2. 青岛海洋科学与技术 国家实验室海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程功能实验室 青岛 266071
2. Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266071
全球大约1/2人口生活在海岸线60 km以内,海洋渔业资源为千百万人口提供着食物和生计(唐启升, 2006)。甲壳类是海洋渔业资源的重要组成部分。2015年中国近海甲壳类捕捞量为242.79万t,占近海捕捞总量的18.47%(国家统计局, 2015)。渤海作为我国的4个海区之一,是多种经济鱼虾类的产卵场和索饵场, 在黄渤海渔业生产上占有极其重要的地位,素有黄渤海“生物资源摇篮”之称(邓景耀等, 1988; 金显仕, 2000)。近几十年来,受过度捕捞和环境污染等方面的影响,渔业生物群落结构发生了巨大改变(Jin, 2003、2004、2013),优势种类从高值的大个体鱼种替代为低值的小型鱼种和虾蟹类等无脊椎动物(Iversen et al, 1993; Iversen et al, 2001; Wu et al, 2016),营养级由1959年的4.4下降至2011年的3.4(张波等, 2015)。作为海洋生态系统中层营养级的重要生态组成(Farina, 1997),甲壳类的生态重要性不断提升。与此同时,随着传统经济鱼类资源的衰退,虾蟹类的捕捞压力日益增加,进而导致甲壳类群落结构的变化(李惠玉等, 2009)。此外,渤海发生的多次溢油事故(沈光玉, 2012)也对渔业生物群落产生一定的影响,尤其以2011年发生的蓬莱19-3油井平台溢油事件对渤海生态的影响最大(宋鹏远, 2013)。本研究以渤海经济甲壳类(虾类、蟹类和虾蛄)为对象,基于2009~2010年与2012~ 2015年夏季(8月)的底拖网调查数据,分析了渤海甲壳类的种类组成、资源变动、数量分布、物种多样性及群落稳定性等群落特征,旨在了解渤海甲壳类的资源现状及其群落动态,以期为渤海甲壳类资源的可持续利用和保护提供科学依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 数据来源数据来自2009~2010年与2012~2015年夏季(8月)的底拖网调查,调查区域及站位设置参考李忠义等(2017)。调查采用205 kW双拖渔船,调查网具规格为网口宽度22.6 m、网口周长1740目、网口高度6 m、囊网网目20 mm,拖速3 knot,每站拖曳1 h,不足1 h渔获率统一为单位时间生物量(kg/h)或丰度(ind./h)。
1.2 分析方法 1.2.1 相对重要性指数利用相对重要性指数(Pinkas et al, 1971)(The index of relative importance, IRI)评价不同种类在群落中的重要程度,当IRI > 500时定为优势种(Ambrose et al, 2013),计算公式为:
| $ {\rm{IRI}} = (w + n) \times f $ | (1) |
式中,w为生物量百分比,n为个体数百分比,f为出现频率(即出现站位百分比)。
1.2.2 物种多样性物种多样性分析采用Margalef丰富度指数(Margalef et al, 1958)、Pielou均匀度指数(Pielou et al, 1966)和Shannon-Wiener多样性指数H(Shannon & Wiener, 1963)。其中,Margalef丰富度指数反映群落物种丰富度,指一个群落或环境中物种数目的多寡,亦表示生物群聚(或样品)中种类丰富度程度;Pielou均匀度指数反映一个群落或生境中全部物种个体数目的分配状况,即各物种个体数目分配的均匀程度;Shannon-Wiener多样性指数中包含2个因素:一是种类数目即丰富度;二是种类中个体分配上的平均性或均匀性,种类数目多, 可增加多样性;同样,种类之间个体分配的均匀性增加也会使多样性提高。各指数的具体计算公式如下:
| $ D = (S - 1)\ln N $ | (2) |
| $ J' = H'/\ln S $ | (3) |
| $ H = - \Sigma {P_i}\ln {P_i} $ | (4) |
式中,S为种类数,N为总个体数,Pi=ni/N为第i种占总个体数的比例。
1.2.3 群落相似性指数利用Bray-Curtis相似性指数计算各年份群落结构间的相似性(Bray et al, 1957),然后采用等级聚类分析(CLUSTER)和多维标度分析(MDS)来分析甲壳类群落结构相似性的年际变化。进一步利用单因子相似性分析(ANOSIM)对不同组群的群落结构进行差异显著性检验,并利用相似性百分比分析(SIMPER)分析各物种对群落结构差异的贡献率。Bray-Curtis相似性指数的计算公式为:
| $ B = 100 \times \left[ {1 - \frac{{\sum\limits_{i = 1}^s {|{x_{ij}} - {x_{im}}|} }}{{\sum\limits_{i = 1}^s {|{x_{ij}} + {x_{im}}|} }}} \right] $ | (5) |
