2. 黑龙江省水产技术推广总站 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150010
2. Heilongjiang Province Fisheries Technology Extension Center, Harbin 150010, China
茴鱼属(Thymallus)鱼类隶属于鲑形目(Salmoniformes)、鲑科(Salmonidae)、茴鱼亚科(Thymallinae),在中国有3处主要分布区,分别为额尔齐斯河流域、黑龙江流域和鸭绿江流域。茴鱼属鱼类为典型山溪型冷水性鱼类(Gönczi, 1989; 向伟等, 2009),喜栖居于水温不高于20 ℃、水流湍急、水质清澈、溶解氧含量高的河流中,主要以水生昆虫为食,也猎食生活于水边或落于水中的陆生昆虫(Zuev et al, 2017; 向伟等, 2009)。研究显示,中国现存茴鱼属鱼类物种多样性丰富,远高于广阔的欧洲和北美洲地区(马波等, 2013、2011),但部分种类的分类结果仍有争议。其中,分类地位已经明确且命名无争议的分别为北极茴鱼(T. arcticus) (马波等, 2013; 马凯等, 2022)、黑龙江茴鱼(T. grubii) (马波等, 2011)和下游黑龙江茴鱼(T. tugarinae)(Knizhin et al, 2007; 马波等, 2007),尚存争议的为鸭绿江茴鱼(T. yaluensis)(Mori, 1928)。鸭绿江茴鱼由Mori (1928)命名,主要分布于鸭绿江流域,并与其他3种茴鱼属鱼类存在地理隔离。Knizhin等(2007)分析发现,鸭绿江茴鱼的可数性状处于黑龙江茴鱼和下游黑龙江茴鱼之间,正式对其分类地位提出了质疑;马波等(2008)利用线粒体DNA控制区序列构建系统发育树,显示鸭绿江茴鱼为黑龙江茴鱼同物异名;Ma等(2016)利用线粒体基因组数据再次印证了鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼没有区别。然而,近年来,仍有部分学者将鸭绿江茴鱼视为独立物种(王秀兰等, 2018)。
形态学方法是物种鉴别中最常用的方法(高天翔等, 2013),可分为传统形态学方法和框架度量法(马凯等, 2023)。传统形态学方法主要分析鱼体的水平和垂直方向的指标,且多局限于头部和尾部特征,无法对整个鱼体表面进行全面度量。而框架度量法则以一定数量的解剖学坐标点为基础,多方向地度量整个鱼体,可以较全面地反映鱼体的形态差异(王新月等, 2022)。迄今为止,有关中国现存茴鱼属鱼类种间差异的研究多集中于分子生物学层面(马波等, 2008、2011; 孙家贤等, 2011),而形态学差异研究较少,仅见于黑龙江茴鱼和下游黑龙江茴鱼(马波等, 2007)。分子标记技术的快速发展为物种分类提供了重要的辅助手段,但表观的形态学差异仍然是公认的最直观的物种分类基础依据(Zhang et al, 2021; 马波等, 2007)。本研究综合运用传统形态学方法和框架度量法,对中国现存的4种茴鱼属鱼类形态特征进行多元统计分析,旨在阐明我国茴鱼属鱼类形态差异,为茴鱼属鱼类的物种分类和进化关系研究提供参考。
1 材料与方法 1.1 样本来源4种茴鱼属鱼类(图 1)分批次于渔业资源与环境调查期间采集自中国黑龙江、鸭绿江和额尔齐斯河流域,样本详细信息见表 1。

|
图 1 4种茴鱼属鱼类 Fig.1 Four species of Thymallus A:黑龙江茴鱼;B:鸭绿江茴鱼;C:下游黑龙江茴鱼;D:北极茴鱼。 A: T. grubii; B: T. yaluensis; C: T. tugarinae; D: T. arcticus. |
|
|
表 1 茴鱼属鱼类样本信息 Tab.1 Sample information of Thymallus |
采集的茴鱼属鱼类样本冷冻保存并运至实验室,冰上解冻后擦干体表水分,使用电子天平称量体重(精确度0.01 g),再将鱼体依次水平和垂直放置,使用数码相机对鱼体侧面和背部进行拍照,然后利用Motic Image Plus 2.0依据照片上的标尺测量所有样本的体长(body length, BL)、体高(body height, BH)、头长(head length, HL)、眼径(eye diameter, ED)、吻长(snout length, SL)、眼后头长(head length behind the eye, HE)、尾柄长(caudal peduncle length, CL)、尾柄高(caudal peduncle height, CH)、眼间距(eye spacing, ES)和体厚(body thickness, BT)等传统形态学数据以及D1–2(表示测量基点1至2之间的距离,下同)、D1–11、D2–3、D2–10、D2–11、D3–4、D3–9、D3–10、D3–11、D4–5、D4–8、D4–9、D4–10、D5–6、D5–7、D5–8、D5–9、D6–7、D6–8、D7–8、D8–9、D9–10、D10–11等框架法形态数据,框架法形态数据测量基点(图 2)参考马凯等(2023)的方法进行设置。最后,计量样本的鳞式、背鳍式、臀鳍式、鳃耙、幽门盲囊和椎骨数等可数性状。

|
