2. 青岛海洋科技中心海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程功能实验室 山东 青岛 266237;
3. 中国海洋大学水产学院 山东 青岛 266003
2. Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Qingdao Marine Science and Technology Center, Qingdao 266237, China;
3. Fisheries College, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, China
神经激肽B (Neurokinin B, NKB),又称神经介素K (neuromedin K),其编码基因在反刍动物和啮齿动物中被命名为tac2,在其他哺乳动物、鸟类、爬行类、两栖类和鱼类中被命名为tac3 (Ogawa et al, 2012)。在鱼类和两栖类中,tac3前体多肽包含NKB和NKB-related peptide (NKBRP) 2种成熟肽,但在哺乳类、鸟类和爬行类中仅存在NKB。在硬骨鱼中,tac3基因在不同的脑区和外周组织中广泛表达,表明NKB和NKBRP可能参与了多种生理功能,当前研究主要集中于生殖调控和摄食调控两方面(Biran et al, 2014; Chen et al, 2018; Qi et al, 2015; Xu et al, 2021a; Zhang et al, 2019)。此外,tac3表达水平随性腺发育而变化,表明NKB可能参与性腺发育(Biran et al, 2012; Chen et al, 2018; Qi et al, 2015; Wang et al, 2021)。本文简要总结鱼类NKB系统的研究进展,主要对NKB及其受体基因结构、组织分布、脑区分布、生理学功能以及信号转导机制等内容进行讨论,以加强对鱼类NKB系统的认识,为后续研究提供便利。
1 鱼类NKB系统鉴定及表达特征 1.1 NKB基因类型及时空表达特征NKB最早是从猪脊髓提取物中纯化得到的,并被命名为神经激肽B或神经介素K (Campo et al, 2022)。NKB是由tac3基因编码的一种神经肽,目前该基因已在斑马鱼(Danio rerio) (Biran et al, 2012; Ogawa et al, 2012; Zhou et al, 2012)、金鱼(Carassius auratus) (Qi et al, 2015)、尼罗罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus) (Biran et al, 2014; Jin et al, 2016)、条纹鲈(Morone saxatilis) (Zmora et al, 2017)、欧洲鳗鲡(Anguilla anguilla) (Campo et al, 2018)、斜带石斑鱼(Epinephelus coioides) (Chen et al, 2018)、花鲈(Lateolabrax maculatus) (Zhang et al, 2019)、草鱼(Ctenopharyngodon idellus) (Hu et al, 2014; Xu et al, 2021a; Ye et al, 2019)、半滑舌鳎(Cynoglossus semilaevis) (Wang et al, 2021)、日本鳗鲡(Anguilla japonica) (Zuo et al, 2022)及中华鲟(Acipenser sinensis) (Xie et al, 2023)等硬骨鱼中鉴定出。由于硬骨鱼在进化过程中经历了第3轮全基因组复制事件(the third round of whole-genome duplication, 3R-WGD),斑马鱼(Biran et al, 2012)、金鱼(Qi et al, 2015)、花鲈(Zhang et al, 2019)、欧洲鳗鲡(Campo et al, 2018)等鱼类中存在tac3a和tac3b两种基因,但在尼罗罗非鱼(Biran et al, 2014)、斜带石斑鱼(Chen et al, 2018)等进化程度更高的鱼中仅存在tac3a基因,tac3b基因已发生丢失。NKB和NKBRP在C末端都具有速激肽特征基序(-FXGLM),其中,X是疏水氨基酸残基或芳香氨基酸残基,该基序对于NKBs与其同源受体的结合很重要。但在尼罗罗非鱼等慈鲷科(Cichlidae)鱼类中,X代表异亮氨酸,NKBs共享-FIGLM的相同特征基序。不同鱼类NKB和NKBRP的氨基酸序列如表 1所示。
|
|
表 1 硬骨鱼NKB和NKBRP成熟肽氨基酸序列 Tab.1 Amino acid sequences of NKB and NKBRP mature peptides in teleosts |