式中,B为群落间的相似性指数,S为种类数目,Xij和Xim分别为第i种类在j月份和m月份的个体数密度(经4次方根转换)。MDS分析用胁迫系数(Stress)来衡量二维点图的优劣,当0.1 < Stress < 0.2时,具有一定的解释意义;当0.05 < Stress < 0.1时,排序效果基本可信;当Stress < 0.05时,二维点图对群落结构排序具有很好的代表性(Clarke et al, 1993、2001)。
1.2.4 群落更替和迁移指数群落更替指数AI反映了物种更替导致群落稳定性降低的节律,数值越大表示群落稳定性越差。迁移指数表示系统外迁入与迁出种在群落中的相对比例,MI为正值表示迁入种多于迁出种,MI为0时表示群落动态平衡,MI为负值表示迁出种多于迁入种(Bray et al, 1957)。
| $ {\rm{AI}} = \frac{{C + B}}{{A - R}} \times 100 $ | (6) |
| $ {\rm{MI = }}\frac{{C - B}}{{A - B}} \times 100 $ | (7) |
式中,A为本年份实际物种数,C为本年份新迁入物种数,B为本年份将要迁出物种数,R为公共物种数目(各年份均出现)。
2 结果 2.1 种类组成2009~2015年夏季(8月)于渤海共捕获甲壳类33种,隶属于2目21科29属,其中虾类16种,蟹类16种,虾蛄1种。按年份,2009年和2012年捕获甲壳类物种数最高,均为25种;2013年捕获甲壳类物种数最低,仅为16种。按类别,虾类物种数以2009年最高,为14种,以2013年最低,仅为8种;蟹类物种数以2012年最高,为13种,以2013年最低,仅为7种;口虾蛄(Oratosquilla oratoria)在各调查年份均有捕获(表 1)。
|
|
表 1 2009~2015年渤海甲壳类种类组成的年际变化 Table 1 Variations of the crustacean species composition in the Bohai Sea during 2009~2015 |
根据相对重要性指数(IRI),夏季渤海甲壳类的优势种(IRI > 500)随年际变化(表 2)。口虾蛄在6个年份均为绝对优势种(4768 < IRI < 13713),其生物量百分比(29.27%~79.39%)与出现频率(68.63%~89.13%)在所有物种中均稳居第一,其数量百分比也在5个年份居第一(仅2015年第二);其次,日本蟳(Charybdis japonica)在4个年份为优势种,中国对虾(Fenneropenaeus chin ensis)、葛氏长臂虾(Palaemon gravieri)、脊腹褐虾(Crangon affinis)和海蜇虾(Latreutes anoplonyx)在2个年份为优势种,三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)和泥脚隆背蟹(Carcinoplax vestitus)在1个年份为优势种。
|
|
表 2 2009~2015年渤海甲壳类优势种的年际变化 Table 2 Variations of the dominant curstacean species in the Bohai Sea during 2009~2015 |
2009~2015年夏季,渤海甲壳类的平均网获生物量为5.87 kg/h;其中以2009年最高(16.88 kg/h),2013年最低(0.64 kg/h)。按类别,虾类的平均网获生物量为0.71 kg/h,其中以2015年最高(1.77 g/h),2013年最低(0.09 kg/h);蟹类的平均网获生物量为0.97 kg/h,其中以2009年最高(2.34 kg/h),2013年最低(0.28 kg/ h);口虾蛄的平均网获生物量为4.19 kg/h,其中以2009年最高(13.40)kg/h,2013年最低(0.28 kg/h)(图 1)。

|
图 1 2009~2015年渤海甲壳类生物量与个体数组成的年际变化 Figure 1 Variations of the biomass and individual composition of curstaceans in the Bohai Sea during 2009~2015 |
2009~2015年夏季,渤海甲壳类的平均网获个体数为622.49 ind./h;其中,以2015年最高(694.71 ind./h)、2013年最低(56.01 ind./h)。按类别,虾类的平均网获个体数为369.01 ind./h,以2015年最高(1169.87 ind./h)、2013年最低(27.97 ind./h);蟹类的平均网获个体数为37.81 ind./h,以2015年最高(68.41 ind./h)、2013年最低(9.49 ind./h);口虾蛄的平均网获个体数为307.95 ind./h,以2009年最高(695.11 ind./h)、2013年最低(18.55 ind./h) (图 1)。
