2. 天津赞兰科技有限公司 天津 300000;
3. 广西壮族自治区水产技术推广站 广西 南宁 530000
2. Tianjin Zanlan Technology Co., LTD., Tianjin 300000, China;
3. Fishery Technology Promotion Station of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning, Guangxi 530000, China
克氏原螯虾(Procambarus clarkii)俗称小龙虾,原产于墨西哥北部和美国南部(蔡凤金等, 2010),于20世纪90年代引入我国(唐鑫生, 2001)。因其适应力强、肉质鲜美、味道独特等特点,成为我国重要的养殖经济虾类(晏明瑶等, 2021),2020年小龙虾产业的总产值达3448.46亿元,市场前景广阔。随着小龙虾产业链的发展,对其专用配合饲料的需求也逐渐增加(惠文杰等, 2020)。
确定和优化主要营养物质是研发配合饲料的重要前提,其中,脂肪是最重要的营养物质之一(Tacon et al, 2008; 何先林等, 2021)。脂肪是必需脂肪酸的主要来源(Yun et al, 2013),在克氏原螯虾生长发育及繁殖过程中发挥着重要作用(Tocher, 2003; Wen et al, 2021)。适宜的饲料脂肪含量不仅能促进虾的健康生长,还能节约饲料蛋白质、降低养殖成本(张家宏等, 2012; 斯烈钢等, 2014; 鲁耀鹏等, 2018)。孟晶等(2016)以1.82%、3.84%、5.79%、7.89%、9.91%和11.95% 6种脂肪水平饲料投喂初始体重为(4.76±0.42) g的克氏原螯虾,发现8.74%的饲料脂肪水平可获得最大增重率;张家宏等(2012)进行饲料蛋白质和脂肪水平双因子试验,发现蛋白水平为24%~28%和脂肪水平为6%时,克氏原螯虾可得到最佳生长;此外,对克氏原螯虾亲虾的研究发现,适宜的饲料脂肪水平为7.60%~7.89% (彭迪等, 2019)。迄今为止,关于克氏原螯虾饲料中脂肪含量的研究主要集中于生长性能、生化指标以及肌肉的常规营养成分方面,而针对肌肉品质的研究还未见报道。
因此,本研究从生长性能及肌肉的质构指标、营养成分和食用风味等方面,比较不同饲料脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾幼虾的影响,旨在为克氏原螯虾幼虾配合饲料的开发及合理评价脂肪对克氏原螯虾肌肉品质的影响提供理论基础和科学依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验饲料实验饲料以鱼粉、豆粕和菜籽粕为主要蛋白源,以鱼油与豆油1∶1比例的混合油为脂肪源,制备2.86%、5.11%、7.67%、10.19%和13.02%脂肪水平的5种等氮饲料,具体营养组成见表 1。主要原料经粉碎过80目筛后,按比例逐级混匀,加入脂肪与适量水在搅拌机中充分混合,用小型绞肉机制成直径3 mm、长度5 mm的颗粒饲料,风干后−20℃保存备用。
1.2 实验虾与饲养管理实验虾购于广西汇洋科技有限公司,养殖实验在广西大学水产基地养殖池(方形,1.0 m×1.0 m×0.6 m)中进行。实验开始前,在养殖池中驯养7 d后,选取健壮、附肢完好、规格相似的幼虾600尾[(4.00±1.00) g],随机分为5组,每组3个重复,每个重复40尾虾。每日早晚(06:00和19:30)按虾体重的3%投喂饲料。每日初投喂前清理池内粪便和残饵,观察并记录水温、摄食及死亡状况,每2天换水1/3。养殖池内以悬挂网片为遮蔽物,实验期间池水溶氧高于5 mg/L,水温为25~30℃,pH为7.0~7.7,氨氮低于0.05 mg/L,养殖周期为60 d。
1.3 样品采集取样前禁食24 h,对每组虾进行计数、称重,用于计算各生长指标。每组随机取10尾虾,解剖分离肝胰腺、肌肉和性腺,称重后于−80℃冰箱储存备用,用于计算肝体指数和出肉率,肌肉样本用于测量其常规成分、质构指标、脂肪酸和氨基酸组成。各生长指标计算公式如下:
| $\begin{array}{l} 成活率({\rm{survival\;rate}},{\rm{SR}},\% ) = 100 \times {N_d}/{N_a};\\ 特定生长率({\rm{specific\;growth\;rate}},{\rm{SGR}},\% /\rm{d}) = \\ \;\;\;\;100 \times \left( {\ln {W_d} - \ln {W_a}} \right)/D;\\ 出肉率({\rm{flesh\;content}},{\rm{FC}},\% ) = 100 \times {W_m}/{W_d};\\ 肝体指数({\rm{hepatosomatic\;index}},{\rm{HSI}},\% ) = \\ \;\;\;\;100 \times {W_h}/{W_d};\\ 饲料系数({\rm{feed\;conversation\;ratio}},{\rm{FCR}}) = {W_f}/{W_o}; \end{array}$ |
式中,Na为初始尾数,Nd为终末尾数,Wa为初始体质量,Wd为终末体质量,D为实验天数,Wm为去壳腹部肌肉重,Wh为虾体肝胰腺重,Wf为摄入饲料量,W0为增重量。
1.4 生化成分分析常规营养成分测定方法:水分含量采用105℃恒温干燥失重法(GB/T5009.3-2016);粗灰分含量使用550℃马弗炉灼烧法(GB/T5009.4-2016);粗蛋白含量用凯氏定氮法(GB/T5009.5-2016);粗脂肪含量为索氏抽提法(GB/T5009.6-2016)。
肌肉的质构指标测定方法:采用TMS-pro型质构仪质地剖面分析法(texture profile analysis, TPA)测定(Cai et al, 2018)。测定肌肉硬度、咀嚼性、弹性、黏性、凝聚性和回复性。
肌肉蒸煮损失率(cooking loss, CL, %)的测定方法:取肌肉样品除去表面水分后称量(Wn),装入自封袋中并于沸腾水中蒸煮5 min,去除表面水分后称重(Wp),CL=(Wn−Wp)/Wn×100%。
