2. 上海海洋大学 农业农村部淡水水产种质资源重点实验室 上海 201306;
3. 江苏省淡水水产研究所 农业农村部淡水虾蟹遗传育种与养殖重点实验室 江苏 南京 210017;
4. 江苏省农业科学院农产品加工研究所 江苏 南京 210014
2. Key Laboratory of Freshwater Aquatic Genetic Resources, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China;
3. Key Laboratory of Genetic Breeding and Cultivation for Freshwater Crustacean, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Freshwater Fisheries Research Institute of Jiangsu Province, Nanjing 210017, China;
4. Institute of Agricultural Products Processing, Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Nanjing 210014, China
近年来,集约化、工厂化养殖的发展,推动了水产品产业的迅速发展,但由于鱼粉鱼油的短缺,植物蛋白质的大量使用等造成的饲料营养的不平衡,尤其是氨基酸的不平衡以及养殖环境恶化和高密度养殖等问题,导致水产品质量下降。随着经济的增长,消费者对水产品质量的要求也大大增加,优质的水产品受到更多的青睐,野生大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea)、东星斑(Plectropomus leopardus)等优质的水产品常常供不应求。为满足消费者的需求,推动优质水产品的研究进展,水产动物肌肉品质及饲料营养对其调控的研究受到众多水产研究者的关注,这也是目前水产养殖研究重点之一。本文综述了氨基酸对水产动物肌肉品质调控的研究进展,以期为深入研究氨基酸等饲料营养素改善水产品肌肉品质提供理论参考。
1 饲料氨基酸对水产动物肌肉品质的影响肌肉是水产动物的主要食用部分,其含量最多可占机体的60% (Houlihan et al, 1995)。研究者常以含肉率、肌肉营养成分(蛋白质、脂肪、灰分、氨基酸、脂肪酸和矿物质等)、肌纤维结构、质构特性(硬度、弹性、内聚性、咀嚼性及胶黏性等)和理化指标(滴水损失率、蒸煮损失率、pH和肉色)等来判断肌肉品质的优劣。肌肉品质受很多因素的影响,如饲料营养素(蛋白质、氨基酸、脂肪、维生素和矿物质等)、饲料添加剂[类胡萝卜素、虾青素、枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)等]、养殖环境(水温、水流、氨氮、溶氧和应激状态等)、不同物种、不同的性别和年龄、产卵前后等。因此,研究氨基酸对水产动物肌肉品质的影响,需系统地了解氨基酸对水产动物肌肉营养物质、肌肉风味、质构特性和理化性质的影响。
1.1 饲料氨基酸对水产动物肌肉组织营养物质的影响肌肉组织中蛋白质含量是肌肉品质的重要指标之一,而氨基酸是蛋白质的构成单位。氨基酸可以调节蛋白质的合成和代谢,从而影响肌肉组织中的营养成分。苏氨酸(threonine, Thr)作为必需氨基酸,在饲料中添加适宜水平的苏氨酸可以提高三倍体虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss)(王亚玲等, 2021)、草鱼(Ctenopharyngodon idella)(胡晓霞, 2012)、吉富罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus)(周兴华等, 2014)、建鲤(Cyprinus carpio var. Jian)(Feng et al, 2013; 白稚子等, 2019)、印度鲶鱼(Heteropneustes fossilis)(Ahmed, 2007)和日本对虾(Penaeus japonicus)(Alam et al, 2015)的粗蛋白、粗脂肪和部分氨基酸的含量。蛋氨酸(methionine, Met)作为水产动物生长的必需氨基酸,是蛋白质合成的重要组分(Kasper et al, 2000)。在饲料中添加适宜水平的蛋氨酸能显著提高草鱼(方闯闯, 2020)、团头鲂(Megalobrama amblycephala)(Liao et al, 2014)、大西洋鲑鱼(Salmo salar)(Espe et al, 2008)、松浦镜鲤(Cyprinus carpio var. specularis ‘Songpu’)(程龙等, 2020)粗蛋白和部分氨基酸含量。色氨酸(tryptophan, Trp)、精氨酸(arginine, Arg)作为必需氨基酸,饲料中不同水平的色氨酸可显著提高凡纳对虾(Penaeus vannamei)营养价值(孙育平等, 2016)。谷氨酰胺(glutamine, Gln)是谷氨酸γ-羧基酰胺化物,是条件性必需氨基酸,并且是生物体内含量最多的游离氨基酸。已有研究表明,不同水平的谷氨酰胺对罗非鱼(Oreochromis mossambicus)(杨奇慧等, 2008)、德国镜鲤(Cyprinus carpio L.)(朱青等, 2009)、松浦镜鲤(赵志刚等, 2018)、幼鲟鱼(Acipenser sinensis)(朱青等, 2010)和草鱼(马晓珍, 2020)肌肉蛋白质均有显著影响。在凡纳对虾饲料中添加不同水平的甘氨酸(glycine, Gly)可以显著影响其粗蛋白等营养物质含量(汤雨, 2021)。此外,氨基酸还可以提高肌肉组织中的肌红蛋白含量,增加肌肉的氧气供应能力,改善肌肉品质(杜俊芳, 2021)。
1.2 饲料氨基酸对水产动物肌肉风味的影响肌肉风味是影响肌肉品质的重要因素,影响着消费者购买的意愿。肌肉组织含有大量氨基酸,能够通过产生肉香味影响肌肉的风味(Hong et al, 2017)。谷氨酸(glutamic acid, Glu)和天冬氨酸(aspartic acid, Asp)等有助于肉的鲜味,赖氨酸(lysine, Lys)和苏氨酸具有甜味,而亮氨酸(leucine, Leu)和异亮氨酸(isoleucine, Ile)可以参与美拉德反应,产生大量挥发性风味物质增加肌肉香味(Tie et al, 2019)。其中,谷氨酸可以缓冲和中和苦味、酸味和咸味,使肉食品具有更好的风味(乔云芳, 2006),还可提高建鲤部分多不饱和脂肪酸(polyunsaturated fatty acid, PUFA)含量(Zhao et al, 2019)。饲料中添加赖氨酸显著提高了天冬氨酸、谷氨酸、甘氨酸和部分PUFA含量(唐延杰, 2022)。Whitfield等(1992)研究发现,在热降解反应过程中,由蛋氨酸和半胱氨酸(Cys)等含硫氨基酸产生的含硫杂环化合物有助于鱼肉香味的产生。赵红霞等(2007)在军曹鱼(Rachycentron canadum L.)中添加适宜水平的精氨酸可显著提高鱼体部分氨基酸含量。另外,水溶性滋味前体物质比如游离氨基酸和核苷酸的变化,会影响鱼肉风味,并可能产生脱味和引起感官排斥(Yu et al, 2018a)。研究报道,谷氨酰胺参与核苷酸合成(Karnaa et al, 2001),核苷酸可以增加草鱼肌肉中风味氨基酸的浓度(Tie et al, 2019)。肌苷酸(inosinemonphosphate, IMP)是肌肉中主要的呈味核苷酸,很少剂量就能产生很强的鲜味。赵叶等(2014)研究表明,饲料中添加谷氨酸显著提高了草鱼肌肉IMP含量。杨翼羽等(2017)对鳙(Aristichthys nobilis)开口苗研究发现,蛋氨酸强化卤虫(brine shrimp)能提高其体内的精氨酸和甘氨酸含量,从而促进肌酸形成。
1.3 饲料氨基酸对水产动物肌肉质构及理化特性的影响水产动物肌肉的质构、色泽、pH等是影响水产动物肌肉品质的重要指标。氨基酸可以影响肌肉中蛋白质的组成和排列方式,从而影响肌肉质构特性。研究发现,赖氨酸可以通过调节ATPase活性和Ca2+含量来影响鲈鱼(Lateolabrax japonicus)肌肉蛋白质合成和降解的平衡,从而改善其肌肉硬度和咀嚼性(Liang et al, 2017)。苏氨酸可通过提高建鲤肌纤维密度与直径从而改善其质构特性(白稚子等, 2019)。色氨酸可增加草鱼和黄颡鱼(Tachysurus fulvidraco)肌纤维数量和直径(Xiao et al, 2023; Jiang et al, 2022)。谷氨酸作为非必需氨基酸又是呈味氨基酸中鲜有的鲜味氨基酸,其对生长中期草鱼肌纤维和质构特性具有一定影响(赵叶等, 2014)。氨基酸可以影响肌肉中色素的合成和代谢,从而影响肌肉色泽。研究表明,在添加谷氨酸和赖氨酸的情况下,肌肉中的色素含量和色度值均有所提高,表明氨基酸可以促进肌肉色素的合成(钱程明等, 2002)。pH也是评价肌肉品质的一个重要参数,其值的快速下降会影响肌肉的滴水损失率、系水力和色泽等肉质特性,从而导致肌肉品质降低(Kralik et al, 2014)。研究表明,蛋氨酸能够增加生长中期草鱼(唐炳荣, 2012)和松浦镜鲤(程龙等, 2020)肌肉的pH,降低滴水损失率。赖氨酸能够改善草鱼肌肉pH,降低蒸煮损失率(唐延杰, 2022)。
本文对一些饲料中氨基酸对水产动物肌肉品质影响总结见表 1。
|
|
表 1 饲料氨基酸对水产动物肌肉品质的影响 Tab.1 Effect of amino acids in feed on muscle quality in aquatic animals |