RT-PCR及ISH (in situ hybridization)结果表明,tac3基因在鱼类多种组织中均有表达,但不同鱼类中表达模式略有差异:tac3a主要在斑马鱼(Biran et al, 2012; Ogawa et al, 2012; Zhou et al, 2012)、欧洲鳗鲡(Campo et al, 2018)、斜带石斑鱼(Chen et al, 2018)、草鱼(Hu et al, 2014)、金鱼(Qi et al, 2015)、尼罗罗非鱼(Biran et al, 2014)、日本鳗鲡(Zuo et al, 2022)、花鲈(Zhang et al, 2019)、中华鲟(Xie et al, 2023)脑中高表达;金鱼和日本鳗鲡tac3a也在垂体中高表达(Qi et al, 2015; Zuo et al, 2022);斜带石斑鱼tac3a在肠中表达量也较高(Chen et al, 2018);尼罗罗非鱼tac3a在肠和视网膜中也存在较高表达(Biran et al, 2014);半滑舌鳎和草鱼tac3a在肠及性腺中也高表达(Hu et al, 2014; Wang et al, 2021)。tac3b基因主要在斑马鱼(Biran et al, 2012)、欧洲鳗鲡(Campo et al, 2018)、日本鳗鲡(Zuo et al, 2022)、金鱼(Qi et al, 2015)、草鱼(叶城, 2020)、花鲈(Zhang et al, 2019)脑中表达。此外,斑马鱼tac3b还在卵巢中高表达(Zhou et al, 2012),脑区分布结果进一步表明,斑马鱼tac3a主要表达于下丘脑、间脑、视顶盖,tac3b主要表达于端脑和下丘脑(Biran et al, 2012; Zhou et al, 2012);草鱼tac3a在下丘脑、嗅球、延脑中也有较高的表达水平(Hu et al, 2014; 叶城, 2020),而tac3b主要表达于端脑(叶城, 2020);尼罗罗非鱼tac3在各个脑区的表达水平相近(Biran et al, 2014);欧洲鳗鲡tac3a和tac3b主要表达于间脑(Campo et al, 2018);日本鳗鲡tac3a和tac3b主要表达于端脑(Zuo et al, 2022)。综上所述,tac3基因在大脑和肠道中的高水平表达与速激肽的生物学功能相符,速激肽是中枢神经系统中的神经递质或神经调节剂,又是脑肠肽的主要成员,对调节胃肠道运动和分泌起着十分重要的作用。
tac3基因在鱼类不同性腺发育时期的表达特征也有相关报道,研究发现,tac3在性腺发育时期的表达特征具有物种特异性。斑马鱼脑tac3a在受精后4周内表达水平较低,而在性腺发育过程中逐渐升高,并在受精后8周达到峰值,12周性腺成熟时表达水平略微下降;tac3b在性腺发育时期表达水平很低,性成熟过程中没有变化(Biran et al, 2012)。雌雄金鱼下丘脑tac3在性腺发育时期呈现相似的表达特征:雌鱼tac3a表达水平在卵黄发生前期、早期、中期和晚期均较低,在完全生长阶段显著升高;而雄鱼tac3a在精子发生早期较低,在精子发生晚期显著升高;tac3b在卵黄发生中期和精子发生晚期高水平表达,其他发育阶段表达水平均较低;垂体中tac3a的表达水平不随性腺发育而变化(Qi et al, 2015)。斜带石斑鱼下丘脑中tac3a在卵巢发育过程中先降低,在卵黄生成期表达量显著增加,随后再次降低(Chen et al, 2018)。半滑舌鳎tac3表达水平在脑中无明显变化,在垂体和卵巢中卵黄发生期显著升高,随后表达水平又下降至本底水平(Wang et al, 2021)。综上所述,tac3可能参与了硬骨鱼性腺发育(Campo et al, 2022):大脑或下丘脑中tac3表达水平在不同性腺发育阶段有波动,表明NKB可能参与GnRH和促性腺激素的神经内分泌控制;tac3在性腺中表达且在性成熟过程中变化,表明其可能通过自分泌或旁分泌的途径直接作用于性腺进而影响其发育。
1.2 NKB受体基因类型及时空表达特征NKB受体NK3R属于G蛋白偶联受体,具有典型的7次跨膜结构,其编码基因为tacr3。哺乳动物只有1种tacr3,由于硬骨鱼特有的3R-WGD,硬骨鱼通常具有tacr3a和tacr3b两种亚型(Campo et al, 2022)。斑马鱼具有3种tacr3亚型(tacr3a1、tacr3a2和tacr3b),tacr3a2是由tacr3a1局部基因组复制而来(Zhou et al, 2012),同为鲤形目(Cyprinidae)的草鱼中也存在3种tacr3基因(叶城, 2020)。
硬骨鱼tacr3基因主要表达于脑、垂体、肠、性腺中。例如,斑马鱼tacr3a1主要表达于脑和卵巢,tacr3a2主要表达于脑、垂体和卵巢,tacr3b主要在脑中高表达(Biran et al, 2012; Zhou et al, 2012)。草鱼tacr3a1主要表达于脑中(叶城, 2020),tacr3a2主要在脑、垂体和性腺中表达,而tacr3b主要表达于垂体和肠等外周组织(Hu et al, 2019; Xu et al, 2021b)。尼罗罗非鱼tacr3a主要表达于脑、肠和视网膜,tacr3b主要表达于脑、垂体和性腺(Biran et al, 2014)。花鲈tacr3a主要表达于胃、肠和精巢中,tacr3b主要表达于下丘脑和肠中(Zhang et al, 2019)。此外,尼罗罗非鱼tacr3b也表达于包含延髓和小脑的后脑(Biran et al, 2014)。金鱼tacr3a主要表达于端脑、视顶盖丘脑、肠和性腺,tacr3b主要表达于端脑和视顶盖丘脑(Liu et al, 2019)。花鲈tacr3b主要表达于下丘脑中(Zhang et al, 2019)。草鱼tacr3a1主要表达于延髓和下丘脑,tacr3a2主要表达于小脑,tacr3b主要表达于下丘脑和端脑(叶城, 2020)。综上所述,tacr3的表达特征与tac3相似,主要表达于脑、垂体、性腺和肠中,这表明硬骨鱼中NKB的功能可能主要与生殖调控和摄食调控相关。
对于性腺发育过程中tacr3基因表达特征的研究较少。斑马鱼脑中tacr3a1和tacr3a2表达水平低,在性成熟过程中没有变化(Biran et al, 2012)。金鱼中tacr3a雌雄表达特征有所不同,在不同组织中表达特征也有所差异:在雌鱼下丘脑中tacr3a在卵黄发育前期至中期表达持续下降,末期升高,垂体中tacr3a在卵黄发育早期表达量升高,中期和末期表达量降低;雄鱼下丘脑tacr3a表达水平不随性腺发育发生变化,但垂体中tacr3a在精子形成阶段表达量逐渐降低;而tacr3b的表达量不随性腺发育而变化(Liu et al, 2019)。