2.4 数量分布2009~2015年夏季渤海甲壳类的个体数分布见图 2。2009年甲壳类密度以渤海中部较高,莱州湾及辽东湾口相对较低;2010年以黄河口、渤海湾中东部和渤海中部密度较高,辽东湾及莱州湾东南部密度较低;2012年以莱州湾及天津近岸密度较高,辽东湾及河北近岸密度较低;2013年以莱州湾西部及渤海湾东南部密度较高,渤海中部及辽东湾密度较低;2014年以渤海中部密度较高,莱州湾东南部及渤海海峡邻近水域密度较低;2015年以渤海中部及辽东湾密度较高,莱州湾密度较低。图 2显示了蓬莱19-3油井平台的位置,可以看到,平台毗邻水域甲壳类的资源密度于2009~2010年较高,2012~2013年则极低,2014~2015年恢复至较高水平。
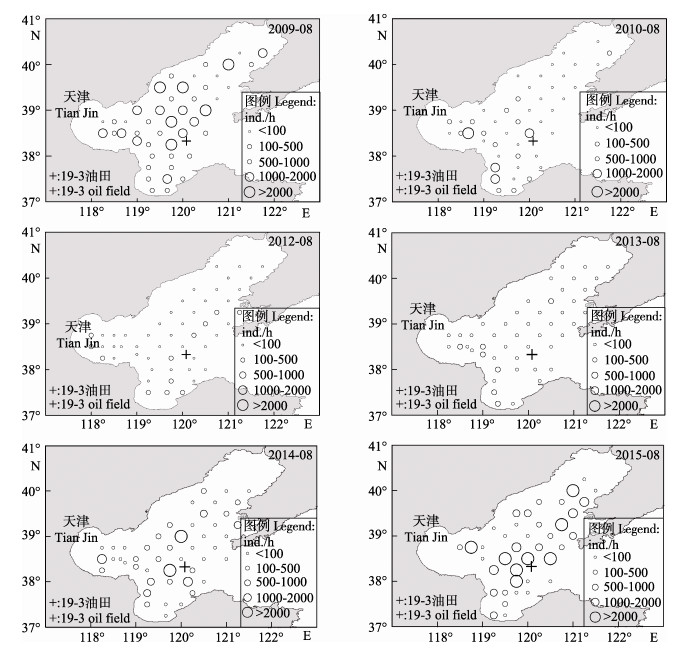
|
图 2 2009~2015年渤海甲壳类个体数分布的年际变化 Figure 2 Variations of the crustacean individual distribution in the Bohai Sea during 2009~2015 |
2009~2015年夏季渤海甲壳类物种多样性指数的年际变化见图 3。可以看到,物种丰富度指数和Shannon-Weiner指数年际变化的趋势是一致的,整体均呈先上升、后下降、再回升的趋势。物种丰富度指数(d)由2009年的0.60上升至2010年的0.76,此后下降至2012年的0.71,2013年和2014年分别回升至0.75和0.96。Shannon-Weiner指数(H)由2009年的0.58上升至2010年的0.79,2012年下降至0.70,此后分别回升至2013年的0.79、2014年的0.87和2015年的0.90。Pielou均匀度指数(J')的年际变化呈先升后降,回升后再次下降的趋势,2009年的0.39上升至2010年的0.59,此后下降至2012年的0.48,回升至2013年的0.57后、再次下降至2014年的0.53和2015年的0.50。
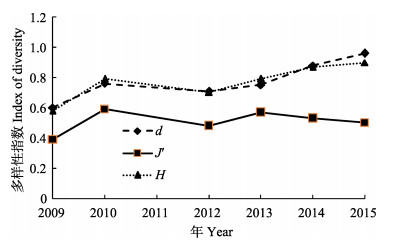
|
图 3 2009~2015年渤海甲壳类的多样性指数 Figure 3 Index of crustacean diversity in the Bohai Sea during 2009~2015 |
根据2009~2015年8月渤海甲壳类个体数矩阵,通过聚类(CLUSTER)和非度量多维标度(MDS)分析,6个调查年在70%相似性水平上被区分为4个群组。2010年、2014年和2015年分别独立为一个群组,2009年、2012年和2013年划为同一个群组(简称为群组2009)。其中,以2010年与其他年份的群落结构相似性指数最低,仅为49%~57%,平均值为51%;以2013年与其他年份的群落结构相似性指数最高,为57%~ 77%,平均值为66%。MDS胁迫系数(Stress)为0,说明二维点图对群落结构排序具有很好的代表性(图 4)。ANOSIM分析显示,不同群组的群落结构均呈显著性差异(P < 0.05)。SIMPER分析表明,口虾蛄对区分群组2009与群组2014、群组2010与群组2014的贡献率分别达67.41%和32.95%;葛氏长臂虾在区分群组2009与群组2015、群组2010和群组2015以及群组2014和群组2015的贡献率分别达到54.44%、44.97%和67.07%;海蜇虾、鹰爪虾和口虾蛄对区分群组2009和群组2010的累积贡献率达71.87%。
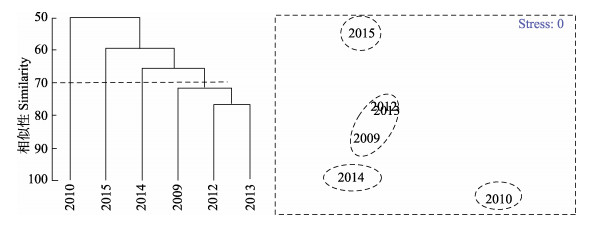
|
图 4 渤海甲壳类个体数密度的时间聚类及MDS分析 Figure 4 Temporal clustering and MDS analysis on the individual density of of crustaceans in the Bohai Sea |
根据相关参数(表 3)计算各年份渤海甲壳类群落更替指数与迁移指数,进而分析甲壳类群落稳定性的变化趋势。2012年、2010年和2015年渤海甲壳类群落的稳定性较好,其更替指数AI均在100以下;2014年渤海甲壳类群落的稳定性较差,其更替指数AI为112.5;2013年甲壳类群落稳定性最差,其更替指数高达300。2010年和2012年渤海甲壳类群落基本处于动态平衡,迁入和迁出物种数大体相当;2014年和2015年渤海甲壳类迁入物种数远大于迁出物种数;2013年甲壳类迁出物种数远大于迁入物种数(图 5)。综合更替指数和迁移指数,渤海甲壳类群落的稳定性以2010年最好、2013年最差。
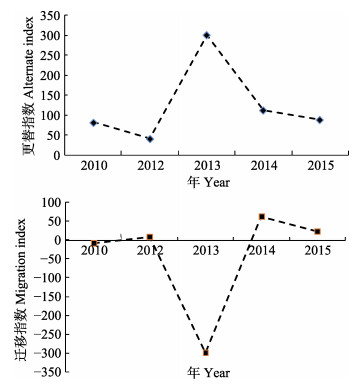
|
图 5 渤海甲壳类群落的更替指数和迁移指数 Figure 5 The alternating index and the migration index of crustacean communities in the Bohai Sea |
|
|
表 3 群落更替指数和迁移指数的参数 Table 3 The parameters of the alternating index and the migration index of crustacean community |