研究表明,结缔组织是动物骨骼肌的重要组成成分(Nishimura, 2010),由蛋白聚糖、糖蛋白、胶原蛋白和弹性蛋白等组成,而且这些大分子物质通过彼此之间的相互作用形成特殊的超分子网状结构,从而对肌纤维的收缩和舒张等过程产生重要的影响(Nishimura, 2015)。在鱼类肌肉中,结缔组织占肌肉质量的2%~8%,而胶原蛋白作为结缔组织的主要成分,占肌肉质量的0.2%~1.4%,具有维持肌肉组织结构的稳定性和完整性的作用,并且是影响肌肉质量品质的重要因素(Sikorski et al, 1984)。Sun等(2017)研究发现,肌肉硬度会随着胶原蛋白含量的增加而提高,从而影响鱼肉品质。I型胶原蛋白,包括a1和a2两种肽链,分别由col1a1和col1a2基因编码,是鱼类肌肉结缔组织中的主要胶原蛋白(Eckhoff et al, 1998; Yu et al, 2014)。对草鱼的研究发现,转化生长因子β1 (TGF-β1)/Smads通路能够调控I型胶原蛋白合成(Yu et al, 2019)(图 1)。研究发现,蛋氨酸能够激活虹鳟和军曹鱼肌肉中雷帕霉素蛋白复合体1 (TORC1)信号通路,促使蛋白质合成,从而影响肌肉品质(Belghit et al, 2014; He et al, 2019) (图 2)。此外,谷氨酰胺也可以通过调控雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)信号通路来提高蛋白合成(姜俊, 2009)。据Zhao等(2019)研究发现,蛋白质合成与降解平衡对骨骼肌蛋白质沉积有重要意义。对鱼类研究发现,亮氨酸可以对肌肉细胞内mTOR在核糖体蛋白S6激酶1 (S6K1)作用下与真核生物翻译起始因子4E结合蛋白1 (4E-BP1)调控蛋白质的合成(Jiang et al, 2017; 蒋志军, 2021)。
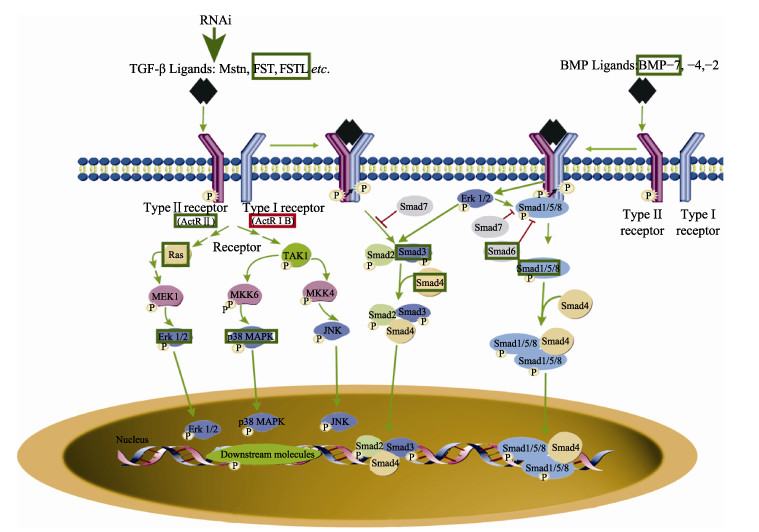
|
图 1 脊椎动物肌肉发育TGF-β/Smad信号通路(闫允君等, 2021) Fig.1 TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway related to muscle development in vertebrates (Yan et al, 2021) |
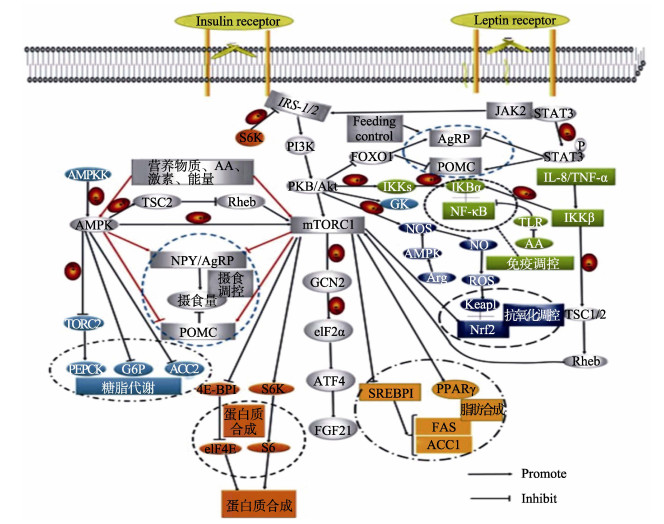
|
图 2 TOR信号通路与蛋白质合成代谢调控(吴龙华等, 2021) Fig.2 TOR signaling pathway and protein anabolism regulation (Wu et al, 2021) |
乙酰辅酶A羧化酶(acetyl-CoA carboxylase, ACC)、脂肪酸合成酶(fatty acid synthase, FAS)和过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ (peroxisome proliferators- activated receptor γ, PPAR-γ)是机体调控脂肪沉积的主要酶和因子(周招洪, 2014)。PPAR-γ参与脂肪的合成,能够激活脂肪细胞的分化并且促进脂肪酸在脂肪组织中沉积,同时还可以调控特殊脂肪基因的表达(Bispham et al, 2005)。TOR通道通过控制调节因子PPAR-γ的翻译来调控脂肪细胞(Bacquer et al, 2007)。研究赖氨酸调控猪肉脂肪沉积机制发现,肌内脂肪沉积随赖氨酸与消化能比下降而增加,猪肉嫩度也随之增强。其原理在于低赖氨酸水平下,肌肉组织中的脂肪合成相关基因PPAR-γ表达得到增强(蒋志军, 2021)。脂肪相关酶的表达受固醇调节元件结合蛋白-1 (sterol regulatory element binding protein-1, SREBP-1)的影响,同时它还可以调控脂肪和胆固醇的稳态。TORC1影响脂肪和甾醇的合成主要是应该激活SREBP-1来间接完成的(Duvel et al, 2010)。精氨酸减少脂肪合成,提高肌肉含量的可能机制:精氨酸通过改变能量摄取与消耗的平衡状态进而减少脂肪,降低白色脂肪组织的生长,具体的机理可能与精氨酸提高细胞信号分子(NO、多胺、环腺苷酸等)促进线粒体和棕色脂肪组织生长有关,也与精氨酸提高能够促进产能底物氧化的基因的表达有关(McKnight et al, 2010)。谷氨酸通过强化肌球蛋白重链(myosin heavy chain, MyHC)Ⅰ和Ⅱ的表达,从而促进脂肪相关基因的表达,但其如何调控肌内脂肪相关基因表达的具体机制还不明确(蒋志军, 2021; 吴龙华等, 2021)。
2.3 风味物质形成天然蛋白质中的氨基酸都属L型,大多带有甜味或苦味,极少数带有鲜味或酸味。而D型氨基酸一般带有甜味(武彦文等, 2001)。美拉德反应(Maillard reaction, MR)是氨基酸、多肽或蛋白质与还原糖发生亲核加成后的复杂反应(Huang et al, 2015),其产物的香气与滋味特征很大程度上取决于热反应过程中添加的氨基酸种类以及反应条件(Yu et al, 2017; Yu et al, 2018b)。其中,半胱氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸作为含硫氨基酸对肉香味的生成具有促进作用(Tie et al, 2019)。谷氨酸与羰基化合物的美拉德反应产物具有诱人的焙烤香、坚果香(Tie et al, 2019);甘氨酸能赋予美拉德反应产物焦甜香(侯莉, 2017)。苏氨酸是动物体内代谢过程中唯一不经过脱氨基和转氨基作用的氨基酸, 它通过苏氨酸脱氢酶(threonine dehydrogenase, TDG)、苏氨酸脱水酶(threonine dehydrase, TDH)和苏氨酸醛缩酶(threonine aldolases, TA)催化转变为琥珀酰CoA、丝氨酸和甘氨酸等物质参与体内代谢过程(麦康森等, 2008)(图 3)。而甘氨酸是鲜味氨基酸,从而可以影响肌肉风味(陈伟兴等, 2012)。
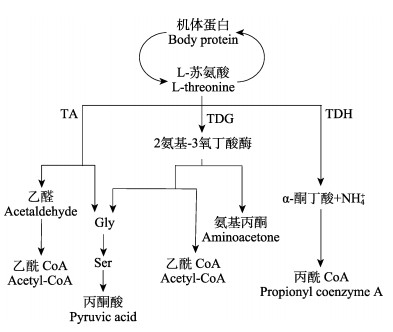
|
图 3 苏氨酸在体内主要代谢途径(徐闰胜等, 2020) Fig.3 Main metabolic pathways of threonine in vivo (Xu et al, 2020) |
肌肉的氧化损伤会造成其系水力下降,进而降低肌肉品质(Wang et al, 2009)。鱼肉中富含的PUFA和过量产生的活性氧(reactive oxygen species, ROS)相互作用,从而导致鱼肉的氧化损伤(Tokur et al, 2007; Martinez-Álvarez et al, 2005)。而肌肉中胶原蛋白含量一定程度上会受氧化损伤的影响。前期研究发现,氧化损伤降低了大西洋鲑鱼肌肉pH值,并导致动物肌肉中PUFA氧化,产生不良的滋味和气味,降低肌肉风味(Lerfall et al, 2015)。肌肉氧化损伤主要原因是其抗氧化能力下降造成,而抗氧化能力取决于抗氧化酶相关基因的调控情况,其相关基因的表达情况与抗氧化通路核因子E2相关因子(nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor, nrf2)密切相关(蒋慧琪, 2021)(图 4)。研究发现,蛋氨酸能够促进草鱼(潘飞宇, 2016)和松浦镜鲤(程龙等, 2020)肌肉中nrf2的基因表达。对草鱼的研究还发现,添加Phe可以通过上调TOR的表达进而提高nrf2的基因表达量,并进一步上调抗氧化酶基因的表达(李文, 2014)。Luo等(2017)研究发现,随饲料缬氨酸水平的增加,幼龄草鱼肌肉中的nrf2表达上调,并且提高了肌肉超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase, SOD)和过氧化氢酶(catalase, CAT)活性。饲料中添加谷氨酰胺显著提高黄颡鱼(张杰等, 2016)和杂交鲟鱼(Zhu et al, 2011)肌肉中SOD和谷胱甘肽过氧化酶(glutathione peroxidase, GPX)的活力。此外,亮氨酸和异亮氨酸可以参与美拉德反应(Tie et al, 2019),其产物具有抗氧化活性。
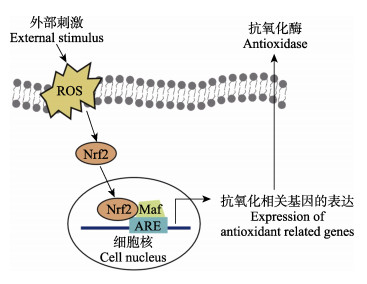
|
图 4 nrf2对抗氧化酶的调控(蒋慧琪等, 2021) Fig.4 Regulation of nrf2 antioxidase (Jiang et al, 2021) |
氨基酸影响水产动物肠道菌群,维持微生物平衡和肠道健康,而肠道菌群的健康可以促进营养物质的良好吸收和动物消化道内环境的稳定,有利于对营养素的消化吸收,增强饲料利用率,从而充分发挥其作用,使得肌肉品质有良好的提升。乳酸杆菌(Lactobacillus)、大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)和嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)的数量可以在一定程度上反映水生动物肠道微生态区系的状态(王光花, 2007)。研究表明,赖氨酸、蛋氨酸对幼建鲤肠道菌群有影响,在饲料中添加包被处理的赖氨酸或蛋氨酸能够显著提高有益菌乳酸杆菌、芽孢杆菌(Bacillus)数量,显著降低有害菌如大肠杆菌、气单胞菌数量,优化幼建鲤的微生态区系(王光花, 2007; 鄢华, 2007)。而肠道微生物稳态有利于肌肉品质的提升,研究表明,厚壁菌门(Phylum firmicutes)可帮助宿主从膳食中吸收能量,从而有效促进肌肉质量的增加(Zhang et al, 2020)。拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)与机体碳水化合物代谢有关,它能够分解糖类产生挥发性脂肪酸被肠道吸收利用,可提高肌肉的风味(Johnson et al, 2015)。苏氨酸可以优化建鲤肠道微生物区系,促进乳酸菌生长,抑制嗜水气单胞菌的生长,促进肌肉和肠道上皮细胞的氨基酸代谢,提高肌肉蛋白沉积能力,保证肠道上皮细胞结构和功能的正常(冯琳, 2010)。苏氨酸还提高了草鱼肠道消化吸收能力,维持肠道正常功能,延缓肌肉pH的降低和提高肌肉剪切力,从而提高草鱼的肌肉品质(洪杨, 2013)。因此,氨基酸改善肌肉品质的机制之一,是通过维持肠道健康来实现的。此外,动物肠道黏膜细胞能够利用大量的谷氨酰胺作为其能氮来源,以保证正常的肠道功能,促进营养物质吸收。研究发现,谷氨酰胺能够显著增加肠道对亮氨酸和脯氨酸的吸收量,显著增加肠道组织游离亮氨酸和脯氨酸量以及肠道蛋白质的合成量(叶元土等, 2007),这可能是通过激活mTOR信号通路来促进肠细胞蛋白质合成和肠细胞的生长(Wu et al, 2010)。谷氨酰胺也有助于表皮生长因子促进小肠细胞增殖(董金格等, 2008)。近年来研究发现,细胞凋亡不仅在维持机体内环境稳态方面发挥重要调控作用,而且在动物屠宰后的肌肉成熟过程中扮演重要角色(Herrera-Mendez et al, 2006)。Pan等(2017)研究发现,蛋氨酸能抑制生长中期草鱼肠道细胞凋亡。