脂肪酸测定方法:参照陈金民等(2010),采用气质联用法,使用GC Smart (GC-2018)气相色谱仪(Shimadzu, 日本)测定肌肉脂肪酸组成和含量。
氨基酸测定方法:参照JY/T019-1996,使用Biochrom30+型氨基酸自动分析仪(Biochrom, 英国)测定氨基酸组成和含量。
1.5 数据分析实验数据均用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计分析,ANOVA法进行单因素分析(one-way ANOVA),Duncan´s法进行多重比较分析,所有数据值均用平均值±标准差(Mean±SD)表示,P < 0.05表示差异显著。
|
|
表 1 实验饲料配方及营养组成(%干物质) Tab.1 Formula and nutrient composition of experimental feed (% dry matter basis) |
表 2显示,饲料脂肪含量显著影响实验虾的终末体质量(FBW)、特定生长率(SGR)、出肉率(FC)、成活率(SR)、肝体指数(HSI)和饲料系数(FCR)(P < 0.05),其中,FBW、SGR及SR先呈上升趋势,在L3组达到最高峰后呈下降趋势;HSI呈上升趋势;FC则呈下降趋势,L5组显著低于L1组(P < 0.05);FCR呈现为先降低后升高的趋势,L3组显著低于其余组(P < 0.05)。
|
|
表 2 脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾幼虾生长和饲料利用的影响 Tab.2 Effects of lipid levels on growth performance and feed utilization of juvenile P. clarkia (Mean±SD, n=3) |
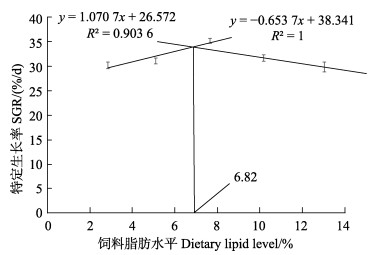
以饲料脂肪水平为自变量(x),以SGR为因变量(y)作折线回归,求得2条直线相交值,即饲料脂肪水平为6.82%时,克氏原螯虾幼虾获得最大特定生长率(图 1)。
|
图 1 基于折线回归分析评估最适脂肪水平 Fig.1 The optimal lipid level evaluated by linear regression analysis |
饲料脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾幼虾肌肉质构特性及蒸煮损失率的影响见表 3,肌肉的硬度、弹性、凝聚性、黏性、咀嚼性和回复性均随饲料脂肪水平的增加而下降,蒸煮损失率则不断上升。其中,L1、L2和L3组之间的硬度、弹性、凝聚性、黏性及蒸煮损失率无显著差异(P > 0.05);与L1组相比,L4、L5组的硬度、弹性、黏性、咀嚼性和回复性显著降低(P < 0.05);L5组的凝聚性最低,显著低于其余4组(P < 0.05);与L1组相比,L4、L5组的蒸煮损失率显著升高(P < 0.05)。
|
|
表 3 不同脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾幼虾肌肉品质的影响 Tab.3 Effects of different lipid levels on muscle quality in muscle of juvenile P. clarkia (Mean±SD, n=3) |
饲料脂肪含量对肌肉水分、粗蛋白以及灰分含量无显著影响(P > 0.05) (表 4),而对粗脂肪含量有显著影响(P < 0.05),且二者之间呈正相关,其中,L5组显著高于其他组(P < 0.05)。
|
|
表 4 脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾幼虾肌肉营养成分的影响 Tab.4 Effects of lipid levels on muscle composition of juvenile P. clarkia (Mean±SD; n=3; %) |
克氏原螯虾幼虾肌肉中共检测出16种脂肪酸,其中,饱和脂肪酸(SFA) 4种,单不饱和脂肪酸(MUFA) 4种,多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFA) 8种(表 5)。饲料脂肪水平对总饱和脂肪酸(∑SFA)含量和总单不饱和脂肪酸(∑MUFA)含量无显著影响(P > 0.05);但显著影响总多不饱和脂肪酸(∑PUFA)含量(P < 0.05),随脂肪水平的增加不断增加,但L2、L3和L4组间差异不显著(P > 0.05);L5组的EPA含量显著大于其余4组(P < 0.05),L5组的DHA含量显著大于L1和L2组(P < 0.05),但与L3组和L4组无显著差异(P > 0.05)。
|
|
表 5 脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾幼虾肌肉脂肪酸组成的影响 Tab.5 Effects of lipid levels on fatty acid composition in muscle of juvenile P. clarkii (Mean±SD; n=3; %) |
由表 6可知,饲料脂肪含量对肌肉的总必需氨基酸(∑EAA)含量、谷氨酸(Glu)、甘氨酸(Gly)含量无显著影响(P > 0.05);与L1组相比,L5组的总鲜味氨基酸(∑FAA)含量、丙氨酸(Ala)及天门冬氨酸(Asp)的含量显著降低(P < 0.05);总氨基酸(∑TAA)含量随脂肪水平的升高呈上升趋势,L5组显著大于L1组(P < 0.05);且∑FAA和∑TAA含量在L1~L4组间均差异不显著(P > 0.05)。