图 2 茴鱼属鱼类框架数据测量示意图 Fig.2 Truss network of Thymallus 1:吻端;2:枕骨末端;3:背鳍基部起点;4:背鳍基部末端;5:脂鳍基部起点;6:尾鳍背部起点;7:尾鳍腹部起点;8:臀鳍基部末端;9:臀鳍基部起点;10:腹鳍基部起点;11:胸鳍基部起点。 1: Tip of snout; 2: Distal tip of occiput; 3: Origin of dorsal fin base; 4: Terminus of dorsal fin base; 5: Origin of adipose fin base; 6: Dorsal origin of caudal fin; 7: Abdominal origin of caudal fin; 8: Terminus of anal fin base; 9: Origin of anal fin base; 10: Origin of pelvic fin base; 11: Origin of pectoral fin base. |
为消除样本体型差异对分析结果的影响,将所有可量性状均除以体长以进行标准化处理(Ai et al, 2021; Hashemzadeh Segherloo et al, 2018)。运用SPSS 19.0软件,对茴鱼属鱼类6个种群的分节和标准化可量性状进行方差齐性检验,然后进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),具有方差齐性的数据使用Tukey法,不具备方差齐性的数据采用Tamahane’s T2法进行显著性检验,显著性水平设为0.05,并依据Mayr等(1953)的公式计算鸭绿江茴鱼和黑龙江茴鱼之间的差异系数(CD)。剔除差异不显著的可量性状后(马凯等, 2023),对剩余的标准化可量性状进行主成分分析,抽取特征值大于1的主成分并根据第一和第二主成分得分绘制二维散点图;采用逐步判别法对6个种群差异显著的标准化可量性状进行判别分析,依据筛选出的标准化可量性状建立6个种群的Fisher线性判别函数;最后,基于差异显著的标准化可量性状的平均值,计算出不同群体之间的平方欧氏距离以绘制聚类图。
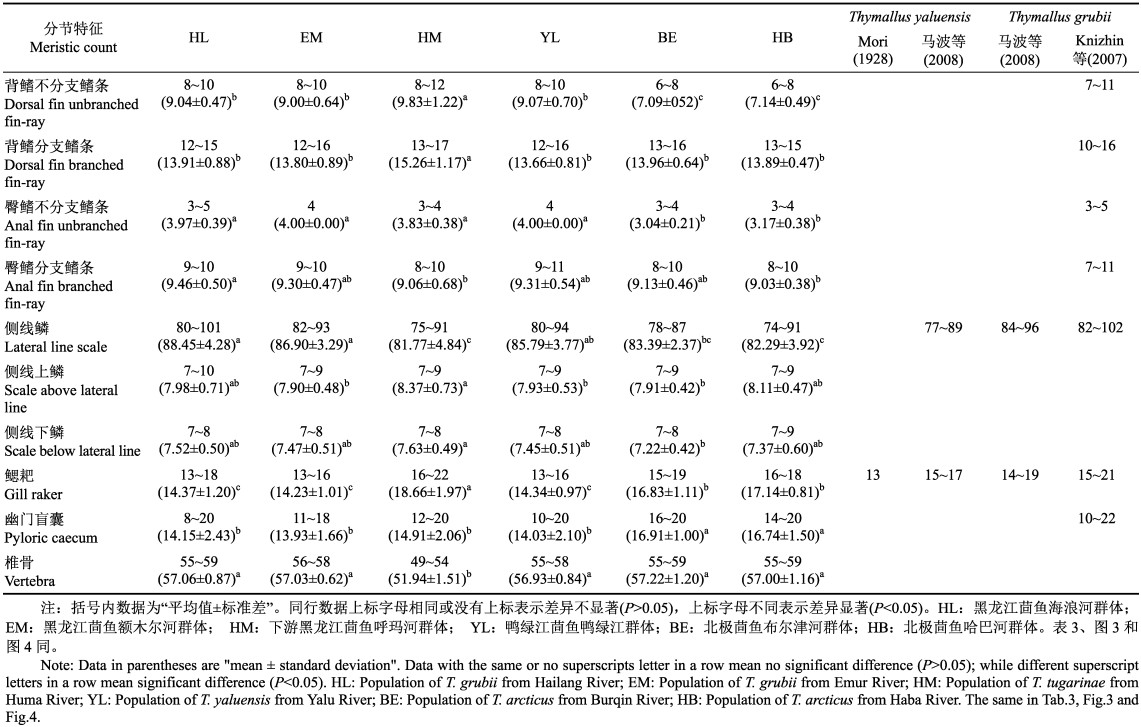
2 结果 2.1 分节特征对茴鱼属鱼类的分节特征进行统计分析,结果见表 2。种内方面,黑龙江茴鱼2个地理群体间(HL和EM)的全部分节特征的数值区间均相互交叉,且其平均值均无显著性差异(P > 0.05);北极茴鱼2个地理种群间(BE和HB)的全部分节特征的数值区间也均相互交叉,且其平均值均无显著性差异(P > 0.05)。种间方面,下游黑龙江茴鱼(HM)的背鳍不分支鳍条数、背鳍分支鳍条数和鳃耙数显著高于其他3种茴鱼(P < 0.05),但其椎骨数显著低于其他3种茴鱼(P < 0.05);北极茴鱼(BE和HB)的幽门盲囊数显著高于其他3种茴鱼(P < 0.05),但其背鳍不分支鳍条数和臀鳍不分支鳍条数显著低于其他3种茴鱼(P < 0.05);黑龙江茴鱼(HL和EM)的侧线鳞数显著高于下游黑龙江茴鱼(HM)和北极茴鱼(BE和HB)(P < 0.05),但其鳃耙数显著低于下游黑龙江茴鱼(HM)和北极茴鱼(BE和HB)(P < 0.05);鸭绿江茴鱼(YL)的侧线鳞数显著高于下游黑龙江茴鱼(HM)(P < 0.05),但其全部分节特征与黑龙江茴鱼(HL和EM)均无显著性差异(P > 0.05)。
|
|
表 2 茴鱼属鱼类的分节特征 Tab.2 Meristic counts of Thymallus |
对茴鱼属鱼类32项标准化后的可量性状进行单因素方差分析(表 3),经方差齐性检验,发现HL/BL、ED/BL、ES/BL、CL/BL、D1–11/BL、D2–10/BL、D3–10/BL、D3–11/BL、D5–6/BL和D5–9/BL等10项形态特征值不具备方差齐性,因而采用Tamahane’s T2法进行差异分析,然后采用Tukey法对剩余22项满足方差齐性的标准化后的可量性状进行多重比较。除D4–10/BL外,茴鱼属鱼类之间的其余可量性状都存在2个以上的群体之间显著性差异(P < 0.05)。比较鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼形态特征的差异系数(表 4)发现,鸭绿江茴鱼仅在CL/BL上与黑龙江茴鱼达到了亚种水平上的差距(CDCL/BL > 1.28),其余形态特征的差异均为亚种以下水平。
|
|
表 3 茴鱼属鱼类可量性状的单因素方差分析结果 Tab.3 The results of one-way ANOVA for morphometric characters of Thymallus |
|
|
表 4 鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼形态形状差异系数 Tab.4 Coefficients of difference of morphological characteristics between T. yaluensis and T. grubii |
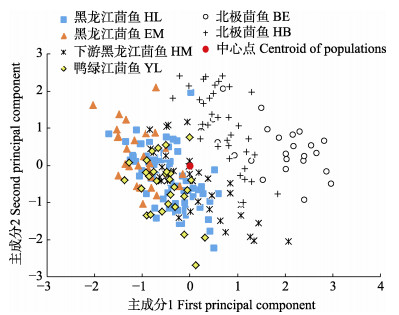