2.6 其他氨基酸影响肌肉品质的作用机制除上述方面外,还可以通过肌纤维相关调节因子及信号通路来影响肌纤维合成与转化。限制赖氨酸水平能够通过增强肌肉中过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体激活因子-1a (pgc-1a) mRNA的丰度来促进氧化肌纤维的生成,增加脂肪在肌肉的沉积(Katsumata et al, 2008)。肌肉中肌纤维的类型会受到日粮精氨酸水平的调控,精氨酸能够通过沉默信息调节因子1 (sirt-1)和腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMPK)途径促进骨骼肌纤维类型由快收缩肌纤维向慢收缩肌纤维的转换,使MyHC-I型肌纤维数量增加,进而提高肌内脂肪(intramuscular fat, IMF)含量(Chen et al, 2019a; Chen et al, 2018)。在仔猪日粮中降低蛋氨酸水平能够通过AMPK途径促进骨骼肌纤维类型的转化、上调pgc-1a的表达来促进骨骼肌中慢收缩肌纤维和IMF的合成,并且这些仔猪(Sus scrofa)到育肥阶段也表现出较高的IMF含量(Wu et al, 2019)。亮氨酸还能够通过sirt-1、AMPK以及pgc-1a信号通路诱导慢收缩肌纤维的表达,使猪骨骼肌纤维类型从快收缩纤维向慢收缩纤维的转化,增加氧化肌纤维的比例(Chen et al, 2019b)。
3 展望 3.1 面临的问题目前关于氨基酸调控水产动物肌肉品质的研究,面临许多问题,有待进一步研究和解决,具体表现为:(1)当前对于水产动物肌肉品质的评价标准并不一致,如有侧重于营养成分的变化,有侧重肌肉的质构特性、风味或者理化性质等,而肌肉品质的评价是综合且多方面的,如何建立科学有效的肌肉品质评价体系是研究营养素包括氨基酸调控肌肉品质的基础和前提;(2)关于氨基酸影响水产动物肌肉品质的研究较少,而且往往集中在少数几种必需氨基酸如蛋氨酸、精氨酸和赖氨酸等,缺乏基础性研究资料,也鲜有关于一些功能性氨基酸、风味氨基酸或者非必需氨基酸对水产动物肌肉品质的影响研究,而氨基酸与其他营养素间的相互作用也尚不清楚,未来还需进一步完善;(3)氨基酸调控水产动物肌肉品质的作用机制缺乏深入的研究,未来在调控肌肉品质的关键功能基因挖掘上还需投入更多的关注。
3.2 展望氨基酸影响水产动物肌肉品质,在宏观上表现为营养组成、理化性质、风味和肉色等的变化,在分子水平上,氨基酸调控水产动物肌肉品质的作用机制还有待深入研究。近年来,随着科学进步和营养学研究的逐步推进,整合生理学、营养基因组学、分子生物学、营养免疫学、营养遗传学等先进技术开始应用于肌肉品质的研究,从组织器官、细胞和分子等方面剖析水产动物肌肉形成过程中关键物质代谢和信号转导通路,分子营养学成为水产动物肉质研究的重要方向。未来要建立科学有效的肌肉品质评价体系,为营养素调控水产动物肌肉品质研究提供依据。此外,参照人和畜禽类营养学研究方法和技术,在一定程度上可以引入到水产动物肉质研究中,如生物标志物检测新技术,通过“一滴血”就可以对矿物质、小分子代谢物、大分子蛋白和多种维生素进行全自动检测。今后通过各项新技术的支持,可以从更多角度解读氨基酸及其他营养素对水产动物肌肉品质的影响,也为营养素对功能性基因精准调控研究辅助水产动物育种提供指导。氨基酸在调控水产动物肌肉品质上的研究,也为其他营养素或饲料添加剂等在肌肉品质方面的研究提供参考和依据,对提高水产动物肌肉品质、提供高质量和绿色健康的水产品和促进水产养殖业的可持续发展具有重要意义。
AHMED I. Dietary amino acid L-threonine requirement of fingerling Indian catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch) estimated by growth and biochemical parameters. Aquaculture International, 2007, 15(5): 337-350 DOI:10.1007/s10499-007-9097-y |
ALAM M S, TESHIMA S, KOSHIO S, et al. Effects of supplementation of coated crystalline amino acids on growth performance and body composition of juvenile Kuruma shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2015, 10(5): 309-316 |
BACQUER O L, PETROULAKIS E, PAGLIALUNGA S, et al. Elevated sensitivity to diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice lacking 4E-BP1 and 4E-BP2. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2007, 117(2): 387-396 DOI:10.1172/JCI29528 |
BAI Z Z, LIU M Y, LI S H, et al. Effect of dietary threonine supplement on the fillet quality and cathepsin B/L level of Jian carp (Cyprlnus carpio var Jian). Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(22): 90-96 [白稚子, 刘明宇, 李树红, 等. 饲料中苏氨酸含量对建鲤肉质及组织蛋白酶B、L的影响. 食品与发酵工业, 2019, 45(22): 90-96] |
BELGHIT I, CASSY S S, GEURDEN I, et al. Dietary methionine availability affects the main factors involved in muscle protein turnover in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). British Journal Nutrition, 2014, 112(4): 493-503 DOI:10.1017/S0007114514001226 |
BISPHAM J, GARDNER D S, GNANALINGHAM M G, et al. Maternal nutritional programming of fetal adipose tissue development: Differential effects on messenger ribonucleic acid abundance for uncoupling proteins and peroxisome proliferator-activated and prolactin receptors. Endocrinology, 2005, 146(9): 3943-3949 DOI:10.1210/en.2005-0246 |
CHEN X, LUO X, CHEN D, et al. Arginine promotes porcine type Ⅰ muscle fibres formation through improvement of mitochondrial biogenesis. British Journal of Nutrition, 2019a, 123(5): 499-507 |
CHEN X L, GUO Y F, JIA G, et al. Arginine promotes skeletal muscle fiber type transformation from fast-twitch to slow-twitch via Sirt1/AMPK pathway. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 2018, 61: 155-162 DOI:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.08.007 |
CHEN X L, XIANG L, JIA G, et al. Leucine regulates slow-twitch muscle fibers expression and mitochondrial function by Sirt1/AMPK signaling in porcine skeletal muscle satellite cells. Animal Science Journal, 2019b, 90(2): 255-263 |
CHEN W X, LIU Q Z, FAN Z T. Recent advances in research on meat quality evaluation and influencing factor of fish. Meat Research, 2012, 26(10): 34-40 [陈伟兴, 刘清振, 范兆廷. 鱼类肉质评价及影响因素研究进展. 肉类研究, 2012, 26(10): 34-40] |
CHENG L, WANG L S, XU Q Y. Effects of dietary methionine level on growth performance, muscle quality and muscle synthesis pathway related gene expression of Songpu mirror carp. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(3): 1293-1304 [程龙, 王连生, 徐奇友. 饲料蛋氨酸水平对松浦镜鲤生长性能、肌肉品质及肌肉合成通路相关基因表达的影响. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(3): 1293-1304 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.03.037] |