3 讨论 3.1 饲料脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾幼虾生长性能的影响本研究中,饲料脂肪含量为2.86%~7.67%时,脂肪的增加对克氏原螯虾幼虾具有显著的促生长作用,而在脂肪含量为10.19%~13.02%时,不产生促生长作用。在三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)(Huo et al, 2014)、红鳌螯虾(Cherax quadricarinatus)(Rodriguez-Gonzalez et al, 2013)和凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei) (Xu et al, 2018)等研究中发现,适宜脂肪含量范围内,脂肪含量越多,生长性能越佳,而添加过量的脂肪则不能促进生长,这与本研究结果相似。本研究中,实验虾的FCR随脂肪含量的增加表现为先下降后上升的趋势,可能是由于饲料中能量随脂肪水平的增加而增加,实验虾根据摄入饲料的能量的不同来调节摄食。
|
|
表 6 脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾幼虾肌肉氨基酸的影响 Tab.6 Effects of lipid levels on amino acids composition in muscle of juvenile P. clarkii (Mean±SD; n=3; %) |
本实验以SGR作为评价依据,采用折线回归分析,得出适宜脂肪含量为6.82%。本实验结果处于徐维娜等(2011)的研究结果范围内,但低于初始体质量4.76 g克的克氏原螯虾(养殖水温22~28℃)的研究结果(孟晶等, 2016),这可能是因为低温需要较高的脂肪含量来满足生长,而本实验的养殖水温(25~30℃)较高。此外,本结果也低于15.46 g的克氏原螯虾亲虾的研究结果(彭迪等, 2019),这可能与虾的生长阶段有关,亲虾需要更多脂肪来维持性腺发育及繁殖能力。
3.2 饲料脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾幼虾肌肉质构特性的影响克氏原螯虾的去壳腹部肌肉是主要食用部位,其品质与经济价值密切相关,脂肪成分和脂肪沉积对肌肉的质地影响较大(Thakur et al, 2002)。肌肉质构反映了肌肉的组织状态和食用口感,蒸煮损失率反映了肌肉营养物质的损失率(Johnston et al, 2000; 王靖等, 2021)。本研究表明,当饲料脂肪水平高于10.19%时,会显著降低肌肉的质构指标,增大营养损失,进而降低了其食用口感和营养成分。马睿(2014)对大黄鱼(Pseudosciaena crocea)的研究发现,饲料中适当的脂肪含量可显著提高肌肉硬度和持水力,而过低或过高的脂肪含量则会降低肌肉品质;吴凡等(2018)通过研究不同脂肪水平对中华鳖(Pelodiscus sinensis)肉质的影响,发现高脂饲料会降低肌肉硬度、黏性和咀嚼性,进而降低肌肉嫩度。以上结果均与本结果一致,其原因可能是,不同的饲料脂肪含量通过影响肌肉脂肪的沉积和效率,进而影响肌肉脂肪含量,高脂饲料会降低肌肉的食用口感。
3.3 饲料脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾幼虾肌肉营养品质的影响肌肉常规营养成分的含量是评价虾类品质的重要指标(万金娟等, 2020)。本研究表明,饲料脂肪含量的增加可显著增加克氏原螯虾肌肉的粗脂肪含量,降低肌肉粗蛋白含量,其原因可能是高脂饲料可促进虾体粗脂肪沉积,提高蛋白质利用率,进而降低肌肉蛋白质的沉积(陈伟兴等, 2012; 何亚丁等, 2013),对澳大利亚红螯虾(Cherax quadricarinatus)(Zhu et al, 2013)、草鱼(Ctenopharyngodon idellus)(Du et al, 2005)、白鲈鱼(Atractoscion nobilis) (Lopez et al, 2006)的研究均证实此结果。
克氏原螯虾的风味与脂肪酸和氨基酸的组成和含量密切相关,且不饱和脂肪酸和鲜味氨基酸的含量越高,风味越佳(Wang et al, 2020; 罗雅婷等, 2021)。肌肉脂肪酸受饲料脂肪酸组成的显著影响,肌肉脂肪酸组成是饲料种类和体内代谢的结果(郑建明等, 2019)。本研究中,肌肉的∑PUFA、EPA和DHA的含量在L5组最高,均在L2、L3和L4组间无显著差异。这可能是由于饲料中脂肪含量影响虾对不同脂肪酸的消化吸收,影响虾体脂肪酸的沉积及组成,因L5组饲料中鱼油含量最多,EPA和DHA含量高,进而显著增加了肌肉中EPA和DHA含量。结果表明,饲料中适宜的脂肪含量可以有效提高克氏原螯虾幼虾的营养价值,还能增加肌肉风味。
本研究在克氏原螯虾肌肉中均检出18种氨基酸,其中,必需氨基酸8种,非必需氨基酸10种,说明实验虾肌肉氨基酸组成种类齐全。本研究中,当饲料脂肪含量为13.02%时,会显著降低∑FAA含量。类延菊等(2020)研究发现,洞庭青鲫(Carassius auratus var. Dongtingking)肌肉的FAA含量随着脂肪水平增加而降低,降低肌肉风味,与本研究结果相吻合。肉质评价分析中,呈鲜味的谷氨酸和天门冬氨酸,呈甘味的甘氨酸和丙氨酸是主要的鲜味氨基酸,决定了肌肉的鲜美程度和口感(李赵嘉等, 2019; 周剑等, 2021)。本研究中,饲料脂肪水平显著影响Ala和Asp含量,当饲料脂肪水平高于10.19%时,会显著降低Ala含量;当饲料脂肪水平高于13.02%时,会显著降低Asp含量。其原因可能是饲料中一定的脂肪含量对提升肌肉的Asp和Ala含量有所帮助,而高脂饲料反而会有抑制作用。在不影响克氏原螯虾肌肉品质的基础上,克氏原螯虾饲料的脂肪含量应不超过10.19%为宜。
4 结论本研究条件下,根据特定生长率折线回归分析,得出饲料中适宜脂肪水平为6.82%;当饲料脂肪水平高于10.19%时,会显著降低克氏原螯虾肌肉的营养价值、食用口感、鲜美程度及风味。综合各项因素分析,建议克氏原螯虾幼虾饲料中脂肪含量为6.82%~10.19%。