排除在茴鱼属各种群鱼类中差异不显著的D4–10/BL,对其他31项差异显著的标准化可量性状进行主成分分析,共获得8项特征值大于1的主成分,第一至第八主成分的特征值分别为8.017、4.528、3.962、3.334、1.845、1.275、1.184和1.018,贡献率分别为25.860%、14.607%、12.781%、10.754%、5.952%、4.112%、3.820%和3.284%,累积贡献率为81.170%,未达到85%的临界值,表明主成分分析不足以解释茴鱼属鱼类的形态差异。各主成分的因子负荷值见表 5,第一主成分中作用最大的3项形态学指标为BH/BL、D3–11/BL和D5–8/BL,负荷值分别为0.815、0.806和0.871,主要反映了体高、背鳍基部起点至胸鳍基部和脂鳍基部起点至臀鳍基部末端等躯干特征。第二主成分中作用最大的3项形态学指标为HL/BL、SL/BL和D1–2/BL,负荷值分别为0.691、0.715和0.719,主要反映了头长、吻长和吻端至枕骨末端等头部特征。构建第一和第二主成分散点图(图 3),显示北极茴鱼群体可与黑龙江茴鱼、下游黑龙江茴鱼及鸭绿江茴鱼区分开。黑龙江茴鱼和鸭绿江茴鱼之间相互交叉,无法区分。此外,下游黑龙江茴鱼的部分个体也与黑龙江茴鱼存在交叉。
|
|
表 5 茴鱼属鱼类主成分分析的因子负荷值 Tab.5 Factor loadings of principal components extracted in Thymallus |
|
图 3 茴鱼属鱼类主成分散点图 Fig.3 Plot of the principal components of Thymallus |
基于31项标准化的差异显著的可量性状对茴鱼属鱼类进行判别分析,排除了17项对形态差异作用较小的可量性状,仅保留BH/BL、BW/BL、EI/BL、HE/BL、CL/BL、CH/BL、D2–3/BL、D3–4/BL、D3–10/BL、D4–5/BL、D5–7/BL、D7–8/BL、D8–9/BL、D10–11/BL等14项可量性状用于判别分析,样本被分类到各自对应群体的综合判别准确率为97.30%。根据判别结果构建茴鱼属鱼类Fisher线性判别函数如下:
黑龙江茴鱼:Y=–549.706X1+503.02X2+2247.397X3+ 5239.563X4+965.426X5+3510.189X6+1910.455X7+2333.521X8–1488.075X9+3315.455X10+3104.822X11+1021.002X12+996.723X13+1737.933X14–1747.534
下游黑龙江茴鱼:Y=–589.305X1+556.465X2+ 2412.827X3+5060.006X4+1091.988X5+3546.538X6+1965.723X7+2507.512X8–1544.726X9+3174.05X10+3273.014X11+965.189X12+672.41X13+1761.716X14–1763.517
鸭绿江茴鱼:Y=–802.54X1+492.769X2+2432.131X3+ 5456.299X4+1304.799X5+3519.915X6+1919.531X7+2382.576X8–1488.604X9+3363.979X10+3321.772X11+820.561X12+1089.721X13+1891.672X14–1862.049
北极茴鱼:Y=–476.043X1+205.976X2+2274.694X3+ 5369.535X4+1385.915X5+4521.623X6+2161.709X7+2330.669X8–1808.551X9+3221.036X10+3426.268X11+609.723X12+917.91X13+2008.009X14–1900.021
式中,Y为函数值,X1为BH/BL,X2为BW/BL,X3为EI/BL,X4为HE/BL,X5为CL/BL,X6为CH/BL,X7为D2–3/BL,X8为D3–4/BL,X9为D3–10/BL,X10为D4–5/BL,X11为D5–7/BL,X12为D7–8/BL,X13为D8–9/BL,X14为D10–11/BL。
2.5 聚类及差异系数分析利用茴鱼属鱼类31项差异显著的标准化的可量性状的平均值进行聚类分析,并依据两两群体之间的平方欧氏距离构建UPGMA聚类树(图 4),结果显示,4种茴鱼属鱼类共聚为2支,2个北极茴鱼群体单独聚为一支,黑龙江茴鱼、下游黑龙江茴鱼和鸭绿江茴鱼聚为另一支,相较于下游黑龙江茴鱼,鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼形态相似度更高。

|
图 4 基于平方欧式距离构建的茴鱼属鱼类UPGMA聚类图 Fig.4 UPGMA tree of Thymallus based on square Euclidean distance |
鸭绿江茴鱼分类地位的主要争议就是其与黑龙江茴鱼的关系。分节特征是对鱼类进行种类鉴定的主要技术指标之一(孙志成等, 2020),比较鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼的分节特征发现,鸭绿江茴鱼分节特征的数值区间与2个黑龙江茴鱼群体的均相互交叉,马波等(2008)分析二者侧线鳞、鳃耙数和背鳍条总数时也得到了类似的结果(表 2),此外,鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼各项分节特征的平均值均无显著性差异(P > 0.05)。
Mori (1928)对鸭绿江茴鱼进行命名时,以吻短、眼大、体色等特征将其区别于黑龙江茴鱼,但本研究的分析结果却与Mori (1928)的结论有一定差异。单因素方差分析结果显示,鸭绿江茴鱼的SL/BL与黑龙江茴鱼的HL群体差异不显著、与EM群体差异显著,而ED/BL却与黑龙江茴鱼的EM群体差异不显著、与HL群体差异显著(表 3),显然鸭绿江茴鱼的吻长和眼径数据居于黑龙江茴鱼HL和EM群体的变异范围之内。马波等(2008)以头长为基准,也比较了黑龙江茴鱼与鸭绿江茴鱼的头长/吻长和头长/眼径,结果与本研究类似。至于体色,仅表现为鸭绿江茴鱼体侧黑斑点数量明显低于黑龙江茴鱼,除此以外,二者体色无明显差异(图 1),但马波等(2008)采集的黑龙江茴鱼松花江群体却显示,其体侧黑斑点数量与鸭绿江茴鱼类似,这说明鸭绿江茴鱼的体色也与黑龙江茴鱼无明显区别。