李忠义等(2017)研究了2010年和2012~2014年夏季(8月)渤海鱼类群落的年际变化,发现鱼类物种数目由2010年的40种下降至2012年的34种以及2013年的29种,2014年恢复至33种。本研究发现渤海甲壳类物种数目的变化趋势与鱼类近似,均以2013年最低、并且2014年逐渐恢复,不同之处在于鱼类物种数目2012年已大幅下降,而甲壳类物种数目2012年时仍然在高位,2013年大幅下降。
本研究中,口虾蛄在2009~2015年各年份均为渤海甲壳类的绝对优势种,其生物量百分比及出现频率在所有物种中稳居第一。吴强等(2016)曾于2011~ 2012年对莱州湾的甲壳类群落进行了逐月调查,发现甲壳类的周年优势种为口虾蛄、褐虾、葛氏长臂虾、日本蟳和日本鼓虾(Alpheus japonicus),尤其以口虾蛄为绝对优势种,这与本研究的结果一致。综合来看,口虾蛄已经成为渤海甲壳类的绝对优势种。
3.2 资源密度及结构组成2010年8月渤海因斑
作为渤海唯一的口足类物种,口虾蛄已经成为渤海甲壳类的绝对优势种,2009~2015年其生物量和个体数百分比的平均值分别为54.88%和46.94%,在虾、蟹和虾蛄3个类别中均最高。其次,蟹类和虾类的生物量百分比平均值分别为29.44%和15.68%,个体数百分比平均值分别为10.66%和42.40%。这一研究结果与近年来对渤海渔业资源结构的的报道一致(李显森等, 2016; 李凡等, 2013)。口虾蛄之所以能够成为渤海甲壳类的绝对优势种,一方面与渤海粉砂泥土底质的比例较高(刘晓收等, 2014)、适宜口虾蛄的掘穴习性有关;另一方面,鉴于其穴居习性,口虾蛄既能避暑抗寒、又能减少台风等灾害性天气的伤害,并且抗病能力强(王波等, 1998);此外,鱼类资源的衰退也降低了口虾蛄被敌害生物捕食的风险。
3.3 蓬莱19-3油井溢油的影响渤海石油平台、管线的数量和密度在中国4个海区中最高,历史上曾发生过多起溢油事故(刘明等, 2015),尤其以2011年蓬莱19-3油井平台溢油对生态系统的影响最大(宋朋远, 2013)。Pan(2015)从捕捞及养殖方面分析了蓬莱19-3油田溢油的影响,认为甲壳类、贝类、藻类和海参等地方性物种产量下降的程度远高于移动性较强的鱼类。除中国对虾、日本对虾和鹰爪虾外,渤海绝大部分甲壳类物种为地方性物种,溢油对其产生的影响相对较大。Dauvin(2000)在研究了Amoco Cadiz号溢油对底栖生物群落的影响后,认为污染海域的生物群落需要10年或更久才能恢复至原来水平。本研究在统计整个渤海甲壳类数量变动的同时,还针对性地分析了蓬莱19-3油田毗邻水域甲壳类的数量变动,发现其变动趋势与整个渤海一致,即无论从整个渤海还是蓬莱19-3油田毗邻水域,2012~2013年甲壳类的资源密度较2009~2010年均大幅下降,此后2014~2015年逐渐恢复。这与周政权等(2016)关于蓬莱19-3油田溢油对大型底栖生物的影响及其恢复年限的结果一致。据报道,蓬莱19-3平台溢油事故1年后渤海中部底质沉积物中石油烃含量显著减少(Pan et al, 2015)。与石油烃的情况相比,溢油对鱼类(李忠义等, 2017)和大型底栖生物(周政权等, 2016)的影响会更加深远。根据本研究,2011年蓬莱19-3平台溢油后的第3~4年,即2014~2015年,甲壳类资源已基本恢复,而无需等到Dauvin(2000)提出的10年或更久,这也反映出蓬莱19-3油田的溢油规模远低于Amoco Cadiz号。
4 总结基于2009~2015年夏季(8月)的底拖网调查数据,对渤海甲壳类群落的研究表明:1)渤海甲壳类的生态优势种类组成随年际变化,口虾蛄在每个年份均为绝对优势种;2) 2009~2013年渤海甲壳类的物种数目、生物量和个体数密度均持续下降,2014~2015年逐步恢复;3)聚类分析(CLUSTER)和多维标度分析(MDS)将6个调查年份分为4个群组,群组间的群落结构差异性显著(P < 0.05),口虾蛄、葛氏长臂虾和海蜇虾对群组区分的贡献率最高;4)群落更替指数和迁移指数显示,渤海甲壳类群落的稳定性以2010年和2012年最好,以2013年最差。总体来看,2011年蓬莱19-3平台溢油后的第3~4年,即2014~2015年渤海的甲壳类群落已逐渐恢复。
| Ambrose ST, Froneman PW, Smale MJ, et al. Winter diet shift of long-beaked common dolphins (Delphinus capensis) feeding in the sardine run off Kwa Zulu-Natal, South Africa. Marine biology, 2013, 160(7): 1543-1561 DOI:10.1007/s00227-013-2208-6 | |
| Bray JR, Curtis JT. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecological Monographs, 1957, 27(4): 326-349 | |