CAI F J, WU Z J, HE N, et al. Research progress in invasion ecology of Procambarus clarkia. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29(1): 124-132 [蔡凤金, 武正军, 何南, 等. 克氏原螯虾的入侵生态学研究进展. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(1): 124-132] |
CAI W C, JIANG G Z, LI X F, et al. Effects of complete fish meal replacement by rice protein concentrate with or without lysine supplement on growth performance, muscle development and flesh quality of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Aquaculture Nutrition, 2018, 24(1): 481-491 DOI:10.1111/anu.12581 |
CHEN J M, WEI H, SHEN H, et al. Lipid content and fatty acid composition in hepatopancreas and ovaries of Procambrus clarkii during ovarian maturation. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2010, 17(6): 1278-1284 [陈金民, 魏华, 沈竑, 等. 克氏原螯虾卵巢发育时期组织脂肪含量及脂肪酸组成. 中国水产科学, 2010, 17(6): 1278-1284] |
CHEN W X, LIU Q Z, FAN Z T, et al. Recent advances in research on meat quality evaluation and influencing factor of fish. Meat Research, 2012, 26(10): 34-40 [陈伟兴, 刘清振, 范兆廷. 鱼类肉质评价及影响因素研究进展. 肉类研究, 2012, 26(10): 34-40] |
DU Z Y, LIU Y J, TIAN L X, et al. Effect of dietary lipid level on growth, feed utilization and body composition by juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture Nutrition, 2005, 11(2): 139-146 DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2095.2004.00333.x |
HE X L, LIU M M, ZHU S C, et al. Effects of dietary protein levels on the growth, ovarian development and biochemical composition of the swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2021, 42(5): 158-166 [何先林, 柳梅梅, 朱筛成, 等. 饲料中蛋白水平对三疣梭子蟹雌体生长、卵巢发育和生化组成的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2021, 42(5): 158-166] |
HE Y D, HUA X M, ZHAO C Y, et al. Fat requirement and optimal dietary fat to carbohydrate ratio for red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2013, 25(5): 1017-1024 [何亚丁, 华雪铭, 赵朝阳, 等. 克氏原螯虾的脂肪需求量及饲料中脂肪与糖类适宜比例的研究. 动物营养学报, 2013, 25(5): 1017-1024 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2013.05.017] |
HUI W J, CAI M L, WANG A M, et al. Effects of feeding frequency on meat content and growth performance of Procambarus clarkii. China Feed, 2020(23): 77–80, 106 [惠文杰, 蔡明浪, 王爱民, 等. 不同投饲频率对克氏原螯虾含肉率及生长性能的影响. 中国饲料, 2020(23): 77–80, 106] |
HUO Y W, JIN M, ZHOU P P, et al. Effects of dietary protein and lipid levels on growth, feed utilization and body composition of juvenile swimming crab, Portunus trituberculatus. Aquaculture, 2014, 434: 151-158 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.08.011 |