2 鱼类Neurokinin B的生理功能目前,关于鱼类NKB生理功能的研究主要集中在生殖调控和摄食调控两方面。由于部分鱼类中存在2种tac3基因,并且每种tac3基因可以编码NKB和NKBRP两种成熟肽,因此,NKBs对鱼类生理活动的调控机制更为复杂(表 2)。
|
|
表 2 硬骨鱼NKB和NKBRP生理功能 Tab.2 Physiological functions of NKB and NKBRP in teleosts |
肌肉注射NKB和NKBRP对条纹鲈gnrh1表达无影响,而大脑切片NKB和NKBRP体外孵育促进gnrh1的表达(Zmora et al, 2017);腹腔注射NKBRP显著降低雌性尼罗罗非鱼gnrh1的表达水平(Jin et al, 2016)。NKBRP对斜带石斑鱼gnrh1和gnrh3无影响,NKB对gnrh3表达也无影响,但显著增加gnrh1的表达(Chen et al, 2018)。NKB系统对金鱼gnrh2表达无影响(Qi et al, 2015),但对gnrh3的影响具有性别二态性,且与性腺发育程度有关:在卵黄发育早期和精子形成早期金鱼中,NKBa抑制gnrh3表达,NKBRPa仅抑制雌鱼gnrh3表达(Liu et al, 2019),但NKBa、NKBRPa和NKBRPb在卵黄发育中期和精子形成晚期金鱼中促进gnrh3表达,NKBb对gnrh3表达无影响(Qi et al, 2015)。NKBa和NKBRPb对日本鳗鲡gnrh2表达无影响,促进了gnrh1表达,NKBb和NKBRPa对gnrh1以及gnrh2表达均无影响(Zuo et al, 2022)。大脑切片与NKB和NKBRP体外孵育、肌肉注射NKB和NKBRP均抑制条纹鲈kiss1和kiss2的表达(Zmora et al, 2017)。腹腔注射NKBRP能够显著促进斜带石斑鱼kiss2的表达,但NKB对kiss2表达无影响(Chen et al, 2018);然而NKBRP显著抑制尼罗罗非鱼雌鱼kiss2的表达(Jin et al, 2016)。NKBa和NKBRP均抑制金鱼kiss2表达(Liu et al, 2019)。此外,腹腔注射NKB和NKBRP显著抑制雌性尼罗罗非鱼tac3的表达水平(Jin et al, 2016),但不影响中华鲟tac1和tac3表达(Xie et al, 2023)。综上所述,NKB和NKBRP多肽对下丘脑gnrh和kiss表达调控具有物种特异性,NKB对金鱼gnrh3作用具有性别二态性,且影响与性腺发育程度有关。
2.2 Neurokinin B对垂体激素的影响肌肉注射NKB能够显著促进条纹鲈lhβ表达,不影响fshβ表达,而NKBRP能够显著促进fshβ表达,不影响lhβ表达(Zmora et al, 2017)。腹腔注射NKBRP对斜带石斑鱼lhβ和fshβ表达均无影响,而NKB能够显著促进lhβ表达,而不影响fshβ表达(Chen et al, 2018);NKB促进中华鲟gh表达,抑制fshβ表达,对lhβ表达无影响(Xie et al, 2023);NKB和NKBRP对金鱼垂体激素表达的影响和性腺发育程度相关,NKBRP对lhβ和fshβ的影响也和性别相关:NKB能够显著抑制卵黄发育早期雌鱼和精子形成早期雄鱼lhβ和fshβ表达,NKBRP仅抑制雌鱼lhβ和fshβ表达,而对雄鱼无作用(Liu et al, 2019),而NKBa、NKBRPa和NKBRPb促进卵黄发育中期和精子形成后期的金鱼lhβ和fshβ表达,NKBb对lhβ和fshβ表达无影响(Qi et al, 2015)。NKBRP对尼罗罗非鱼lhβ和fshβ表达无影响(Jin et al, 2016; Mizrahi et al, 2019),但NKB的影响可能与处理方式有关:处理6 h后对lhβ和fshβ表达无影响(Jin et al, 2016),处理24 h后显著促进了lhβ和fshβ表达(Mizrahi et al, 2019);此外,NKB还能显著促进gh表达(Mizrahi et al, 2019)。肌肉注射NKB能够促进条纹鲈LH分泌(Zmora et al, 2017)。腹腔注射NKBa、NKBRPa和NKBRPb显著促进斑马鱼LH释放(Biran et al, 2012);NKB注射后促进中华鲟LH和FSH的分泌(Xie et al, 2023);腹腔注射NKB和NKBRP促进尼罗罗非鱼LH释放,但NKBRP对FSH分泌无影响(Biran et al, 2014; Mizrahi et al, 2019),NKB对尼罗罗非鱼FSH分泌的作用与性别有关:NKB能够促进雄鱼FSH分泌,而对雌鱼无影响;NKB和NKBRP还会促进尼罗罗非鱼GH分泌(Mizrahi et al, 2019)。
垂体细胞离体孵育实验结果表明,NKBs对条纹鲈(Zmora et al, 2017)、斜带石斑鱼(Chen et al, 2018)、草鱼(Hu et al, 2014) lhβ和fshβ表达无影响;NKBa和NKBRPa促进草鱼slα以及prl表达,对slβ、gthα、gh、pomc和tshβ表达无作用(Hu et al, 2014、2019);4种NKB神经肽显著抑制欧洲鳗鲡垂体细胞中lhβ和gnrhr2表达(Campo et al, 2018);NKBs对尼罗罗非鱼lhβ和fshβ表达作用与性别相关:NKB促进雌鱼lhβ和fshβ表达,抑制雄鱼lhβ和fshβ表达,NKBRP抑制雌鱼lhβ和fshβ表达,促进雄鱼lhβ和fshβ表达(Mun et al, 2022)。此外,NKBa和NKBRPa促进草鱼SLα和PRL分泌,而对LH、SLβ和GH分泌无影响(Hu et al, 2014);NKBs也促进条纹鲈(Zmora et al, 2017)和尼罗罗非鱼(Biran et al, 2014) LH和FSH分泌。垂体组织离体孵育结果表明,NKB对尼罗罗非鱼lhβ和fshβ表达无影响(Jin et al, 2016; Mun et al, 2022),但NKBRP的作用与性别有关:NKBRP抑制雌鱼fshβ和lhβ表达,对雄鱼lhβ和fshβ表达无影响(Mun et al, 2022)。综上所述,NKB和NKBRP对垂体激素表达和分泌的影响具有物种特异性和性别二态性,此外还与处理方式有关,NKB和NKBRP调节生殖的方式可能存在差异。