| Clarke KR, Ainsworth M. A method of linking multivariate community structure to environmental variables. Marine Ecology Progress, 1993, 92(3): 205-219 | |
| Clarke KR, Warwick RM. Change in the marine communities: An approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. PRIMER-E Ltd., Plymouth P144, 2001 | |
| Dauvin JC. The muddy fine sand abra alba-melinna palmata, community of the bay of morlaix twenty years after the amoco cadiz oil spill. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2000, 40(6): 528-536 DOI:10.1016/S0025-326X(99)00242-8 | |
| Deng JY, Zhu JS, Cheng JS, et al. Main invertebrates in the bohai sea and their fishery biology. Marine Fisheries Research, 1988(9): 91-120 [邓景耀, 朱金声, 程济生, 等. 渤海主要无脊椎动物及其渔业生物学. 海洋水产研究, 1988(9): 91-120] | |
| Fariña AC, Freire J, González-Gurriarán E. Megabenthic decapod crustacean assemblages on the Galician continental shelf and upper slope (north-west Spain). Marine Biology, 1997, 127(3): 419-434 DOI:10.1007/s002270050029 | |
| Iversen SA, Johannessen A, Jin XS, et al. Development of stock size, fishery and biological aspects of anchovy based on R/V "Bei Dou" 1984-1999 surveys. Marine Fisheries Research, 2001, 22(4): 33-39 [IversenSA, JohannessenA, 金显仕, 等. Development of stock size, fishery and biological aspects of anchovy based on R/V "Bei Dou" 1984-1999 surveys. 海洋水产研究, 2001, 22(4): 33-39] | |
| Iversen SA, Zhu DS, Johannessen A, et al. Stock size, distribution and biology of anchovy in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Fisheries research, 1993, 16(2): 147-163 DOI:10.1016/0165-7836(93)90049-D | |
| Jin XS, Shan XJ, Li XS, et al. Long-term changes in the fishery ecosystem structure of Laizhou Bay, China. Science China (Earth Sciences), 2013, 56(3): 366-374 DOI:10.1007/s11430-012-4528-7 | |
| Jin XS. Long-term changes in fish community structure in the Bohai Sea, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2004, 59(1): 163-171 DOI:10.1016/j.ecss.2003.08.005 | |
| Jin XS. The dynamics of major fishery resources in the Bohai Sea. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2000, 7(4): 22-26 [金显仕. 渤海主要渔业生物资源变动的研究. 中国水产科学, 2000, 7(4): 22-26] | |