DONG J G, WAN X Y, ZOU X T, et al. Effects of exogenous glutamine supplementation on growth performance and antioxidant indices of broilers. Feed Industry, 2008, 22: 4-6 [董金格, 万晓媛, 邹晓庭, 等. 外源添加谷氨酰胺对肉仔鸡生长性能及抗氧化指标的影响. 饲料工业, 2008, 22: 4-6] |
DU J F. The effects of glutamate/histidine in heme active site on the structure and functions of myoglobin. Master′s Thesis of University of South China, 2021 [杜俊芳. 血红素活性中心谷氨酸/组氨酸对肌红蛋白结构及功能的影响. 南华大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2021]
|
DUVEL K, YECIES J L, MENON S, et al. Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream of mTOR complex 1. Molecular Cell, 2010, 39(2): 171-183 DOI:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.06.022 |
ECKHOFF K M, AIDOS I, HEMRE G I, et al. Collagen content in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) and subsequent changes in solubility during storage on ice. Food Chemistry, 1998, 62(2): 197-200 |
ESPE M, HEVROY E M, LIASET B, et al. Methionine intake affect hepatic sulphur metabolism in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. Aquaculture, 2008, 274(1): 132-141 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.10.051 |
FANG C C. Effects and mechanisms of different levels of methionine on growth performance and flesh quality as well as mechanism in on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Master′s Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2020 [方闯闯. 不同水平蛋氨酸对生长中期草鱼生产性能和肌肉品质的作用及其机制. 四川农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2020]
|
FANG C C, FENG L, JIANG W D, et al. Effects of dietary methionine on growth performance, muscle nutritive deposition, muscle fibre growth and type Ⅰ collagen synthesis of on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). British Journal of Nutrition, 2020, 126(3): 1-36 |
FENG L, PENG Y, WU P, et al. Threonine affects intestinal function, protein synthesis and gene expression of TOR in Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e69974 DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0069974 |
FENG L. Effect of threonine on digestive, absorb, immune function and TOR gene expression in organ and tissues of juvenile Jian carp. Doctoral Dissertation of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2010 [冯琳. 苏氨酸对幼建鲤消化吸收能力和抗病力以及组织器官中蛋白质调控信号分子TOR表达的影响. 四川农业大学博士研究生学位论文, 2010]
|
HE Y, CHI S, TAN B, et al. DL-methionine supplementation in a low-fishmeal diet affects the TOR/S6K pathway by stimulating ASCT2 amino acid transporter and insulin-like growth factor-Ⅰ in the dorsal muscle of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum). British Journal of Nutrition, 2019, 122(7): 734-744 DOI:10.1017/S0007114519001648 |
HERRERA-MENDEZ C H, BECILA S, BOUDJELLAL A, et al. Meat ageing: Reconsideration of the current concept. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 2006, 17(8): 394-405 DOI:10.1016/j.tifs.2006.01.011 |
HONG H, REGENSTEIN J M, LUO Y. The importance of ATP-related compounds for the freshness and flavor of post-mortem fish and shellfish muscle: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2017, 57(9): 1787-1798 |
HOU L. Initial Maillard pathways to form meat flavors in "cysteine-xylose-glycine" reaction systems. Master′s Thesis of Beijing Technology and Business University, 2017 [侯莉. "半胱氨酸–木糖–甘氨酸"体系有利于形成肉香味的初期美拉德反应途径. 北京工商大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2017]
|
HOULIHAN D F, CARTER C G, MCCARTHY I D. Chapter 8: Protein synthesis in fish. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Fishes, 1995, 4: 191-120 |
HONG Y. Studies on effects of dietary threonine on digestive ability and antioxidative ability of sub-adult grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Master′s Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2013 [洪杨. 苏氨酸对生长后期草鱼消化吸收功能和抗氧化能力影响的研究. 四川农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2013]
|
HU X X. The dietary threonine requirement of young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Master′s Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2012 [胡晓霞. 生长中期草鱼的苏氨酸需要量研究. 四川农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2012]
|
HUANG M G, ZHANG X M, KARANGWA E. Comparation sensory characteristic, non-volatile compounds, volatile compounds and antioxidant activity of MRPs by novel gradient temperature-elevating and traditional isothermal methods. Journal of Food Science and Technology-Mysore, 2015, 52(2): 858-866 DOI:10.1007/s13197-013-1083-y |