2.3 Neurokinin B对性类固醇激素的影响腹腔注射NKB能够增加斑马鱼和斜带石斑鱼雌二醇(E2)的释放(Chen et al, 2018; Qi et al, 2016),NKBRP则对斜带石斑鱼E2的分泌无影响(Chen et al, 2018);NKB和NKBRP对尼罗罗非鱼E2和11-KT的分泌均无影响(Jin et al, 2016)。体外NKB处理斑马鱼卵巢卵黄发生期的卵泡,促进类固醇生成酶编码基因cyp11a1和cyp19a1的表达,进而促进E2的产生(Qi et al, 2016)。值得一提的是,敲除斑马鱼tac3a和tac3b基因后,构建了tac3a–/–、tac3b–/–和tac3a–/–tac3b–/–品系,其生长发育均不受影响,成熟个体能够正常进行配子发生和繁殖,表明可能在斑马鱼中存在某种生殖补偿机制,使得敲除某种神经肽编码基因后不影响斑马鱼的正常生殖能力(Li et al, 2021)。
2.4 Neurokinin B的其他生理功能NKB能够参与调节硬骨鱼摄食。腹腔注射NKBa刺激草鱼垂体中厌食因子uts1、cart、pomcb和nmb的表达(Xu et al, 2021a),NKBa、NKBRPa以及NKBRPb还促进草鱼垂体细胞中uts1、cart、pomcb和nmb的表达,而NKBb无此作用(Xu et al, 2021a)。NKBRPb能够促进花鲈胃中gas、mln和ghrl的表达,NKBRPa也促进gas表达;NKBa、NKBRPa和NKBRPb均能促进肠中cck表达,NKBb促进gas表达,NKBa促进mln表达(Zhang et al, 2019)。上述结果表明,NKB和NKBRP促进厌食因子表达,并促进肠胃蠕动。NKB对鱼类生长也有影响,NKBb和NKBRPb体外处理花鲈大脑细胞促进其ghrh表达,NKBa促进igf1表达,NKBa、NKBRPa和NKBRPb促进大脑细胞内prlr表达,这4种NKB多肽对gh的表达无影响(Zhang et al, 2019)。上述研究表明,NKB和NKBRP可通过对脑中神经肽、垂体激素和性类固醇激素的合成与分泌产生影响,进而参与鱼体的生殖功能调控,但NKB和NKBRP的作用具有物种特异性和性别二态性,还和处理方式等因素相关。除此之外,NKB还可作为一种厌食因子调节摄食(Xu et al, 2021a; Zhang et al, 2019),而对其他生理功能的研究还比较有限。
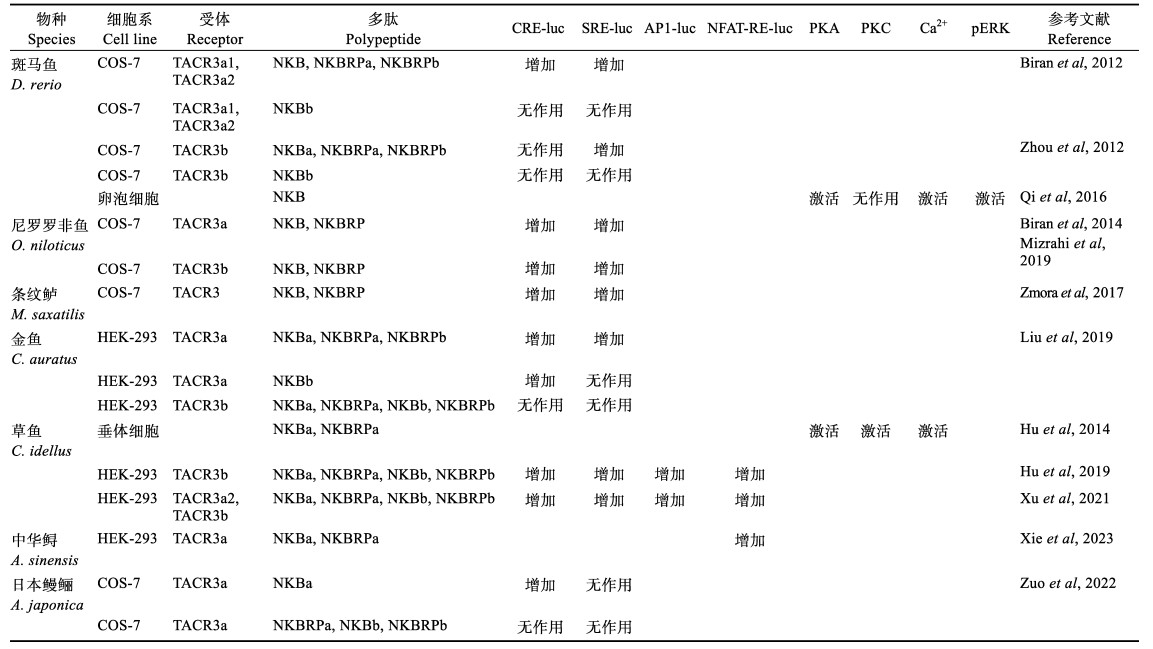
3 鱼类Neurokinin B的信号转导机制目前,对NKBs信号转导机制研究主要集中在PKA、PKC和Ca2+ 3条通路(表 3)。关于PKA通路,多数NKB和NKBRP能激活转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3a的细胞内CRE-luc活性,但对转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3b的细胞,NKB和NKBRP对CRE-luc的作用效果不同。斑马鱼NKBa、NKBRPa和NKBRPb能增加转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3a1和pcDNA3.1-TACR3a2的COS-7细胞中CRE-luc活性,而对转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3b的细胞内CRE-luc活性无影响,NKBb对转染了其受体质粒的细胞中CRE-luc活性也无影响(Biran et al, 2012; Zhou et al, 2012);尼罗罗非鱼NKB和NKBRP能增加转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3a和pcDNA3.1-TACR3b的细胞中CRE-luc活性(Biran et al, 2014; Mizrahi et al, 2019);草鱼NKBa、NKBRPa、NKBb和NKBRPb能增加转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3b的细胞中CRE-luc活性(Hu et al, 2019);条纹鲈NKB和NKBRP能够增加转染其受体的细胞内CRE-luc活性(Zmora et al, 2017);金鱼4种NKB多肽均能增加转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3a的细胞中CRE-luc活性,而对转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3b的细胞中CRE-luc活性无影响(Liu et al, 2019);日本鳗鲡NKBa能增加转染pcDNA3.1-TACR3a的细胞中CRE-luc活性,而NKBRPa、NKBb和NKBRPb均对转染了该受体质粒的细胞中CRE-luc活性无影响(Zuo et al, 2022)。总体而言,在硬骨鱼中,NKBa、NKBRPa和NKBRPb都能增加转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3a的细胞中CRE-luc活性,而不同硬骨鱼NKB对转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3b的细胞中CRE-luc活性情况有所差异。此外,使用PKA通路阻断剂H89和NKB共同处理斑马鱼卵泡细胞(Qi et al, 2016)和草鱼垂体细胞(Hu et al, 2014)的实验进一步证实NKB能够激活细胞内PKA通路。