JOHNSTON I A, ALDERSON R, SANDHAM C, et al. Muscle fibre density in relation to the colour and texture of smoked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L. ). Aquaculture, 2000, 189(3/4): 335-349 |
LEI Y J, YAN J, TANG Z T, et al. Effects of dietary lipid level on growth performance and flesh quality of juvenile Carassius auratus var. Dongtingking. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(12): 5839-5849 [类延菊, 晏锦, 唐忠天, 等. 饲料脂肪水平对洞庭青鲫幼鱼生长性能及肉品质的影响. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(12): 5839-5849] |
LI Z J, ZHEN Z Y, ZUO Y M, et al. Analysis and evaluation on nutritional components in muscle of Procambarus clarkii in Rice Area of Eastern Hebei. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(20): 206-209 [李赵嘉, 郑振宇, 左永梅, 等. 冀东稻区克氏原螯虾肌肉营养成分分析及评价. 安徽农业科学, 2019, 47(20): 206-209] |
LOPEZ L M, TORRES A L, DURAZO E, et al. Effects of lipid on growth and feed utilization of white seabass (Atractoscion nobilis) fingerlings. Aquaculture, 2006, 253(1/2/3/4): 557-563 |
LU Y P, WANG L, ZHANG X X, et al. Effects of dietary lipid levels on growth, muscle composition, activities of digestive enzyme and immunity of juvenile red claw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus. Feed Industry, 2018, 39(24): 17-23 [鲁耀鹏, 汪蕾, 张秀霞, 等. 饲料脂肪水平对红螯螯虾幼虾生长、肌肉组分、消化酶活力和免疫力的影响. 饲料工业, 2018, 39(24): 17-23] |
LUO Y T, LIU Y, LIU J M, et al. Analysis and evaluation on nutritional components in muscle of Procambarus clarkii in Rice Area of Eastern Hebei. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(8): 4592-4603 [罗雅婷, 刘益, 刘金梦, 等. 湖南省稻田养殖的不同规格克氏原螯虾的肌肉营养成分分析. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(8): 4592-4603] |
MA R. Preliminary study on relationship between nutrition and fish quality of farmed large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Doctoral Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2014 [马睿. 营养与养殖大黄鱼品质之间关系的初步研究. 中国海洋大学博士研究生学位论文, 2014]
|
MENG J, WANG Z X, WANG H W. The effects of dietary lipid levels on the growth, bodycomposition and fatty acid composition of Procambarus clarkii. Journal of Aquaculture, 2016, 37(7): 19-26 [孟晶, 王中霞, 汪海卫. 日粮脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾的生长、体组成及脂肪酸组成的影响. 水产养殖, 2016, 37(7): 19-26] |
PENG D, CHEN X R, WEN H, et al. Effects of dietary lipid levels on growth performance, muscle composition, reproductive performance and hemolymph biochemical indices of Procambarus clarkii broodstock. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2019, 43(10): 2175-2185 [彭迪, 陈效儒, 文华, 等. 饲料脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾亲虾生长性能、肌肉成分、繁殖性能以及血淋巴生化指标的影响. 水产学报, 2019, 43(10): 2175-2185] |