Mayr等(1953)确定了差异系数的临界值为1.28,并认为当两群体间的差异系数在临界值以上,表明二者达到了亚种间的差异水平,反之则属于地理群体间的形态差异。比较鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼的32项标准化可量性状的差异系数发现,鸭绿江茴鱼仅在CL/BL上与黑龙江茴鱼存在亚种以上的差异,其他可量性状均属于地理群体间的差异。主成分分析结果显示,二者的第一、二主成分散点图相互交叉,无法进行区分;聚类分析结果也显示,鸭绿江茴鱼相较于北极茴鱼和下游黑龙江茴鱼,与黑龙江茴鱼具有较近的亲缘关系。
马波等(2008)利用线粒体DNA控制区序列分析得出鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼的遗传距离为0.007~0.015,但黑龙江茴鱼种内的呼玛河和甘河群体的遗传距离却也达到了0.012~0.015,表明鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼的遗传差异属于种内水平。Ma等(2016)利用线粒体全基因组序列再次分析了鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼的系统进化关系,在线粒体全基因组水平上,鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼的遗传距离为0.013~0.018,小于黑龙江茴鱼种内个体之间的遗传距离(0.019),再次印证了鸭绿江茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼的遗传差异属于种内水平。结合马波等(2008)和Ma等(2016)的遗传学分析结果以及本研究的形态学分析结果,综合分析表明,鸭绿江茴鱼不应为有效种,其学名应修订为黑龙江茴鱼。
3.2 茴鱼属鱼类的形态差异及多元分析方法效果的比较鱼类的分节特征是其种质评价标准的重要组成部分,一般较为稳定。这在黑龙江茴鱼种内(HL、EM和YL)和北极茴鱼种内(BE和HB)的分节特征上得到了印证,分析发现,不同地理种群间黑龙江茴鱼和北极茴鱼的分节特征差异均不显著(P > 0.05)。种间方面,黑龙江茴鱼、下游黑龙江茴鱼和北极茴鱼两两之间均存在差异显著的分节特征(P < 0.05),体现了其种质的差异性。
为了更全面地分析茴鱼属鱼类的形态特征差异,对其标准化可量性状进行多元统计分析。单因素方差分析结果显示(表 3),黑龙江茴鱼、下游黑龙江茴鱼和北极茴鱼两两之间仅D4–10/BL差异不显著(P > 0.05),表明3种茴鱼属鱼类之间除了背鳍基部末端至腹鳍基部起点的距离外,在其他31项标准化可量性状上均存在2种以上的鱼差异显著(P < 0.05)。虽然单因素方差分析结果比较直观,但其对数据的简化作用有限,得到的结果过于冗杂,因此,有必要对茴鱼属鱼类之间的形态差异进行进一步分析。
主成分分析可以将复杂的数据进行降维和压缩,是一种常用的多变量分析方法(孙志成等, 2020),可以通过线性变换将原始数据从高维空间映射到低维空间,以捕捉数据中的主要结构和方差,以便有效简化数据分析过程(马凯等, 2023),目前已经广泛运用于鱼类(Ai et al, 2021)、甲壳类(樊云鹏等, 2021; 孙东昱等, 2021; Du et al, 2022)、爬行类(贺刚等, 2023)和贝类(邹琰等, 2021)等水生生物形态学分析中。对3种茴鱼差异显著的31项标准化可量性状进行主成分分析,共筛选出8项特征值大于1的主成分,其中,贡献率最大的第一、二主成分分别主要反映了黑龙江茴鱼、下游黑龙江茴鱼和北极茴鱼的躯干部和头部特征,表明3种茴鱼属鱼类的形态差异主要集中于躯干部和头部(表 5)。基于第一、二主成分构建二维散点图(图 3),发现其对黑龙江茴鱼和北极茴鱼的区分作用较好,但对下游黑龙江茴鱼的区分效果较差,表现为50%以上的下游黑龙江茴鱼均与黑龙江茴鱼掺杂在一起,这可能与主成分分析的局限性有关。主成分分析的主要可视化手段即是构建主成分散点图,为了直观地进行显示,就意味着二维散点图是最佳的,由于所筛选出主成分的累积贡献率的临界值为85% (Resende et al, 2016),因此,要求第一、二主成分的累积贡献率应为85%以上才能达到较理想的分析效果,但3种茴鱼属鱼类的第一、二主成分的累积贡献率仅为40.467%,对下游黑龙江茴鱼的分辨效果欠佳。相似的研究结果也见于哲罗鲑(Hucho taimen)和川陕哲罗鲑(Hucho bleekeri)(马凯等, 2023)、黑鳃梅童鱼(Collichthys niveatus)和棘头梅童鱼(Collichthys lucidus)(高天翔等, 2013)以及新疆3种雅罗鱼(Leuciscus idus、Leuciscus baicalensis和Leuciscus merzbacheri)(王业宁等, 2019)等亲缘关系较近的鱼类形态学比较结果中。