JI K, LIANG H, CHISOMO-KASIYA H, et al. Effects of dietary tryptophan levels on growth performance, whole body composition and gene expression levels related to glycometabolism for juvenile blunt snout bream, Megalobrama amblycephala. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2018, 24(5): 1474-1483 DOI:10.1111/anu.12684 |
JIANG H, BIAN F, ZHOU H, et al. Nutrient sensing and metabolic changes after methionine deprivation in primary muscle cells of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 2017, 50: 74-82 DOI:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.08.015 |
JIANG H Q, WANG J, WANG Y C, et al. Research progress of flesh quality evaluation and nutrition regulation of farmed large yellow croaker. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 2021, 47(3): 275-283 [蒋慧琪, 王晶, 汪愈超, 等. 养殖大黄鱼肌肉品质评价及其营养调控的研究进展. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2021, 47(3): 275-283] |
JIANG J. Carp Cyprinus carpio IECs GLS and TOR gene cDNA clone and Gln to IECs protein synthesis influence and mechanism research. Doctoral Dissertation of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2009 [姜俊. 鲤鱼IECs GLS和TOR基因cDNA克隆及Gln对IECs蛋白合成的影响和机理研究. 四川农业大学博士研究生学位论文, 2009]
|
JIANG Q, ZHAO Y, ZHOU X Q, et al. Effects of dietary tryptophan on muscle growth, protein synthesis and antioxidant capacity in hybrid catfish Pelteobagrus vachelli ♀× Leiocassis longirostris ♂. British Journal of Nutrition, 2022, 127(12): 1761-1773 DOI:10.1017/S0007114521002828 |
JIANG Z J. Research progress on the effect of amino acid nutrition on pork quality. Graziery Veterinary Sciences, 2021, 3: 23-24 [蒋志军. 氨基酸营养对猪肉质影响研究进展. 畜牧兽医科学, 2021, 3: 23-24] |
JOHNSON D R, LEE T K, PARK J, et al. The functional and taxonomic richness of wastewater treatment plant microbial communities are associated with each other and with ambient nitrogen and carbon availability. Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 17(12): 4851-4860 DOI:10.1111/1462-2920.12429 |
KARNAA E, MILTYKA W, WOLCZYNSKIB S, et al. The potential mechanism for glutamine-induced collagen biosynthesis in cultured human skin fibroblasts. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2001, 130(1): 23-32 DOI:10.1016/S1096-4959(01)00400-6 |
KASPER C S, WHITE M R, BROWN P B. Choline is required by tilapia when methionine is not in excess. Journal of Nutrition, 2000, 130(2): 238-242 DOI:10.1093/jn/130.2.238 |
KATSUMATA M, MATSUMOTO M, KOBAYASHI S I, et al. Reduced dietary lysine enhances proportion of oxidative fibers in porcine skeletal muscle. Animal Science Journal, 2008, 79(3): 347-353 DOI:10.1111/j.1740-0929.2008.00536.x |
KRALIK G, DJURKIN I, KRALIK Z, et al. Quality indicators of broiler breast meat in relation to colour. Animal Science Papers and Reports, 2014, 32(2): 173-178 |
LERFALL J, ROTH B, SKARE E F, et al. Pre-mortem stress and the subsequent effect on flesh quality of pre-rigor filleted Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) during ice storage. Food Chemistry, 2015, 175: 157-65 |
LI W. The effect of dietary phenylalanine supplement on growth, flesh quality parameters, antioxidant capacity and intestine immune function of young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Master′s Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2014 [李文. 苯丙氨酸对生长中期草鱼生长性能、肌肉品质和肠道黏膜免疫功能的影响研究. 四川农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2014]
|
LIANG X F, HU L, DONG Y C, et al. Substitution of fish meal by fermented soybean meal affects the growth performance and flesh quality of Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus). Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2017, 229: 1-12 DOI:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.03.006 |
LIAO Y J, REN M C, LIU B, et al. Dietary methionine requirement of juvenile blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) at a constant dietary cystine level. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2014, 20(6): 741-752 DOI:10.1111/anu.12131 |
LUO J B, FENG L, JIANG W D, et al. Physical and flavor characteristics, fatty acid profile, antioxidant status and Nrf2-dependent antioxidant enzyme gene expression changes in young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) fillets fed dietary valine. PLoS One, 2017, 12(1): e0169270 DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0169270 |
MA X Z. Effects of dietary glutamine on the growth performance, flesh quality and potential mechanisms in on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Master′s Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2020 [马晓珍. 谷氨酰胺对生长中期草鱼生产性能和肌肉品质的作用及其机制. 四川农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2020]