| Jin XS. Fishery biodiversity and community structure in the Yellow and Bohai Seas. American Fisheries Society Symposium, 2003: 643-650 | |
| Li F, Zhang HJ, Lv ZB, et al. Species composition and community diversity of nekton in Laizhou Bay, China. Biodiversity Science, 2013, 21(5): 537-546 [李凡, 张焕君, 吕振波, 等. 莱州湾游泳动物群落种类组成及多样性. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(5): 537-546] | |
| Li HY, Ling JZ, Li SF. Seasonal composition of crustacean species in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2009, 30(3): 13-19 [李惠玉, 凌建忠, 李圣法. 黄、东海底栖性甲壳动物种类组成的季节变化. 渔业科学进展, 2009, 30(3): 13-19] | |
| Li XS, Wu YF, You ZB, et al. Analysis on the the catch composition by trammel net and its fishing performance for Oratosquilla oratoria in the Bohai Sea. Marine Fisheries, 2016, 38(5): 516-524 [李显森, 吴亚飞, 尤宗博, 等. 渤海口虾蛄三重刺网渔获组成及其捕捞性能分析. 海洋渔业, 2016, 38(5): 516-524] | |
| Li ZY, Wu Q, Shan XJ, et al. Interannual variations in fish community structure in the Bohai Sea. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2017, 24(2): 403-413 [李忠义, 吴强, 单秀娟, 等. 渤海鱼类群落结构的年际变化. 中国水产科学, 2017, 24(2): 403-413] | |
| Liu M, Zhang AB, Liao YJ, et al. Environmental quality of petroleum hydrocarbons in the surface sediment of the oil and gas exporation zone in the central of Bohai Sea. Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(1): 12-16 [刘明, 张爱滨, 廖永杰, 等. 渤海中部油气开采区沉积物中石油烃环境质量. 海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(1): 12-16] | |
| Liu XS, Fan Y, Shi SJ, et al. Stduies on the species composition and structure of macrofauna in the Bohai Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 36(12): 53-66 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.12.005 [刘晓收, 范颖, 史书杰, 等. 渤海大型底栖动物种类组成与群落结构研究. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(12): 53-66] | |
| Margalef DR. Information theory in ecology. Society for General Systems Research. 1958, 36-71 | |
| National Bureau of Statistics of China. Chinese fishery statistical yearbook. Beijing: Science Press, 2015. [国家统计局. 中国渔业统计年鉴. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2015.] | |
| Pan G, Qiu S, Liu X, et al. Estimating the economic damages from the Penglai 19-3 oil spill to the Yantai fisheries in the Bohai Sea of northeast China. Marine Policy, 2015(62): 18-24 | |