判别分析的结果以Fisher线性判别函数的形式展现,无需作图,避免了主成分分析结果必须可视化的局限性。对茴鱼属鱼类差异显著的标准化后可量性状进行判别分析,得到其Fisher线性判别函数,交叉验证结果显示,判别函数的综合判别率为97.30%,表明茴鱼属鱼类的形态差异主要表现于BH/BL、BW/BL、EI/BL、HE/BL、CL/BL、CH/BL、D2–3/BL、D3–4/BL、D3–10/BL、D4–5/BL、D5–7/BL、D7–8/BL、D8–9/BL和D10–11/BL等14项可量性状上,利用这14项可量性状,不仅可以有效区分不同的茴鱼物种,还可以对同种茴鱼的不同地理群体进行区分(如区分鸭绿江流域和黑龙江流域的黑龙江茴鱼)。
聚类分析是比较数据相似性的分析方法(马凯等, 2023)。利用茴鱼属鱼类差异显著的标准化可量性状的平方欧氏距离构建UPGMA聚类树(图 4),结果表明,在3种茴鱼属鱼类中,下游黑龙江茴鱼的可量性状与黑龙江茴鱼较为相似,北极茴鱼与黑龙江茴鱼和下游黑龙江茴鱼的相似程度较低,黑龙江茴鱼和北极茴鱼种内不同地理群体间的可量性状差异均较小。
鱼类的可量性状受遗传和环境共同作用,根据DNA序列构建的进化树不一定与根据形态数据构建的进化树一致(Pamilo et al, 1988)。马波等(2008)和Ma等(2016)的遗传学分析结果显示,黑龙江茴鱼与北极茴鱼的亲缘关系比其与下游黑龙江茴鱼的亲缘关系近,与本研究的形态学聚类结果相反,原因可能是北极茴鱼分布的额尔齐斯河流域环境条件与黑龙江茴鱼分布的黑龙江流域环境条件有较大差异,从而导致二者形态特征具有较大差异,这是二者适应不同环境条件的直接表现(Frederich et al, 2012),而黑龙江茴鱼与下游黑龙江茴鱼同域分布,相似的水质、底质、温度、水流和饵料等(Senay et al, 2017)栖息环境塑造了其相似的形态特征。这种现象被称为表型可塑性(Poulet, 2008),在鱼类中很常见,如生活于湍急水流中的美洲红点鲑(Salvelinus fontinalis) (Imre et al, 2002)和大甲鲹(Megalaspis cordyla) (Sajina et al, 2011)拥有更粗大的尾柄,主要以无脊椎动物为食的威氏白鲑(Prosopium williamsoni) (Whiteley, 2007)因需要翻动石块觅食而具有更突出的吻部。
AI Q Y, SANG L L, TAN H X, et al. Genetic and morphological differences between yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi) from the Bohai Sea, China and the Southern Ocean, Australia. Aquaculture and Fisheries, 2021, 6(3): 260-266 DOI:10.1016/j.aaf.2020.03.004 |
DU J H, HOU C X, CHEN X L, et al. Morphometric analysis and fluorescent microsatellite markers to evaluate the genetic diversity of five populations of Penaeus japonicus in China. Aquaculture and Fisheries, 2022, 7(3): 321-327 DOI:10.1016/j.aaf.2020.10.005 |
FAN Y P, TAN J, LUAN S, et al. Morphological differences in four introduced populations of Litopenaeus vannamei. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2021, 42(5): 62-69 [樊云鹏, 谭建, 栾生, 等. 四种不同引进群体的凡纳滨对虾种虾形态差异性分析. 渔业科学进展, 2021, 42(5): 62-69] |
FREDERICH B, LIU S Y V, DAI C F. Morphological and genetic divergences in a coral reef damselfish, Pomacentrus coelestis. Evolutionary Biology, 2012, 39: 359-370 DOI:10.1007/s11692-011-9158-z |
GAO T X, HAN G, MA G Q, et al. Morphological variation analysis of C. lucidus and C. niveatus. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2013, 43(1): 27-33 [高天翔, 韩刚, 马国强, 等. 黑鳃梅童鱼和棘头梅童鱼的形态学比较研究. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 43(1): 27-33] |
GÖNCZI A P. A study of physical parameters at the spawning sites of the European grayling (Thymallus thymallus L.). Regulated Rivers: Research and Management, 1989, 3(1): 221-224 DOI:10.1002/rrr.3450030121 |