|
MAI K S, HE Z G, AI Q H. Recent advances in threonine nutrition physiology of fish. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science), 2008(2): 195–200, 216 [麦康森, 何志刚, 艾庆辉. 鱼类苏氨酸营养生理研究进展. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2008(2): 195–200, 216] |
MARTINEZ-ÁLVAREZ R M, MORALES A E, SANZ A. Antioxidant defenses in fish: Biotic and abiotic factors. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 2005, 15(1/2): 75-88 |
MCKNIGHT J R, SATTERFIELD M C, JOBGEN W S, et al. Beneficial effects of L-arginine on reducing obesity: Potential mechanisms and important implications for human health. Amino Acids, 2010, 39(2): 349-357 DOI:10.1007/s00726-010-0598-z |
NISHIMURA T. Role of extracellular matrix in development of skeletal muscle and postmortem aging of meat. Meat Science, 2015, 109: 48-55 DOI:10.1016/j.meatsci.2015.05.015 |
NISHIMURA T. The role of intramuscular connective tissue in meat texture. Animal Science Journal, 2010, 81(1): 21-27 DOI:10.1111/j.1740-0929.2009.00696.x |
PAN F Y, WU P, FENG L, et al. Methionine hydroxy analogue improves intestinal immunological and physical barrier function in young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2017, 64: 122-136 DOI:10.1016/j.fsi.2017.03.012 |
PAN F Y. Effects of dietary methionine hydroxy analogue on growth performance, the health status of intestine, organism and gill, flesh quality and potential modulation mechanism in young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Master′s Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2016 [潘飞宇. 蛋氨酸羟基类似物对生长中期草鱼生长、肠道、机体和鳃健康以及肌肉品质的影响及其作用机制. 四川农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2016]
|
QIAN C M, WANG R H, WANG W H, et al. Effects of surface negatively charged amino acid mutation on binding between cytochrome b5 and cytochrome c. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2002, 7: 1294-1298 [钱程明, 王韵华, 王文虎, 等. 表面带负电荷氨基酸残基的突变对细胞色素b5与细胞色素c结合和识别的影响. 高等学校化学学报, 2002, 7: 1294-1298 DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0251-0790.2002.07.017] |
QIAO Y F. Effects of glutamine on growth performance and meat quality of broilers and approach to the mechanism. Master′s Thesis of Zhejiang University, 2006 [乔云芳. 谷氨酰胺对肉仔鸡生长性能和肉质的影响及其机理研究. 浙江大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2006]
|
SIKORSKI Z E, SCOTT D N, BUISSON D H. The role of collagen in the quality and processing of fish. Food Science and Nutrition, 1984, 20(4): 301-43 |
SUN W T, XU X Y, LI X Q, et al. Effects of dietary geniposidic acid on growth performance, flesh quality and collagen gene expression of grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2017, 24(3): 1112-1121 |
SUN Y P, QIU J M, WANG G X, et al. Effects of tryptophan supplemented in low protein diets on apparent digestibility coefficients, digestive enzyme activity and amino acids composition of Litopenaeus vannamei. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2016, 40(4): 720-727 [孙育平, 裘金木, 王国霞, 等. 低蛋白质饲料中添加色氨酸对凡纳滨对虾饲料表观消化率、消化酶活和全虾氨基酸组成的影响. 水生生物学报, 2016, 40(4): 720-727] |
TANG B R. Effects of dietary methionine on digestive and absorptive ability and antioxidative ability of young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idell). Master′s Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2012 [唐炳荣. 蛋氨酸对生长中期草鱼消化吸收能力和抗氧化能力影响的研究. 四川农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2012]
|
TANG Y J. Effects of dietary lysine on growth performance and flesh quality of sub-adult grass carp and its mechanism. Master′s Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2022 [唐延杰. 饲粮赖氨酸对生长后期草鱼生长性能与肌肉品质的影响及作用机制. 四川农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2022]
|
TANG Y. Effects of glycine on growth, biochemical indexes and body composition of Penaeus vannamei. Master′s Thesis of Tianjin Agricultural University, 2021 [汤雨. 甘氨酸对凡纳滨对虾生长、生化指标及体成分的影响. 天津农学院硕士研究生学位论文, 2021]
|
TANG Z T, LI C Y, XU G, et al. Effects of dietary glutathione on growth performance, muscle quality and lipid metabolism of hybrid crucian carp (Carassius auratus cuvieri♀×Carassius auratus red var. ♂) fed a high-fat diet. Reproduction and Breeding, 2023, 3: 89-98 DOI:10.1016/j.repbre.2023.07.001 |
TIE H M, WU P, JIANG W D, et al. Dietary nucleotides supplementation affect the physicochemical properties, amino acid and fatty acid constituents, apoptosis and antioxidant mechanisms in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) muscle. Aquaculture, 2019, 502: 312-325 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.12.045 |