| Pielou EC. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1966, 13(1): 131-144 | |
| Pinkas L, Oliphant S, Iverson I. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna and bonito in Californian waters.. Fish Bulletin, 1971(152): 1-105 | |
| Shannon CE, Weaver, W. Mathematical theory of communication. University Illinois Press, 1963 | |
| Shen GY. The research on risk assessment and avoidance of Bohai Sea ship oil spill accident. Master's Thesis of Dalian Maritime University, 2012 [沈光玉. 渤海及邻近海域船舶溢油事故风险评价及规避研究. 大连海事大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2012] | |
| Song PY. Numerical simulation research on oil spill diffusion and drift process of the Bohai Sea oil field. Master's Thesis of Ocean University of China, 2013 [宋朋远. 渤海油田溢油扩散与漂移的数值模拟研究. 中国海洋大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2013] | |
| Tang QS. Chinese marine biological resources in the exclusive economic zone and habitats. Beijing: Science Press, 2006: 364-407. [唐启升. 中国专属经济区海洋生物资源与栖息环境. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006: 364-407.] | |
| Wang B, Zhang XL, Sun PX. On biological characters and artificial seedling-rearing techniques of Mantis Shrimp (Oratosquilla oratoria). Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai and Bohai Seas, 1998(2): 64-73 [王波, 张锡烈, 孙丕喜. 口虾蛄的生物学特征及其人工苗种生产技术. 黄渤海海洋, 1998(2): 64-73] | |
| Wu Q, Wang J, Zhang B, et al. Monthly variation in crustacean assemblage (Decapod and Stomatopod) structure and its relationships with environmental variables in Laizhou Bay, China. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2016, 15(2): 370-378 DOI:10.1007/s11802-016-2714-5 | |
| Zhang B, Jin XS, Wu Q, et al. Enhancement and release of Chinese shrimp in Laizhou Bay. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2015, 22(3): 361-370 [张波, 金显仕, 吴强, 等. 莱州湾中国明对虾增殖放流策略研究. 中国水产科学, 2015, 22(3): 361-370] | |
| Zhou ZQ, Li XJ, Chen LL, et al. Long-term effects of Penglai 19-3 oil spill event on the microbenthic community structure in Bohai Sea. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 2016, 32(2): 92-100 [周政权, 李晓静, 陈琳琳, 等. 蓬莱19-3平台溢油事故对渤海大型底栖生物群落结构的长期影响. 广西科学院学报, 2016, 32(2): 92-100] |