HASHEMZADEH SEGHERLOO I, NORMANDEAU E, BENESTAN L, et al. Genetic and morphological support for possible sympatric origin of fish from subterranean habitats. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 2909 DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-20666-w |
HE G, XU J G, HE L, et al. Morphological differences analysis of hybrid (Chinemys reevesii ♀ × Ocadia sinensis♂) and their parents. Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 2023, 36(2): 1-7 [贺刚, 徐金根, 何力, 等. 中华草龟、中华花龟及其杂种F1代形态差异分析. 水产学杂志, 2023, 36(2): 1-7] |
IMRE I, MCLAUGHLIN R L, NOAKES D L G. Phenotypic plasticity in brook charr: Changes in caudal fin induced by water flow. Journal of Fish Biology, 2002, 61(5): 1171-1181 DOI:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2002.tb02463.x |
KNIZHIN I B, ANTONOV A L, SAFRONOV S, et al. New species of grayling Thymallus tugarinae sp. nova (Thymallidae) from the Amur River Basin. Journal of Ichthyology, 2007, 47(2): 123-139 |
MA B, FAN Z T. Genetic diversity of Arctic grayling (Thymallus sp.) population from upper Heilongjiang River based on mitochondrial control region sequence. Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 2013, 26(6): 7-12 [马波, 范兆廷. 利用线粒体D-loop基因序列分析黑龙江上游北极茴鱼群体遗传结构. 水产学杂志, 2013, 26(6): 7-12] |
MA B, HUO T B, JIANG Z F. A new record species of the genus Thymallus (Salmoniformes, Thymallidae) in China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 2007, 32(4): 986-988 [马波, 霍堂斌, 姜作发. 中国黑龙江水系茴鱼属一新纪录种(鲑形目, 茴鱼科). 动物分类学报, 2007, 32(4): 986-988] |
MA B, HUO T B, JIANG Z F. Thymallus arcticus yaluensis is a synonym of T. grubii by mitochondrial control region sequences analysis. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 2008, 33(2): 414-419 [马波, 霍堂斌, 姜作发. 线粒体DNA序列变异显示鸭绿江茴鱼为黑龙江茴鱼同物异名. 动物分类学报, 2008, 33(2): 414-419] |
MA B, JIANG H Y, SUN P, et al. Phylogeny and dating of divergences within the genus Thymallus (Salmonidae: Thymallinae) using complete mitochondrial genomes. Mitochondrial DNA Part A, 2016, 27(5): 3602-3611 DOI:10.3109/19401736.2015.1079824 |
MA B, SUN J X, JIANG Z F, et al. Taxonomic status of three fish species in Thymallus from upper Heilongjiang River based on mitochondrial control region sequence variation. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2011, 18(2): 314-321 [马波, 孙家贤, 姜作发. 黑龙江上游3种茴鱼分类地位的线粒体D-loop序列变异分析. 中国水产科学, 2011, 18(2): 314-321] |
