestinal digestion hydrolysate from filefish Navodon septentrionalis skin protein. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(8): 211-216 [周存山, 秦晓佩, 余筱洁, 等. 绿鳍马面鲀鱼皮蛋白抗氧化肽模拟胃肠消化制备. 农业机械学报, 2015, 46(8): 211-216] |