|
|
表 3 硬骨鱼NKB系统的信号转导机制 Tab.3 Signal transduction mechanisms of the NKB system in teleosts |
NKBs对PKC通路的激活情况同PKA相似,但略有差异。斑马鱼NKBa、NKBRPa和NKBRPb能增加转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3a1、pcDNA3.1-TACR3a2和pcDNA3.1-TACR3b的细胞内SRE-luc活性,NKBb则无作用(Biran et al, 2012; Zhou et al, 2012)。尼罗罗非鱼NKB和NKBRP能增加转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3a和pcDNA3.1-TACR3b的COS-7细胞中的SRE-luc活性(Biran et al, 2014; Mizrahi et al, 2019)。草鱼NKBa、NKBRPa、NKBb和NKBRPb均能增加转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3a2和pcDNA3.1-TACR3b的HEK293细胞内的SRE-luc活性(Hu et al, 2019; Xu et al, 2021b)。金鱼NKBa、NKBRPa和NKBRPb均能增加转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3a的细胞内SRE-luc活性,而对转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3b的细胞中SRE-luc活性无影响(Liu et al, 2019)。条纹鲈NKB和NKBRP能够增加转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3的细胞内SRE-luc活性(Zmora et al, 2017)。但日本鳗鲡NKBa、NKBRPa、NKBb和NKBRPb均对转染了其受体的细胞内的SRE-luc活性无作用(Zuo et al, 2022)。这表明在硬骨鱼中,NKBa、NKBRPa和NKBRPb能激活转染pcDNA3.1-TACR3a的细胞中SRE-luc活性,而对转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3b细胞中SRE-luc活性具有物种特异性。此外,PKC抑制剂GF109203X同NKB神经肽共处理斑马鱼卵泡细胞,不能阻断该细胞中的PKC通路(Qi et al, 2016)。而在草鱼垂体细胞中,则可以阻断NKB和NKBRP诱导的slα表达和SLα分泌作用(Hu et al, 2014)。除了PKA和PKC通路以外,斑马鱼卵泡细胞和草鱼垂体细胞中的实验也表明,NKB能激活钙离子通路(Hu et al, 2014; Qi et al, 2016)。在转染了pcDNA3.1-TACR3a2和pcDNA3.1-TACR3b的HEK293细胞中,NKBa、NKBRPa和NKBRPb还能显著增加AP1-luc和NFAT-RE-luc活性(Hu et al, 2019; Xu et al, 2021b);中华鲟NKBa和NKBRPa能增加转染了其受体HEK-293细胞的NFAT-RE-luc活性(Xie et al, 2023)。上述研究表明,硬骨鱼NKBa和NKBRPa是TACR3的内源性配体,NKB的C末端基序对于受体激活很关键,NKBb不能激活TACR3的下游信号可能是由其NKBb的C末端基序发生突变导致的。
4 鱼类Neurokinin B系统表达调控性类固醇激素影响了tac3基因表达水平。对性未成熟的斑马鱼进行E2处理增强了gnrh3、kiss1和kiss2的表达,同时显著增加了tac3a、tacr3a、tacr3b和kiss1ra的表达,这些结果说明,在斑马鱼中雌激素对NKB系统的转录具有促进作用(Biran et al, 2012)。在金鱼中,tac3b的表达水平不受卵巢切除以及雌激素处理的影响,tac3a的表达水平在卵巢切除后显著增加,雌激素处理后恢复,表明雌激素对下丘脑tac3a的表达具有负调节作用(Qi et al, 2015),该实验结果与斜带石斑鱼中的结果类似(Chen et al, 2018),与斑马鱼中的结果相反(Biran et al, 2012),原因可能是由雌激素处理时间、处理方式、性腺发育阶段、物种差异、检测大脑区域不同引起的。在斜带石斑鱼中,腹腔注射NKB多肽显著升高了血清雌激素水平,进一步证实了NKB参与调节斜带石斑鱼生殖轴。在雄激素诱导斜带石斑鱼性逆转的过程中,tac3的表达水平没有变化,表明tac3不受睾酮的调节(Chen et al, 2018)。这些结果表明,雌激素促进或抑制tac3a的表达水平,同时又受到NKB肽的调控,但性类固醇激素对NKB系统的表达调控作用的研究较少,需要进一步深入研究。