RODRIGUEZ-GONZALEZ H, HERNANDEZ-LLAMAS A, GARCIA-ULLOA M, et al. Effect of dietary protein and lipid levels on gonadal development of female redclaw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus. Aquaculture Research, 2013, 45(1): 80-86 |
SI L G, ZOU L C, SHENTU J G, et al. Effects on different dietary lipid and protein levels on growth performance, body composition and digestive enzyme activities of freshwater shrimp Macrobrachium nipponensis. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2014, 45(2): 400-408 [斯烈钢, 邹李昶, 申屠基康, 等. 饲料添加不同脂肪及蛋白质水平对日本沼虾(Macrobrachium nipponensis)生长性能、体成分及消化酶活力的影响. 海洋与湖沼, 2014, 45(2): 400-408] |
TACON A G J, METIAN M. Global overview on the use of fish meal and fish oil in industrially compounded aquafeeds: Trends and future prospects. Aquaculture, 2008, 285(1/2/3/4): 146-158 |
TANG X S. Procambarus clarkii. Bulletin of Biology, 2001(9): 19–20 [唐鑫生. 克氏原螯虾. 生物学通报, 2001(9): 19–20]
|
THAKUR D P, MORIOKA K, ITOH Y, et al. Influence of muscle biochemical constituents on the meat texture of cultured yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata) at different anatomical locations. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2002, 82(13): 1541-1550 |
TOCHER D R. Metabolism and functions of lipids and fatty acids in teleost fish. Reviews in Fisheries Science, 2003, 11(2): 107-184 |
WAN J J, CHEN Y M, SHAO J J, et al. Comparative analysis on muscle quality of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkia) cultured under different aquaculture modes in Xuyi Region. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(2): 965-972 [万金娟, 陈友明, 邵俊杰, 等. 盱眙地区不同养殖模式下克氏原螯虾肌肉品质的比较分析. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(2): 965-972] |
WANG J, YAO W X, LI X Q, et al. Dietary effects of Enteromorpha prolifera on growth performance and flesh quality of Litopenaeus vannamei. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2021, 45(2): 246-254 [王靖, 姚文祥, 李小勤, 等. 饲料中添加浒苔对凡纳滨对虾生长性能和肌肉品质的影响. 水产学报, 2021, 45(2): 246-254] |
WANG Z Y, ZU L, LI Q Q, et al. A comparative evaluation of the nutritional quality of Eriocheir sinensis and Eriocheir japonica (Brachyura, Varunidae). Crustaceana, 2020, 93(6): 567-585 |
WEN B, JIANG Y, YUAN R, et al. Effects of dietary lipid sources on the survival, growth, body composition, antioxidant capacity and expression of antioxidant and proinflammatory genes in juvenile Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) reared under three salinities. Aquaculture Research, 2021, 52(11): 5307-5320 |