MA K, TONG G X, KUANG Y Y, et al. Effect of morphological traits on body weight of Thymallus arcticus. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2022, 29(6): 825-833 [马凯, 佟广香, 匡友谊, 等. 北极茴鱼形态性状对体重影响效果分析. 中国水产科学, 2022, 29(6): 825-833] |
MA K, TONG G X, ZHANG L L, et al. Multivariate analysis of Hucho taimen and Hucho bleekeri populations based on morphological characteristics. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2023, 30(1): 1-10 [马凯, 佟广香, 张澜澜, 等. 哲罗鲑和川陕哲罗鲑群体多变量形态特征比较. 中国水产科学, 2023, 30(1): 1-10] |
MAYR E, LINSLEY E G, USINGER R L. Methods and principles of systematic zoology. New York: McGraw Hill Book Company, Inc, 1953: 23-39
|
MORI T. On the fresh water fishes from the Yalu River, Korea, with descriptions of new species. Journal of the Chosen Natural History Society, 1928, 6: 54-70 |
PAMILO P, NEI M. Relationships between gene trees and species trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1988, 5(5): 568-583 |
POULET N. Evidence of morphological discrete units in an endemic fish, the rostrum dace (Leuciscus burdigalensis Valenciennes 1844), within a small river basin. Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems, 2008(388): 03 |
RESENDE S V, KAVALCO K F, PAZZA R. Morphological and genetic divergence of a small stream fish species along a watershed. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 2016, 68: 66-73 DOI:10.1016/j.bse.2016.06.007 |
SAJINA A M, CHAKRABORTY S K, JAISWAR A K, et al. Stock structure analysis of Megalaspis cordyla (Linnaeus, 1758) along the Indian coast based on truss network analysis. Fisheries Research, 2011, 108(1): 100-105 DOI:10.1016/j.fishres.2010.12.006 |
SENAY C, HARVEY-LAVOIE S, MACNAUGHTON C J, et al. Morphological differentiation in northern pike (Esox lucius): the influence of environmental conditions and sex on body shape. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 2017, 95(6): 383-391 DOI:10.1139/cjz-2016-0159 |
SUN D Y, WANG L, QIU S Y, et al. Morphological comparison of Oratosquilla oratoria stocks along the coast of Haiyang and Yantai. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2021, 42(1): 154-164 [孙东昱, 王蕾, 邱盛尧, 等. 海阳和烟台近岸口虾蛄群体的形态比较. 渔业科学进展, 2021, 42(1): 154-164] |