5 小结与展望NKB是速激肽家族成员之一,通过NK3R介导参与了哺乳类生殖调控和摄食调控等多种生理过程。目前,仅在少数几种鱼类中鉴定出tac3以及其受体tacr3基因,并对其表达特征和信号转导机制进行了初步研究分析,对生理功能的研究也主要集中于摄食和生殖调控两方面。目前研究仍存在诸多不足之处,解决以下问题将有助于更好地了解NKB系统在硬骨鱼生殖和摄食等生理过程的协同作用机制:(1)当前在某些鱼类中存在2种tac3基因,但在其他鱼类中只鉴定出了1种tac3基因,2种tac3基因是否广泛存在于硬骨鱼中还不明确;(2)Kiss-NKB-Dynorphin (KNDy)神经元可见于哺乳动物正中隆起,在哺乳类生殖调控中发挥重要作用,但KNDy神经元是否广泛存在硬骨鱼中仍有待证实;(3)使用基因编辑技术敲除tac3a/tac3b对斑马鱼的生殖功能无影响,表明硬骨鱼中存在NKB的补偿机制,但该机制是否广泛存在于其他鱼类还有待研究,敲除tac3系统对其他生殖调控因子的分泌和基因表达的影响仍有待探索;(4)已知其他下丘脑神经肽,例如,Kiss (王滨等, 2018)、GnIH (Muñoz-Cueto et al, 2017; 刘权等, 2017)和GnRH (Zohar et al, 2022)等在鱼类生殖调控中发挥重要作用,但尚未开展NKB与它们之间的功能与信号互作研究,鱼类生殖神经内分泌调控网络还有待进一步解析。总之,解决上述问题才能更好地了解NKB参与鱼类摄食和生殖等生理功能的分子机制。
BIRAN J, GOLAN M, MIZRAHI N, et al. Direct regulation of gonadotropin release by neurokinin B in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Endocrinology, 2014, 155(12): 4831-4842 DOI:10.1210/en.2013-2114 |
BIRAN J, PALEVITCH O, BEN-DOR S, et al. Neurokinin Bs and neurokinin B receptors in zebrafish-potential role in controlling fish reproduction. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(26): 10269-10274 DOI:10.1073/pnas.1119165109 |
CAMPO A, DUFOUR S, ROUSSEAU K. Tachykinins, new players in the control of reproduction and food intake: A comparative review in mammals and teleosts. Frontiers in Endocrinology (Lausanne), 2022, 13: 1056939 DOI:10.3389/fendo.2022.1056939 |
CAMPO A, LAFONT A G, LEFRANC B, et al. Tachykinin-3 genes and peptides characterized in a basal teleost, the European eel: Evolutionary perspective and pituitary role. Frontiers in Endocrinology (Lausanne), 2018, 9: 304 DOI:10.3389/fendo.2018.00304 |
CHEN H, XIAO L, LIU Y, et al. Neurokinin B signaling in hermaphroditic species, a study of the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2018, 260: 125-135 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2018.01.009 |
HU G, HE M, KO W K W, et al. IGFs potentiate TAC3-induced SLalpha expression via upregulation of TACR3 expression in grass carp pituitary cells. Cells, 2019, 8(8): 887 DOI:10.3390/cells8080887 |
HU G, HE M, KO W K W, et al. Novel pituitary actions of TAC3 gene products in fish model: receptor specificity and signal transduction for prolactin and somatolactin alpha regulation by neurokinin B (NKB) and NKB-related peptide in carp pituitary cells. Endocrinology, 2014, 155: 3582-3596 DOI:10.1210/en.2014-1105 |
JIN Y H, PARK J W, KIM J H, et al. Neurokinin B-related peptide suppresses the expression of GnRH I, Kiss2 and tac3 in the brain of mature female Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Development and Reproduction, 2016, 20(1): 51-61 DOI:10.12717/DR.2016.20.1.051 |