TOKUR B, KORKMAZ K. The effects of an iron-catalyzed oxidation system on lipids and proteins of dark muscle fish. Food Chemistry, 2007, 104(2): 754-760 DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.12.033 |
WANG G H. Effects of methionine on intestinal microflora, digestive enzyme and immune function of juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Master′s Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2007 [王光花. 蛋氨酸对幼建鲤肠道菌群、肠道酶活力和免疫功能的影响. 四川农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2007]
|
WANG Y L, WANG C A, LIU H B, et al. Effects of dietary threonine in low fish meal diet on growth performance, body composition, amino acid composition in muscle of triploid Oncorhynchus mykiss. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(4): 2390-2400 [王亚玲, 王常安, 刘红柏, 等. 低鱼粉饲料中添加苏氨酸对三倍体虹鳟生长性能、体成分及肌肉氨基酸组成的影响. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(4): 2390-2400 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.04.056] |
WANG Z G, PAN X J, PENG Z Q, et al. Methionine and selenium yeast supplementation of the maternal diets affects color, water-holding capacity, and oxidative stability of their male offspring meat at the early stage. Poultry Science, 2009, 88(5): 1096-1101 DOI:10.3382/ps.2008-00207 |
WHITFIELD F B, MOTTRAM D S. Volatiles from interactions of maillard reactions and lipids. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 1992, 31(1/2): 1-58 |
WU L, ZHANG H W, NA LIN, et al. Methionine restriction at the post-weanling period promotes muscle fiber transition in piglets and improves intramuscular fat content in growing-finishing pigs. Amino Acids, 2019, 51(10/11/12): 1657-1666 |
WU L H, LIANG H L, GE X P, et al. Research progress on biological function of target of rapamycin signaling pathway in fish. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(10): 5486-5496 [吴龙华, 梁化亮, 戈贤平, 等. 鱼类雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路生物学功能的研究进展. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(10): 5486-5496 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.10.010] |
WU X, RUAN Z, GAO Y, et al. Dietary supplementation with L-arginine or N-carbamylglutamate enhances intestinal growth and heat shock protein-70 expression in weanling pigs fed a corn- and soybean meal-based diet. Amino Acids, 2010, 39(3): 831-839 DOI:10.1007/s00726-010-0538-y |
WU Y W, OUYANG J. The role of amino acids and peptides in flavor in food. China Condiment, 2001, 1: 20-22 [武彦文, 欧阳杰. 氨基酸和肽在食品中的呈味作用. 中国调味品, 2001, 1: 20-22] |
XIAO L Q, JIANG W D, WU P, et al. Improvement of flesh quality, muscle growth and protein deposition in adult grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): The role of tryptophan. Aquaculture, 2023, 577: 740005 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.740005 |
XU R S, SHANG X G, CHEN W, et al. Research progress on threonine in poultry nutrition. China Poultry, 2020, 42(1): 93-99 [徐闰胜, 尚秀国, 陈伟, 等. 家禽苏氨酸营养研究进展. 中国家禽, 2020, 42(1): 93-99] |
YAN H. The effect of dietary lysine deficient on intestinal microflora, digestive enzyme and immune function of Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Master′s Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2007 [鄢华. 赖氨酸缺乏对幼建鲤肠道菌群、消化酶活力和免疫功能的影响. 四川农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2007]
|
YAN Y J, LU X, MENG X H, et al. Screening of genes related to muscle growth under the myostatin regulation by RNA-Seq in Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2021, 42(4): 55-63 [闫允君, 卢霞, 孟宪红, 等. 基于转录组分析对中国对虾Myostatin基因调控的肌肉生长相关基因的筛选. 渔业科学进展, 2021, 42(4): 55-63 DOI:10.19663/j.issn2095-9869.20200324002] |
YANG Y Y, CHEN Y K, LIN W J, et al. Effects of L-methionine enriched Artemia nauplii on growth, amino acids composition and enzyme activities of the first feeding larvae of bighead carp (Aristichthys nobillis). Journal of Northwest A &F University (Natural Science), 2017, 45(1): 14–20, 27 [杨翼羽, 陈玉珂, 林伟杰, 等. L-蛋氨酸强化卤虫对鳙开口苗生长、氨基酸组成及相关酶活性的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(1): 14–20, 27] |
YANG Q H, ZHOU Q C, TAN B P, et al. Effects of dietary glutamine on growth performance, feed utilization and anti-disease ability of hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus♀×O. aureus♂). Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2008, 15(6): 1016-1023 [杨奇慧, 周歧存, 谭北平, 等. 谷氨酰胺对杂交罗非鱼生长、饲料利用及抗病力的影响. 中国水产科学, 2008, 15(6): 1016-1023] |