SUN J X, MA B. Genetic differentiation and taxonomic status of three species in grayling Thymallus in Huma River by microsatellite analysis. Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 2011, 24(1): 19-25 [孙家贤, 马波. 呼玛河3种茴鱼遗传分化及属内地位的微卫星分析. 水产学杂志, 2011, 24(1): 19-25] |
SUN Z C, LI Y D, SONG C Y, et al. Comparative studies on morphology and genetics between Acanthogobius ommaturus and Acanthogobius flavimanus. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2020, 44(8): 1237-1248 [孙志成, 李亚东, 宋晨雨, 等. 斑尾刺虾虎鱼和黄鳍刺虾虎鱼的形态学、遗传学比较. 水产学报, 2020, 44(8): 1237-1248] |
WANG X L, XIAO Z G, DU X Y, et al. Large scale breeding technology of Thymallus yaluensis. Fisheries Science & Technology Information, 2018, 45(6): 311-313 [王秀兰, 肖志国, 杜晓燕, 等. 鸭绿江茴鱼规模化繁育综合技术研究. 水产科技情报, 2018, 45(6): 311-313] |
WANG X Y, ZHANG Y J, LIU F, et al. Analysis on the morphological differences of Triplophysa yarkandensis in different geographic populations. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2022, 43(6): 199-206 [王新月, 张永杰, 刘斐, 等. 叶尔羌高原鳅不同地理群体形态差异分析. 渔业科学进展, 2022, 43(6): 199-206] |
WANG Y N, LI S Z, LIU C L. Multivariate analysis on the morphological among three species of Leuciscus in Xinjiang. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2019, 26(4): 636-645 [王业宁, 李胜忠, 刘长龙. 新疆3种雅罗鱼的多元形态. 中国水产科学, 2019, 26(4): 636-645] |
WHITELEY A R. Trophic polymorphism in a riverine fish: morphological, dietary, and genetic analysis of mountain whitefish. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 2007, 92(2): 253-267 |
XIANG W, FAN Z M, YIN J G, et al. Preliminary study on biology of Thymallus arcticus grubei in Yertex River. Journal of Hydroecology, 2009, 30(4): 75-78 [向伟, 范镇明, 殷建国, 等. 叶尔特斯河野生北极茴鱼生物学研究. 水生态学杂志, 2009, 30(4): 75-78] |
ZHANG D R, LIU S, ZHANG L X, et al. A new species of Glyphoglossus Günther, 1869 (Anura: Microhylidae) from western Yunnan, China. Asian Herpetological Research, 2021, 12(4): 371-388 |
ZOU Y, LI L, WANG Y J, et al. Morphological variation analysis of seven populations of Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum). Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 2021, 34(3): 28-33 [邹琰, 李莉, 王英俊, 等. 山东沿海不同地理群体菲律宾蛤仔形态变异分析. 水产学杂志, 2021, 34(3): 28-33] |
ZUEV I V, SHULEPINA S, TROFIMOVA E, et al. Seasonal changes in feeding and relative condition factors of Arctic grayling (Thymallus arcticus) in a stretch of the middle reaches of the Yenisei River. Contemporary Problems of Ecology, 2017, 10(3): 250-258 |