LI Y, ZHAO T, LIU Y, et al. Knockout of tac3 genes in zebrafish shows no impairment of reproduction. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2021, 311: 113839 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2021.113839 |
LIU Q, WANG B, LIU X Z, et al. Effects of gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone peptides on the reproduction-related gene expression in the hypothalamus of half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2017, 38(1): 56-62 [刘权, 王滨, 柳学周, 等. GnIH多肽对半滑舌鳎(Cynoglossus semilaevis)下丘脑生殖相关基因表达的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2017, 38(1): 56-62] |
LIU Y, WANG Q, WANG X, et al. NKB/NK3 system negatively regulates the reproductive axis in sexually immature goldfish (Carassius auratus). General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2019, 281: 126-136 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2019.05.020 |
MIZRAHI N, GILON C, ATRE I, et al. Deciphering direct and indirect effects of neurokinin B and GnRH in the brain-pituitary axis of tilapia. Frontiers in Endocrinology (Lausanne), 2019, 10: 469 DOI:10.3389/fendo.2019.00469 |
MUN S H, OH H J, KWON J Y. Response of pituitary cells and tissues to neurokinin B and F in the Nile tilapia. Development and Reproduction, 2022, 26(1): 13-21 DOI:10.12717/DR.2022.26.1.13 |
MUÑOZ-CUETO J A, PAULLADA-SALMERÓN J A, ALIAGA-GUERRERO M, et al. A journey through the gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone system of fish. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2017, 8: 285 DOI:10.3389/fendo.2017.00285 |
OGAWA S, RAMADASAN P N, GOSCHORSKA M, et al. Cloning and expression of tachykinins and their association with kisspeptins in the brains of zebrafish. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 2012, 520(13): 2991-3012 DOI:10.1002/cne.23103 |
QI X, SALEM M, ZHOU W, et al. Neurokinin B exerts direct effects on the ovary to stimulate estradiol production. Endocrinology, 2016, 157: 3355-3365 DOI:10.1210/en.2016-1354 |
QI X, ZHOU W, LI S, et al. Goldfish neurokinin B: Cloning, tissue distribution, and potential role in regulating reproduction. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2015, 221: 267-277 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.10.017 |
WANG B, LIU X Z, XU Y J, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of Kisspeptin on the reproductive axis in fish. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, 39(4): 173-184 [王滨, 柳学周, 徐永江, 等. Kisspeptin对鱼类生殖轴的调控机制研究. 渔业科学进展, 2018, 39(4): 173-184] |