WU F, LU X, WEN H, et al. Effects of different protein and lipid levels on the growth performance, muscle textural parameters, and genes expression in liver of Pelodiscus sinensis. Freshwater Fisheries, 2018, 48(1): 47-54 [吴凡, 陆星, 文华, 等. 饲料蛋白质和脂肪水平对中华鳖生长性能、肌肉质构指标及肝脏相关基因表达的影响. 淡水渔业, 2018, 48(1): 47-54] |
XU C, LI E, LIU Y, et al. Effect of dietary lipid level on growth, lipid metabolism and health status of the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei at two salinities. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2018, 24(1): 204-214 |
XU W N, LIU W B, SHEN M F, et al. Effects of different dietary protein and lipid level on growth performance, body composition and digestive enzyme activities of red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2011, 42(4): 521-529 [徐维娜, 刘文斌, 沈美芳, 等. 饲料中不同蛋白质和脂肪水平对克氏螯虾(Procambarus clarkii)生长性能、体组成和消化酶活性的影响. 海洋与湖沼, 2011, 42(4): 521-529] |
YAN M Y, WANG H, HUANG X L, et al. Effects of different commercial feed on the growth, intestinal structure and digestive capacity of juvenile red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkia. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2021, 39(4): 433-439 [晏明瑶, 王浩, 黄小丽, 等. 不同饲料对克氏原螯虾幼虾生长、肠道结构和消化能力的影响. 四川农业大学学报, 2021, 39(4): 433-439] |
YUN B A, XUE M, WANG J, et al. Effects of lipid sources and lipid peroxidation on feed intake, growth, and tissue fatty acid compositions of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture International, 2013, 21(1): 97-110 |
ZHANG J H, WANG S H, KOU X M, et al. Study on effect of dietary protein and lipid levels on growth of Procambarus clarkii. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2012, 24(8): 88-93 [张家宏, 王守红, 寇祥明, 等. 饲料中蛋白质和脂肪水平对克氏原螯虾生长的影响研究. 江西农业学报, 2012, 24(8): 88-93] |
ZHENG J M, ZHAO J J, CHEN S Q, et al. Growth and fatty acid composition of juvenile spotted halibut (Verasper variegatus) fed diets with fish oil replaced by soybean oil. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2019, 40(4): 39-46 [郑建明, 赵捷杰, 陈四清, 等. 豆油替代鱼油对圆斑星鲽幼鱼生长和肌肉脂肪酸的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2019, 40(4): 39-46] |
ZHOU J, ZHAO Z M, HUANG Z P, et al. Comparison of nutrient components in muscles and hepatopancreas of pond- and paddy field-cultured Procambarus clarkii. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2021, 42(2): 162-169 [周剑, 赵仲孟, 黄志鹏, 等. 池塘和稻田养殖模式下克氏原螯虾肌肉和肝脏营养成分比较. 渔业科学进展, 2021, 42(2): 162-169] |
ZHU H X, JIANG Q C, WANG Q, et al. Effect of dietary carbohydrate-to-lipid ratios on growth performance, body composition, hepatic enzyme activities, and digestive enzyme activities of juvenile Australian redclaw crayfish, Cherax quadricarinatus (von Martens). Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 2013, 44(2): 173-186 |