YE Y T, WANG Y L, CAI C F, et al. Effects of the L-glutamine on the absorption of L-leucine, L-proline and the protein synthesis in intestine of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) in vitro. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2007, 19(1): 28-32 [叶元土, 王永玲, 蔡春芳, 等. 谷氨酰胺对草鱼肠道L-亮氨酸、L-脯氨酸吸收及肠道蛋白质合成的影响. 动物营养学报, 2007, 19(1): 28-32] |
YU A N, ZHOUY Y, YANG Y N. Kinetics of browning and correlations between browning degree and pyrazine compounds in L-ascorbic acid/acidic amino acid model systems. Food Chemistry, 2017, 221: 1678-1684 |
YU D, XU Y, REGENSTEIN J M, et al. The effects of edible chitosan-based coatings on flavor quality of raw grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fillets during refrigerated storage. Food Chemistry, 2018a, 242: 412-420 |
YU E M, LIU B H, WANG G J, et al. Molecular cloning of type Ⅰ collagen cDNA and nutritional regulation of type Ⅰ collagen mRNA expression in grass carp. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2014, 98(4): 755-765 |
YU E M, MA L L, JI H, et al. Smad4-dependent regulation of type Ⅰ collagen expression in the muscle of grass carp fed with faba bean. Gene, 2019, 685: 32-41 |
YU M, HE S D, TANG M M, et al. Antioxidant activity and sensory characteristics of Maillard reaction products derived from different peptide fractions of soybean meal hydrolysate. Food Chemistry, 2018b, 243: 249-257 |
ZHANG J, CHEN H M, ZHOU Q C, et al. Effects of glutamine on antioxidant capacity and non-specific immunity of juvenile yellow catfish (Pelteoobagrus fulvidraco). Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2016, 28: 133-139 [张杰, 陈海敏, 周歧存, 等. 谷氨酰胺对黄颡鱼幼鱼抗氧化能力和非特异性免疫力的影响. 动物营养学报, 2016, 28: 133-139] |
ZHANG L, JIANG X, LI A, et al. Characterization of the microbial community structure in intestinal segments of yak (Bos grunniens). Anaerobe, 2020, 61: 102115 |
ZHAO H X, CAO J M, WU J K, et al. Studies of arginine requirement for juvenile cobia. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2007, 28(4): 87-90 [赵红霞, 曹俊明, 吴建开, 等. 军曹鱼幼鱼对饲料中精氨酸的需要量. 华南农业大学学报, 2007, 28(4): 87-90] |
ZHAO Y, JIANG Q, ZHOU X Q, et al. Effect of dietary threonine on growth performance and muscle growth, protein synthesis and antioxidant-related signaling pathways of hybrid catfish Pelteobagrus vachelli♀ × Leiocassis longirostris♂. British Journal of Nutrition, 2019, 123(2): 121-134 |
ZHAO Y, ZHOU X Q, HU Y, et al. Effects of dietary glutamate on muscle quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) during middle growth period. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2014, 26(11): 3452-3460 [赵叶, 周小秋, 胡肄, 等. 饲料中添加谷氨酸对生长中期草鱼肌肉品质的影响. 动物营养学报, 2014, 26(11): 3452-3460] |
ZHAO Y L, YIN J Y, FENG L, et al. Effects of dietary glutamate supplementation on flesh quality, antioxidant defense and gene expression related to lipid metabolism and myogenic regulation in Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Aquaculture, 2019, 502: 212-222 |
ZHAO Z G, SONG F J, WANG L S, et al. Effects of Gln and its precursors on muscular approximate composition, amino acid composition and AKP activities in Songpu mirror carp Cyprinus carpio Songpu. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 2018, 33(3): 341-346 [赵志刚, 宋芳杰, 王连生, 等. 谷氨酰胺及其前体物对松浦镜鲤肌肉成分、氨基酸组成及AKP活性的影响. 大连海洋大学学报, 2018, 33(3): 341-346] |
ZHU Q, XU H, XU Q Y, et al. Effect of glutamine on serum, hepatopancreas biochemical index and body composition of juvenile hybrid sturgeon. Chinese Journal Fisheries, 2010, 23(2): 16-20 [朱青, 许红, 徐奇友, 等. 谷氨酰胺对幼鲟鱼血清、肝胰脏生化指标及体成分的影响. 水产学杂志, 2010, 23(2): 16-20] |
ZHOU X H, XIANG X, LUO L, et al. Dietary threonine requirement of GIFT Oreochromis niloticus. Freshwater Fisheries, 2014, 44(4): 83-89 [周兴华, 向枭, 罗莉, 等. 吉富罗非鱼对饲料中苏氨酸的需要量. 淡水渔业, 2014, 44(4): 83-89] |
ZHOU Z H. Effects of dietary energy and arginine levels on pork quality and lipid metabolism of fininshing pigs. Master′s Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2014 [周招洪. 饲粮能量和精氨酸水平对育肥猪肉品质和脂肪代谢的影响. 四川农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2014]
|
ZHU Q, XU Q Y, XU H, et al. Dietary glutamine supplementation improves tissue antioxidant status and serum non-specific immunity of juvenile hybrid sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii♀ × Huso dauricus♂). Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 2011, 27(2): 715-720 |
ZHU Q, XU Q Y, WANG C A, et al. Effect of alanyl-glutamine on serum biochemical index and body composition of juveniles German mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 2009, 22(4): 12-15 [朱青, 徐奇友, 王长安, 等. 丙氨酰-谷氨酰胺对德国镜鲤幼鱼(Cyprinus carpio L.)血清生化指标及体组成的影响. 水产学杂志, 2009, 22(4): 12-15] |