WANG B, CUI A, ZHANG Y, et al. Neurokinin B in a flatfish species, the half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis), and its potential role in reproductive functions. Aquaculture Reports, 2021, 20: 100651 DOI:10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.100651 |
XIE Y, SHI X, XIAO K, et al. Sequences analysis and pituitary actions of tachykinins in Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Gene, 2023, 879: 147592 DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2023.147592 |
XU S, ZHOU L, CHEN X, et al. Novel pituitary actions of NKB for anorectic peptides regulation in grass carp. Aquaculture, 2021a, 531: 735857 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735857 |
XU S, ZHOU L, GUO S, et al. Different pituitary action of NK3Ra and NK3Rb in grass carp. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2021b, 313: 113829 DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2021.113829 |
YE C. Discovery of neuropeptides in grass crap brain and pituitary and functional characterization of tachykinins. Master's Thesis of Huazhong Agriculture University, 2020 [叶城. 草鱼大脑和垂体中神经肽挖掘及速激肽功能鉴定. 华中农业大学硕士研究生学位论文, 2020]
|
YE C, XU S, HU Q, et al. Global view of neuropeptides and their receptors in the brain and pituitary of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Aquaculture, 2019, 512: 734360 DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734360 |
ZHANG Z, WEN H, LI Y, et al. TAC3 gene products regulate brain and digestive system gene expression in the spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Frontiers in Endocrinology (Lausanne), 2019, 10: 556 DOI:10.3389/fendo.2019.00556 |
ZHOU W, LI S, LIU Y, et al. The evolution of tachykinin/tachykinin receptor (TAC/TACR) in vertebrates and molecular identification of the TAC3/TACR3 system in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 2012, 361: 202-212 DOI:10.1016/j.mce.2012.04.007 |
ZMORA N, WONG T T, STUBBLEFIELD J, et al. Neurokinin B regulates reproduction via inhibition of kisspeptin in a teleost, the striped bass. Journal of Endocrinology, 2017, 233: 159-174 DOI:10.1530/JOE-16-0575 |
ZOHAR Y, ZMORA N, TRUDEAU V L, et al. A half century of fish gonadotropin-releasing hormones: Breaking paradigms. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, 2022, 34: e13069 DOI:10.1111/jne.13069 |
ZUO C, LYU L, ZOU W, et al. TAC3/TACR3 system function in the catadromous migration teleost, Anguilla japonica. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2022, 13: 848808 DOI:10.3389/fendo.2022.848808 |